Method for removing residual print wire, FDM printing device, storage medium and processor
A storage medium and printing filament technology, applied in the field of 3D printing, can solve problems such as increasing cost and increasing mechanical complexity, and achieve the effects of increasing cost, avoiding scrap, and simple mechanical structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
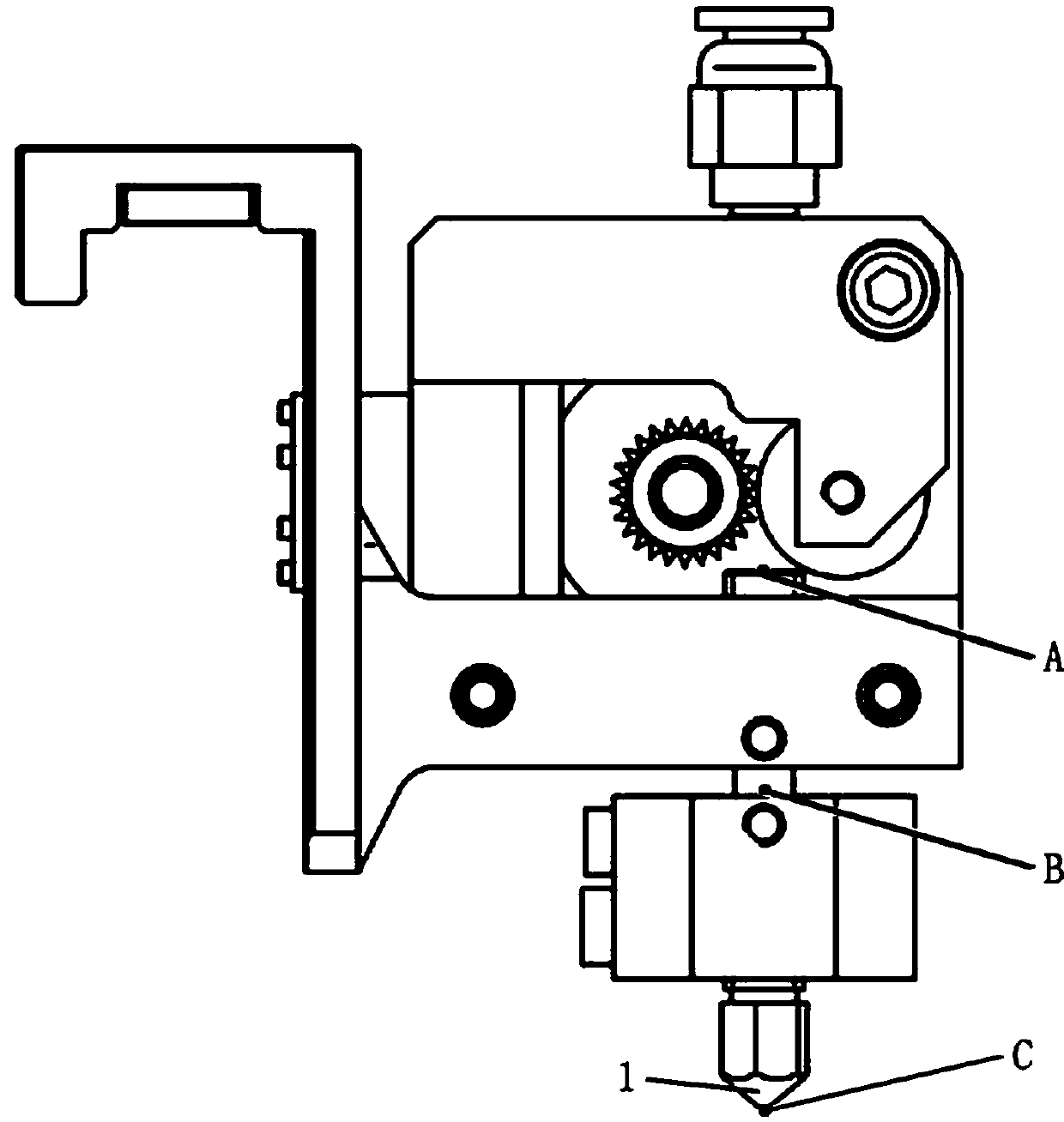
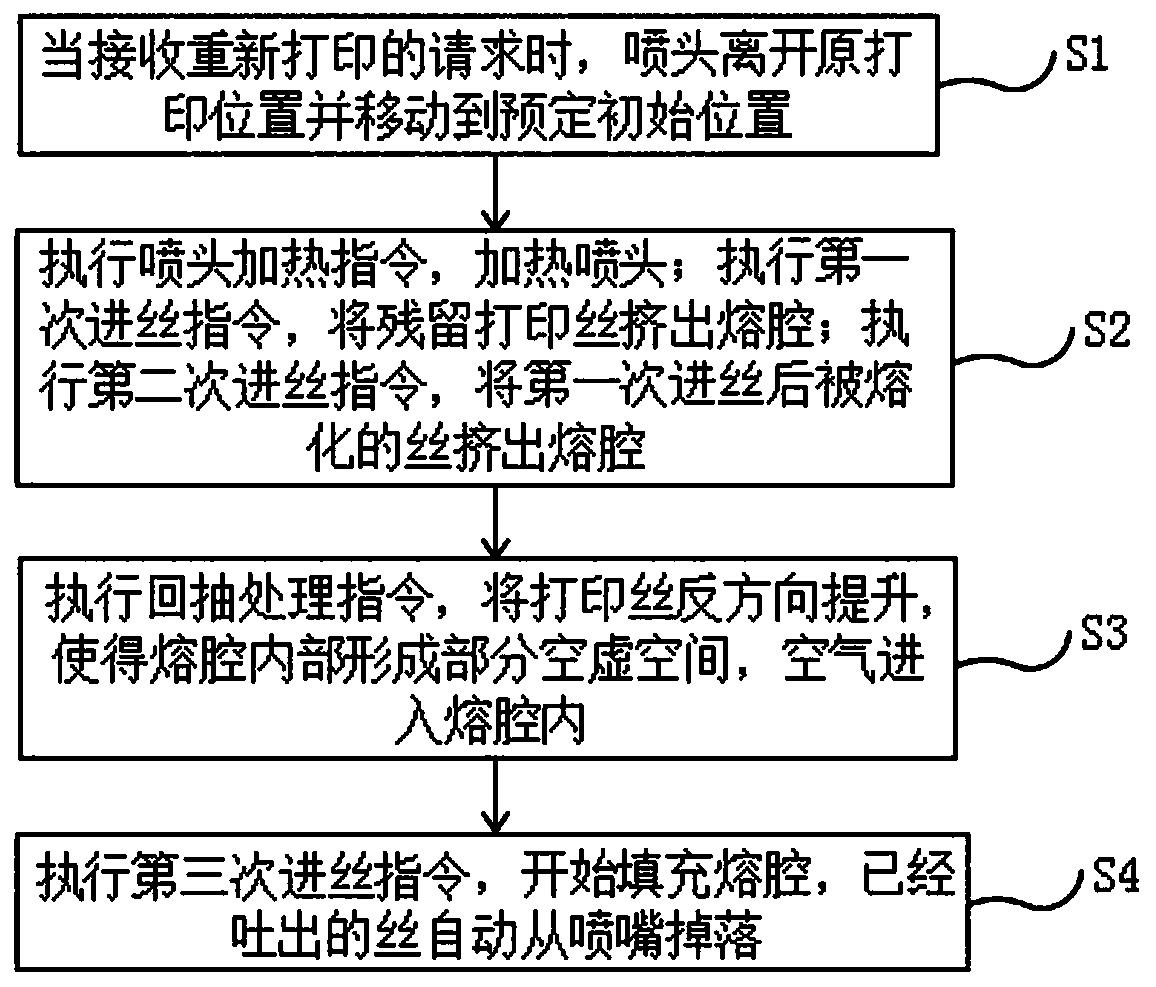
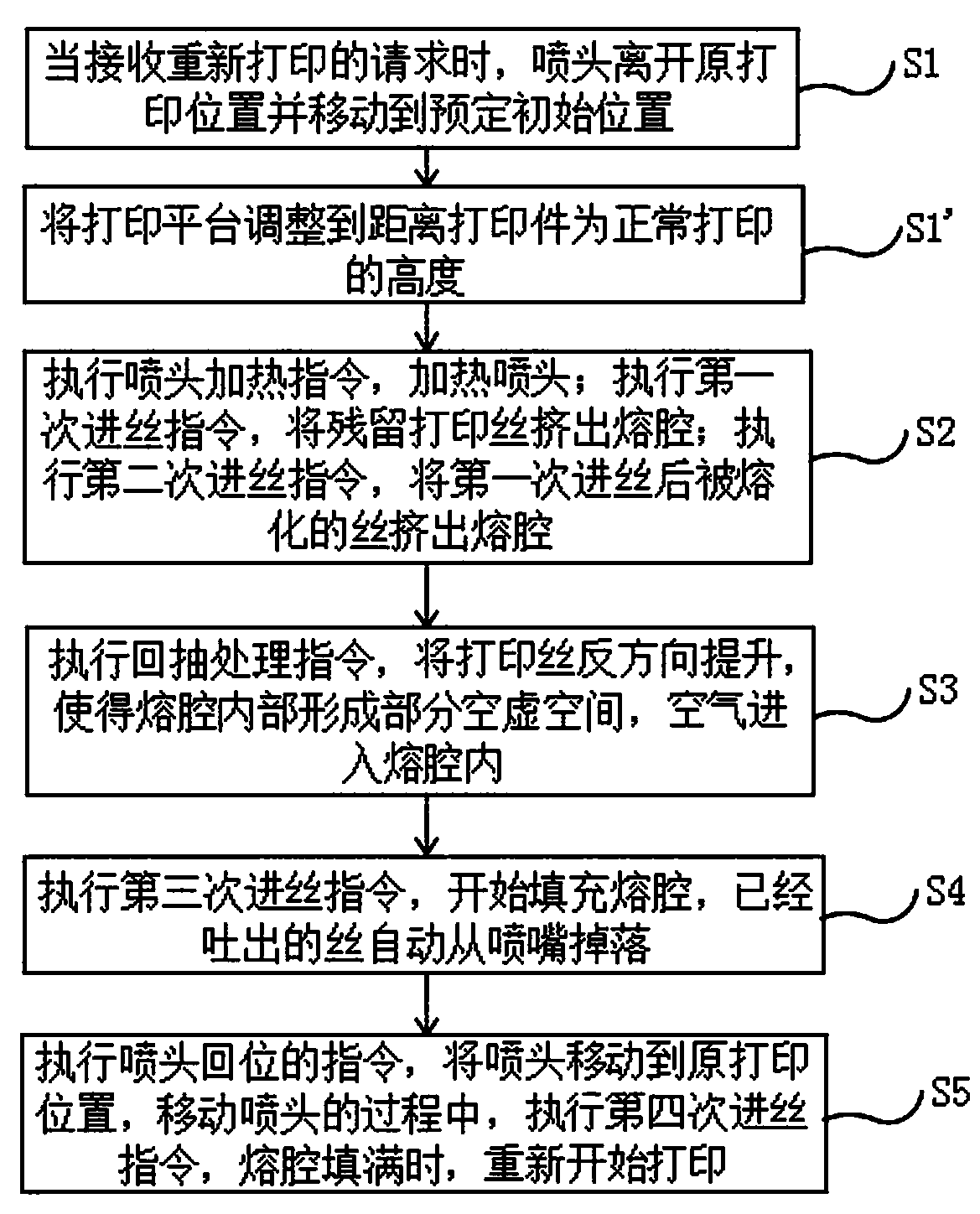
[0029] A method for removing residual printing filament according to the present invention is specifically a method for removing residual printing filament in the nozzle when the FDM printer is powered off for printing or printing is suspended, such as figure 2 shown, including the following steps:
[0030] S1. When receiving a request for reprinting, the nozzle of the printer leaves the original printing position and moves to a predetermined initial position. The predetermined initial position in this embodiment refers to a position avoiding the printing platform.
[0031] S2. The printer executes the instruction of heating the nozzle, the nozzle is heated to the temperature required to melt the printing filament, and then executes the first filament feeding instruction, the heated nozzle melts the residual printing filament in the melting chamber, and the first feeding The printing filament pushes the remaining printing filament out of the melting cavity. Then execute the sec
Embodiment 2
[0045] An FDM printing device, using the method for removing residual printing filament as described in Embodiment 1.
[0046] As a preferred embodiment, the FDM printing device further includes a nozzle assembly, a heating assembly and a filament extrusion assembly.
Embodiment 3
[0048] A storage medium, the storage medium includes a stored program, wherein the method for removing residual printing filament described in Embodiment 1 is executed when the program is running.
[0049] For the purposes of this specification, a "storage medium" may be any device that can contain, store, communicate, propagate or transmit programs for use in or in conjunction with instruction execution systems, devices or devices.
[0050] The storage medium described in this embodiment may be a computer-readable signal medium, a computer-readable storage medium, or any combination of the above two. More specific examples of storage media include at least (non-exhaustive list) the following: electrical connection with one or more wiring (electronic device), portable computer disk case (magnetic device), random access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM), erasable editable read-only memory (EPROM or flash memory), fiber optic devices, and portable read-only memory (CDROM).
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap