Linear burst mode synchronizer for passive optical networks
a passive optical network and synchronizer technology, applied in the field of passive optical networks, can solve the problems of data loss, burst loss, and inapplicability of conventional clock recovery and resynchronization feedback mechanisms, and achieve the effects of improving synchronized jitter performance, additional timing margin, and longer fiber length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
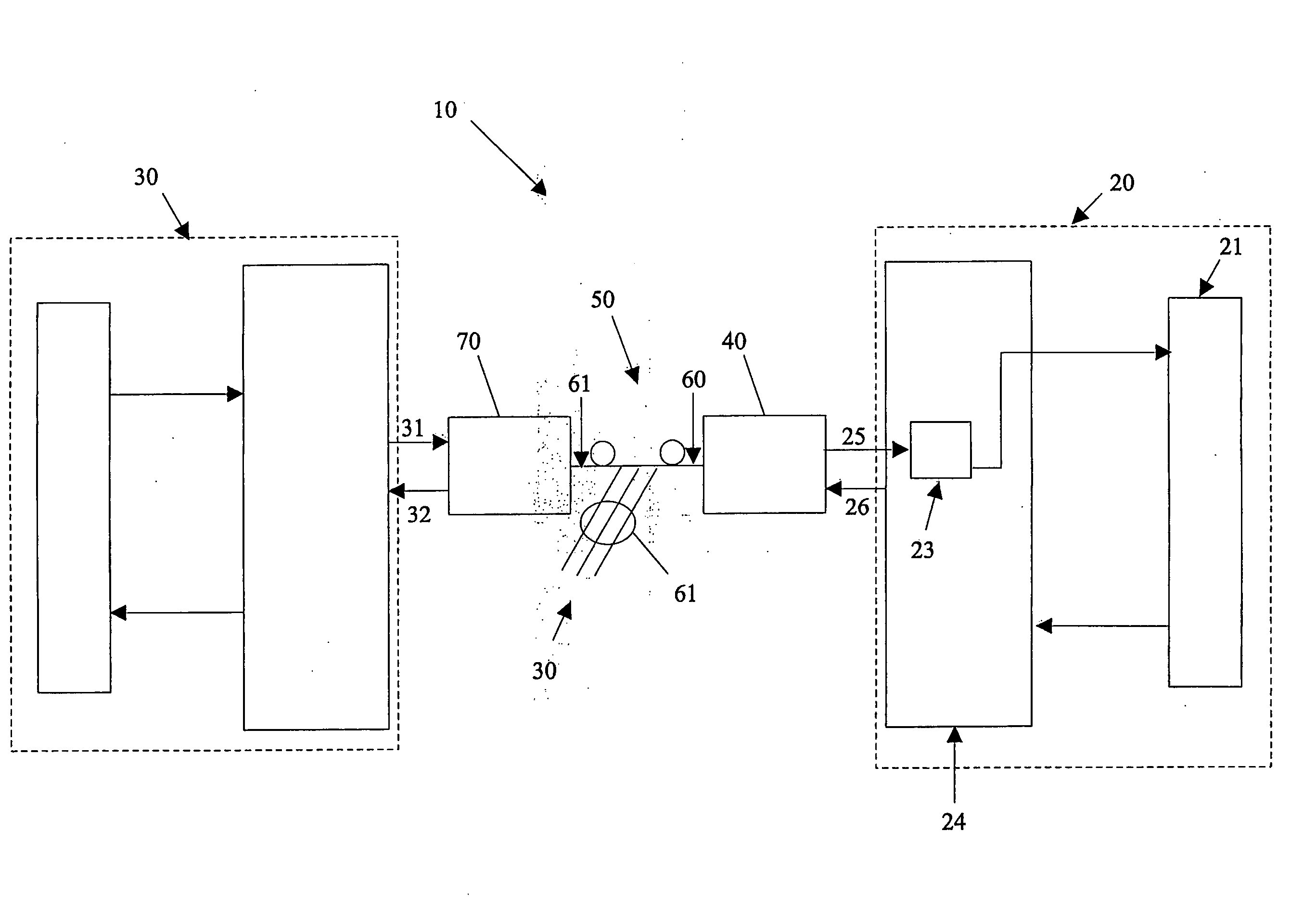
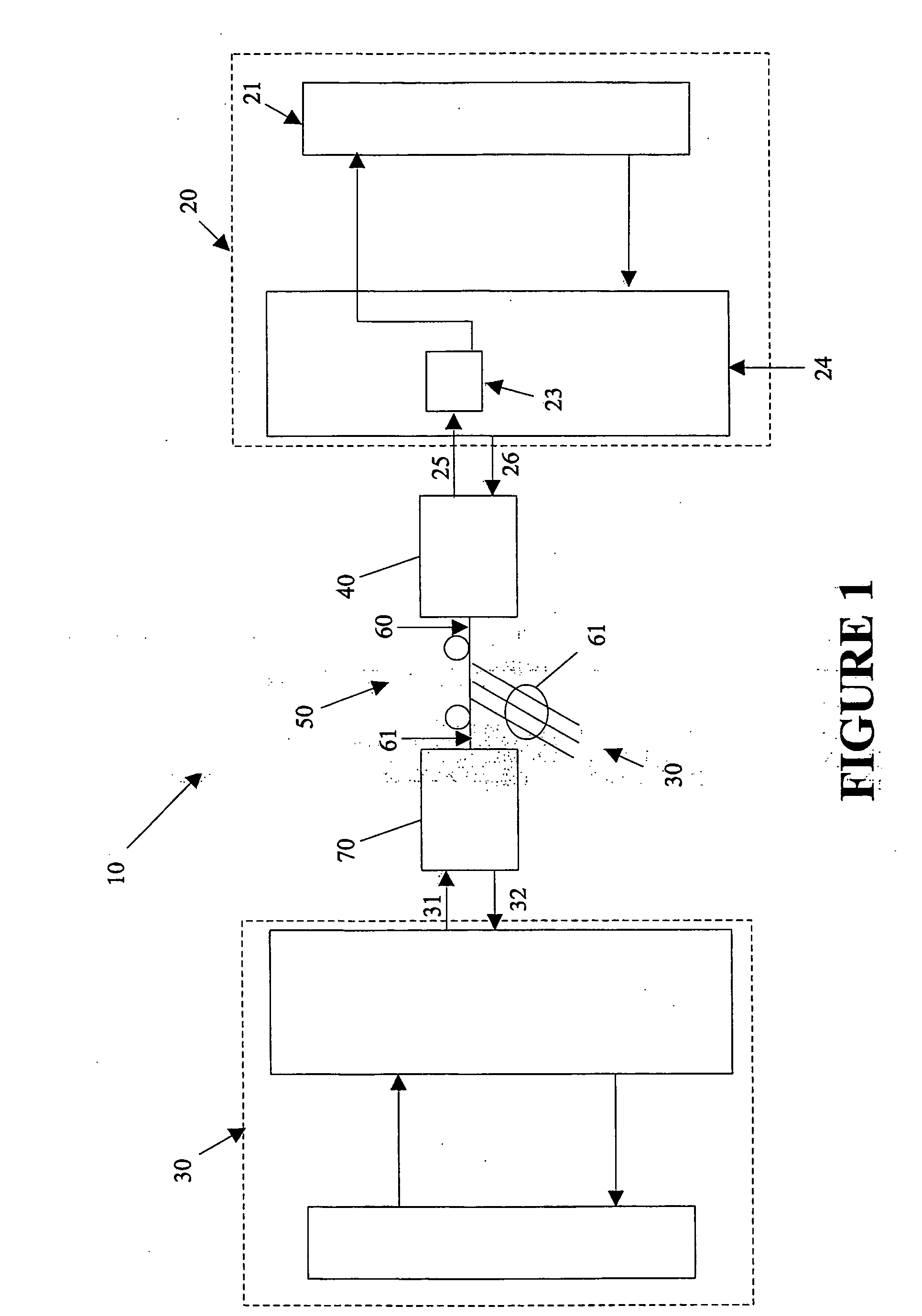
[0044]Referring now to FIG. 1, there is shown a system block diagram of a PON system 10 in which the present invention might find application.
[0045]The system 10 comprises a PON host 20, a plurality of substantially identical (for purposes of the present discussion) PON subscribers 30, of which an exemplary subscriber is shown in detail, a PON host optical module 40, at least one optical splitter 50, a plurality of fibers 60, 61 and a plurality of PON subscriber optical modules 70.
[0046]The host 20 is connected to the host optical module 40 by a pair of serial connections 25 and 26. Serial connection 26 conveys serial data from the host 20 to the host optical module 40 (downstream data) while serial connection 25 conveys serial data from the host optical module 40 to the host 20 (uplink data). As mandated by the PON standard specifications, the downstream data is transmitted in continuous fashion while the uplink data is received in bursts.
[0047]As shown in FIG. 1, the host 20 may acce
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap