Transmission device, receiving device, transmission method, and receiving method
a technology of receiving device and transmission device, which is applied in the direction of signal allocation, transmission path sub-channel allocation, payload allocation, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the increase in the number of base stations, reasonable costs for installation of base stations, etc., and achieves the effect of increasing the resource amount of the first data resource and avoiding collisions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
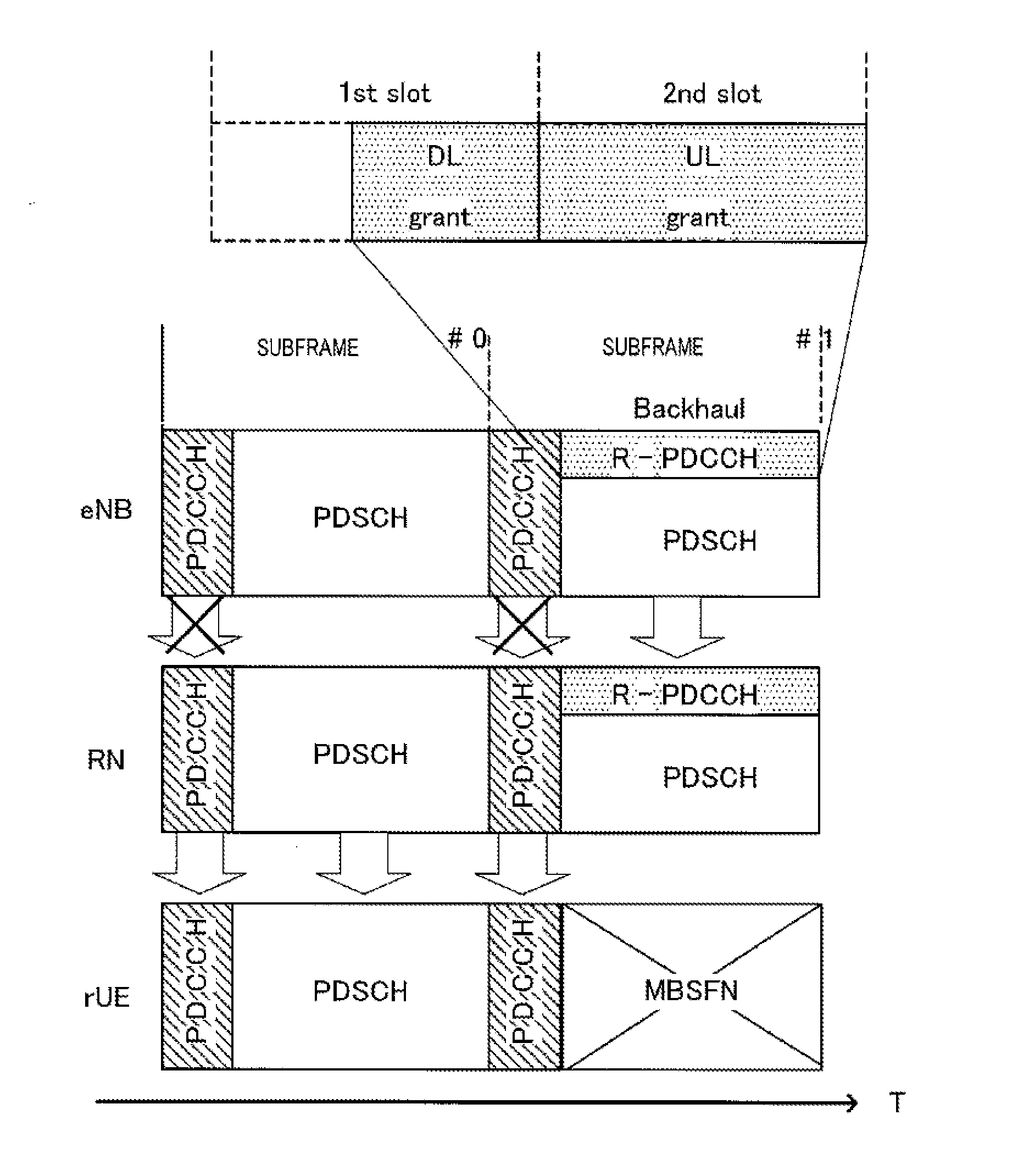
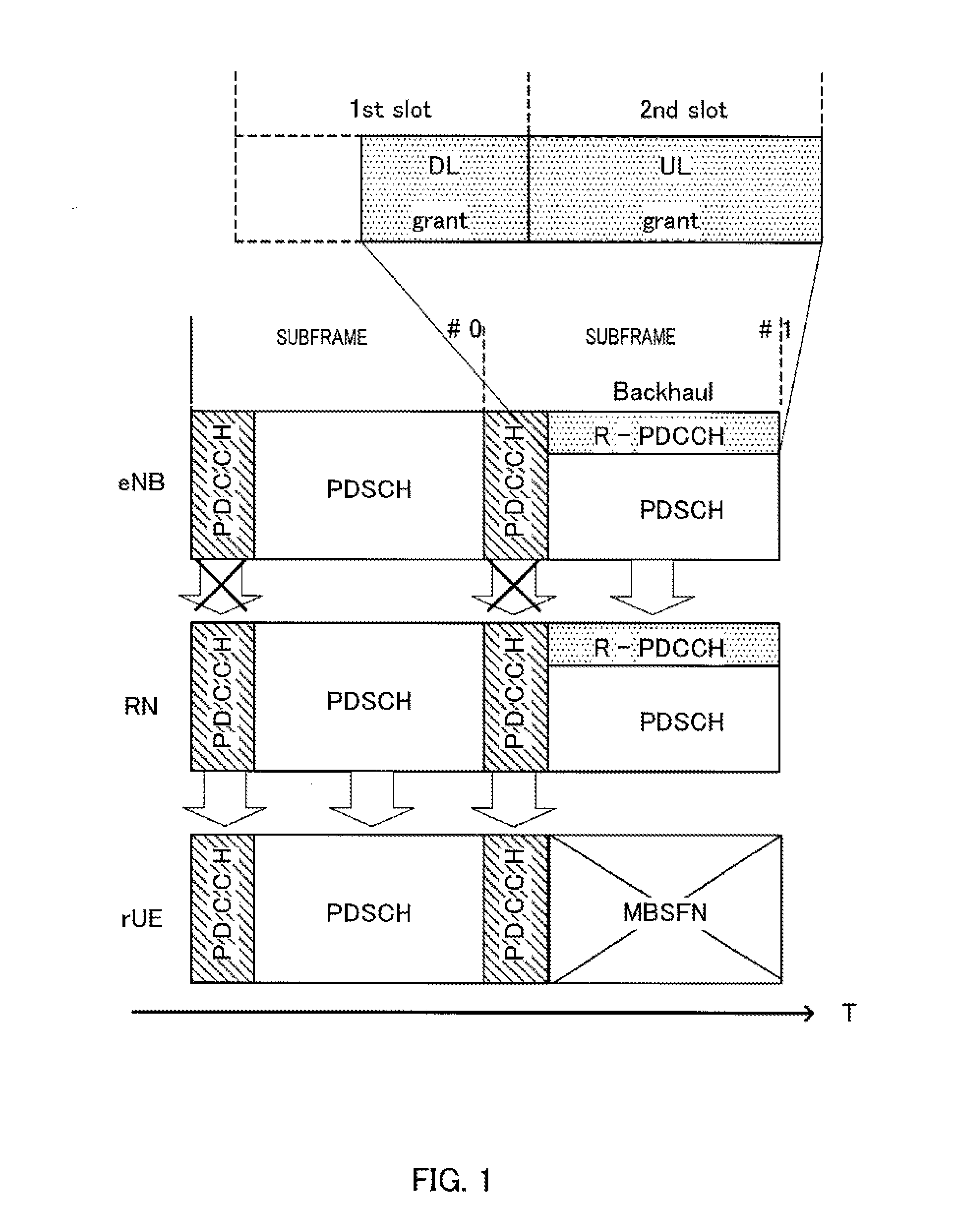
[0053](Overview of Communication System)
[0054]A communication system according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention includes a transmitting apparatus and a receiving apparatus. Specifically, in this embodiment of the present invention, a description will be provided while the transmitting apparatus is referred to as base station 100, and the receiving apparatus is referred to as terminal 200. The communication system is an LTE-A system, for example. Base station 100 is an LTE-A base station, and terminal 200 is an LTE-A terminal, for example.
[0055]FIG. 5 illustrates a main configuration of base station 100 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. Base station 100 transmits a control signal for terminal 200 after mapping the control signal to a first resource region usable for a control channel or a data channel (R-PDCCH for a terminal, in this case) or in a second resource region usable for a control channel (a PDCCH, in this case). Furthermore, base station 100 transmit
embodiment 2
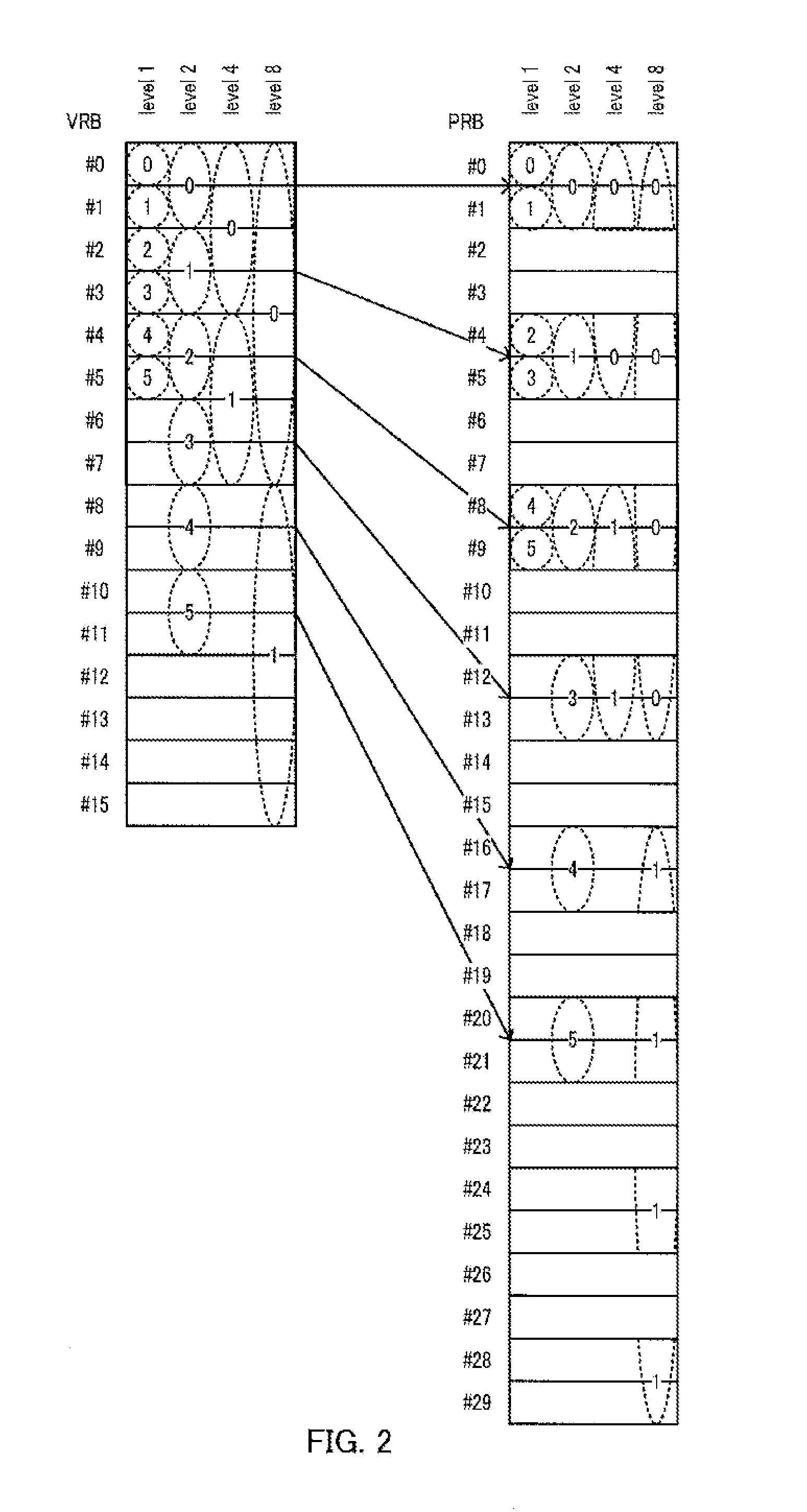
[0114]Embodiment 2 is an embodiment when the number of layers to be used is equal to or greater than two. Since a base station and a terminal according to Embodiment 2 are similar to base station 100 and terminal 200 according to Embodiment 1, the base station and terminal be described with reference to FIGS. 7 and 9.
[0115]In base station 100 of Embodiment 2, when the number of layers to be used is equal to or greater than two, transmission controlling section 102 sets a data resource region in the whole first resource region in an RBG so as to overlap with a control resource region.
[0116]When the number of layers to be used is equal to or greater than two, signal allocation section 106 punctures transmission data corresponding to a portion of the data resource region that overlaps with the control resource region and then maps the punctured transmission data to a portion of the data resource region that does not overlap with the control resource region. This transmission data is trans
embodiment 3
[0124]As a resource allocation method different from the resource allocation methods in Embodiments 1 and 2, there is a method that adds an additional bit (1 bit) other than the resource allocation bit to a DL grant and reports whether or not the 2nd slot of the PRB pair in which the DL grant is placed is used for the data resource region. That is, as shown in FIGS. 11A and B, when a DL grant is mapped to a region (a) of a given RBG, this additional bit can report whether the DL grant allocates regions (b) and (c) (FIG. 11A) or allocates only region (c) (FIG. 11B) to a PDSCH.
[0125]However, adding the additional bit to the DL grant is not desirable although the number of additional bits is small. This is because such a design change leads to an increase in the number of test man-hours. Thus, the present embodiment reports the antenna port to be used from a base station to a terminal instead of the additional bit and thereby reports whether or not to allocate region (b) to the data resou
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap