Viewing method for substrate with uneven surface
A technology for leveling the surface and substrate, applied in the field of inspection, can solve the problems that the carrier film cannot be seen through, increase the risk of damage, time-consuming and labor-intensive, etc., and achieve the effect of increasing the risk of chip damage, increasing production efficiency, and reducing the inspection process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
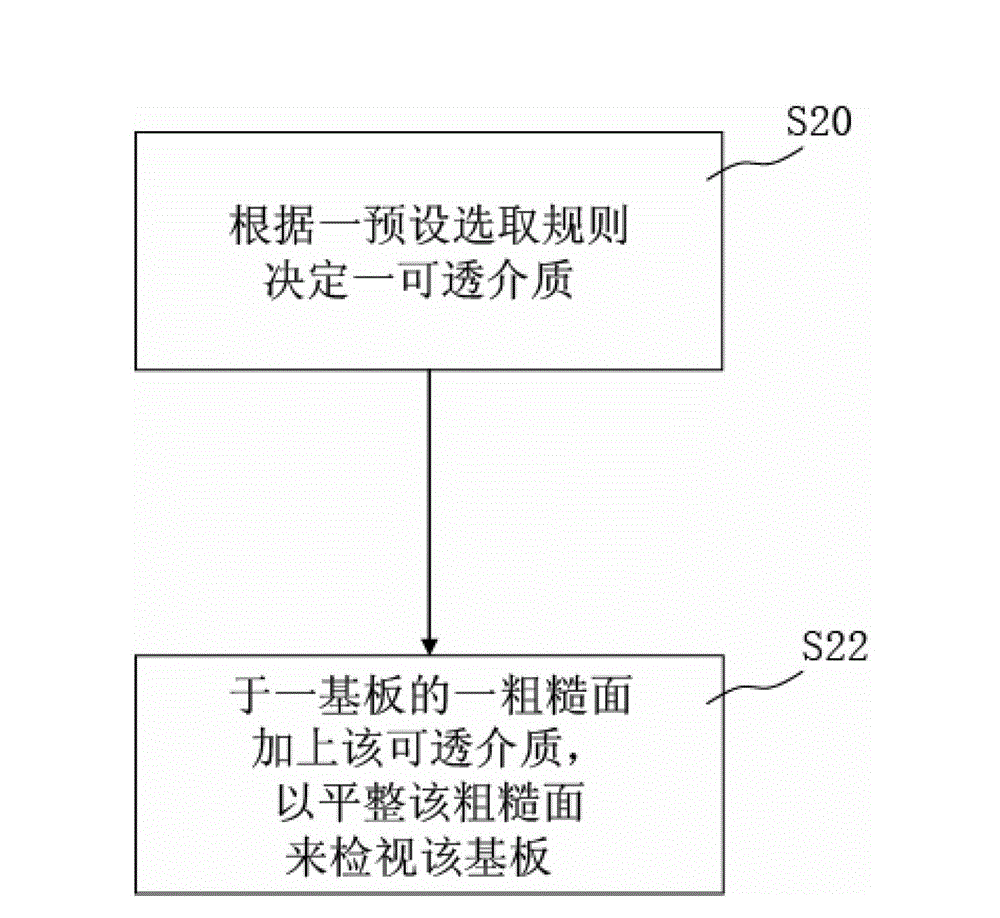
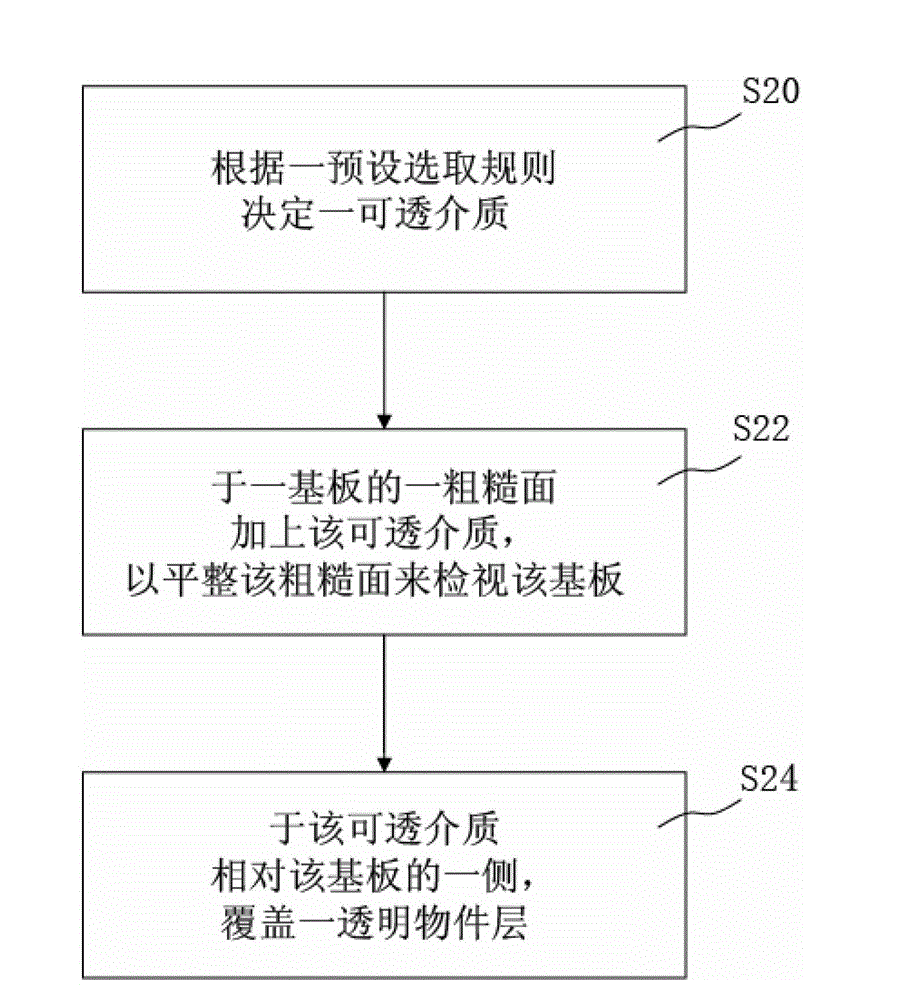
[0035] Please refer to Figure 2A as shown, Figure 2A It is a flowchart of an embodiment of the inspecting method for a substrate with an uneven surface of the present invention. In one embodiment, a method for inspecting a substrate with an uneven surface includes the following steps:
[0036] S20 determining a permeable medium according to a preset selection rule; and
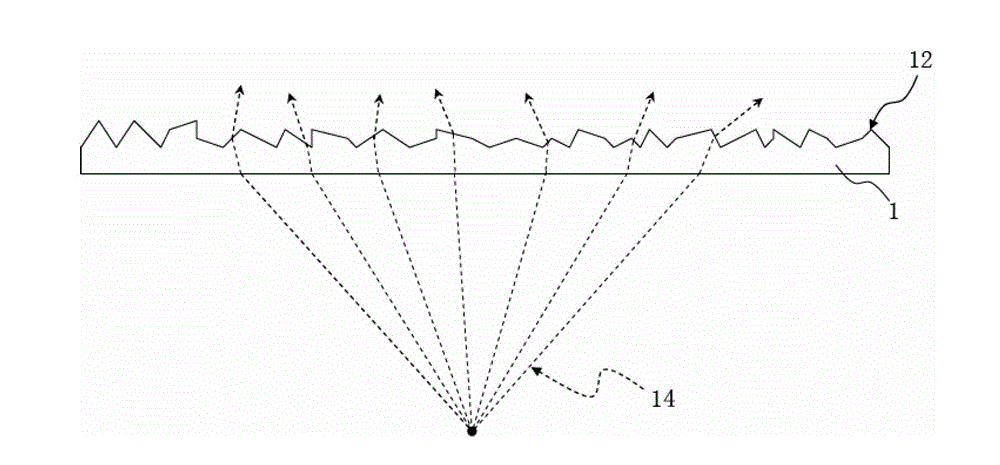
[0037] S22 adding the transparent medium on a rough surface of a substrate to flatten the rough surface to inspect the substrate.
[0038] Wherein, the selection rule is set by calculating a refractive index difference between the transparent medium and the substrate, and the smaller the refractive index difference is, the better the transparency is. For example, when the refractive index of the substrate is n 1 , the refractive index of the transparent medium is n 2 , then the calculation method of the refractive index difference value can be:
[0039]
[0040] According to the summary of the inventor
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap