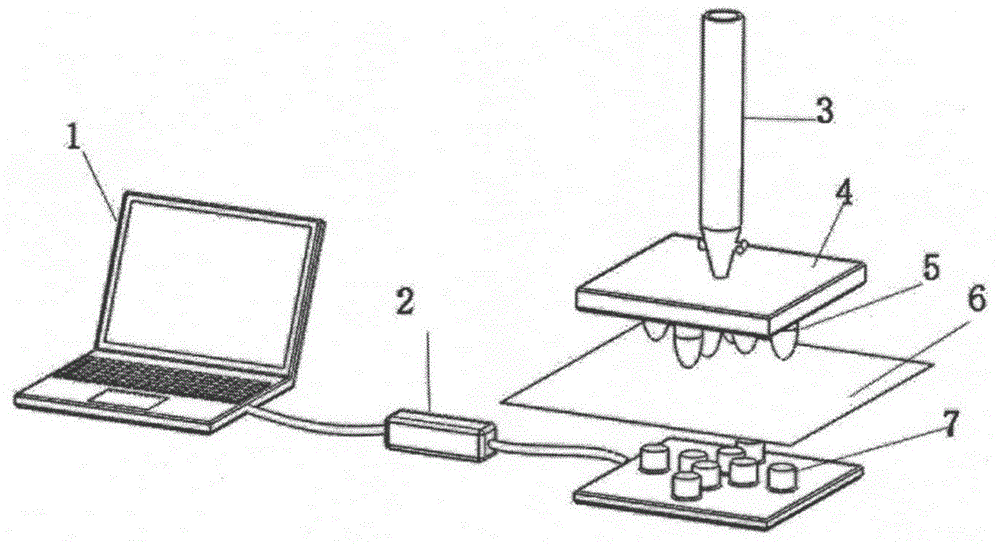
Device and method for evaluating liquid absorbability of textile material
A textile material and absorption performance technology, applied in the field of textile material evaluation, can solve the problems of quantitative and objective evaluation of textile material liquid absorption performance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
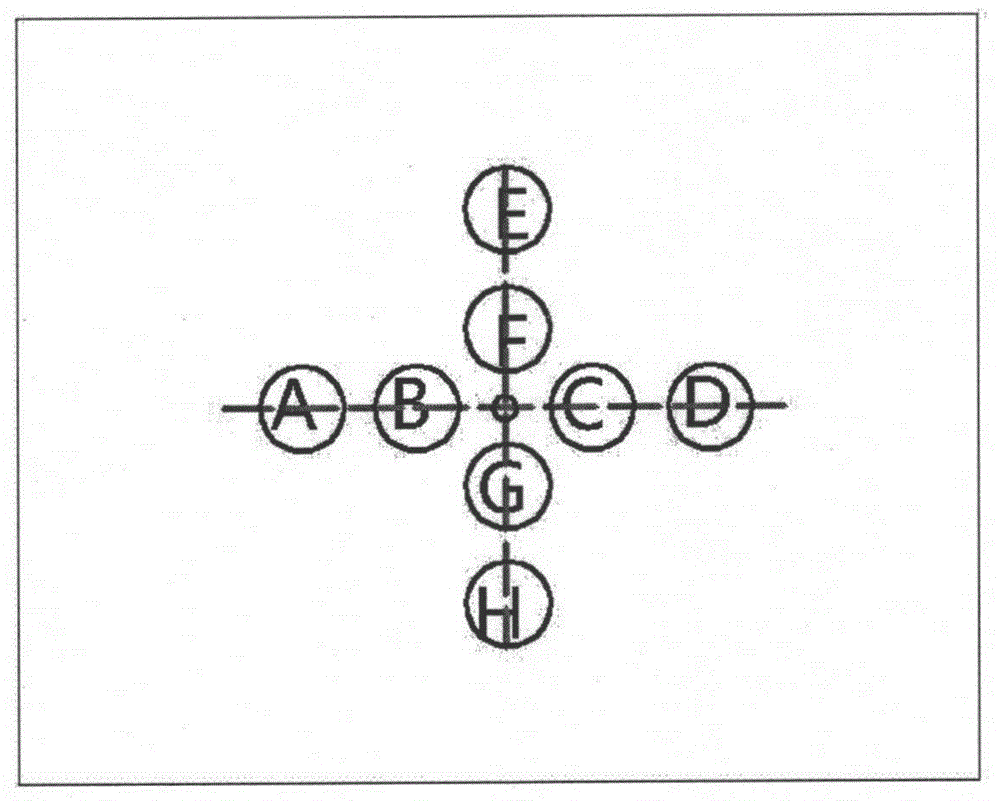
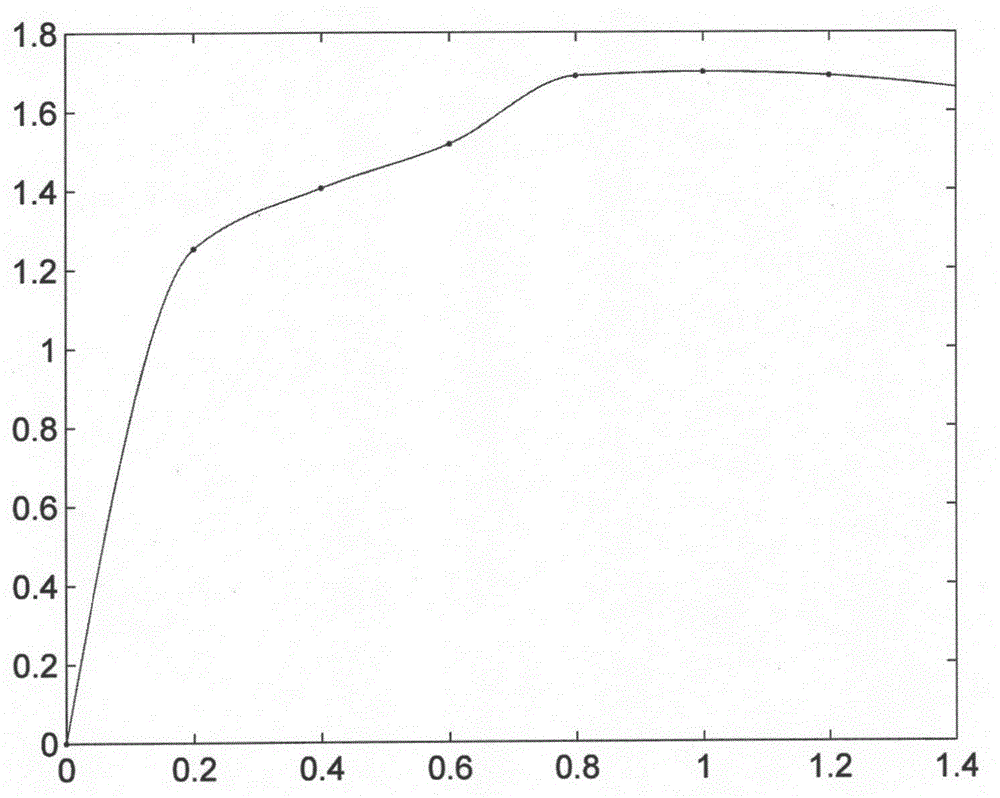
[0043] This method was used to evaluate the oil absorption performance of PP spunbonded nonwovens. The net weight of non-woven fabric is 40g / m2. The liquid is selected from commercially available Arowana soybean edible oil. Cut the same batch of spunbond fabrics into 10*10 (mm) pieces for later use. During the experiment, the sample to be tested is placed on the tray. Firstly, the pre-test is carried out, that is, 0.2ml, 0.4ml, 0.6ml, 0.8ml, 1ml, 1.2ml, and 1.4ml of oil are dropped on the surface of the spunbond cloth, and the voltage values before and after the experiment are recorded. Then carry out the liquid dynamic absorption test experiment. A fixed volume of oil was dropped on the surface of the spunbonded cloth within a specified time, and the voltage change with time before and after the receiver experiment was recorded. image 3 is the curve of the previous experiment. Figure 4 It is the voltage change curve of receivers E and F in the liquid dynamic absorptio
Embodiment 2
[0047] This batch of PP spunbonded nonwovens is still used. The liquid is commercially available No. 0 diesel oil. The implementation process is the same as in Example 1. The four indicators for obtaining the oil absorption performance of textile materials are:
[0048] Table 2
[0049] IAR(ml / 0.02s) AV(ml) ST(s) OWSC 0.0039 0.346 84.36 2.41
[0050] It can be seen that the spreading of No. 0 diesel oil on the surface of the spunbonded nonwoven fabric reflects the outstanding one-way transfer performance. Comparing Examples 1 and 2, it can be seen that the initial absorption rate and maximum absorption volume of diesel oil by spunbond cloth are greater than that of edible oil. The surface spreading time used by diesel oil is less than that of edible oil, indicating that diesel oil has a faster transfer speed on the surface of spunbond fabric.
Embodiment 3
[0052] The commercially available Arowana soybean oil was used to evaluate the oil absorption performance of five nonwoven fabrics. The five nonwoven specifications are listed in Table 3. The testing process is the same as above. The test results are listed in Table 4. The liquid absorption rate change curves of the five samples are shown in Figure 7 . From the test results in Table 4, we can evaluate the oil absorption performance of these five nonwoven fabrics. The maximum oil absorption volume of sample 3 is the largest among the five textile materials, followed by sample 1, sample 4, sample 2, and sample 5. Sample 5 had a larger one-way transport coefficient, indicating that the edible oil was transported significantly more in one direction than the other across the surface of this sample. In addition, by Figure 6 It can be seen that sample 3 has a faster initial oil absorption rate, which means that sample 3 can quickly absorb edible oil in a short time. However, th
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap