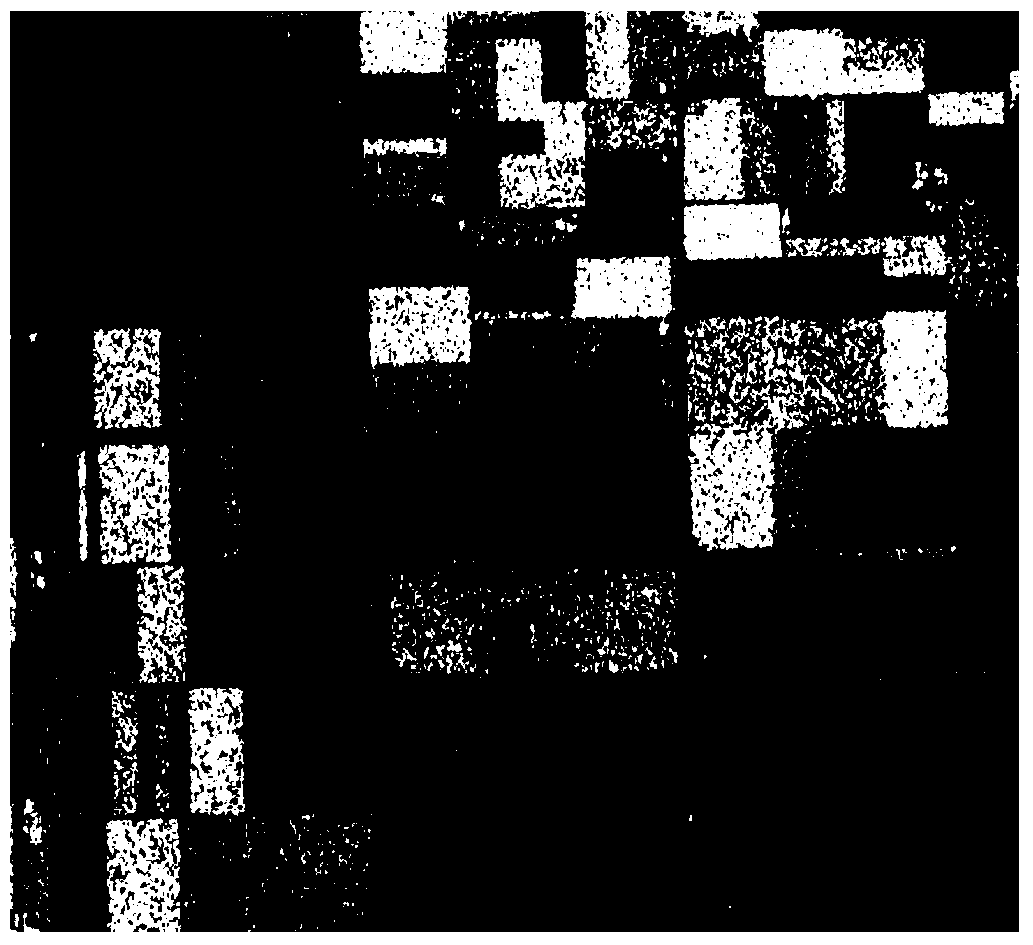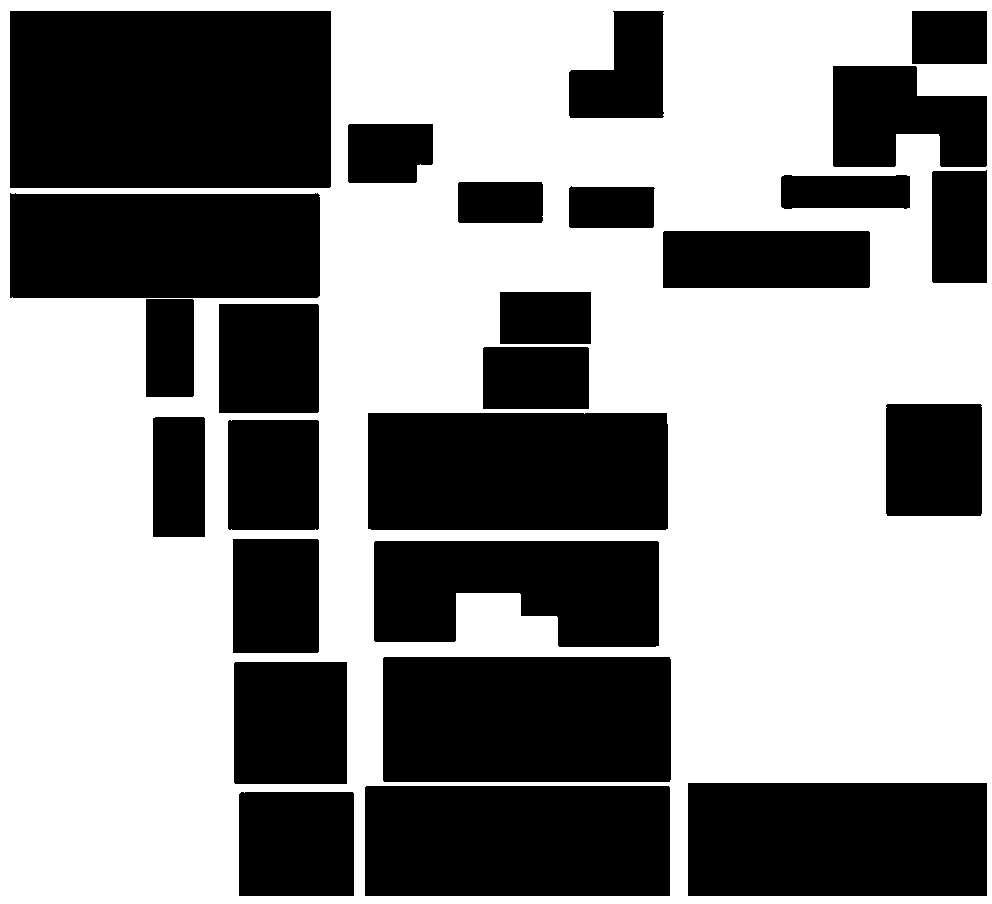Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7 results about "Synthetic aperture radar" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
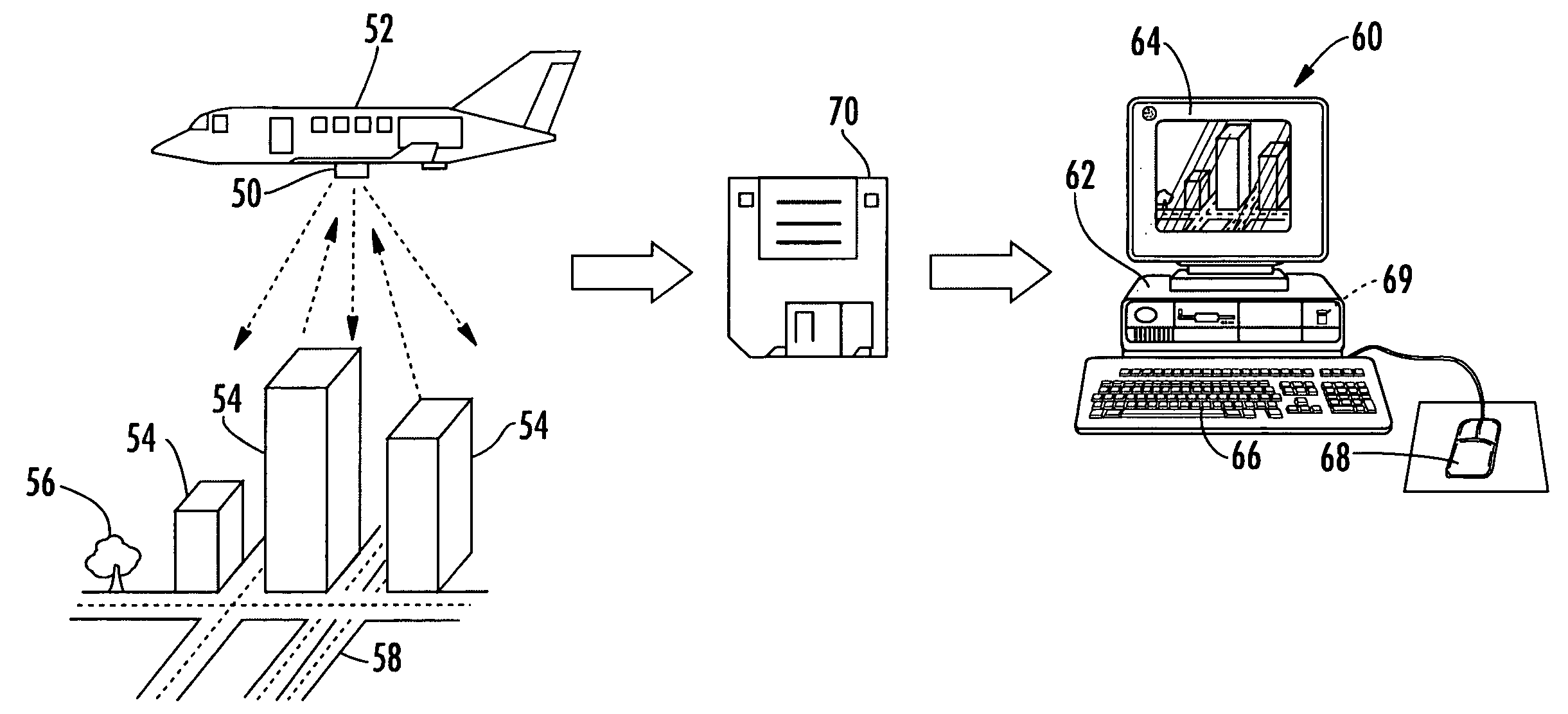
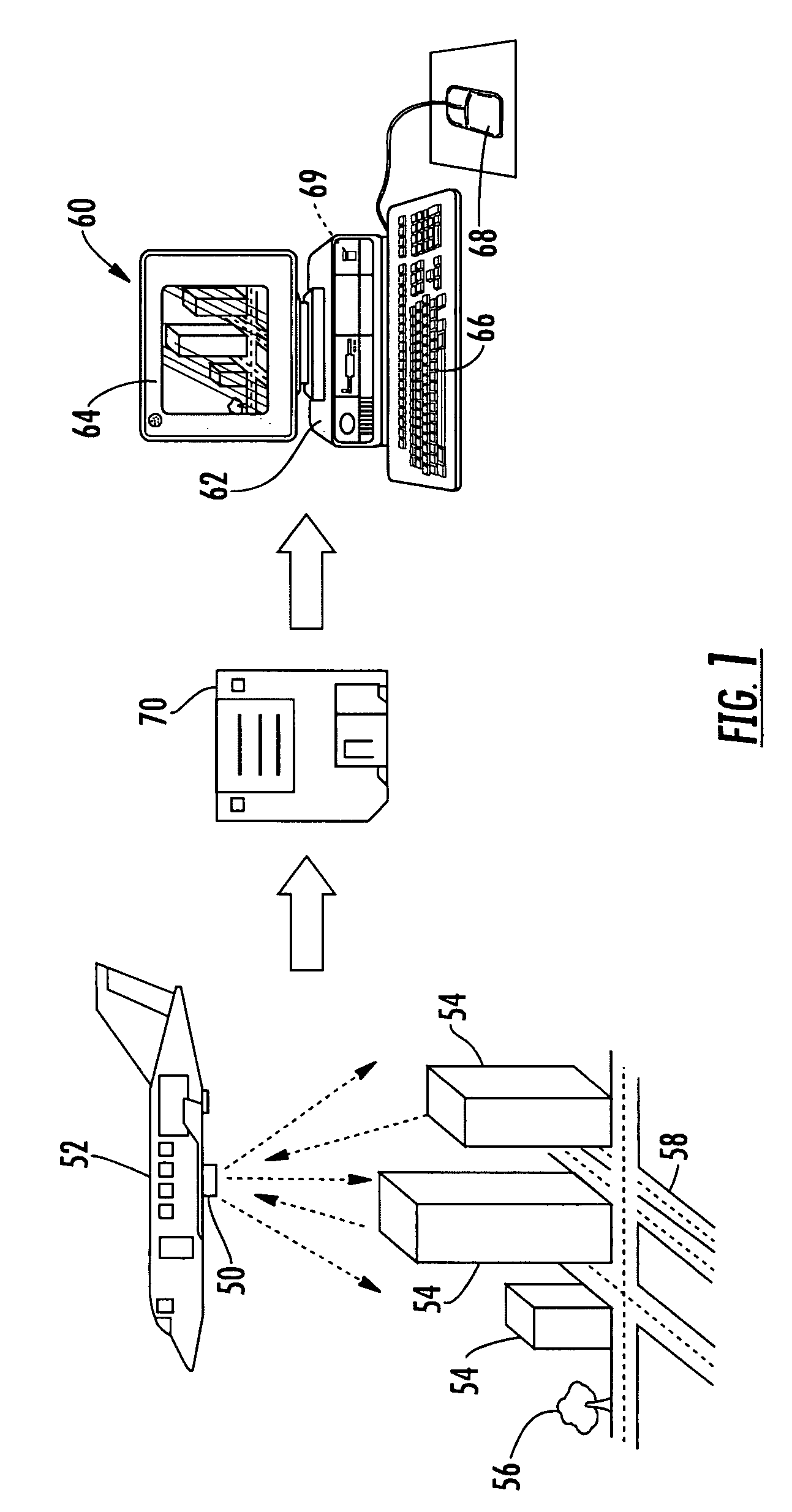
Synthetic-aperture radar (SAR) is a form of radar that is used to create two-dimensional images or three-dimensional reconstructions of objects, such as landscapes. SAR uses the motion of the radar antenna over a target region to provide finer spatial resolution than conventional beam-scanning radars. SAR is typically mounted on a moving platform, such as an aircraft or spacecraft, and has its origins in an advanced form of side looking airborne radar (SLAR). The distance the SAR device travels over a target in the time taken for the radar pulses to return to the antenna creates the large synthetic antenna aperture (the size of the antenna). Typically, the larger the aperture, the higher the image resolution will be, regardless of whether the aperture is physical (a large antenna) or synthetic (a moving antenna) – this allows SAR to create high-resolution images with comparatively small physical antennas. Additionally, SAR has the property of having larger apertures for more distant objects, allowing consistent spatial resolution over a range of viewing distances.
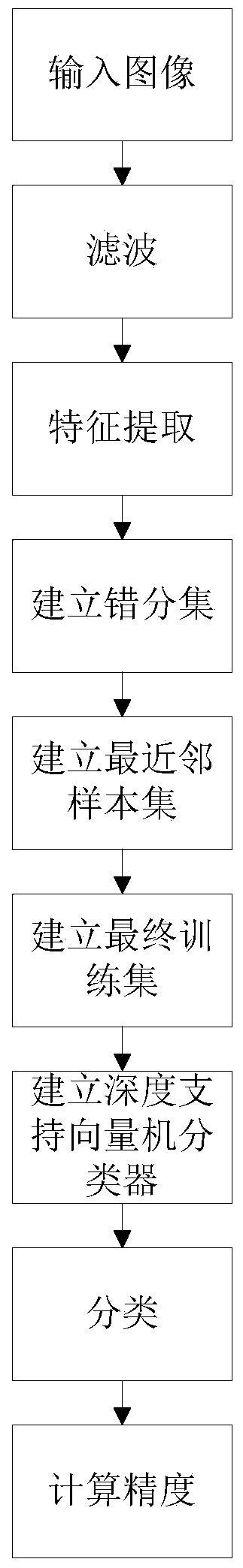
Polarized SAR image classification method based on K mean value and depth SVM
ActiveCN104239900AReduce the numberReduce sorting timeCharacter and pattern recognitionFeature extractionSynthetic aperture radar
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
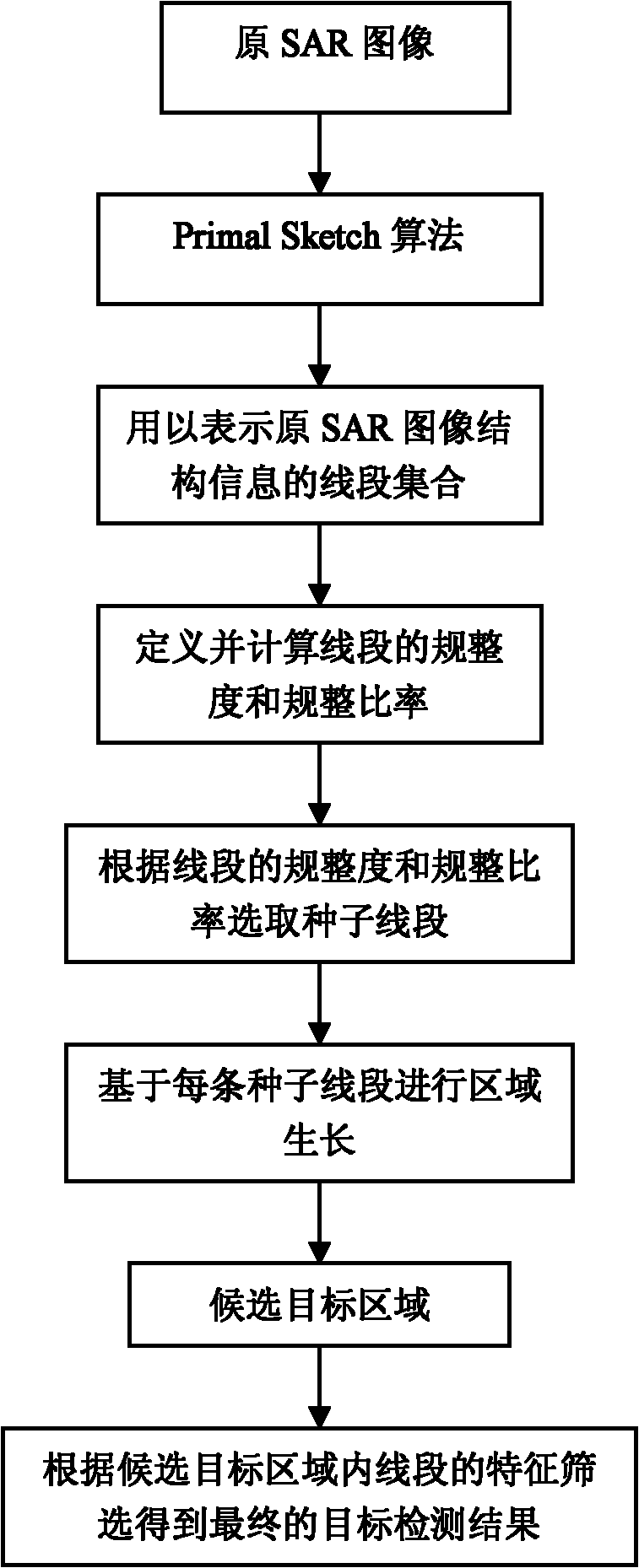
SAR (Synthetic Aperture Radar) image object detection method based on Primal Sketch algorithm
InactiveCN102129559AAccurate target detection resultsFalse Alarm Rate ReducedCharacter and pattern recognitionSynthetic aperture radarInverse synthetic aperture radar
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Method and apparatus for processing SAR images based on an anisotropic diffusion filtering algorithm
InactiveUS20080231502A1Improves subsidence measurementImprove boundary qualityImage enhancementImage analysisRadarSynthetic aperture radar
Owner:HARRIS CORP
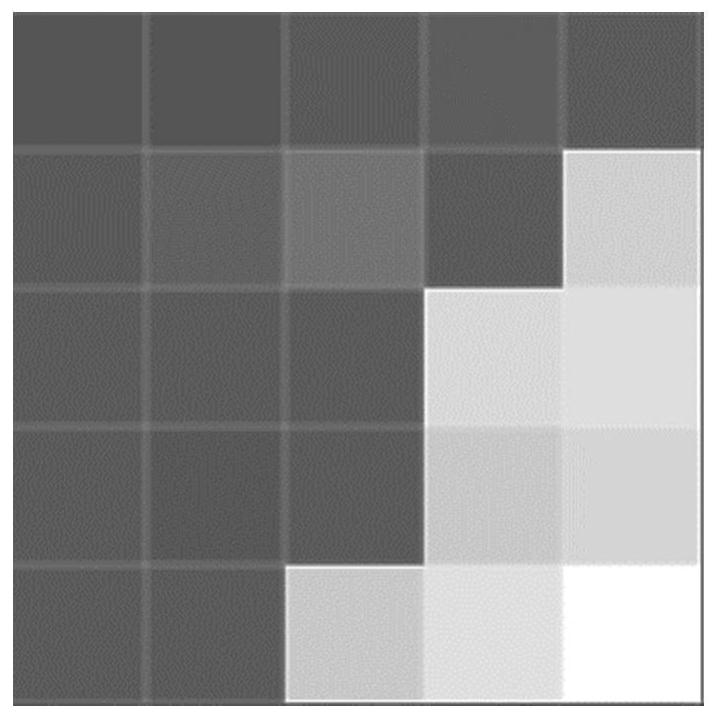
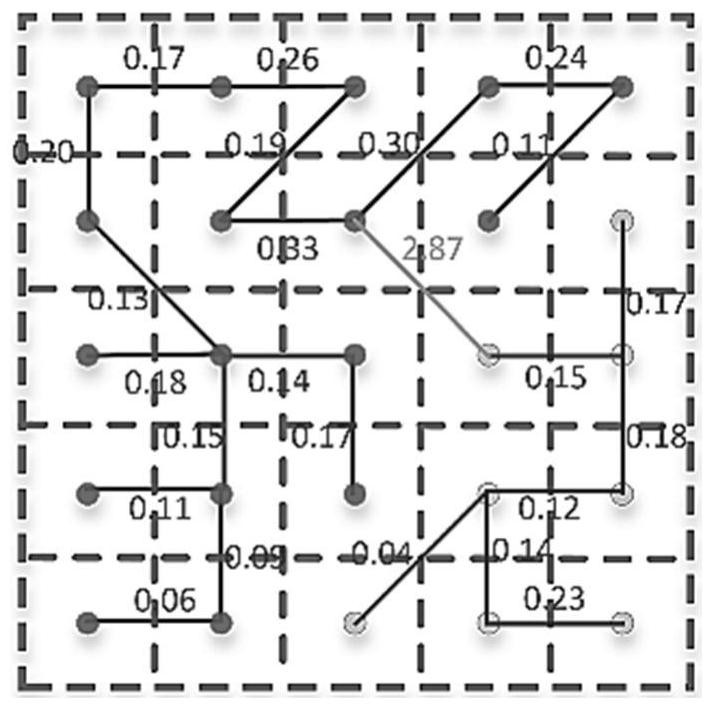
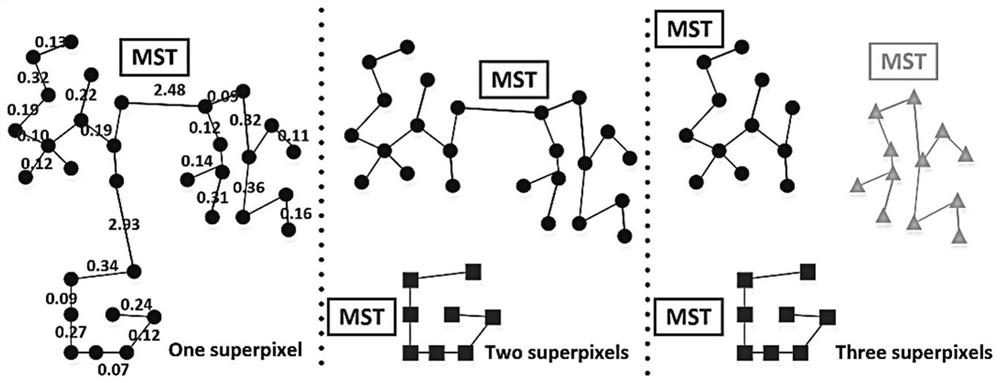
Rapid multi-scale super-pixel segmentation method for synthetic aperture radar image
PendingCN112116621AHelp to getKeep image bordersImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionSynthetic aperture radar
Owner:HANGZHOU SHIPING INFORMATION & TECH
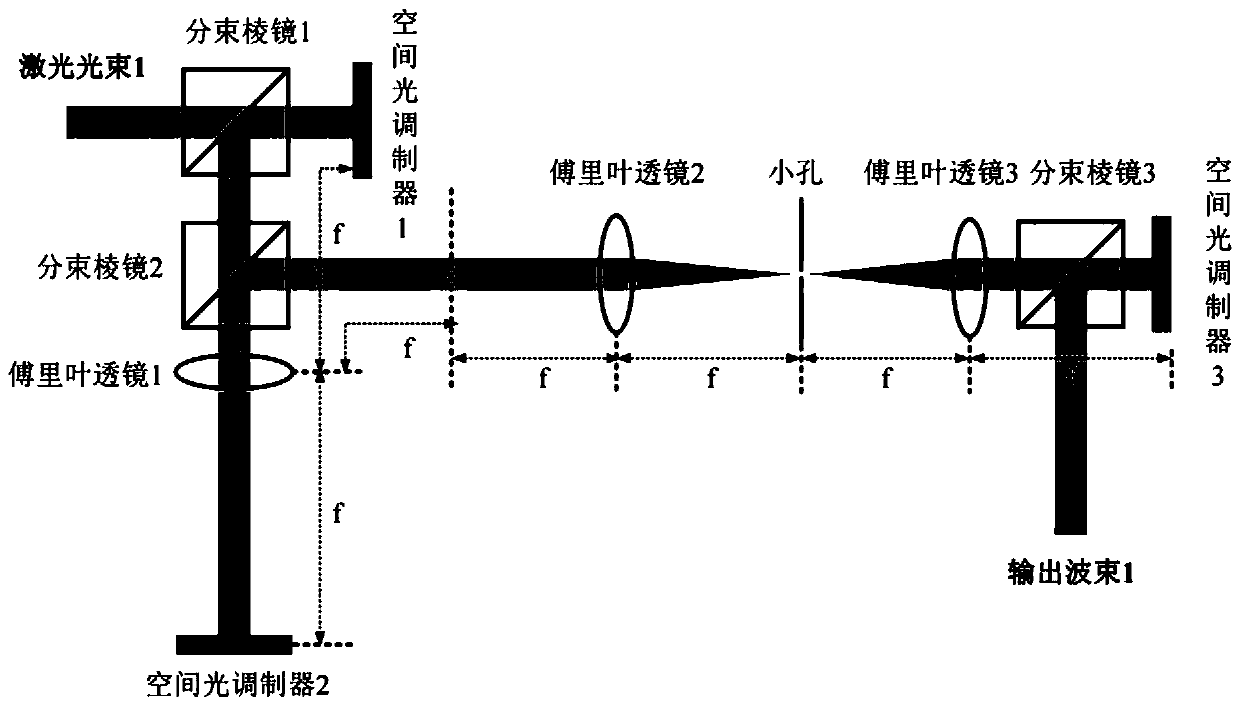
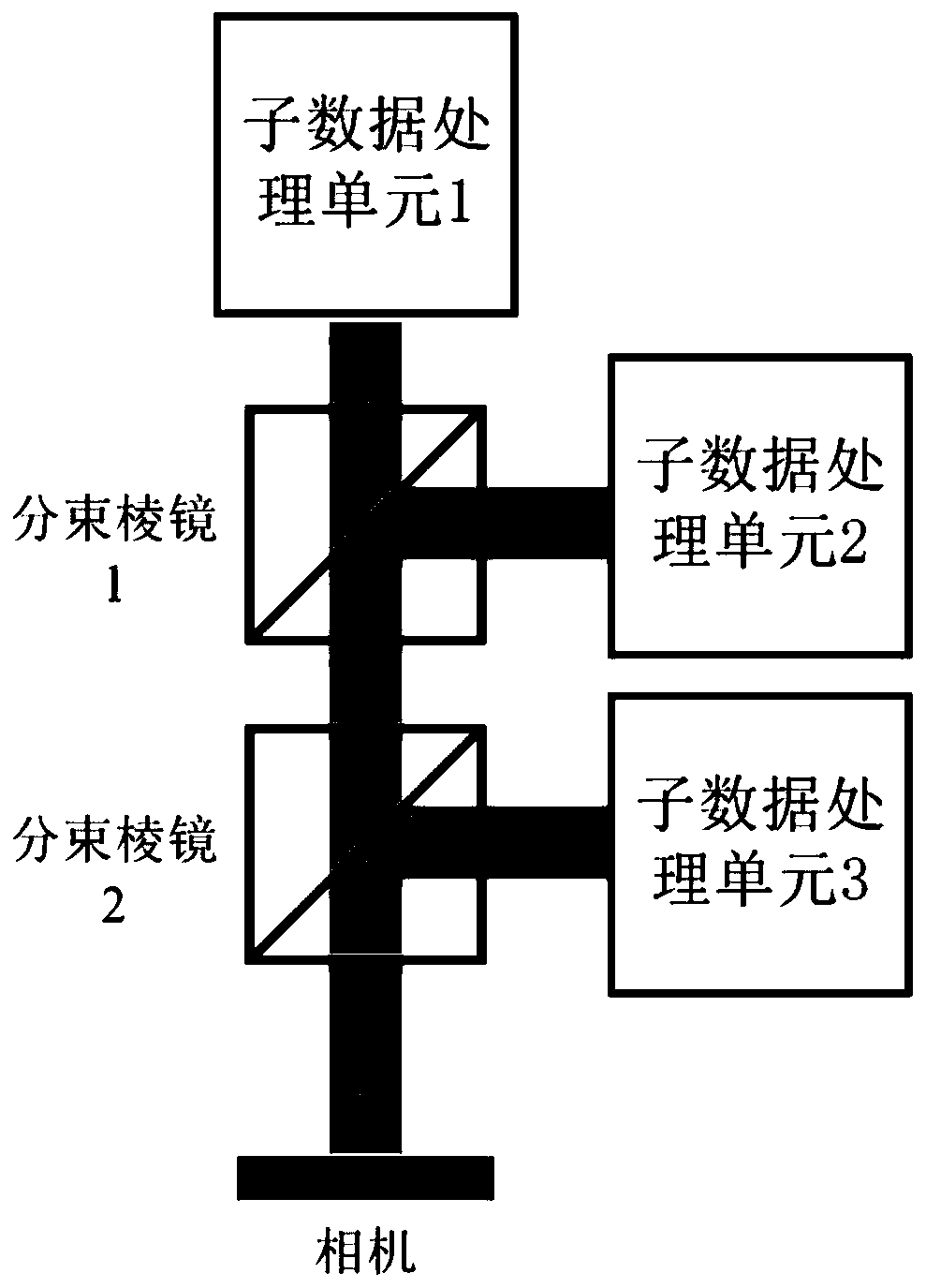
Photoelectric collaborative processing system for panoramic imaging of high-resolution synthetic aperture radar signal
InactiveCN110488290AIncrease processing scaleIncrease flexibilityRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFrequency spectrumSynthetic aperture radar
Owner:苏州兴钊防务研究院有限公司
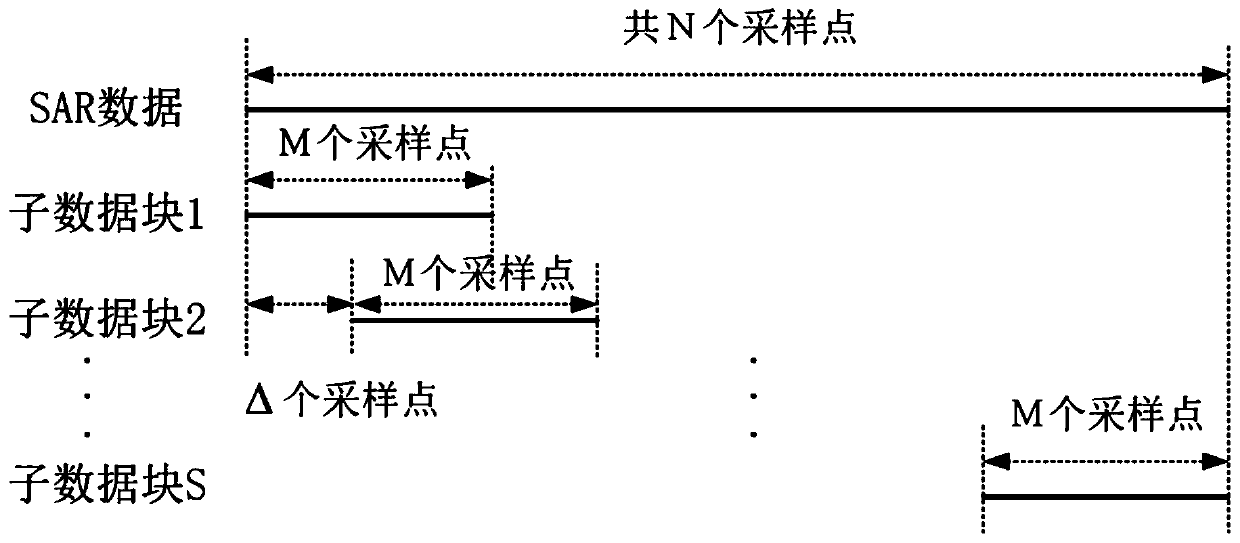
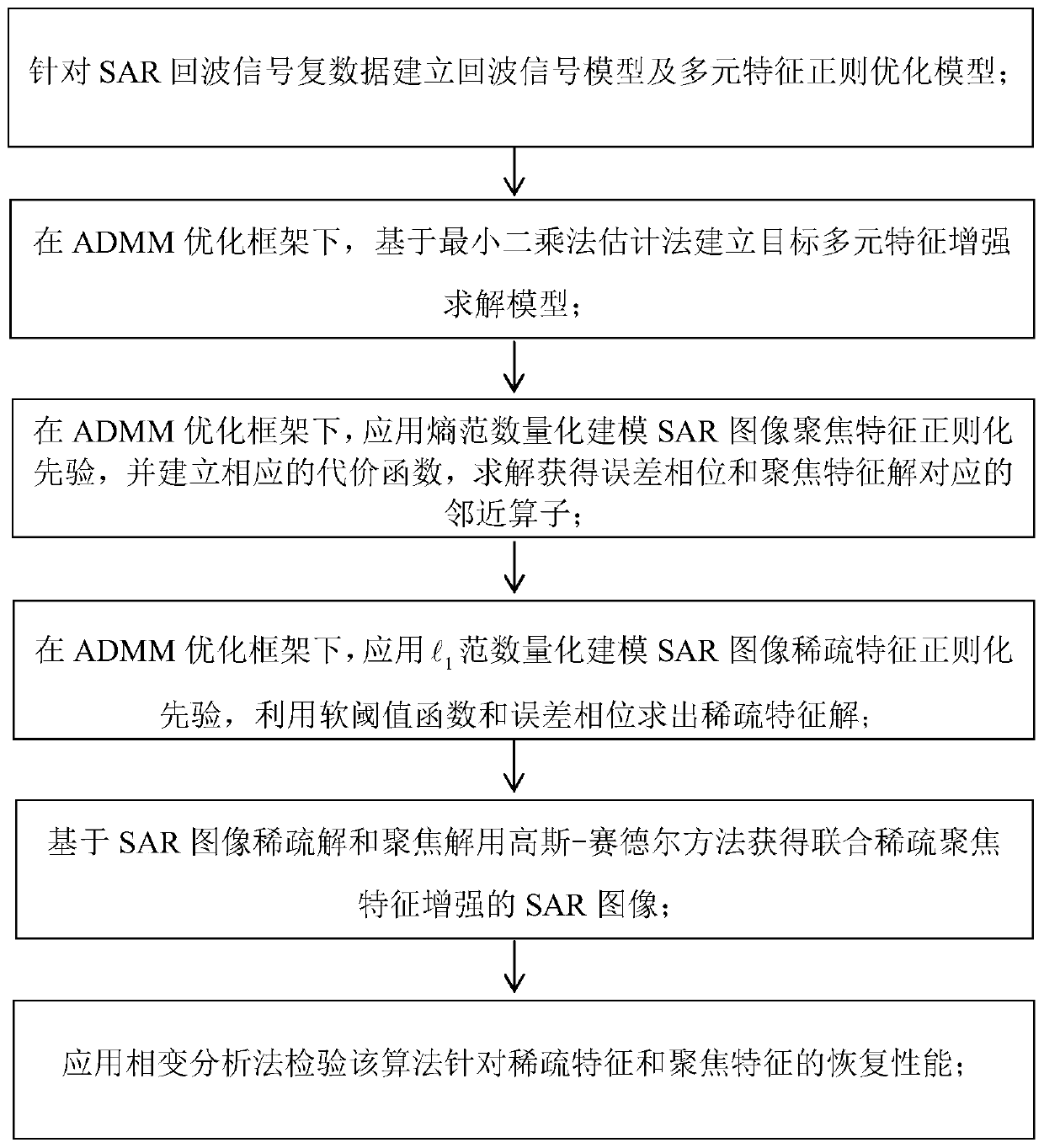
Robust and efficient synthetic aperture radar multi-feature enhanced imaging method
ActiveCN110703249AImprove featuresAvoid derivationImage enhancementImage analysisAlgorithmSynthetic aperture radar
Owner:CIVIL AVIATION UNIV OF CHINA
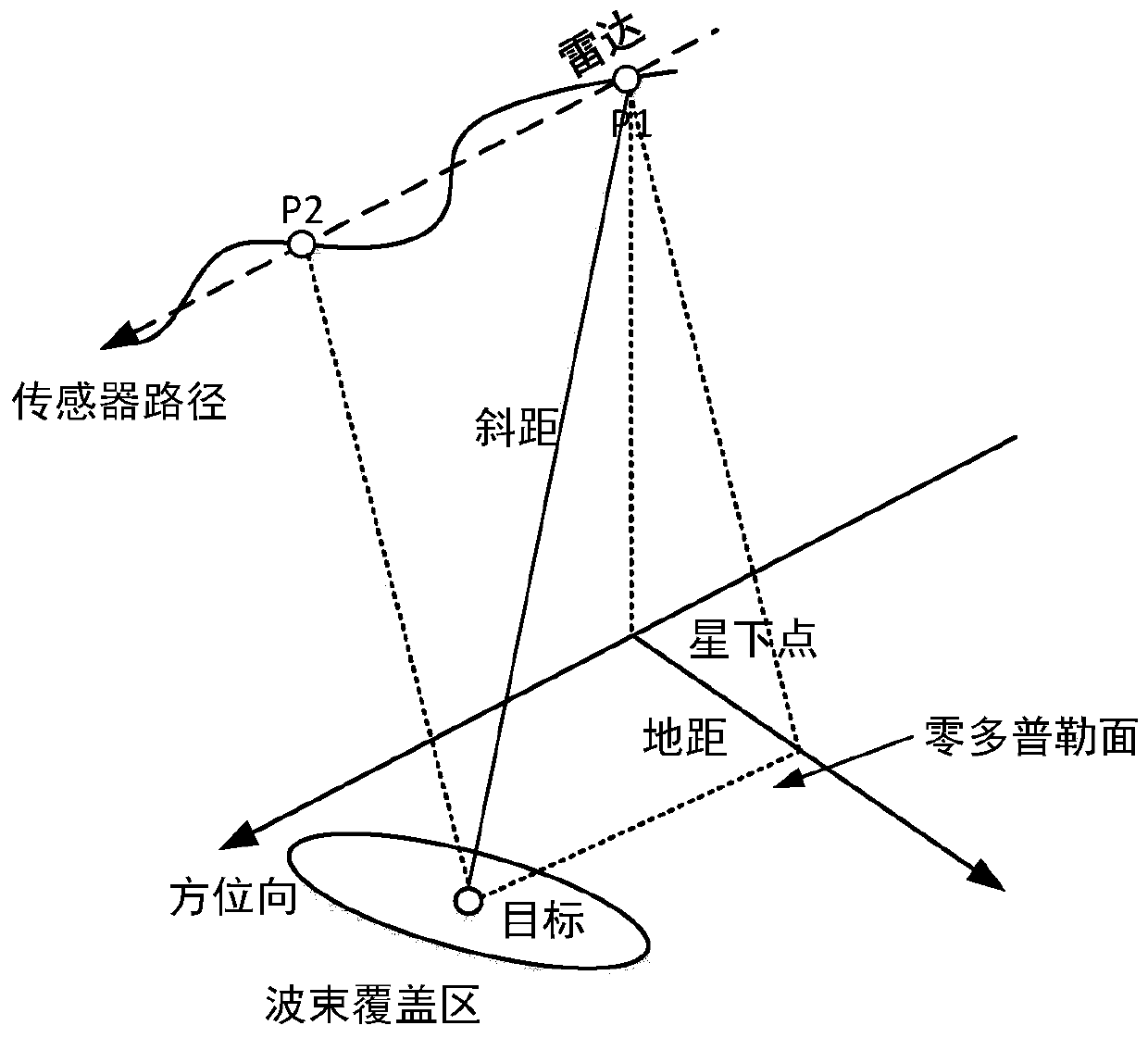
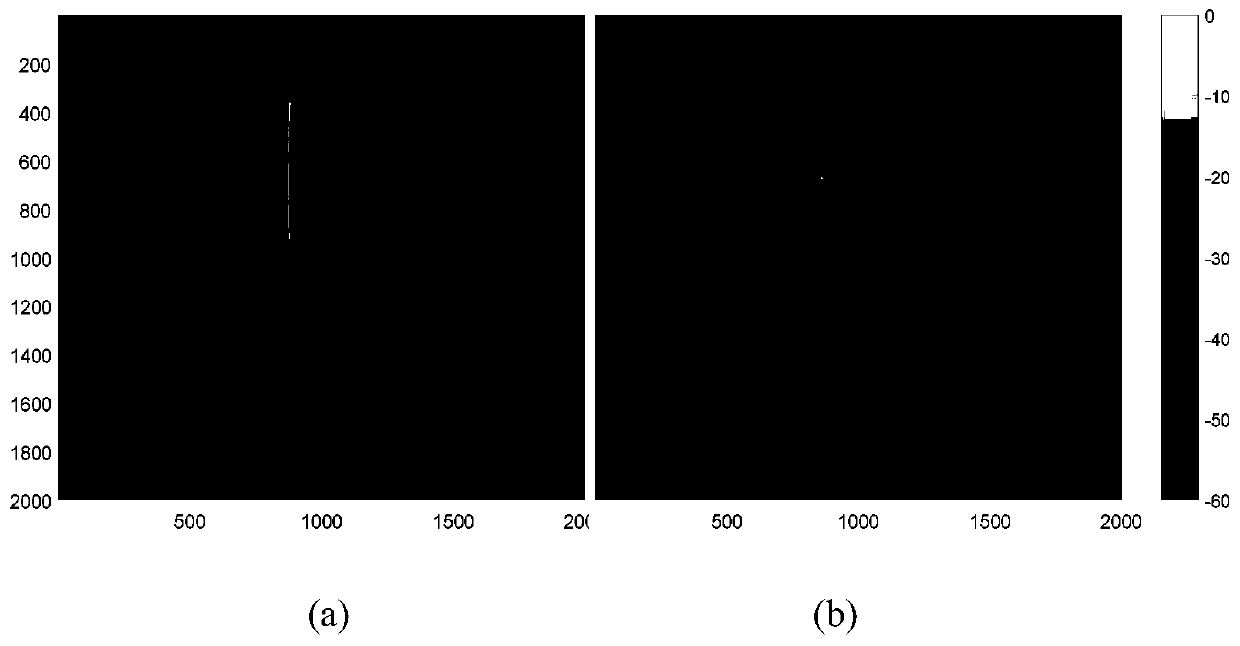
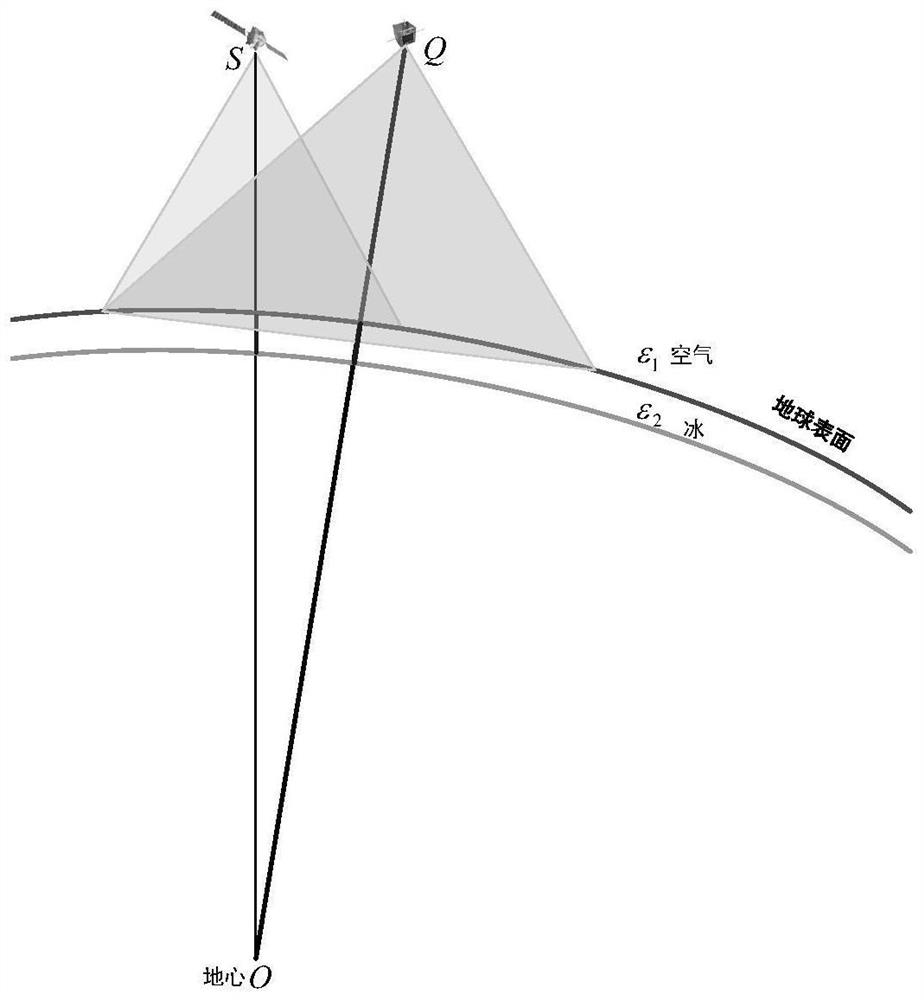
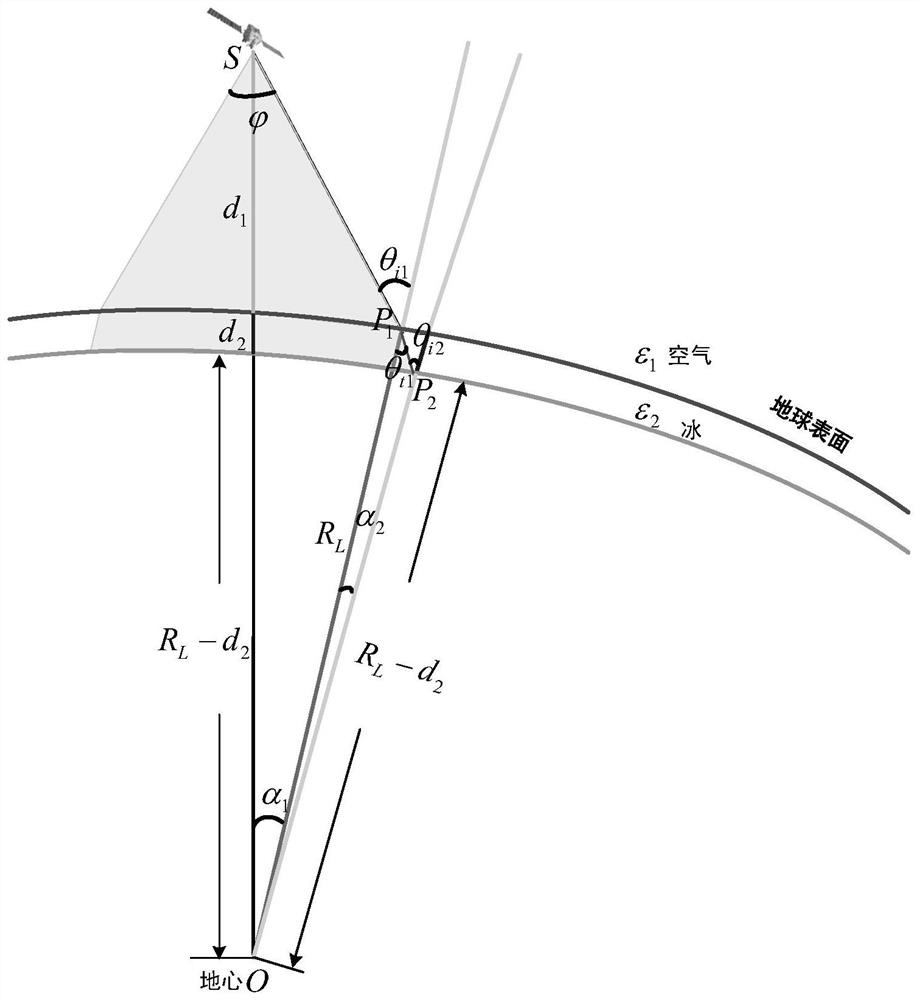
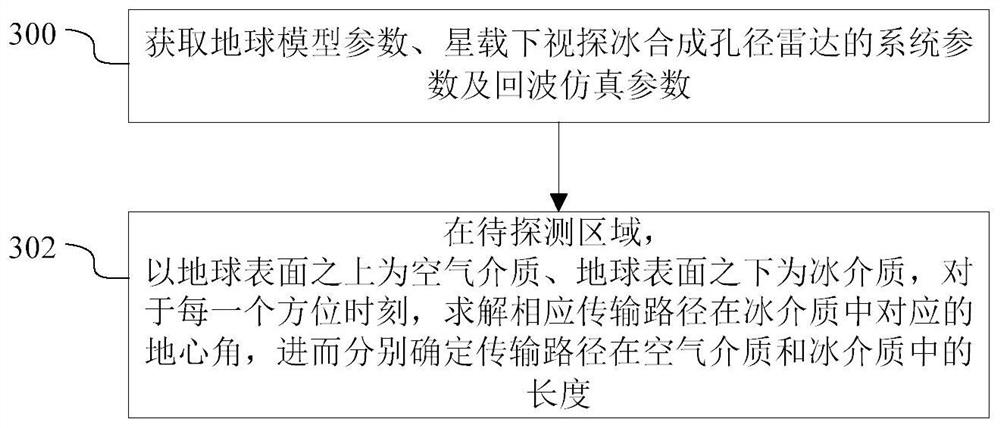
Satellite-borne down-looking ice-penetrating synthetic aperture radar transmission path calculation method
Owner:CHINA ACADEMY OF SPACE TECHNOLOGY +1
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap