Method for preventing loss of molten salt phase-change heat storage material by utilizing activated carbon
A phase change heat storage material and a phase change material technology, which are applied in the field of using activated carbon to prevent the loss of molten salt phase change heat storage materials, can solve problems such as material failure, loss of molten salt, shedding and aging, and achieve a simple preparation method and mechanical properties. Excellent, long service life effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
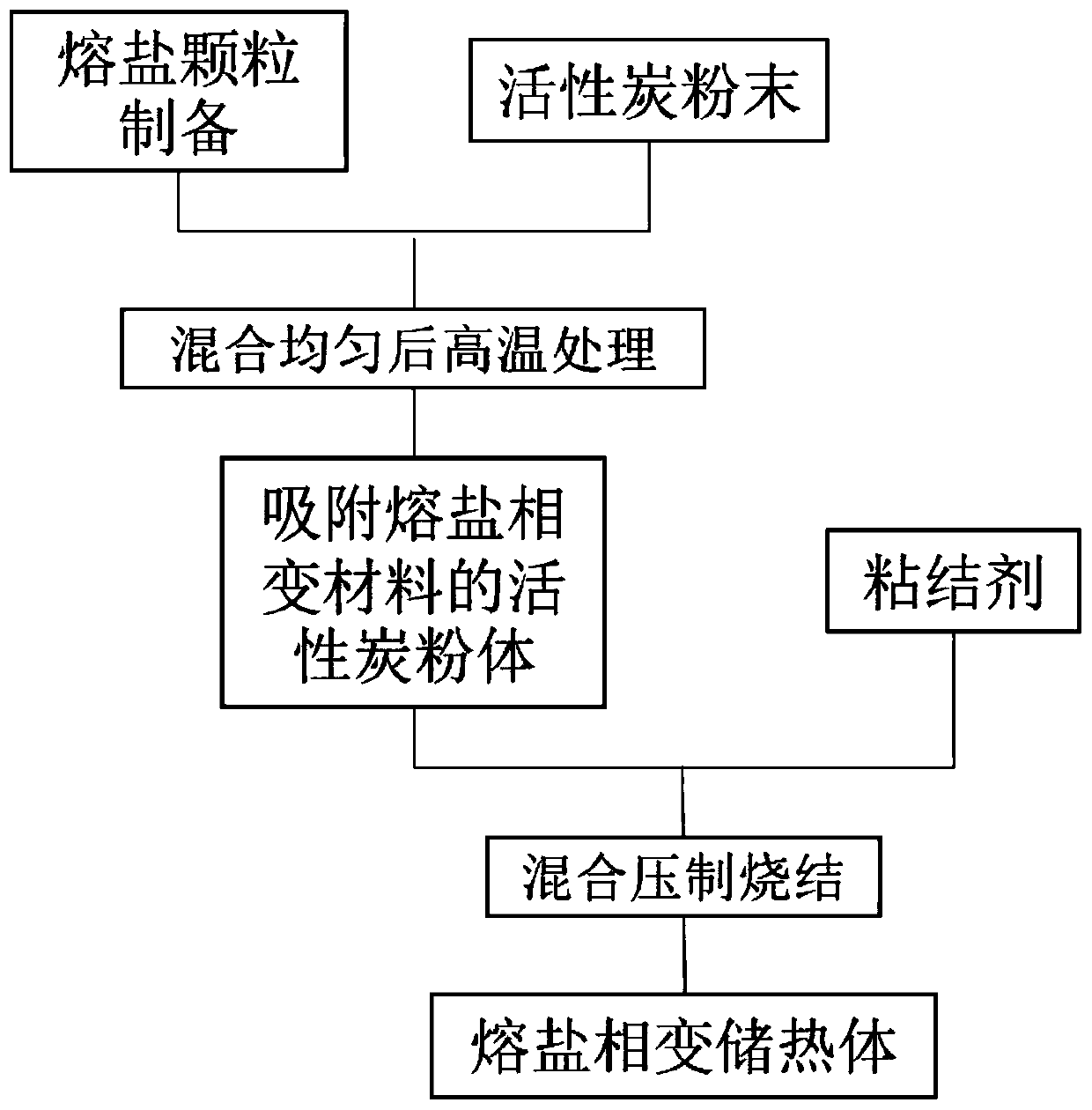
[0033] The method for using activated carbon to prevent the loss of molten salt phase change heat storage material provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0034] 1. Activated carbon adsorbs molten salt particles
[0035] (1) The prepared activated carbon and the sun salt particles are ground and mixed in a mass ratio of activated carbon: sun salt=2:3, so that the two components are evenly distributed; wherein the sun salt is composed of 60%wt NaNO 3 and 40%wt KNO 3 Mixed eutectic composition.
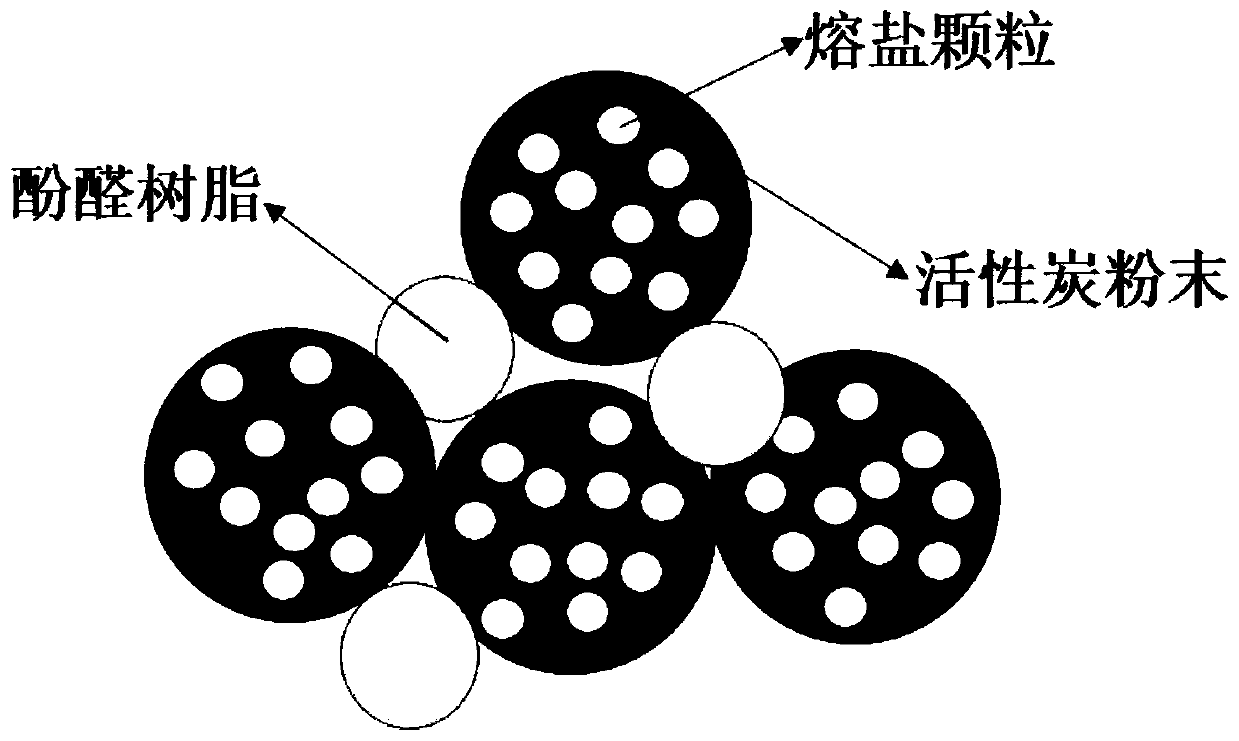
[0036] (2) Put the mixed powder into a tube furnace and keep it at 250°C for 3 hours, so that the solar salt is completely melted and flows into the activated carbon hole, and cooled to room temperature to obtain the activated carbon powder carrying the molten salt phase change material.
[0037] 2. Press and sinter the molten salt phase change material sample
[0038] (1) Grinding and mixing the activated carbon powder carrying the molten salt phase change material
Embodiment 2
[0044] The method for using activated carbon to prevent the loss of molten salt phase change heat storage material provided in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0045] 1. Activated carbon adsorbs molten salt particles
[0046] (1) The prepared activated carbon and the sun salt particles are ground and mixed in a mass ratio of activated carbon: sun salt=2:3, so that the two components are evenly distributed; wherein the sun salt is composed of 60%wt NaNO 3 and 40%wt KNO 3 Mixed eutectic composition.
[0047] (2) Put the mixed powder into a tube furnace and keep it at 250°C for 3 hours, so that the solar salt is completely melted and flows into the activated carbon hole, and cooled to room temperature to obtain the activated carbon powder carrying the molten salt phase change material.
[0048] 2. Press and sinter the molten salt phase change material sample
[0049] (1) Grinding and mixing the activated carbon powder carrying the molten salt phase change material
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap