Dual-mode converter with linear and comparative feedback modes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example
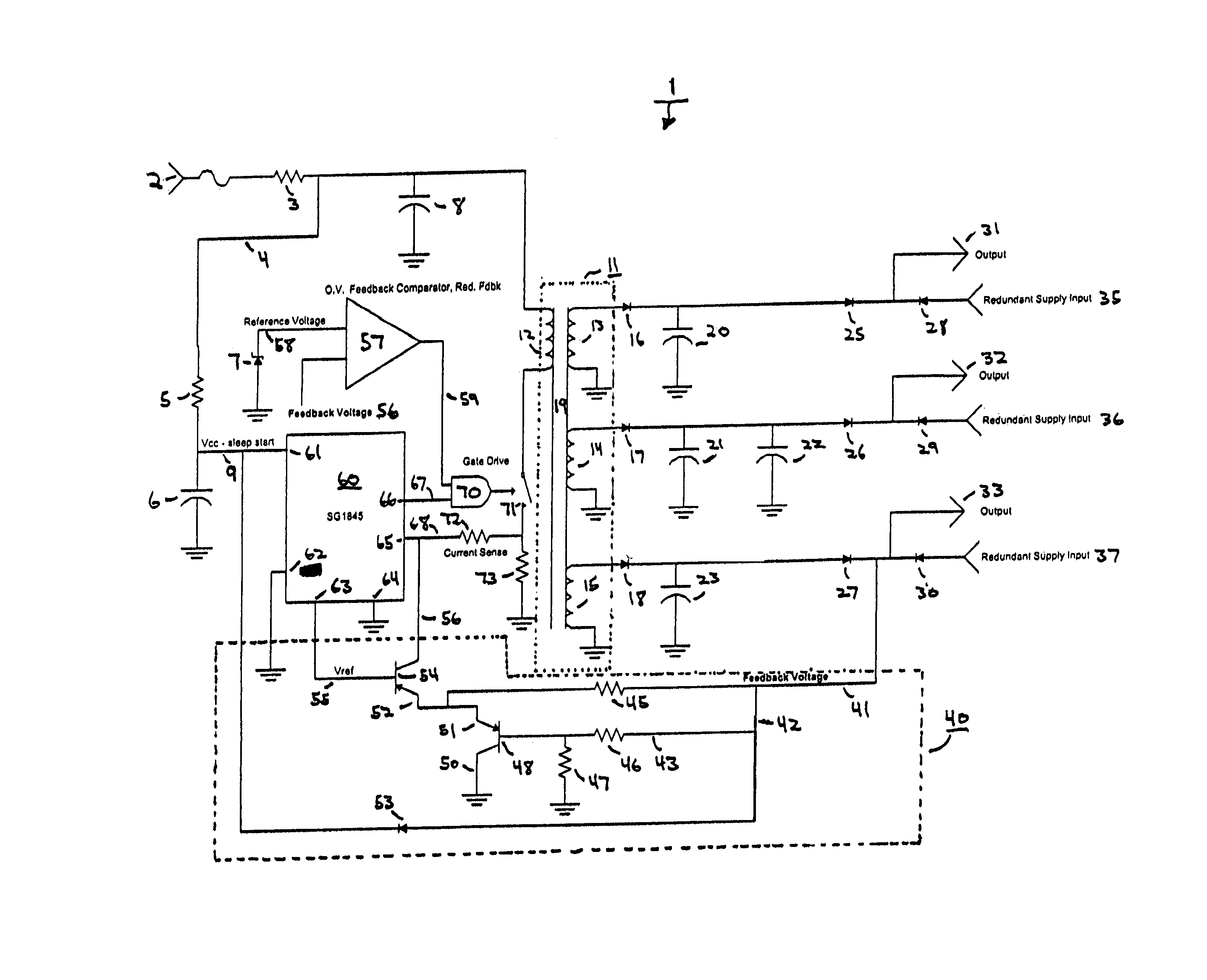
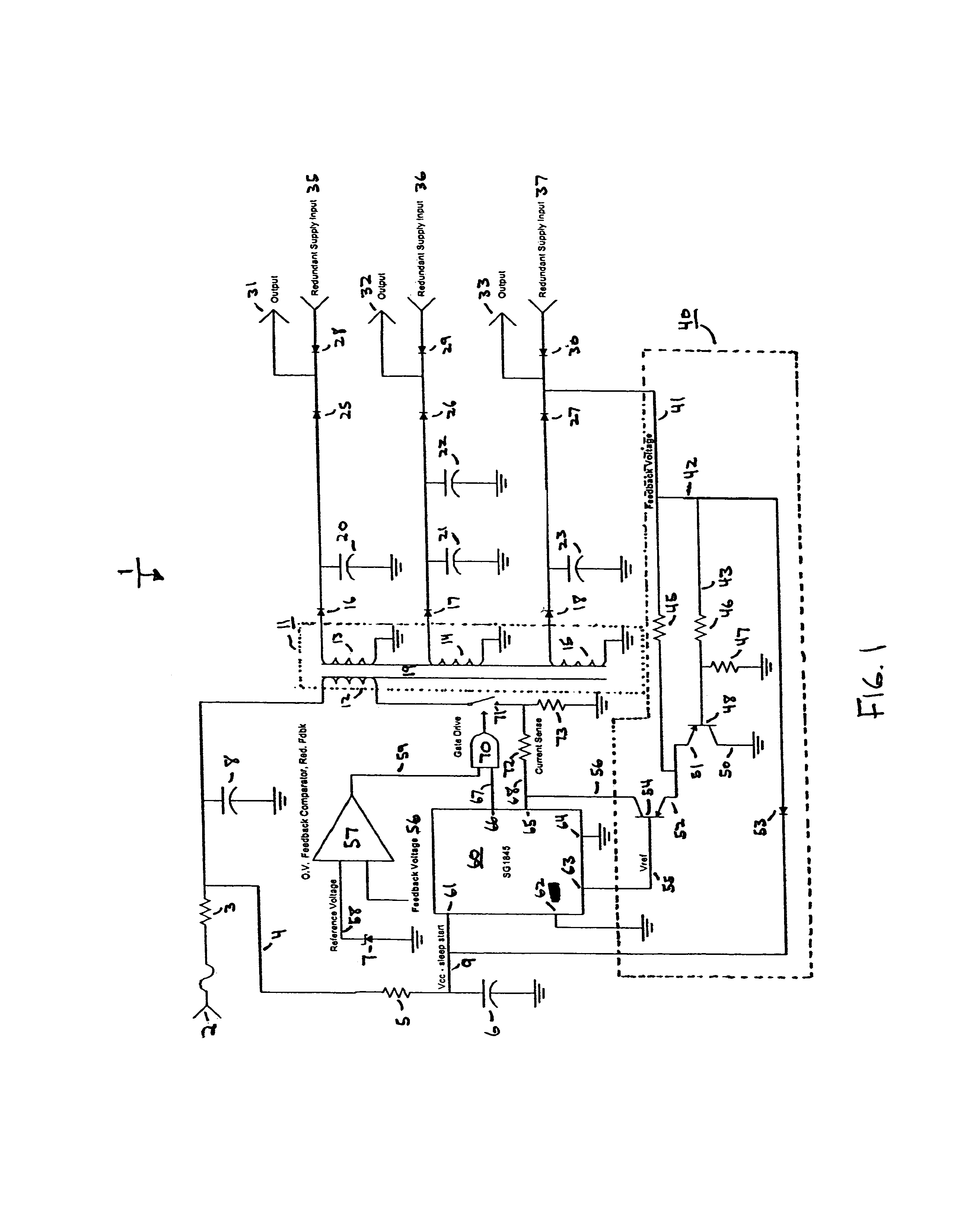
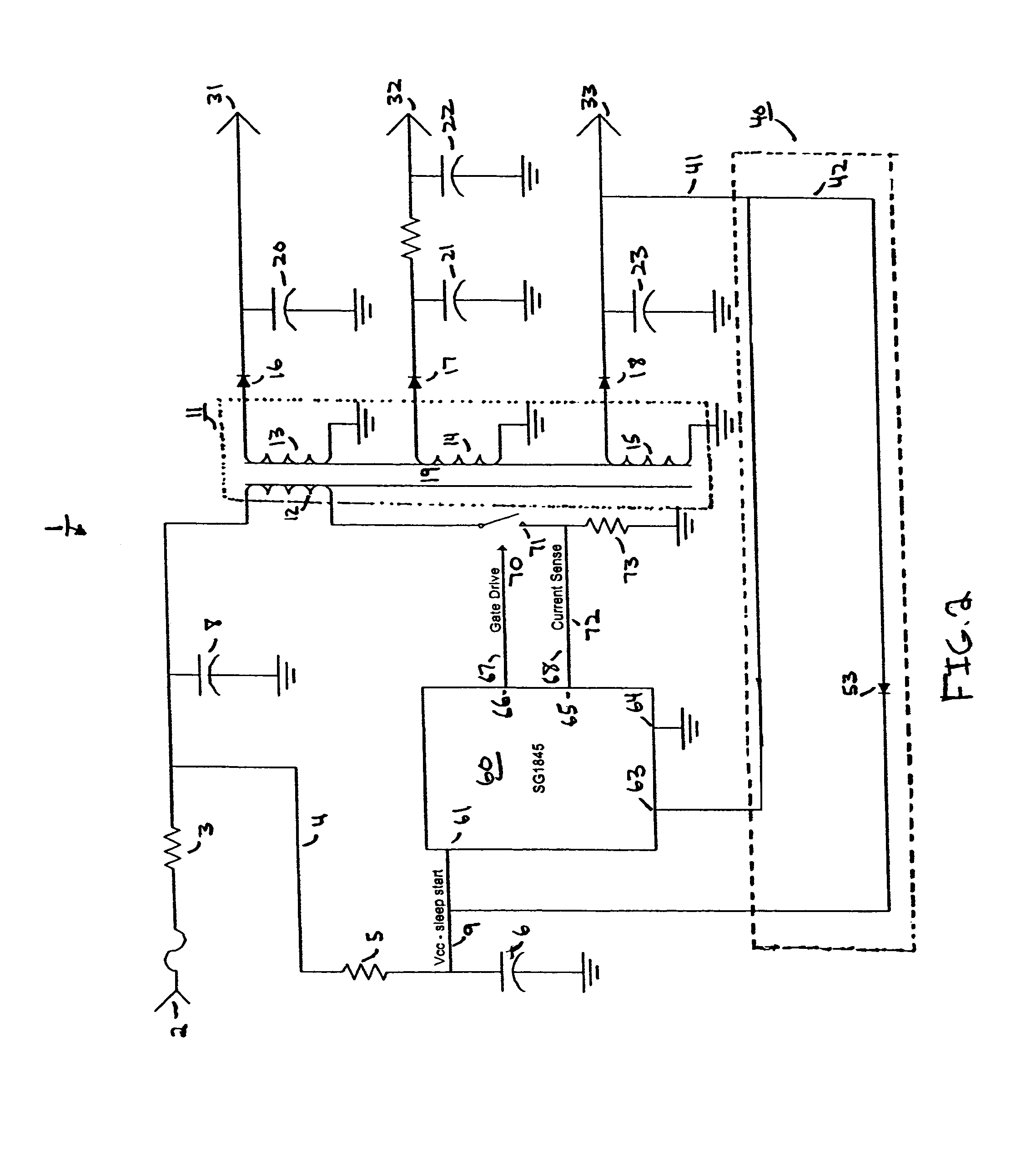
[0018]FIG. 1 shows a schematic of a converter according to one embodiment of the present invention. As seen in FIG. 1, converter 1 includes many common circuit components and is configured to provide a controlled dual-mode converter with a feedback loop that operates in a linear mode under continuous loads, and that operates in a comparative mode under non-continuous step loads.
[0019]Converter 1 receives input signal (load) 2 from a source such as a power supply. Input signal 2 is passed through resistor 3, which is a known type of resistor and may be of a desired resistance to step down the voltage level of input signal 2 to a desired level. Next, input signal 2 is branched to signal 4 which is passed through resistor 5 and split to input signal 9. Also on the path of signal 4 is capacitor 6 for filtering signal 4. The other side of capacitor 6 is grounded. As with resistor 3, resistor 5 and capacitor 6 are known types of components and may be of desired values in different embodiment
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap