Regeneration method for removing oxygen compound containing adsorbent in low-carbon olefins
A technology of low-carbon olefins and adsorbents, which is applied in the field of regeneration of adsorbents used to remove oxygenated compounds in low-carbon olefins, and can solve the problems of attenuation of adsorption performance of adsorbents, easy coking of adsorbents, and low regeneration efficiency , to achieve the possibility of reducing carbonization, good regeneration effect, and the effect of slowing down aggregation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
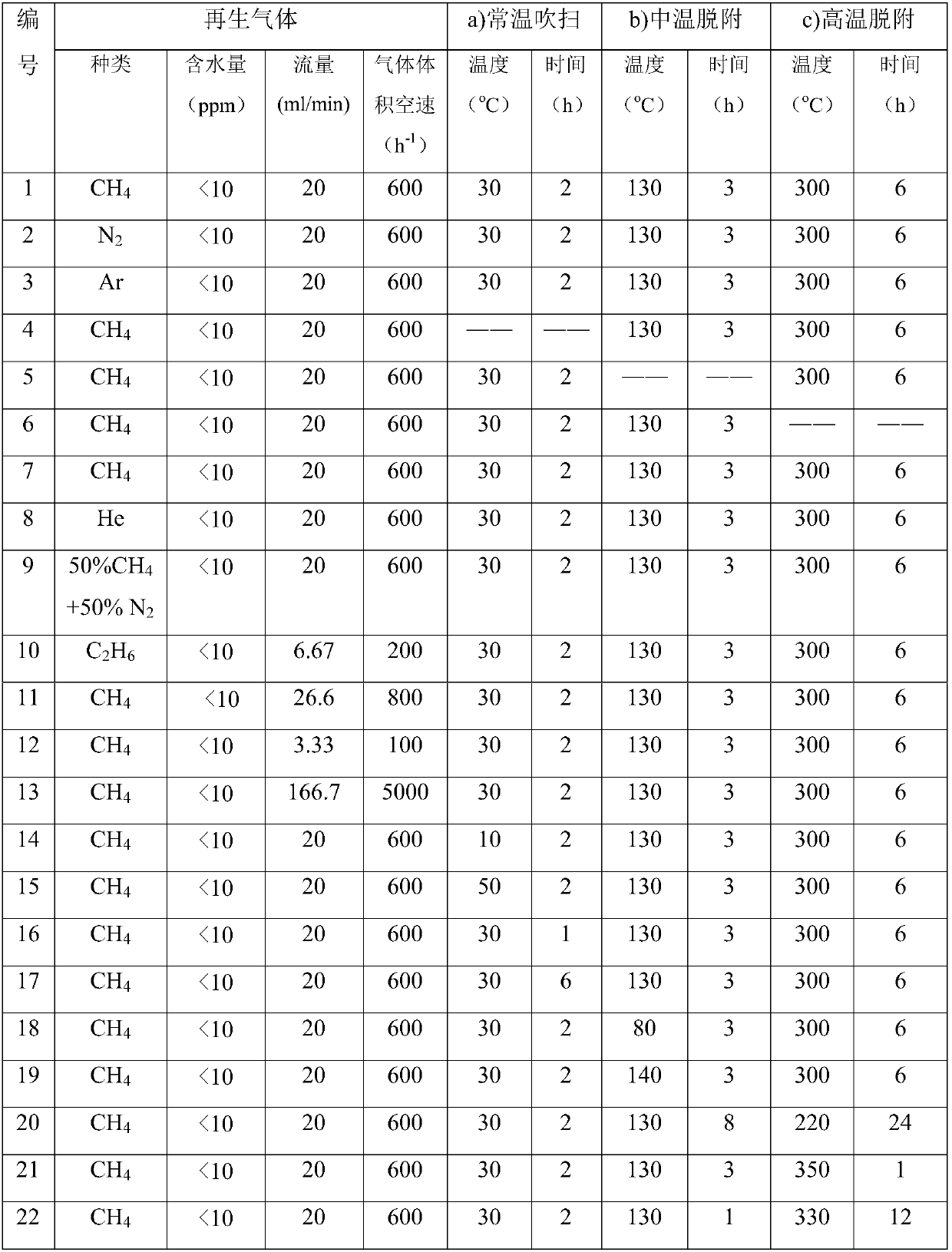
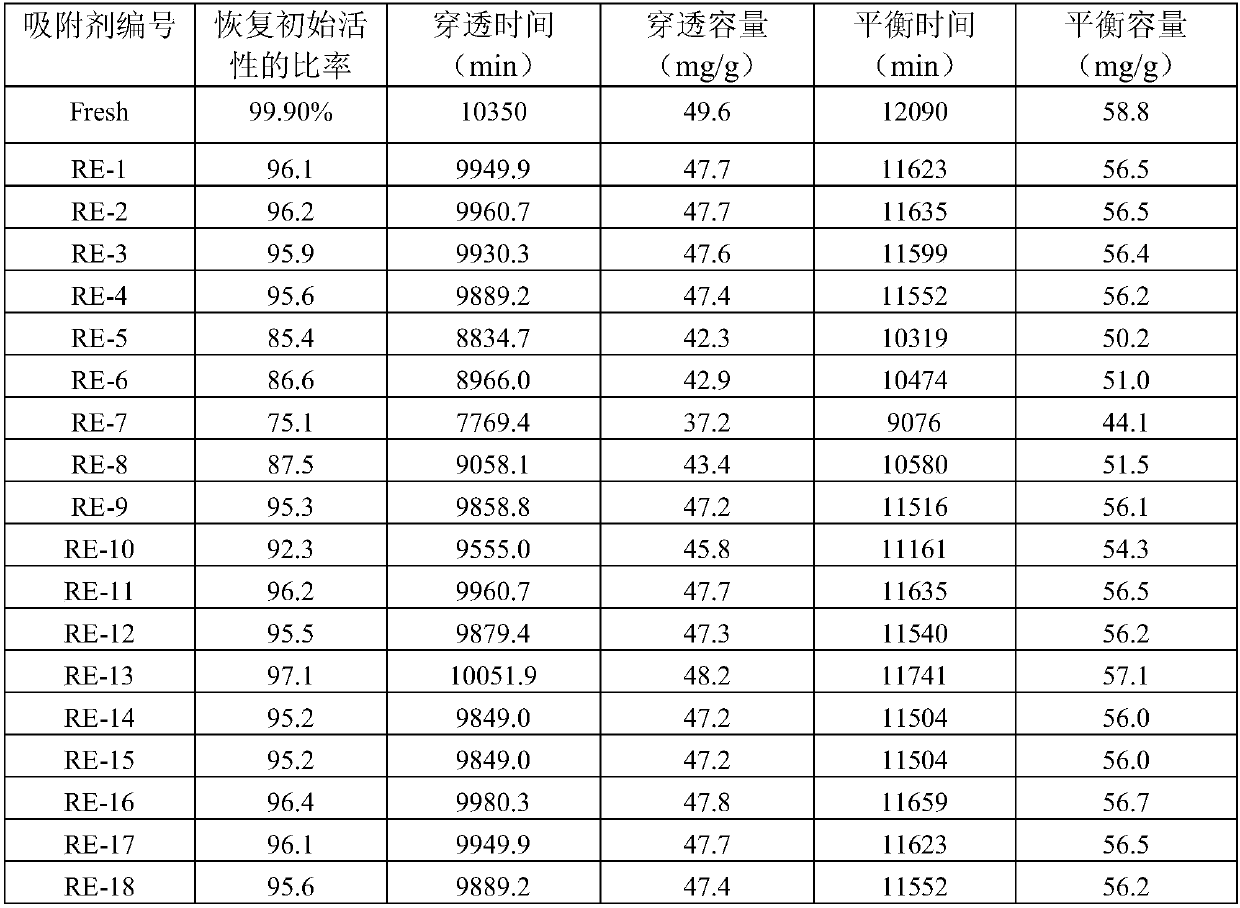
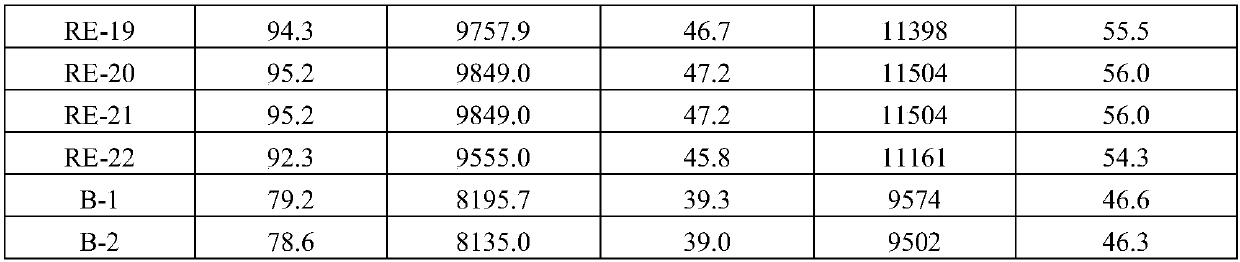
[0020] The fresh adsorbent used in the present invention is recorded as Fresh, and the solid adsorbent adopts Zn 2+ Ion-exchange modified Y-type molecular sieves for the adsorption and removal of oxygenates from mixed C4 hydrocarbons. In the experiment, dimethyl ether in a C4 hydrocarbon stream is used as a probe molecule to remove oxygen-containing impurities. The content of dimethyl ether was 150 ppmw based on the total weight of the supplied C4 hydrocarbon stream. The adsorption evaluation conditions are: at 2.0MPa, 35°C, 2h -1 The volumetric space velocity of the liquid is 2ml, and the loading capacity of the adsorbent is 2ml. The appearance of the adsorbent is a cylindrical particle with a particle diameter of 10-20 mesh. After the adsorption experiment was carried out for 72 hours, the adsorbent deactivated and needed to be regenerated, and the deactivated adsorbent was recorded as S-1.
[0021] After the adsorption experiment, the adsorbent needs to be regenerated befor
Embodiment 2
[0024] The fresh adsorbent used in the present invention is recorded as Fresh, and the solid adsorbent adopts Zn 2+ Ion-exchange modified Y-type molecular sieves for the adsorption and removal of oxygenates from mixed C4 hydrocarbons. In the experiment, dimethyl ether in a C4 hydrocarbon stream is used as a probe molecule to remove oxygen-containing impurities. The content of dimethyl ether was 150 ppmw based on the total weight of the supplied C4 hydrocarbon stream. The adsorption evaluation conditions are: at 2.0MPa, 35°C, 2h -1 The volumetric space velocity of the liquid is 2ml, and the loading capacity of the adsorbent is 2ml. The appearance of the adsorbent is a cylindrical particle with a particle diameter of 10-20 mesh. After the adsorption experiment was carried out for 72 hours, the adsorbent deactivated and needed to be regenerated, and the deactivated adsorbent was recorded as S-2.
[0025] After the adsorption experiment, the adsorbent needs to be regenerated befor
Embodiment 3
[0028] The fresh adsorbent used in the present invention is recorded as Fresh, and the solid adsorbent adopts Zn 2+ Ion-exchange modified Y-type molecular sieves for the adsorption and removal of oxygenates from mixed C4 hydrocarbons. In the experiment, dimethyl ether in a C4 hydrocarbon stream is used as a probe molecule to remove oxygen-containing impurities. The content of dimethyl ether was 150 ppmw based on the total weight of the supplied C4 hydrocarbon stream. The adsorption evaluation conditions are: at 2.0MPa, 35°C, 2h -1 The volumetric space velocity of the liquid is 2ml, and the loading capacity of the adsorbent is 2ml. The appearance of the adsorbent is a cylindrical particle with a particle diameter of 10-20 mesh. After the adsorption experiment was carried out for 72 hours, the adsorbent deactivated and needed to be regenerated, and the deactivated adsorbent was recorded as S-3.
[0029] After the adsorption experiment, the adsorbent needs to be regenerated befor
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap