Device for micromechanical switching of signals
a micromechanical and signal technology, applied in the direction of thermal micromechanical switches, thermal switch details, contacts, etc., can solve the problems of large losses, high energy consumption, and procedure wear on the free ends of arms and contact surfaces, and achieve the effect of low power consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
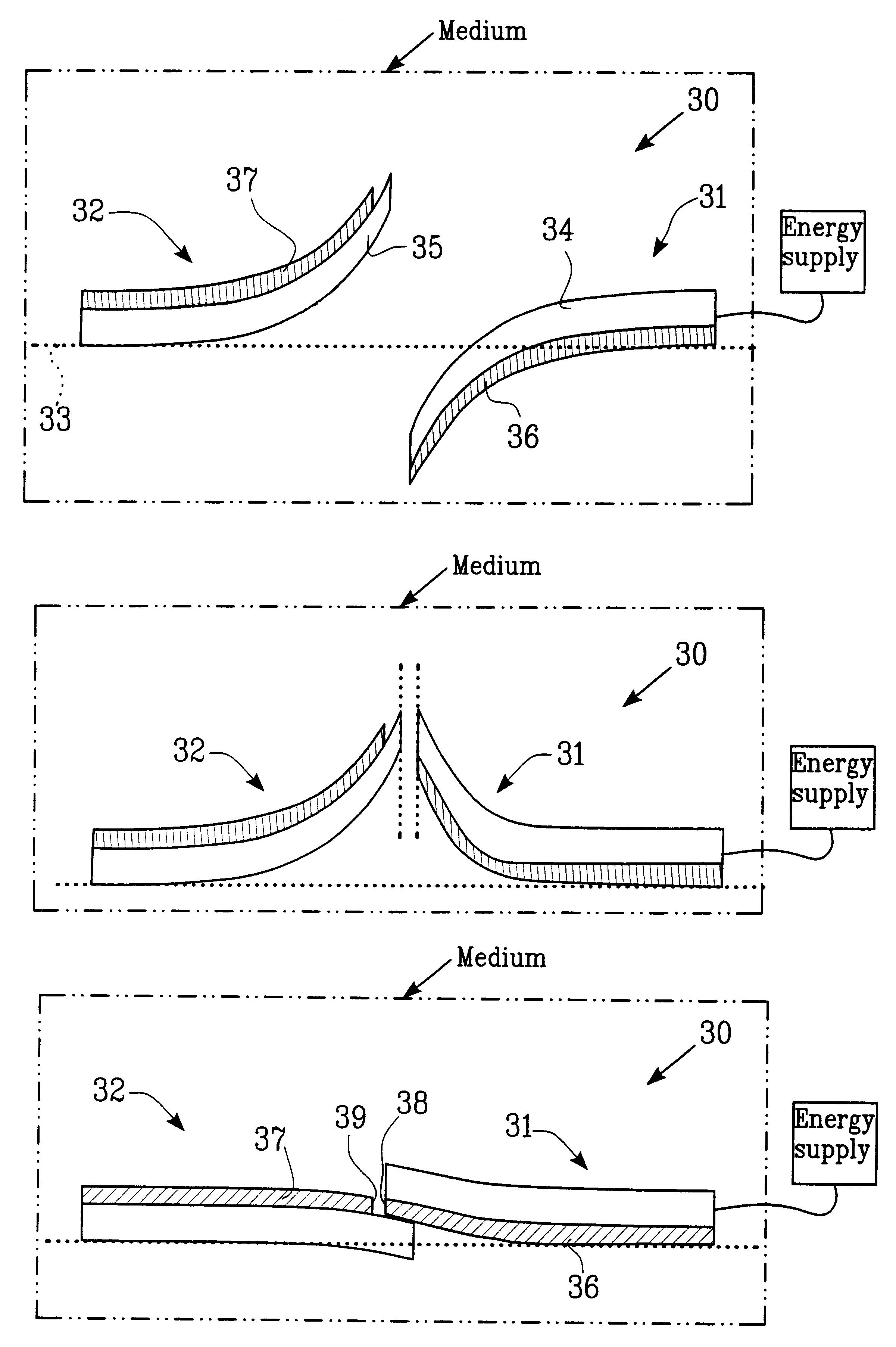
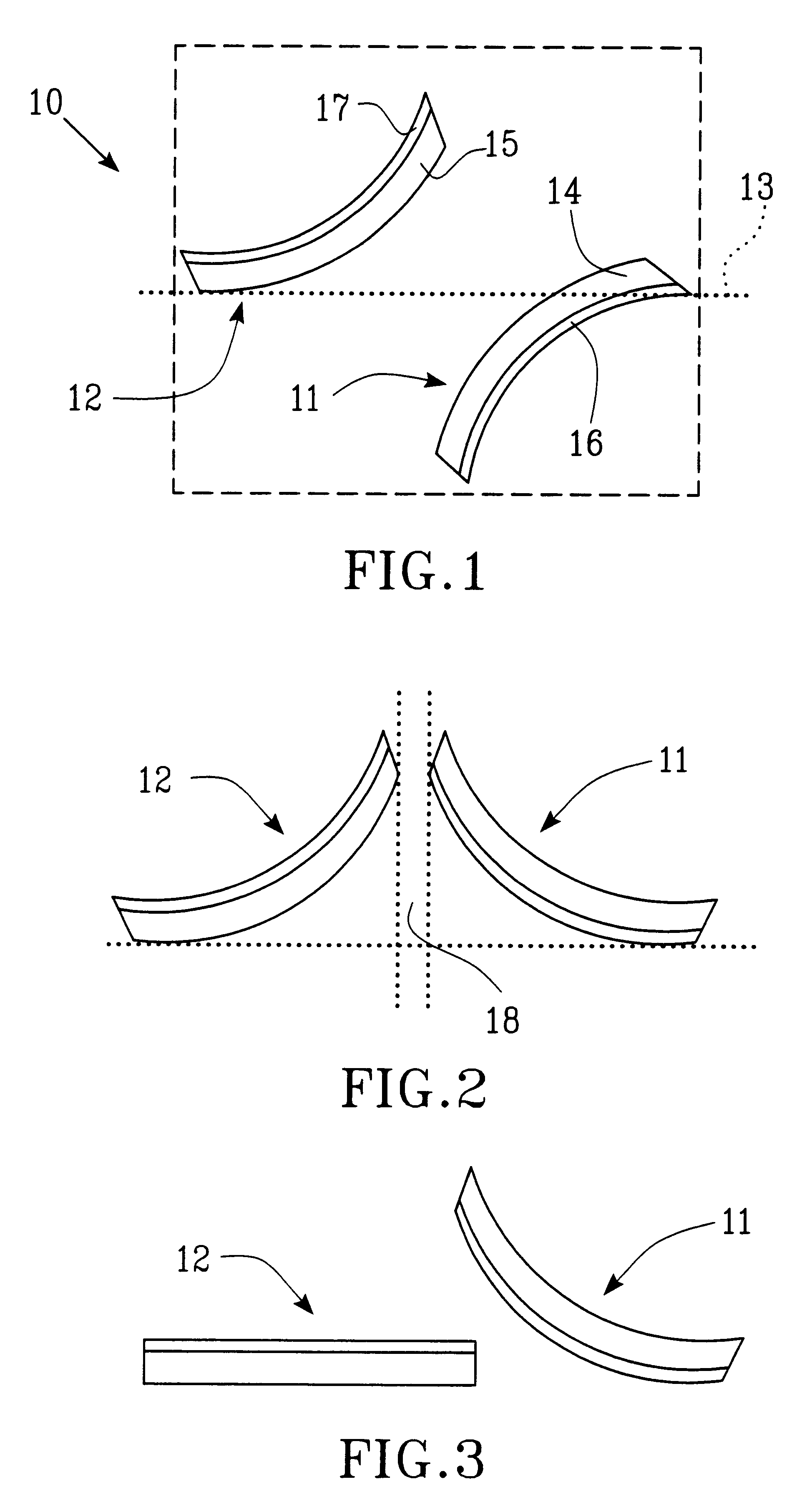
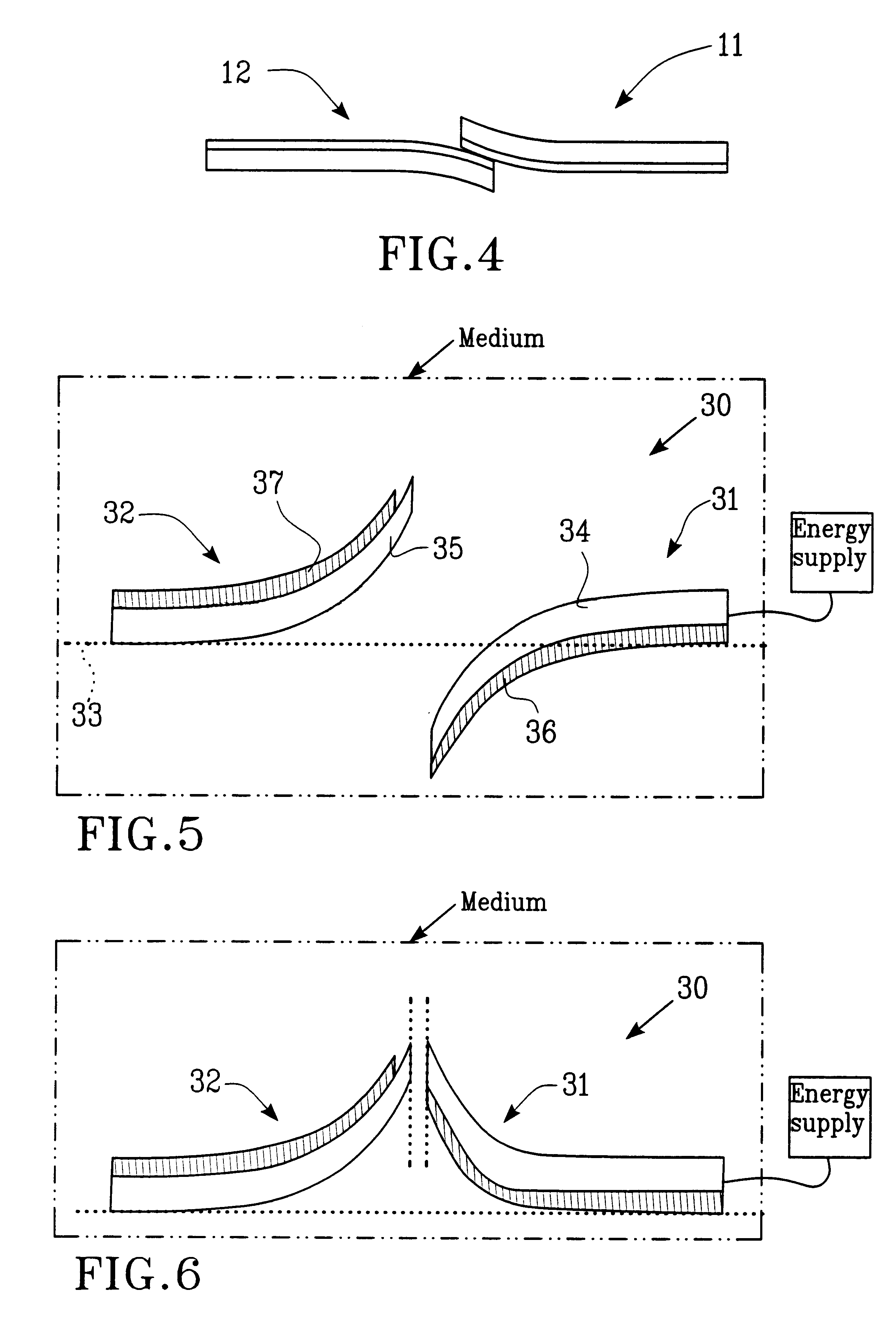
A device according to the invention includes at least two movable elements, realized as arms, which through thermal actuation can close and open a circuit. Suitable material combinations will be chosen so that two resisting switching arms deflect in different directions, for example one of them deflects upwards while the other one deflects downwards at the intended operating temperature and that arms can be arranged to deflect in opposite directions through heating. Moreover, the arms are arranged so that they essentially overlap each other in the position where they should interlock or contact, for example when both arms are straightened and at least one of them through heating could deflect so much that it can be constrained to pass the other arm.
A bistable micromechanical switch 10 is shown in FIG. 1 in an open state and it includes a first and a second switching arm 11 and 12, respectively, provided on or in a conveyer or a substrate (shown with broken and dotted line), for example
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap