High frequency control of a semiconductor switch
A semiconductor and switching technology, applied in the control field of semiconductor switches, can solve the problems of inability to achieve switching speed, inappropriate switching frequency, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
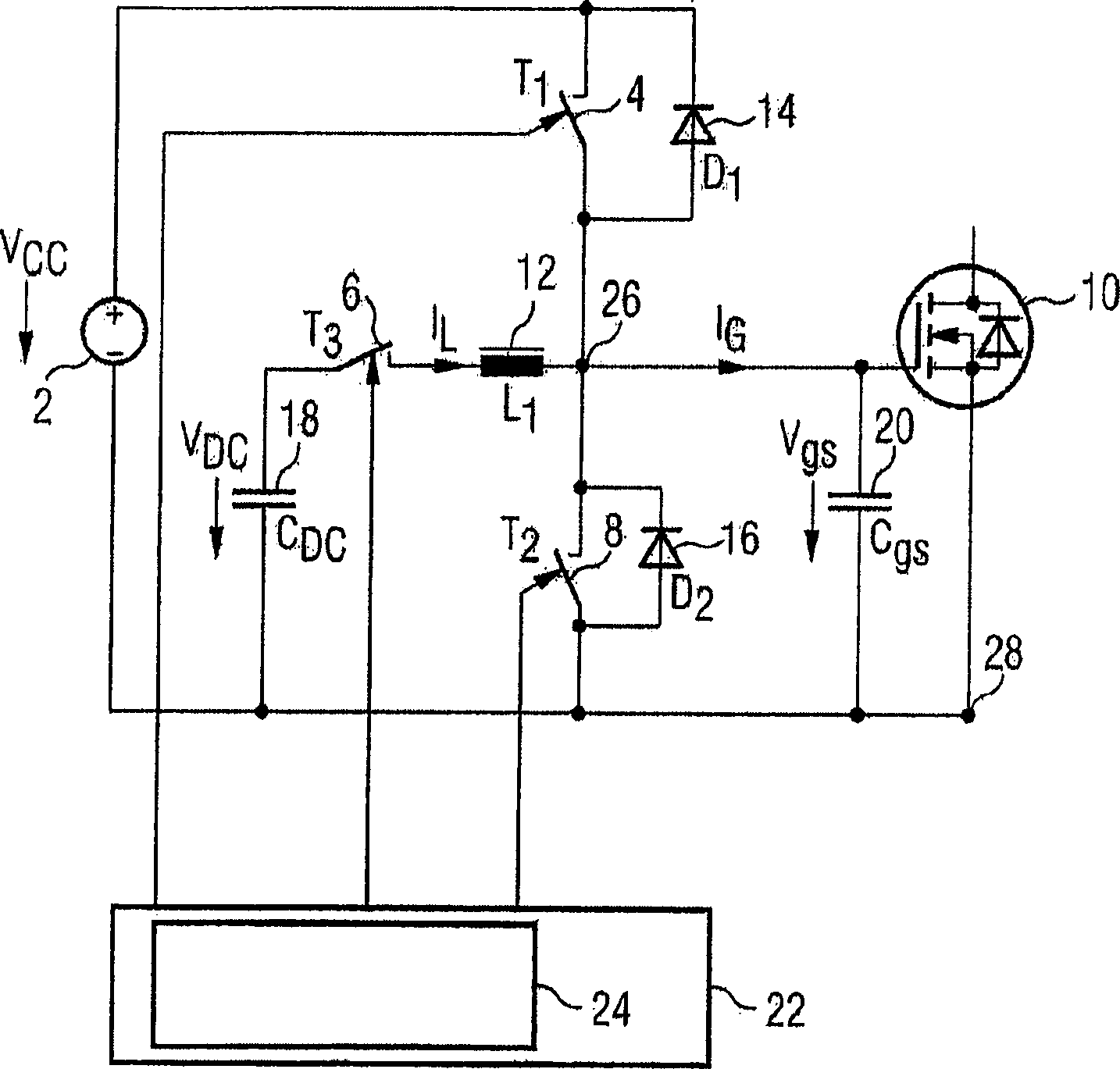
[0021] figure 1 A simplified circuit diagram of a resonant gate driver for driving a MOSFET 10, such as a power MOSFET, is shown. Although this exemplary embodiment of the invention is explained for driving a MOSFET 10, it should be understood that the invention is equally applicable to most types of voltage-controlled semiconductor switches, such as eg IGBTs. Furthermore, the present invention can also be applied to current controlled semiconductors such as bipolar transistors, thyristors and triacs. Reference numeral 22 designates an exemplary embodiment of a control circuit for controlling the operation of the resonant gate drive circuit according to the method of the present invention.
[0022] figure 1 The reference number 2 in the designates the power supply, which generates the supply voltage V cc . at supply voltage V cc and the control terminal 26 of the MOSFET 10, i.e. the gate of the MOSFET 10, a first switch T denoted by the reference numeral 4 is provided 1 .
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap