System and method for x-ray fluorescence with filtering
a filtering and x-ray technology, applied in the field of laboratory-based x-ray fluorescence analysis systems and methods, can solve the problems of reducing the signal-to-noise ratio of the x-ray detector, reducing the background contribution of detection and quantification of trace elements, and avoiding the effect of transmission filters
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
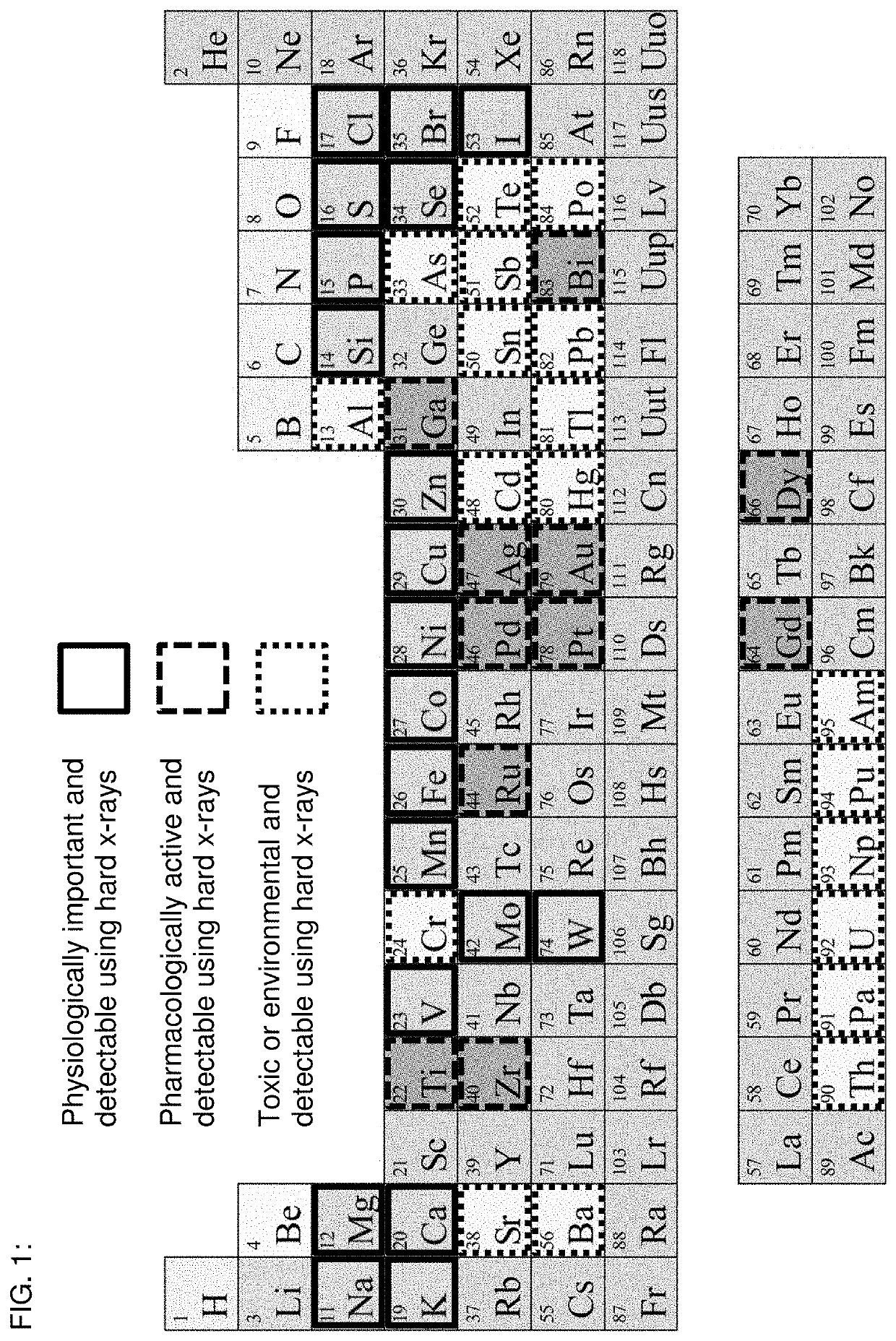
[0032]One example area in which x-ray fluorescence (XRF) can provide information is the interactions of metals in biological systems (e.g., role of metals in biological processes; metal-based drugs). These trace elements are typically found in concentration of parts per million (ppm) and spatially specific at organ, tissue, cell, and sub-cellular levels. Abnormal trace element distribution in tissues has been directly linked to many diseases, including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Huntington disease. Recent studies are also linking pathologies such as arthritis and schizophrenia to abnormal trace element concentrations of blood serum in human populations, which are driving questions on elemental distributions in the diseased tissues. In addition, promising new metal-based therapeutics (e.g., anti-cancer and anti-HIV) are driving the need for metal mapping capabilities to better understand the in vivo uptake of the drugs and to determine targeting strat
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap