Formulations
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example
[0124]Other staphylococcal strains were also tested, as described in Example 5 below. These included certain antibiotic resistant staphylococci, such as the methicillin resistant S. aureus (MRSA) strains EMRSA-15 and EMRSA-16, both available from the Central Public Health Laboratory (CPHL), Colindale, UK. These strains are resistant not only to all beta-lactams but also to a number of other antibiotics in clinical use, making them a serious threat to human health. They are also responsible for the majority (>95%) of hospital-acquired MRSA infections in the UK.
[0125]S. aureus and other staphylococci are common causes of a wide range of skin, skin structure and wound infections. S. aureus itself is also known to exacerbate eczema.
[0126]2. Propionibacterium spp.—the principal propionibacterial strain used in these studies was Propionibacterium acnes NCTC 737. This is the type strain of the genus; it is fully susceptible to antibiotics.
[0127]The propionibacteria are clinically significant
Example
[0129]Other propionibacterial strains were also tested, as described in Example 8 below. These included certain antibiotic resistant propionibacteria, such as the two P. acnes strains PRP-010 and PRP-053 which are resistant respectively to macrolides-lincosamides-streptogramins-ketolides (MLSK) and to macrolides-lincosamides-streptogramins (MLS) and tetracycline—in other words, PRP-010 is resistant to erythromycin and clindamycin, and PRP-039 to erythromycin, clindamycin and tetracycline.
[0130]In addition, certain strains of P. granulosum and a type strain of P. avidum, both other propionibacteria involved in acne, were also tested in Example 8.
[0131]3. Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212—this is a Gram-positive bacterium belonging to the genus Enterococcus. Enterococci have similar properties to streptococci, but differ in their ability to grow on bile-salt containing media such as MacConkey's Agar. Their principal habitat is the mammalian gastrointestinal tract. They cause a number of i
Example
EXAMPLE 1
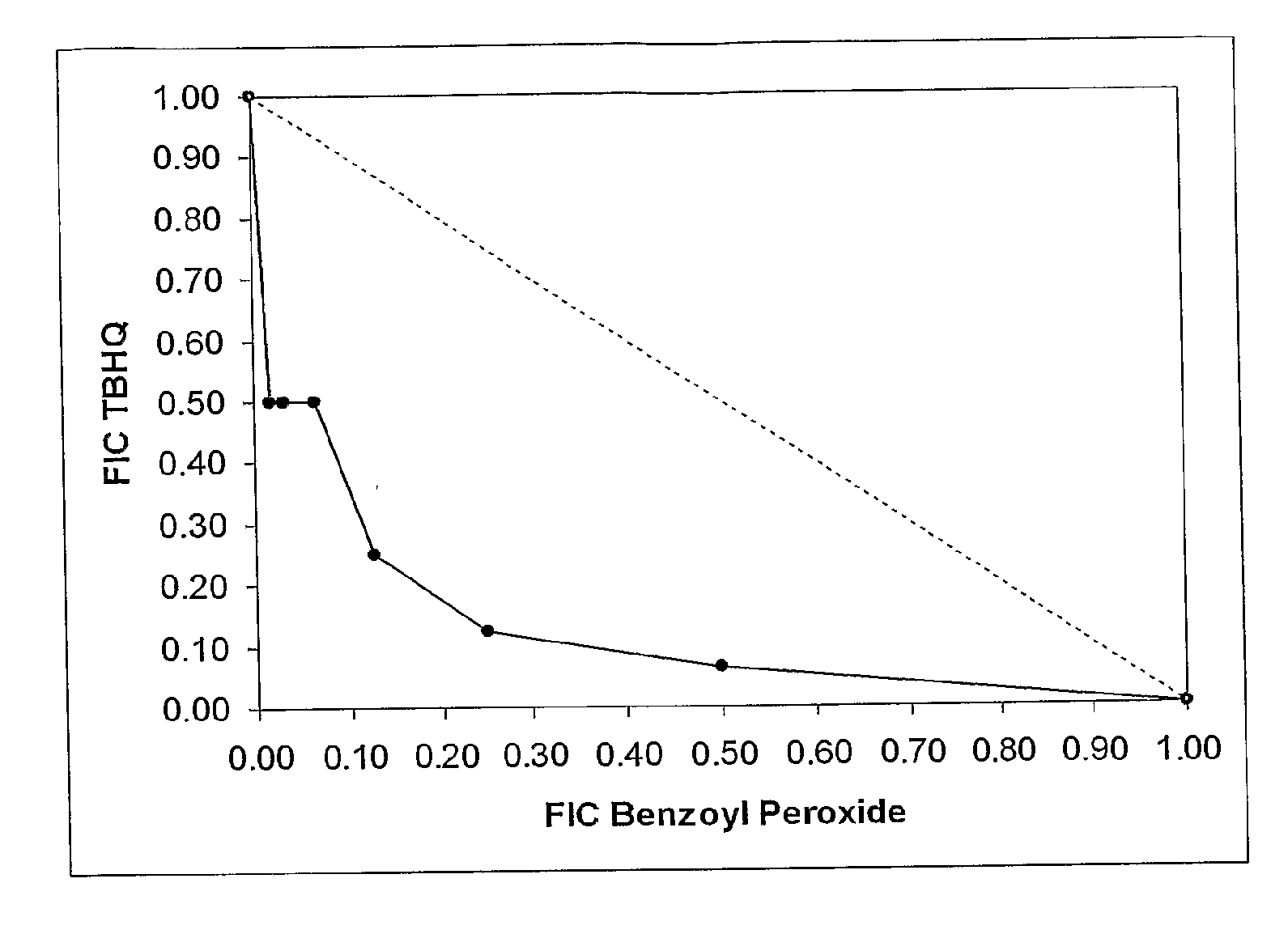
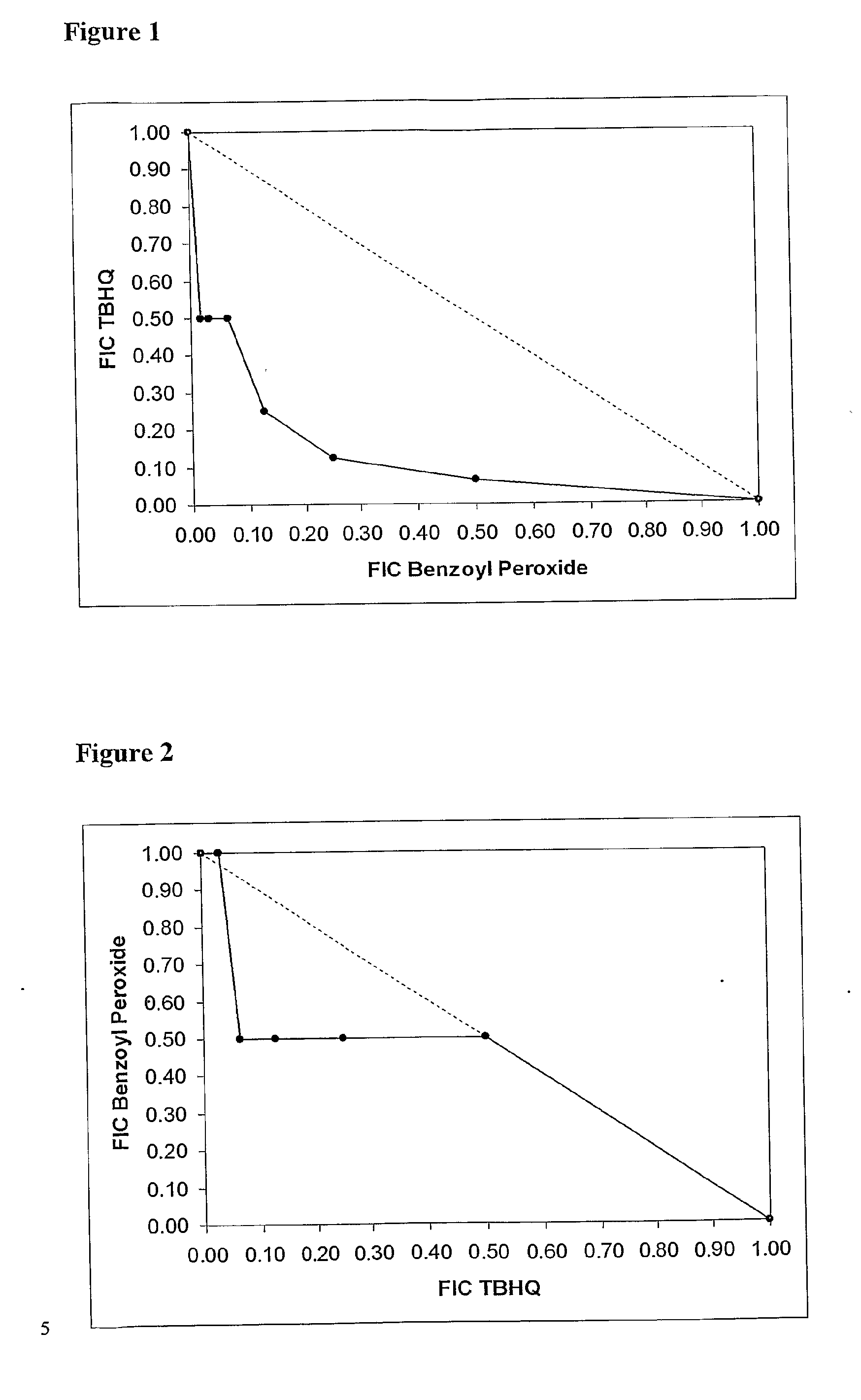
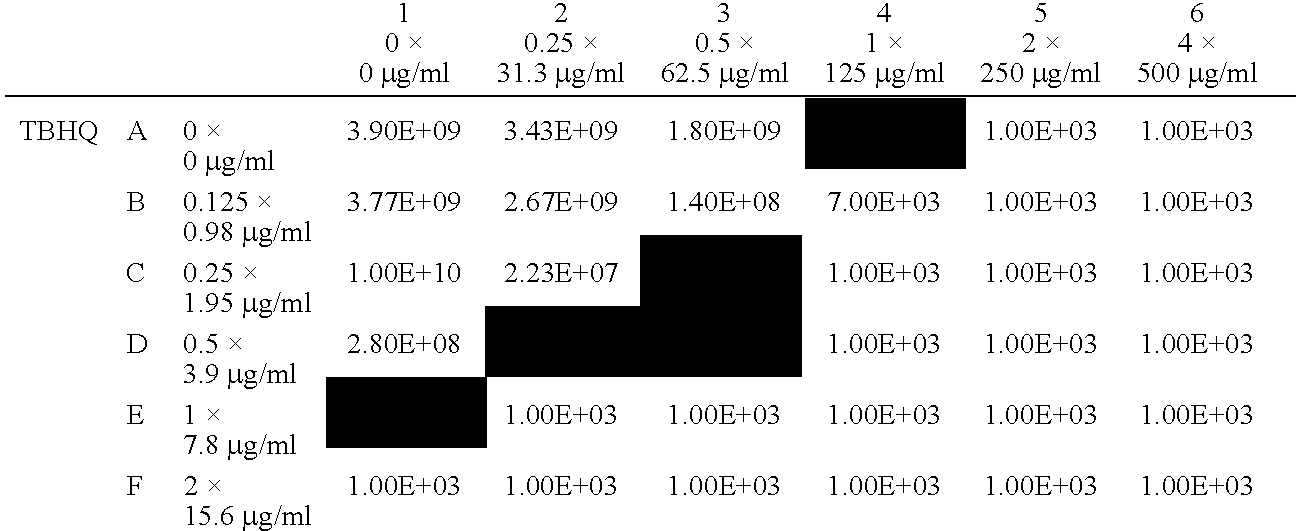
Activity Against S. aureus—MIC, MBC & (S)DDA Assays
[0175]The following experiments all used S. aureus ATCC 29213 as the test organism.
[0176]MIC, MBC and DDA assays, as described above, were carried out using the test compound benzoyl peroxide (BP) and a range of different benzoquinones and hydroquinones. Supplemented DDA assays, in the presence of salt, lipid and blood, were also conducted.
[0177]Each of the quinones was then subjected, in combination with BP, to the SDDA assay described above. In each case, increases in zone diameter (mm) and area (%) were measured with respect to those observed for the compound showing the larger zone diameters during the previous disc diffusion assays on the individual compounds.
[0178]For most (S)DDA assays, 200 μg of each compound was loaded onto each disc. The exceptions were the thymoquinone assays, in which only 50 μg of the benzoquinone was used. The solvents used were DMSO (for benzoyl peroxide, 2-methyl-p-hydroquinone, 2,3-dimethyl-p-
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap