Image forming apparatus and fixing temperature control method for the apparatus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
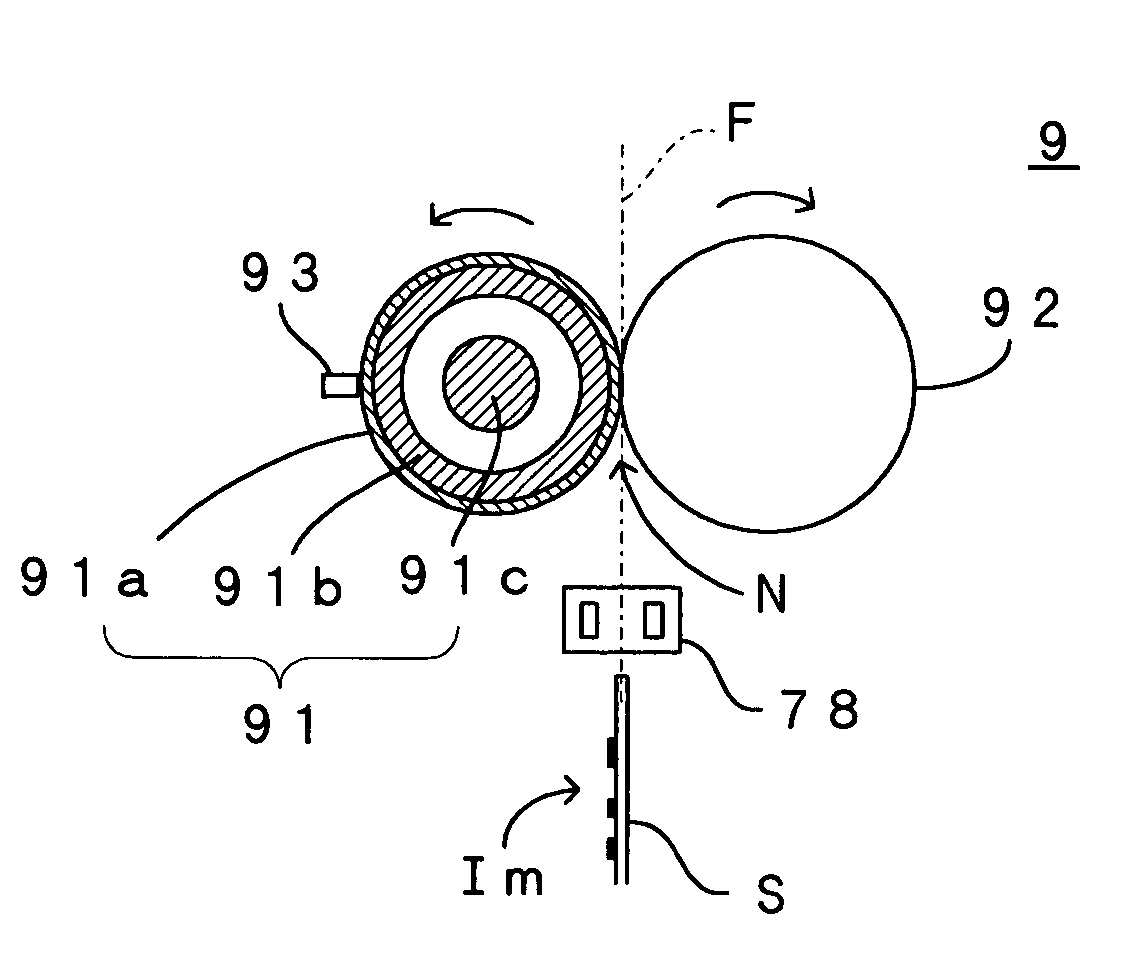
[0069]Hence, the embodiment defines the start timing of energization of the heater 91c such that, as shown in FIG. 7A, when the shift of the output signal from the pre-fixing sensor 78 is detected, a constant time period Δt2 is provided between the detection of the signal shift and the start of energization of the heater 91c. Similarly to the apparatus of the first embodiment, this arrangement ensures that a time difference t4 between the start of energization of the heater 91c and the actual arrival of the sheet S at the nip N is constant. Hence, the temperature of the heating roller 91 during the passage of the sheet S through the nip N can be maintained in the predetermined range. As a result, the heating roller 91 is maintained at the optimum temperature during the fixing operation and the good fixing performance can be achieved.
[0070]Where the output signal from the pre-fixing sensor 78 is retained at H-level, the temperature control may be carried out based on the constant contro
third embodiment
[0077]According to the temperature control operation thus arranged, as well, the same working effects as those offered by the apparatus of the third embodiment can be attained. That is, the energization of the heater 91c is started a given time period t7 earlier than the time t0 when the sheet S arrives at the nip N, whereby the temperature is stably maintained during the passage of the sheet S through the nip N.
[0078]Given the same length of period Ts of the vertical synchronous signal Vsync, such a temperature control operation has a longer control time period Tc than that of the operation of the third embodiment. Hence, the control operation is less suited for coping with fine temperature fluctuations. However, the operation reduces the load on the CPU 101 because of a lower frequency of the processings. Accordingly, such a control method is favorable in a case where, for example, the heating roller 91 has a relatively great heat capacity so that the roller is slow to be raised in t
fifth embodiment
[0082]Next, description is made on the invention which is suited for a case where the repetition period of the vertical synchronous signal Vsync is varied. In such a case, the temperature control method on assumption that the vertical synchronous signal Vsync has the constant period does not naturally hold.
[0083]FIGS. 11A and 11B are charts each representing a relation between the timing of energizing the heating roller and the temperature fluctuations on assumption that the control period is constant. In a state where the color image formation is not carried out so that the sheet S is not present in the nip N, it is relatively easy to maintain the temperature at a constant level because the heater 91c substantially presents a constant heat load. As shown in FIG. 11A, therefore, the temperature of the heating roller 91 can be maintained in the predetermined range by sensing the surface temperature of the heating roller 91 per constant control period Tc; comparing the sensed temperature
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap