Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2 results about "Side lobe" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In antenna engineering, side lobes or sidelobes are the lobes (local maxima) of the far field radiation pattern of an antenna or other radiation source, that are not the main lobe. The radiation pattern of most antennas shows a pattern of "lobes" at various angles, directions where the radiated signal strength reaches a maximum, separated by "nulls", angles at which the radiated signal strength falls to zero. This can be viewed as the diffraction pattern of the antenna. In a directional antenna in which the objective is to emit the radio waves in one direction, the lobe in that direction is designed to have a larger field strength than the others; this is the "main lobe". The other lobes are called "side lobes", and usually represent unwanted radiation in undesired directions. The side lobe directly behind the main lobe is called the back lobe. The longer the antenna relative to the radio wavelength, the more lobes its radiation pattern has. In transmitting antennas, excessive side lobe radiation wastes energy and may cause interference to other equipment. Another disadvantage is that confidential information may be picked up by unintended receivers. In receiving antennas, side lobes may pick up interfering signals, and increase the noise level in the receiver.
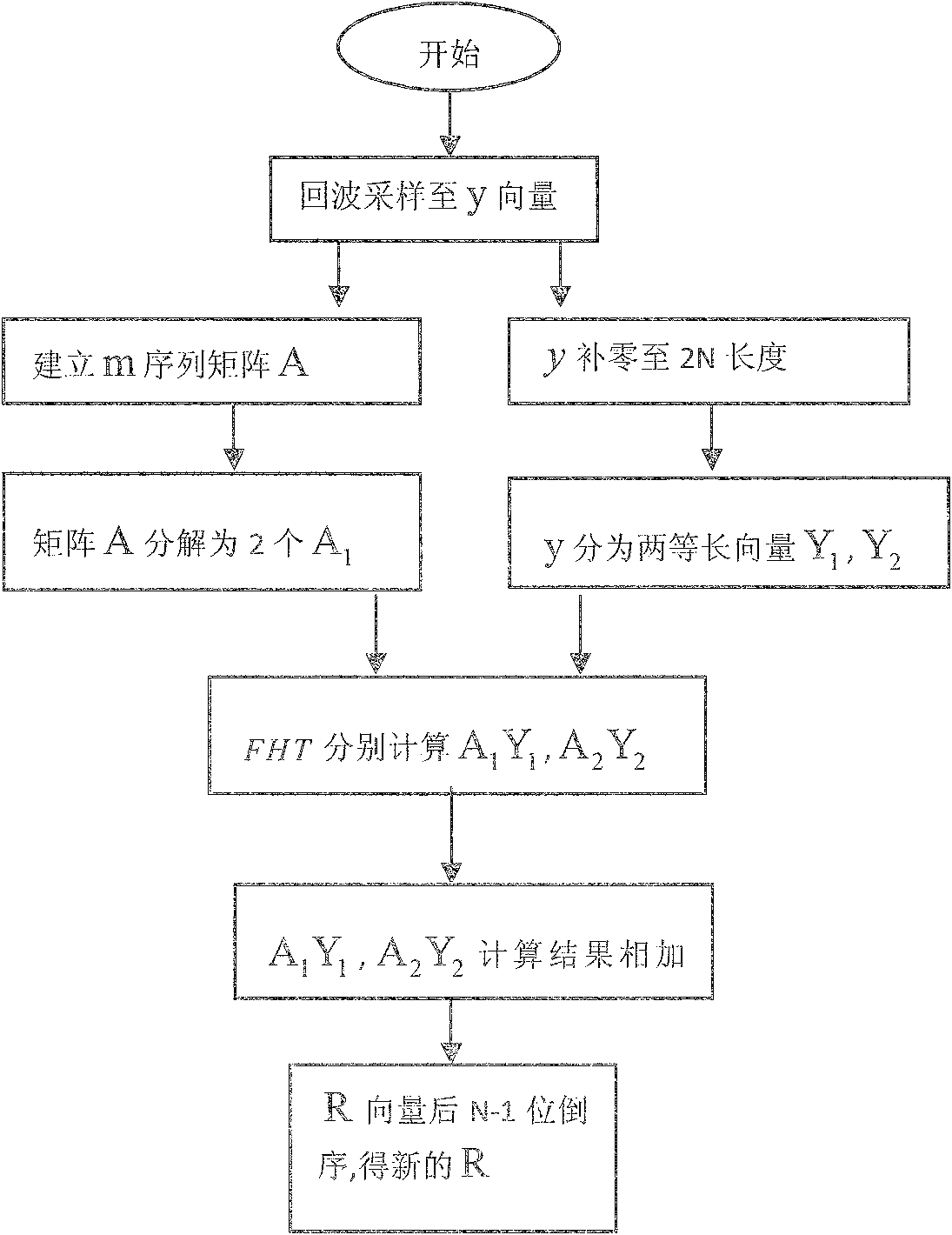
Processing method for m-sequential code pulse modulation ultra-wide-band radar echo
ActiveCN102721950ARatio of main and side lobe is improvedFast operationWave based measurement systemsRadarUltra wideband radar
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Same-frequency interference suppression method based on protection area and directional antenna
ActiveCN113950065AReduce distractionsReduce the strength of interfering signalsNetwork topologiesRadio transmissionAccess networkInterference (communication)
The invention discloses a same-frequency interference suppression method based on a protection area and a directional antenna, relates to a same-frequency interference mechanism analysis technology in a satellite-5G integrated network, and aims to solve the problem that the strength of a same-frequency interference signal is high when a frequency spectrum is shared in an existing satellite-5G integrated indirect access network. The method comprises: obtaining the minimum radius of a protection area by constructing an indirectly-accessed satellite-ground integrated network model; analyzing the directional antenna model, and normalizing the 5G base station antenna beam model and the satellite relay base station antenna beam model to obtain a main lobe gain and a side lobe gain of the satellite relay base station and a main lobe gain and a side lobe gain of the 5G base station; constructing a protection area network model with directional antenna nodes, and analyzing the interference threshold of the satellite relay base station to obtain the probability that the satellite relay base station keeps normal communication; therefore, the elevation angle of the directional antenna of the satellite relay base station is adjusted, and same-frequency interference is suppressed. The beneficial effect is that the intensity of receiving the interference signal from the 5G base station is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap