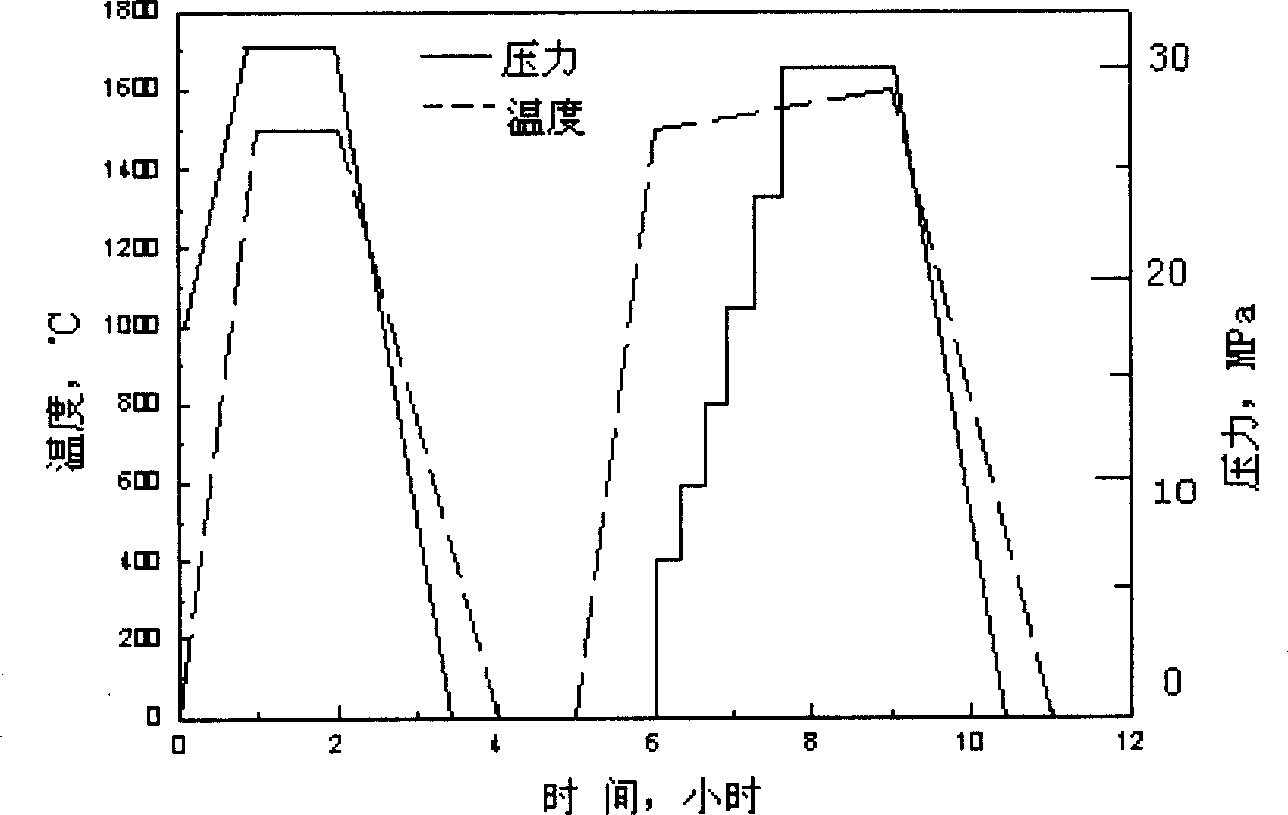
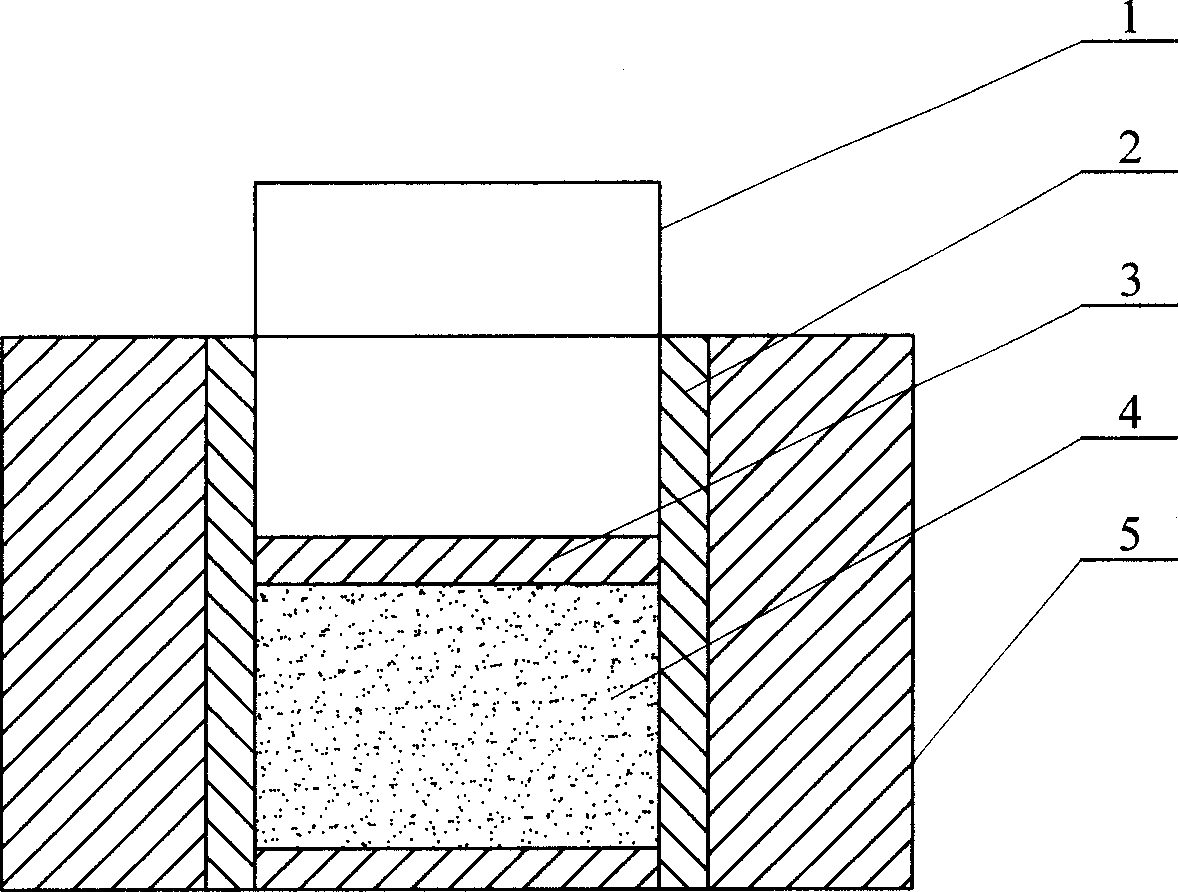
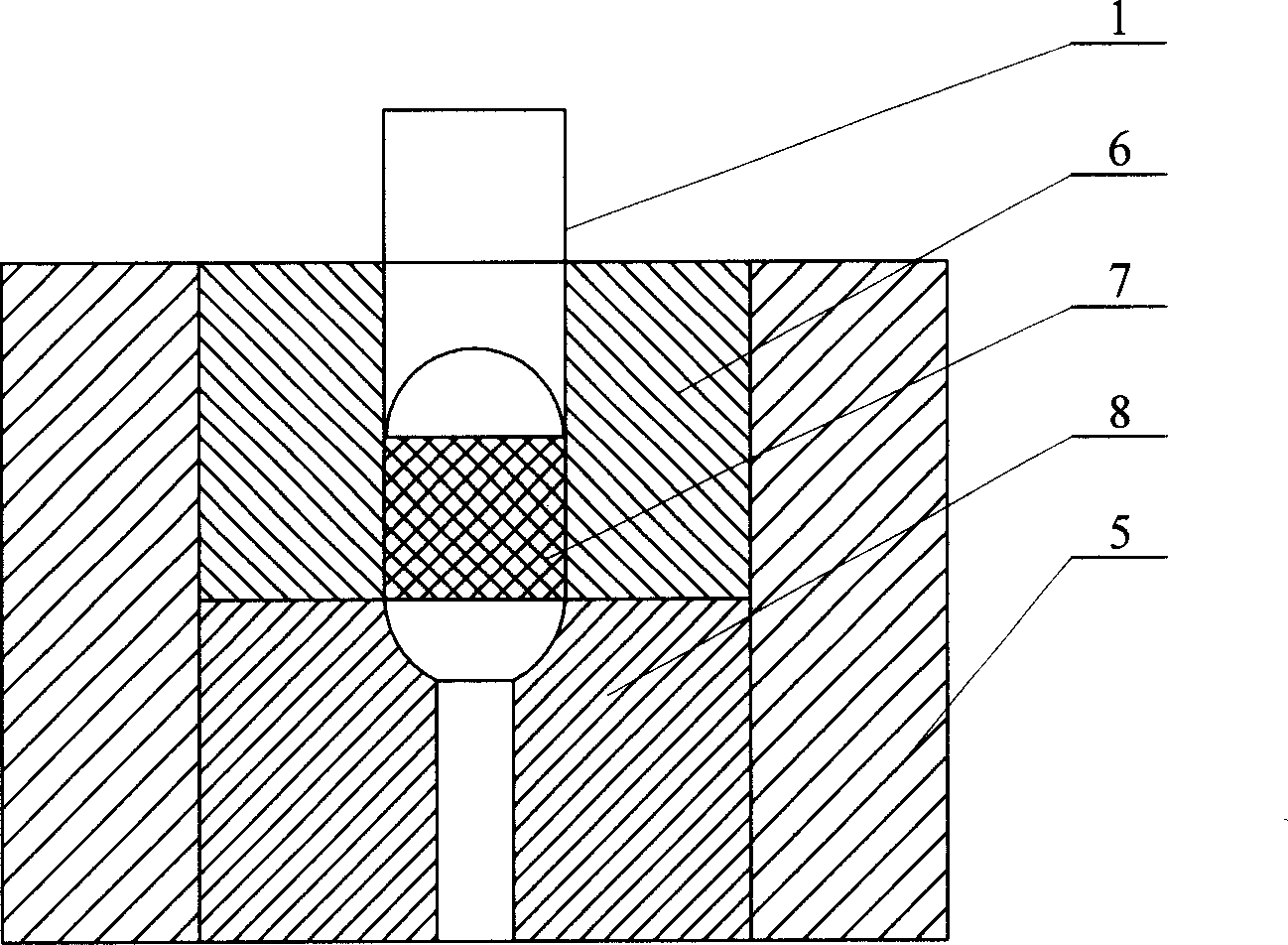
Shaping method of nanometer bioceramic artificial joint
A technology for bioceramics and artificial joints, applied in medical science, prosthesis and other directions, can solve the problems of difficult preparation and processing of complex-shaped ceramic parts, and achieve the effects of shortening processing cycle, saving processing cost and simple forming process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0016] Specific implementation mode 1: In this implementation mode, the preparation and forming process of nano-biological ceramic materials are completed according to the following steps:
[0017] 1. Preparation of Al by alcohol-water solution heating method 2 o 3 , ZrO 2 Nano powder. When the alcohol-water solution is heated, a gel-like precipitate is produced in the solution, and the following hydrolysis reaction occurs:
[0018] (1),
[0019] (2).
[0020] Al(NO 3 ) 3 9H 2 O, ZrOCl 2 ·8H 2 O and Y (NO 3 ) 3 ·6H 2 O is formulated into a mixed solution with a certain molar concentration by molar ratio, adding absolute ethanol at a ratio of alcohol to water of 5:1, and adding a certain amount of polyethylene glycol 200 and polyethylene glycol 1540 as a dispersant. The solution was placed in a constant temperature water bath and slowly heated to 75°C, and kept at this temperature for 6 hours to obtain a white sol. Using NH 4 HCO 3 As a precipitating ag
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Specific implementation mode two: this implementation mode completes the preparation and forming process of nano-biological ceramic materials according to the following steps:
[0029] 1. Prepare hydroxyapatite HAP powder by chemical precipitation method.
[0030] The chemical reaction equation of hydroxyapatite is as follows:
[0031] (3),
[0032] (4),
[0033] (5).
[0034] The overall equation is:
[0035] (6).
[0036] Prepare a certain concentration of (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 solution and Ca(NO 3 ) 2 solution. where Ca(NO 3 ) 24H 2 O prepared with absolute ethanol, (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 Prepare with deionized water. According to formula (6), the two solutions are chemically reacted. Ca(NO 3 ) 2 solution, and then add a small amount of (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 solution, to generate HAP crystal nuclei in the reaction mixture, and then dropwise add (NH 4 ) 2 HPO 4 Solution, along with the progress of the reaction, add ammonia water dropwise at
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is different from Embodiment 1 and Embodiment 2 in that, according to the different ratios of materials, the composition ratio of nano-biological ceramics is shown in Table 3.
[0045] Al 2 o 3
[0046] Note: Al 2 o 3 : ZrO 2 is the mole fraction ratio; ZrO 2 : HAP is the mass fraction ratio.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Granularity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap