Complementary type resistive random access memory and preparation method thereof
A resistive memory, complementary technology, applied in electrical components and other directions, can solve the problems of increasing the complexity of the circuit and the area of the components, and achieve the effects of compatible manufacturing processes, simple circuits and stable properties.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0027] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with specific examples, but the present invention is not limited to the following examples. The methods are conventional methods unless otherwise specified.
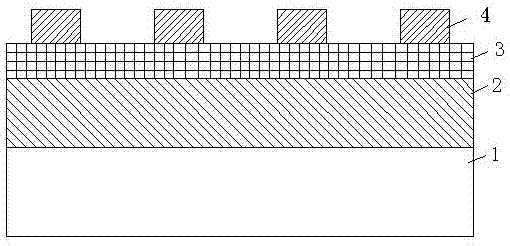
[0028] like figure 1 As shown, the complementary RRAM in this embodiment includes, as the bottom layer, an AZO conductive electrode 1 , a polycrystalline CuO storage medium layer 2 , an amorphous ZrO storage medium layer 3 , and a W electrode 4 . The bottom conductive electrode can also be made of materials such as ITO, FTO or GZO, preferably AZO; the thickness of the AZO electrode 1 is 100nm-500nm, preferably 200nm; the thickness of the polycrystalline CuO storage medium layer 2 is 10nm-200nm, preferably 50nm; amorphous The thickness of the ZrO storage medium layer 3 is 5nm-200nm, preferably 20nm. The thickness of the top electrode W is 50nm-500nm, preferably 100nm.
[0029] figure 1 The specific preparation process of the complementary RRAM in
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap