Vacuum Insulation Panel, Insulated Masonry Structure Comprising Same, And Method Of Construction
a technology of vacuum insulation and masonry structure, applied in the field of vacuum insulation panels, can solve the problems of inability to meet the newly mandated insulative properties of the home, the limitation of the amount of thermal resistance possible from the constrained thickness wall, and the traditional insulator, so as to reduce the vacuum level, improve the control of water vapor, and reduce the specific surface area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
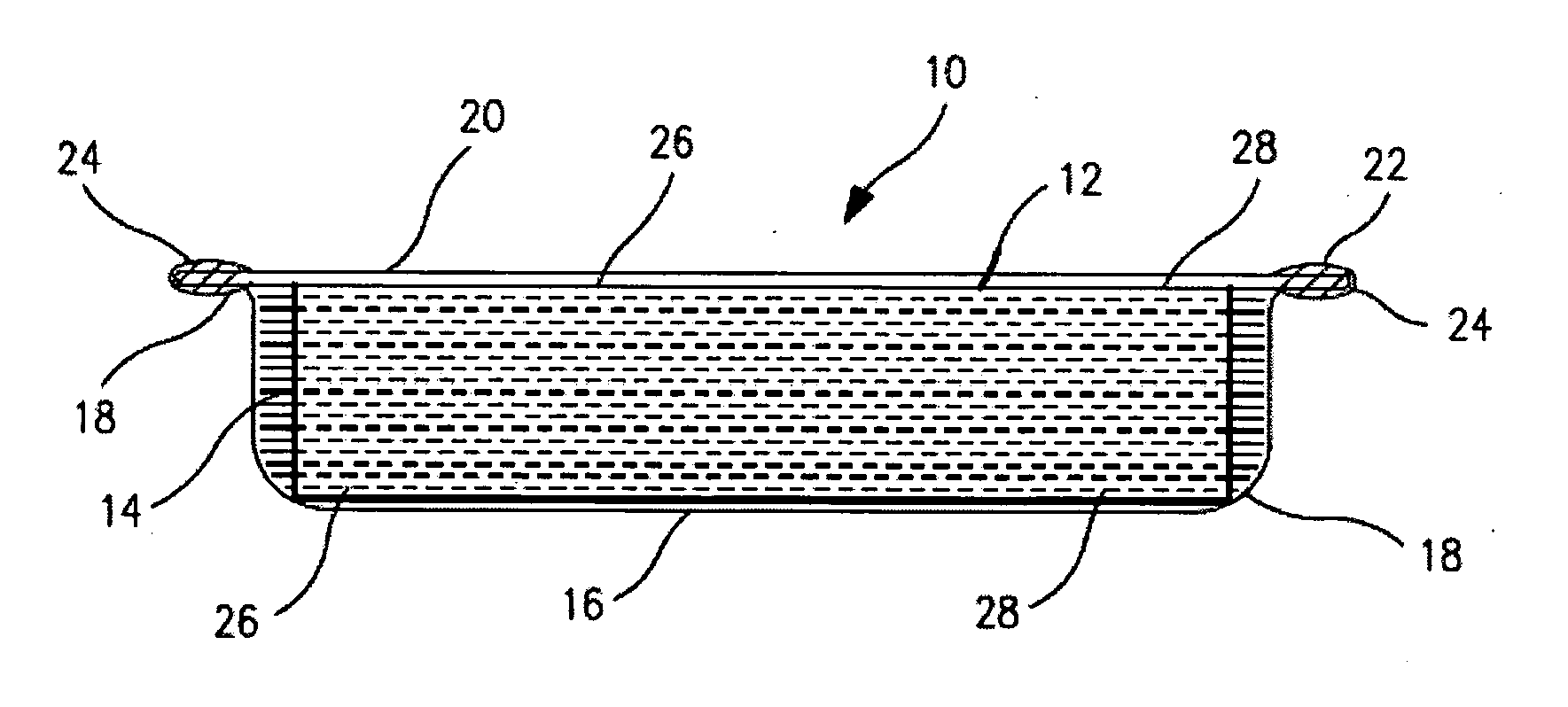
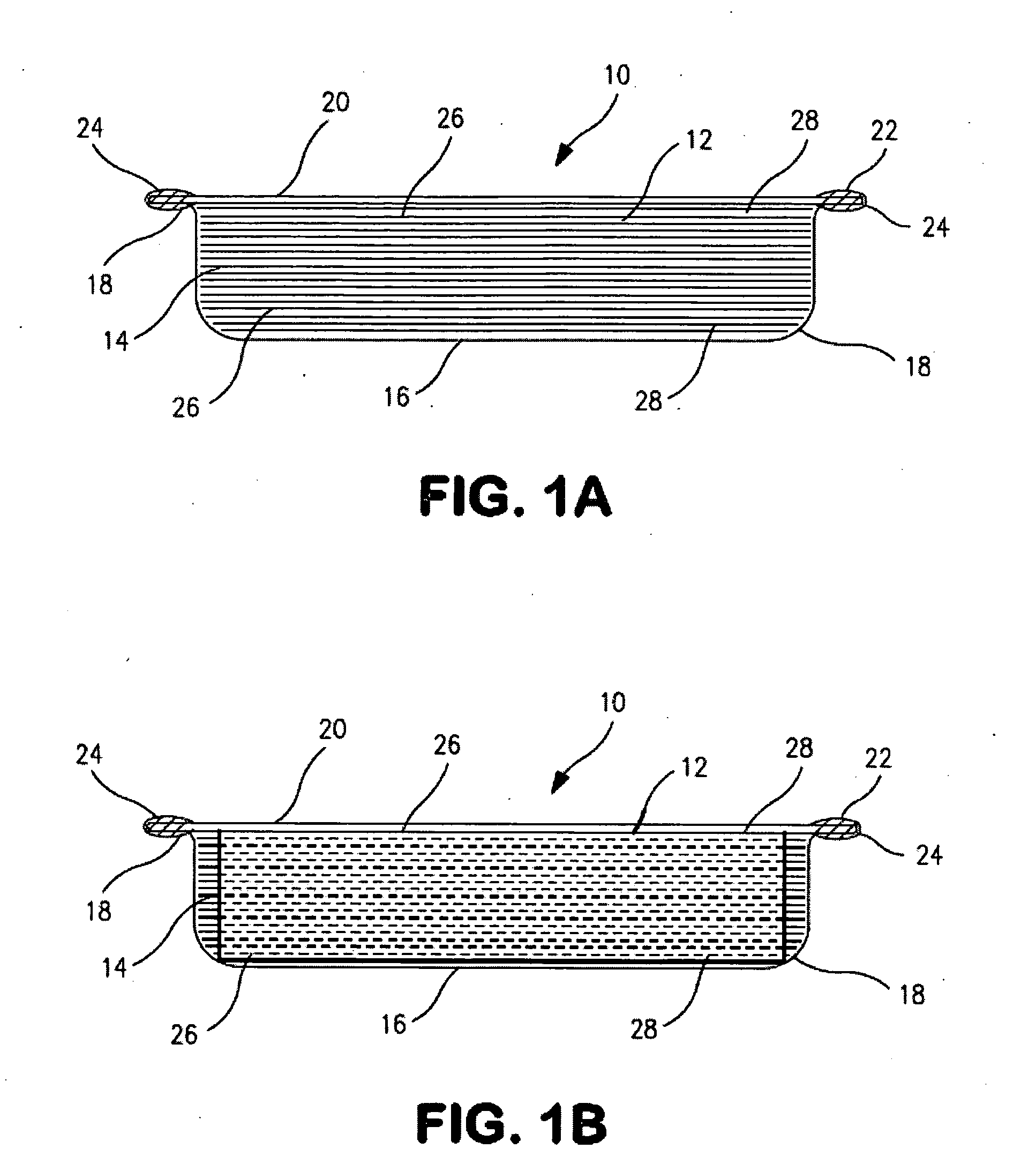
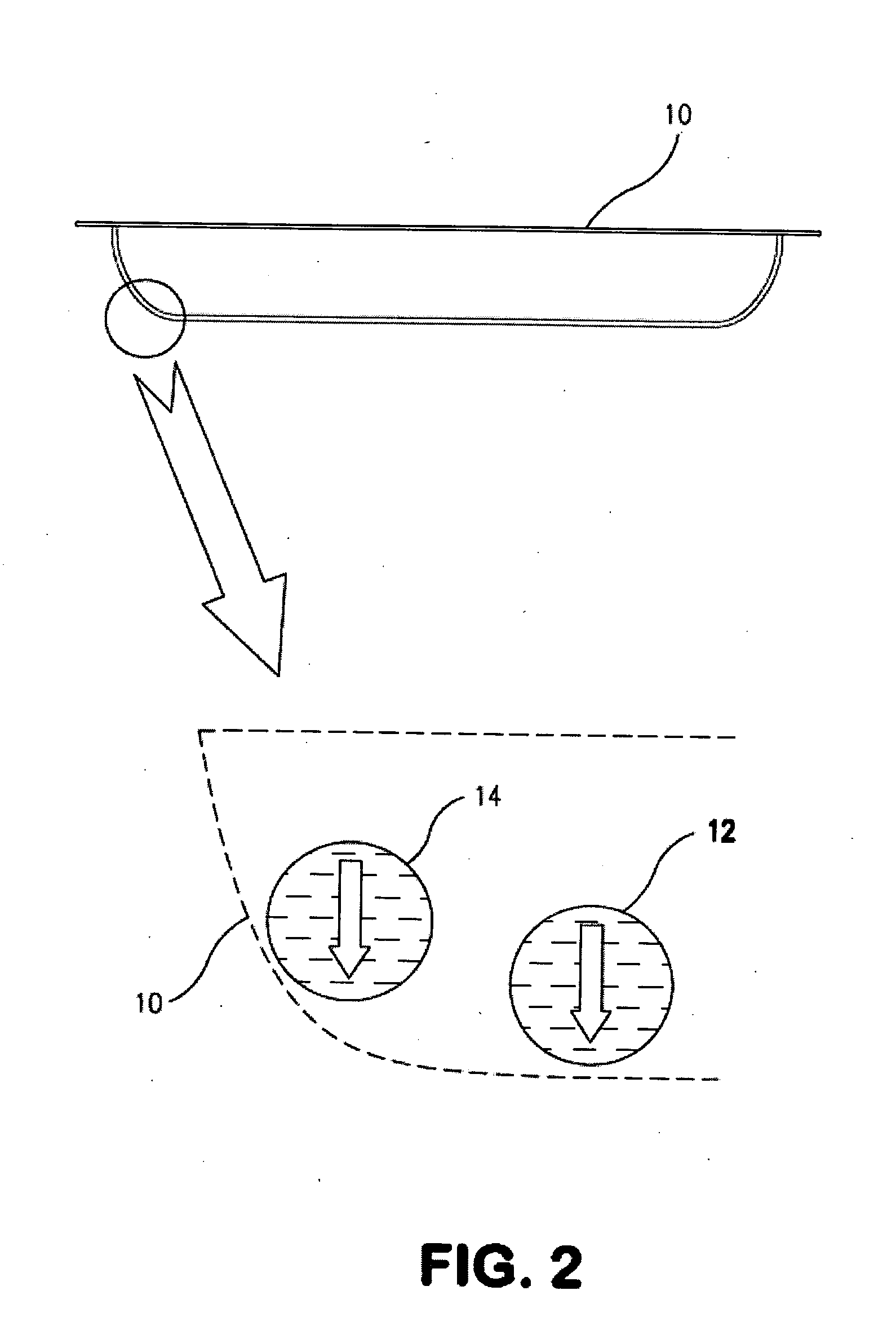
[0069]The present invention is described in terms of a vacuum insulation panel which is particularly suitable for use in the construction industry. This insulation panel can be formed in any shape although for illustration purposes panel 10 is shown rectangular in shape. As illustrated in FIG. 1A, an insulation panel shown generally at 10 produced according to the present invention has a core 12 comprised of multiple stacked layers of non-woven organic free fiberglass sheets or plies 14. In a preferred embodiment, as illustrated in FIG. 1A, vacuum insulation panel 10 is formed from two stainless steel foil sections, viz. a first pan-shaped section 16 having rounded corners 18, and a second pan of equal or shallower depth or a flat section 20 formed from a rolled sheet of the same stainless steel foil as pan section 16. The joint 22 at the edge of enclosure 10 is preferably sealed by resistance seam welding.
[0070]Although conventional stamping can be used to form pan 16, in a preferred
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap