Supplemental heat conduction path for card to chassis heat dissipation
a heat dissipation path and heat conduction path technology, applied in the direction of electrical apparatus construction details, mounting of support structures, lighting and heating apparatus, etc., can solve the problems of card and/or system failure, improper operation, card failure or system failure, etc., to increase the heat dissipation capacity of the frame 12. , the effect of increasing the conductive area or the path
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
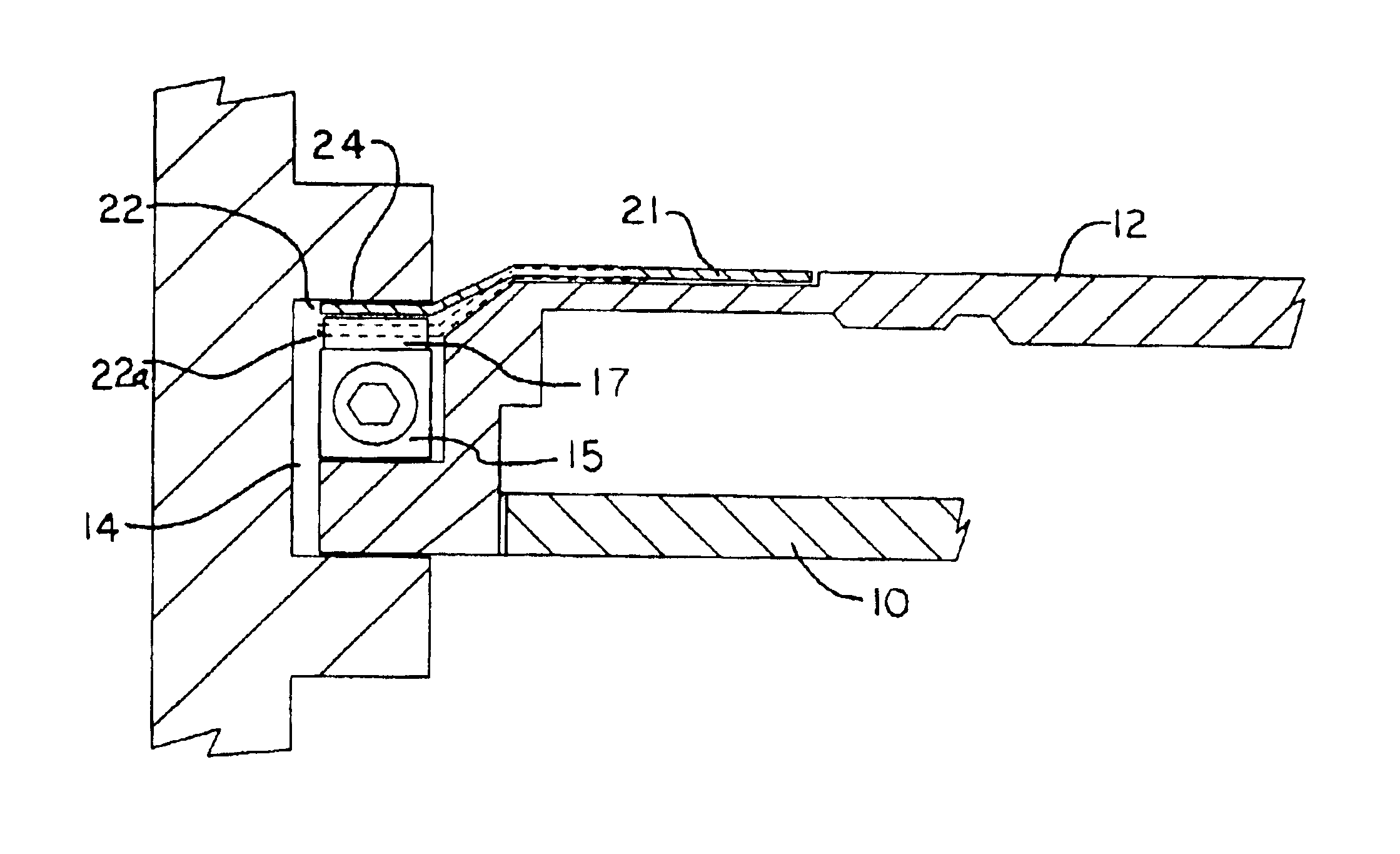
The heat plate 21 of the present invention, is made of rigid, semi-rigid or flexible, heat conductive material such as copper or an alloy commonly used in construction of heat dissipation frames. The plate is thin to allow for the flexibility necessary when the wedge lock 15 is moved into position. The flange 22 of the plate 21 can be a single continuous piece positioned between the wedge lock and the channel or it can have cut outs and notches to allow for greater flexibility. The upper segments 17 of the wedge lock 15 move laterally when the wedge lock is expanded and the heat plate must be constructed to accommodate the lateral movement of the wedge lock segments.
The heat plate 21, as illustrated in FIGS. 5, 6 and 7, extends between the wedge lock 15 and the wall of channel 14. As illustrated in FIG. 6B, flange 22 will flex slightly when the wedge lock is expanded to secure the card 10 into position. The plate 21 is constructed so that flange 22a, illustrated in broken line, is in c
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap