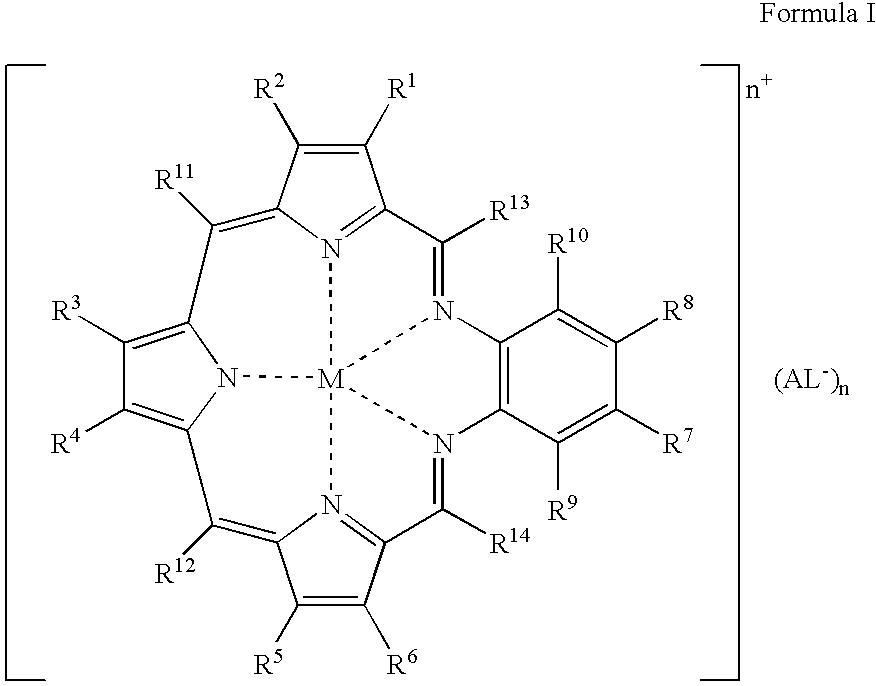
Agents for neutron capture therapy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of .sup.157Gadolinium Texaphyrin
[0215] .sup.157Gadolinium texaphyrin metal complex was prepared using standard methods previously described in Sessler et al., J. Phys. Chem., vol. 103, pgs. 787-794 (1999) and Young et al., Photochem. Photobiol., vol. 63, pgs. 892-897 (1996). The macrocyclic ligand, 9,10-diethyl-7,12-dihydro-20,21-bis[2-[2-(2-methoxyethoxy)ethoxy]ethoxy]--4,15-dimethyl-3,6:8, 11:13,16-triimino-1,18-benzodiazacycloeicosine-5,14-d-ipropanol hydrochloride (IP-NP2, 2.2 g, 2.39 mmol), was oxidatively metallated using gadolinium(157) nitrate pentahydrate (1.02 g, 2.39 mmol) and triethylamine (3.3 mL, 23.9 mmol) in air-saturated methanol (200 mL) at reflux. After completion of the reaction (as judged by the optical spectrum of the reaction mixture), the deep green solution was cooled to room temperature and the solvent reduced to 150 mL under reduced pressure. The dark green solution was loaded onto a column (8 cm length.times.2.5 cm diameter) of pretreated Amberse
example 2
Determination of Neutron Capture Activity In Vitro Utilizing the V79 Chinese Hamster Cell Survival Assay
[0216] The effect of neutron irradiation on V79 Chinese hamster cells incubated for twelve hours with .sup.157Gd-Tex is determined by a modification of the procedure originally described by Fairchild et al., Cancer Research 50 (1990). Three sets of sample plates of V79 cells are prepared. The first set (control cells) are suspended with 30ppm .sup.157Gd-Tex in growth medium. The second set (washed cells) are suspended with 30ppm .sup.157Gd-Tex in growth medium, then washed 3 times with PBS, trypsinized and harvested with gadolinium from reagents prior to suspension. The third set (ambient cells) are suspended in a 30ppm .sup.157Gd containing medium.
[0217] All of the cells are irradiated within 1-2 hours following suspension in growth medium at a population density of 3.0.times.10.sup.5 cells / ml. The neutron beam fluence rate at the center of the sample is 2.8.times.10.sup.11 n / cm
example 3
Determination of Neutron Capture Activity Utilizing Glioma 261 Cells
[0219] This procedure is a modification of a procedure initially described by Saris et al., Cancer Research, vol. 52 (1992). Glioma 261 tumor fragments are injected approximately 2 mm deep to the dura of the brain in 42 female C57BL / 6 mice. The mice are randomized into 5 groups. The mice in group A receive ???? mg / kg Gd-Tex and 1.2.times.10.sup.12 neutrons / cm.sup.2 resulting in 20 Gy. Group B mice receive 1.2.times.10.sup.12 neutrons / cm.sup.2 resulting in 20 Gy. The mice in group C receive ???? mg / kg Gd-Tex and 10 Gy of photon irradiation. Group D receives ???? mg / kg of Gd-Tex alone. Group E receives no treatment.
[0220] After 5 days (when the tumor is approximately 2 mm), ???? mg / kg of a texaphyrin is administered by intravenous injection (groups A, C and D only). ???? Hours later, the mice in groups A and B are anesthetized and irradiated with a neutron beam of 1.2.times.10.sup.12 neutrons / cm.sup.2 to
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Digital information | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap