Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2 results about "Supercontinuum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
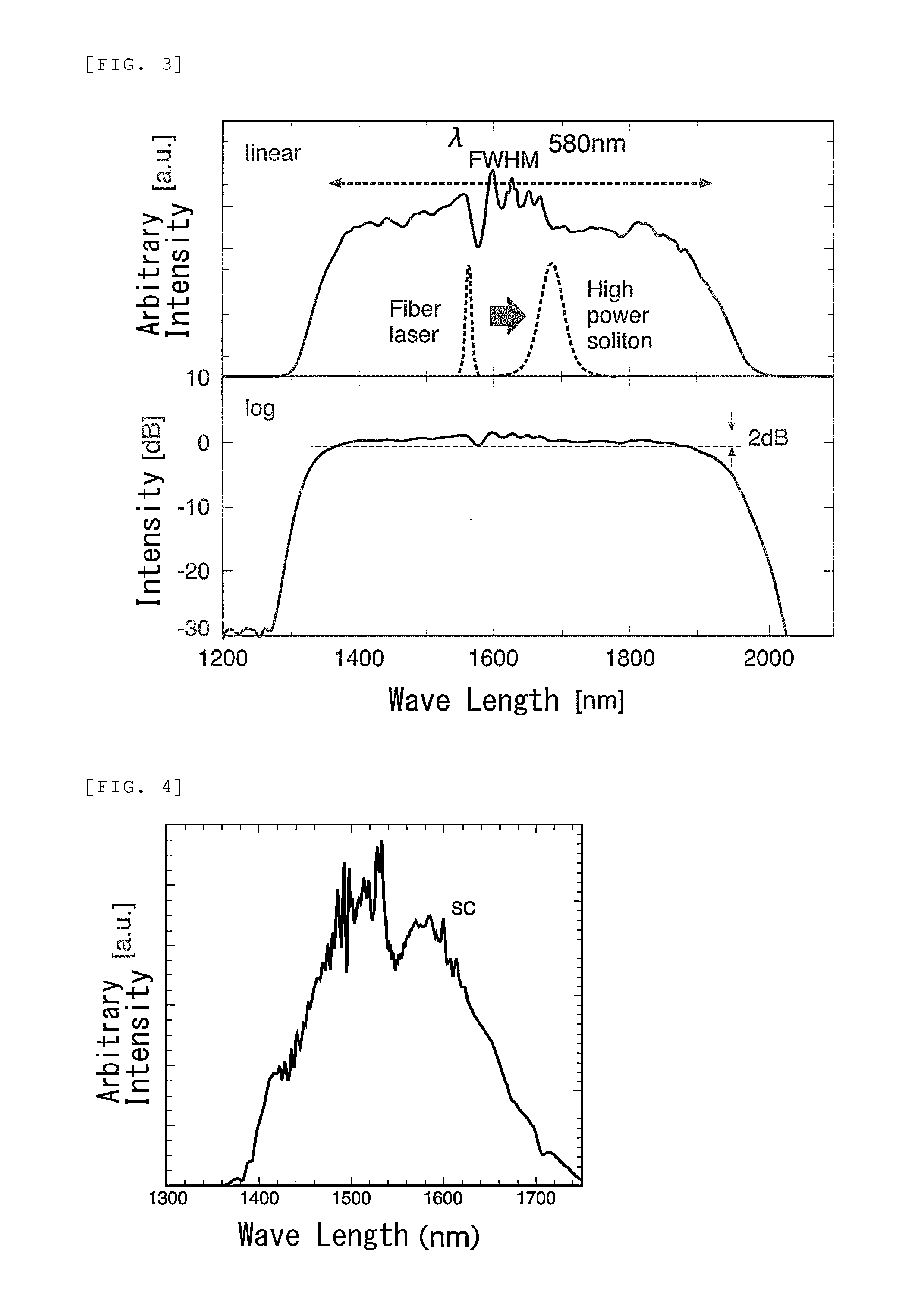
In optics, a supercontinuum is formed when a collection of nonlinear processes act together upon a pump beam in order to cause severe spectral broadening of the original pump beam, for example using a microstructured optical fiber. The result is a smooth spectral continuum (see figure 1 for a typical example). There is no consensus on how much broadening constitutes a supercontinuum; however researchers have published work claiming as little as 60 nm of broadening as a supercontinuum. There is also no agreement on the spectral flatness required to define the bandwidth of the source, with authors using anything from 5 dB to 40 dB or more. In addition the term supercontinuum itself did not gain widespread acceptance until this century, with many authors using alternative phrases to describe their continua during the 1970s, 1980s and 1990s.
Distributed surface plasma resonance optical fiber sensor and measuring method of liquid refractive index
InactiveCN106066313AReduce lossGood attentionPhase-affecting property measurementsResonance wavelengthSurface plasmon
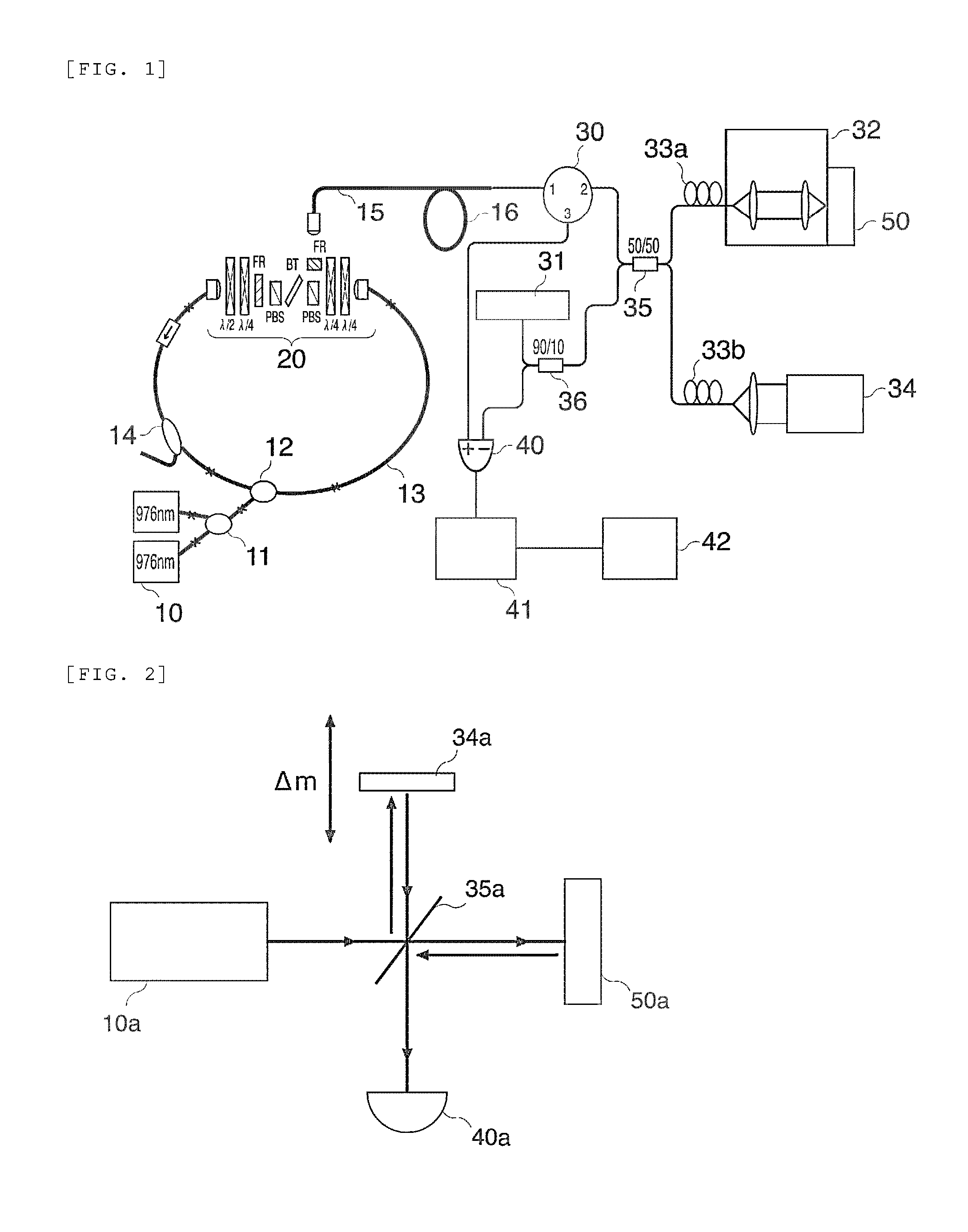
The invention provides a distributed surface plasma resonance optical fiber sensor and a measuring method of liquid refractive index. The sensor comprises a step refractive index multimode fiber, a supercontinuum source and a spectrometer, which are located at both ends of the step refractive index multimode fiber. Two sensing areas are processed on the step refractive index multimode fiber; a first sensing area and a second sensing area region have different shapes, and are coated with nano metal films. The light source emitted by the supercontinuum light is coupled to the step refractive index multimode fiber and excites surface plasma resonance in the first sensing area, and the light intensity attenuates at the corresponding resonant wavelength; the light source emitted by the supercontinuum light reaches the second sensing area for the excitation of surface plasma resonance, and the light intensity attenuates at the corresponding resonant wavelength; the resonance wavelength generated by the first sensing area and the second the sensing area are different significantly, so as to realize distributed sensing. The invention has the advantages of small volume, low optical loss and simple structure, and has wide application prospect in the biomedical field.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
Method for observing protein crystal
InactiveUS20130184445A1Improve accuracyQuality improvementMaterial analysis by optical meansDepsipeptidesBroadbandSupercontinuum
Owner:OSAKA UNIV
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap