Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1 results about "Solar cell efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solar cell efficiency refers to the portion of energy in the form of sunlight that can be converted via photovoltaics into electricity by the solar cell. The efficiency of the solar cells used in a photovoltaic system, in combination with latitude and climate, determines the annual energy output of the system. For example, a solar panel with 20% efficiency and an area of 1 m² will produce 200 W at Standard Test Conditions, but it can produce more when the sun is high in the sky and will produce less in cloudy conditions or when the sun is low in the sky. In central Colorado, which receives annual insolation of 2000 kWh/m²/year, such a panel can be expected to produce 400 kWh of energy per year. However, in Michigan, which receives only 1400 kWh/m²/year, annual energy yield will drop to 280 kWh for the same panel. At more northerly European latitudes, yields are significantly lower: 175 kWh annual energy yield in southern England.
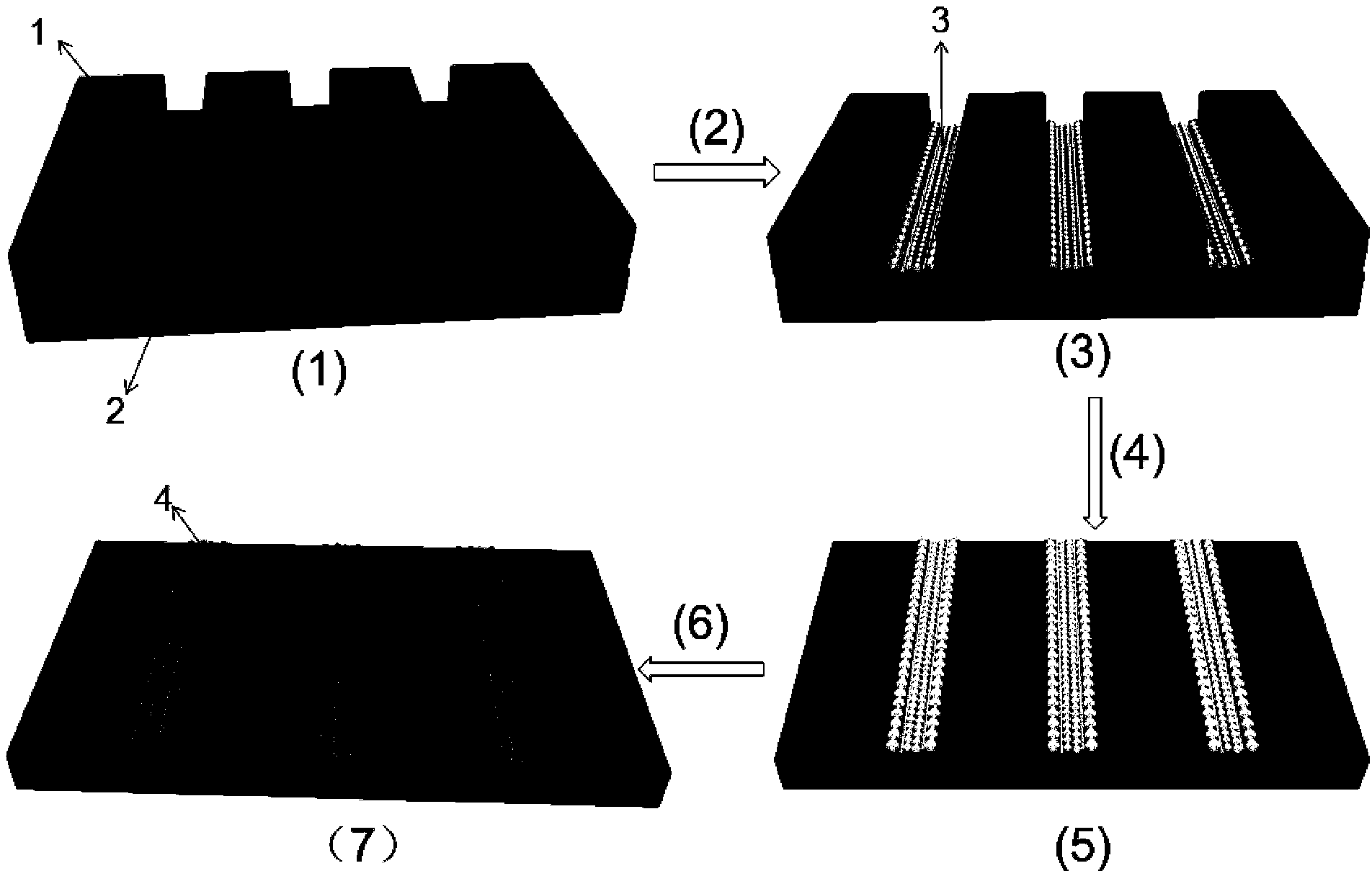
Method for preparing solar cell silver wire grid electrode based on photolithographic mask method and liquid phase method
ActiveCN103367541AFinal product manufacturePhotomechanical exposure apparatusSolar cell efficiencyElectrochemical response
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap