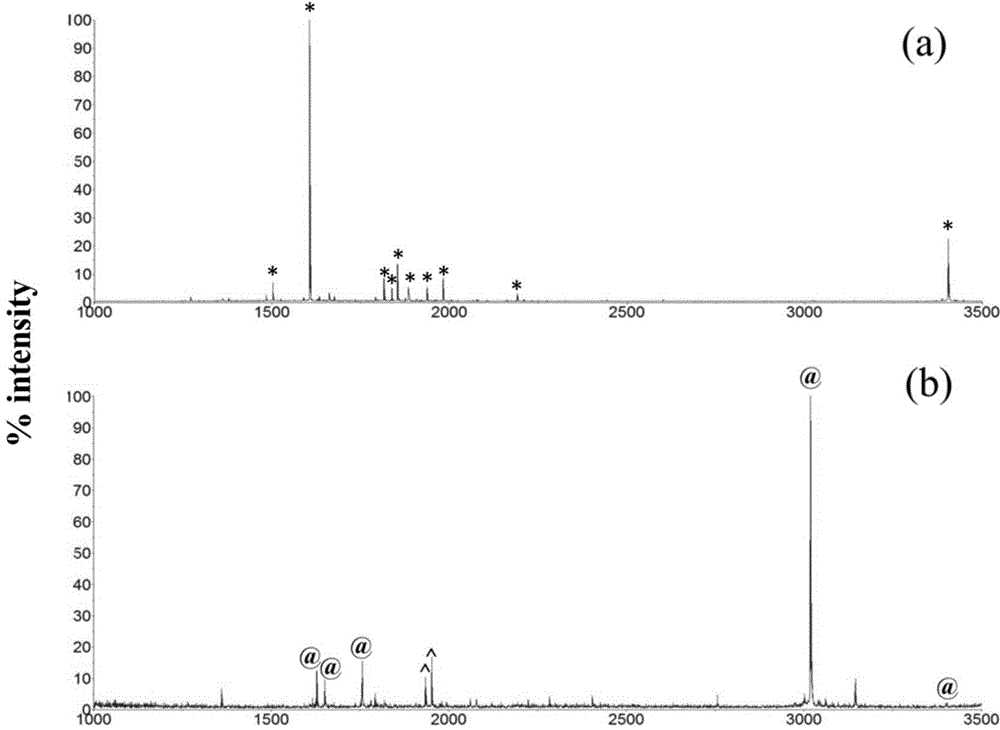
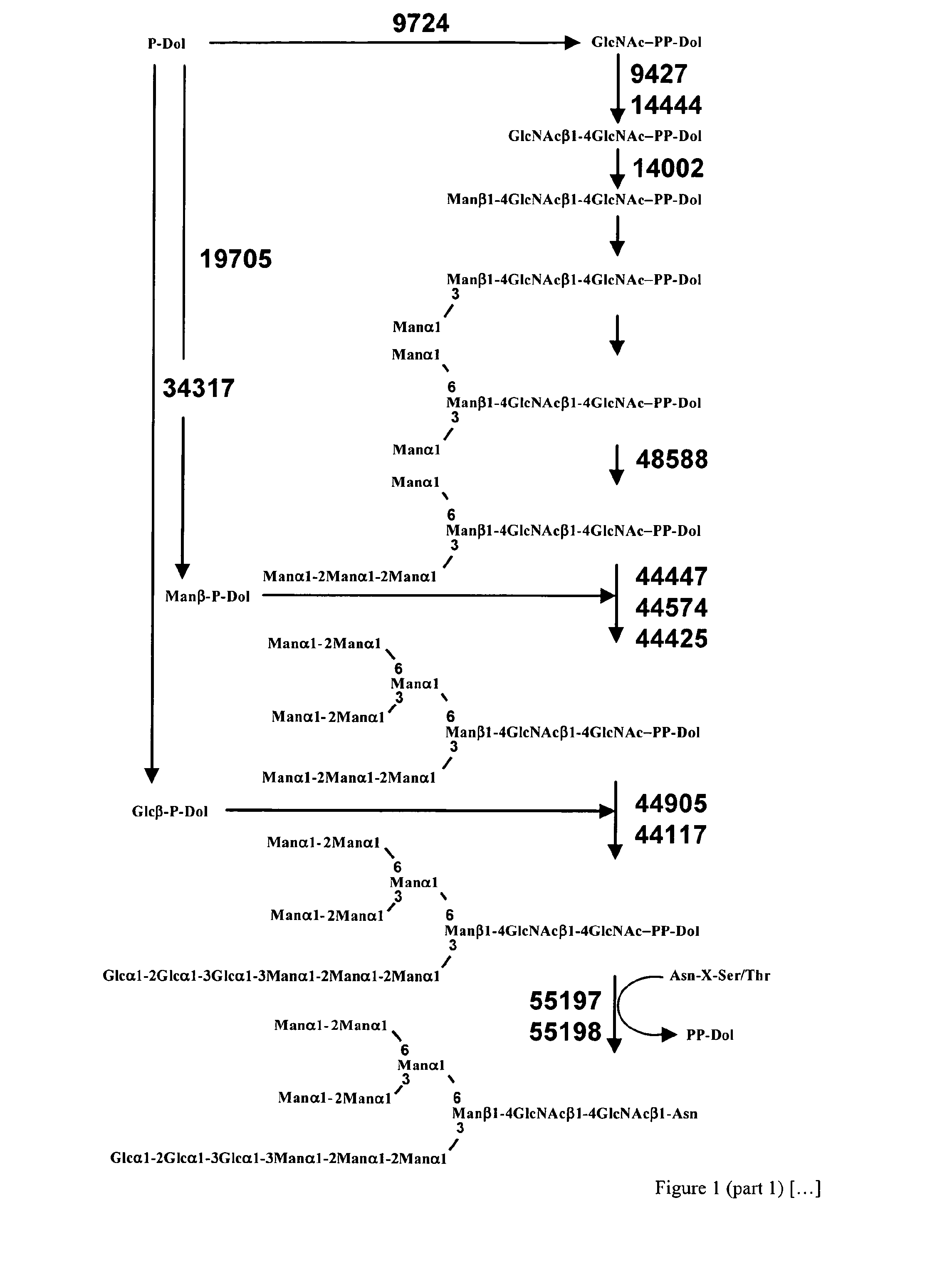
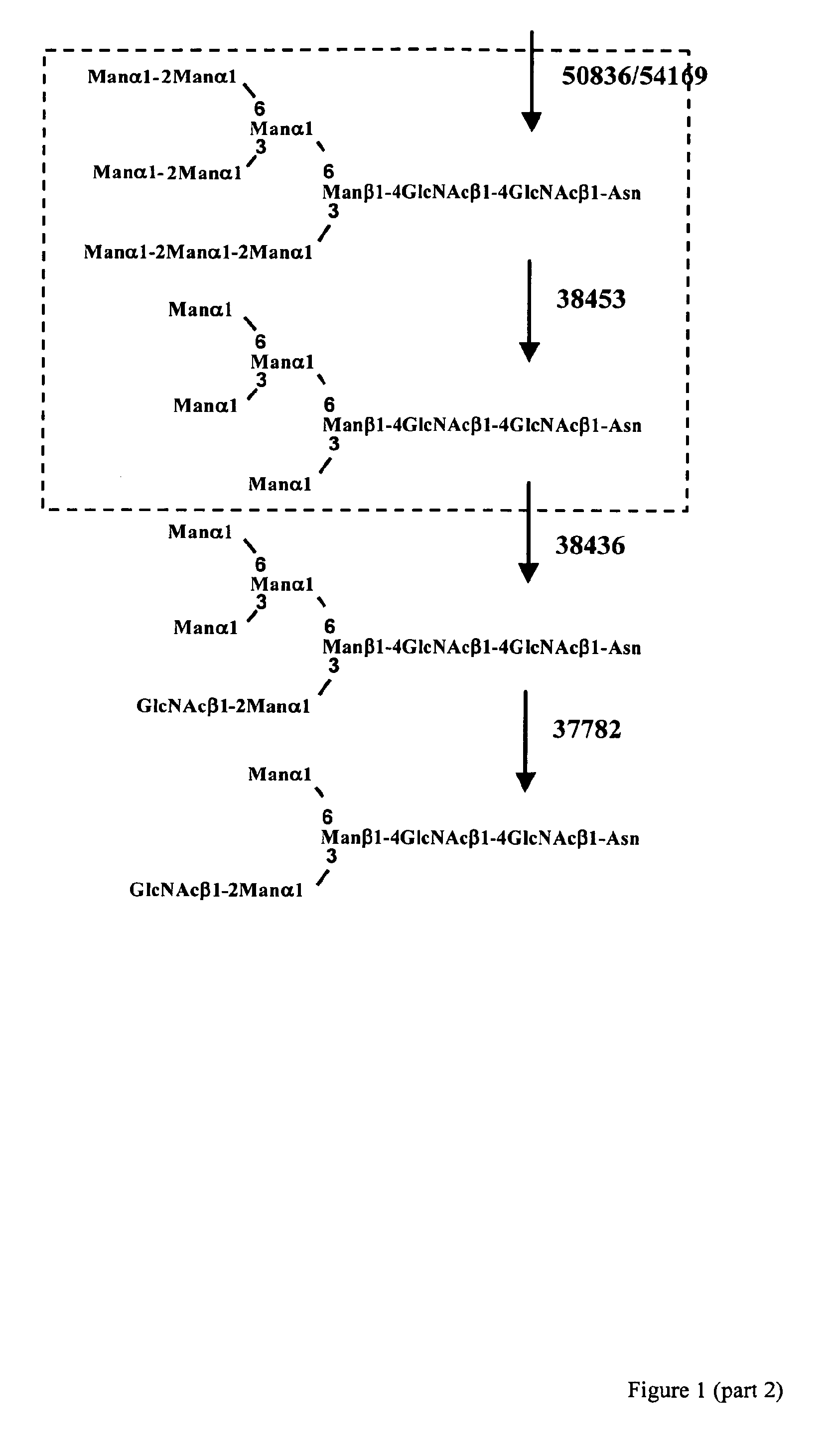
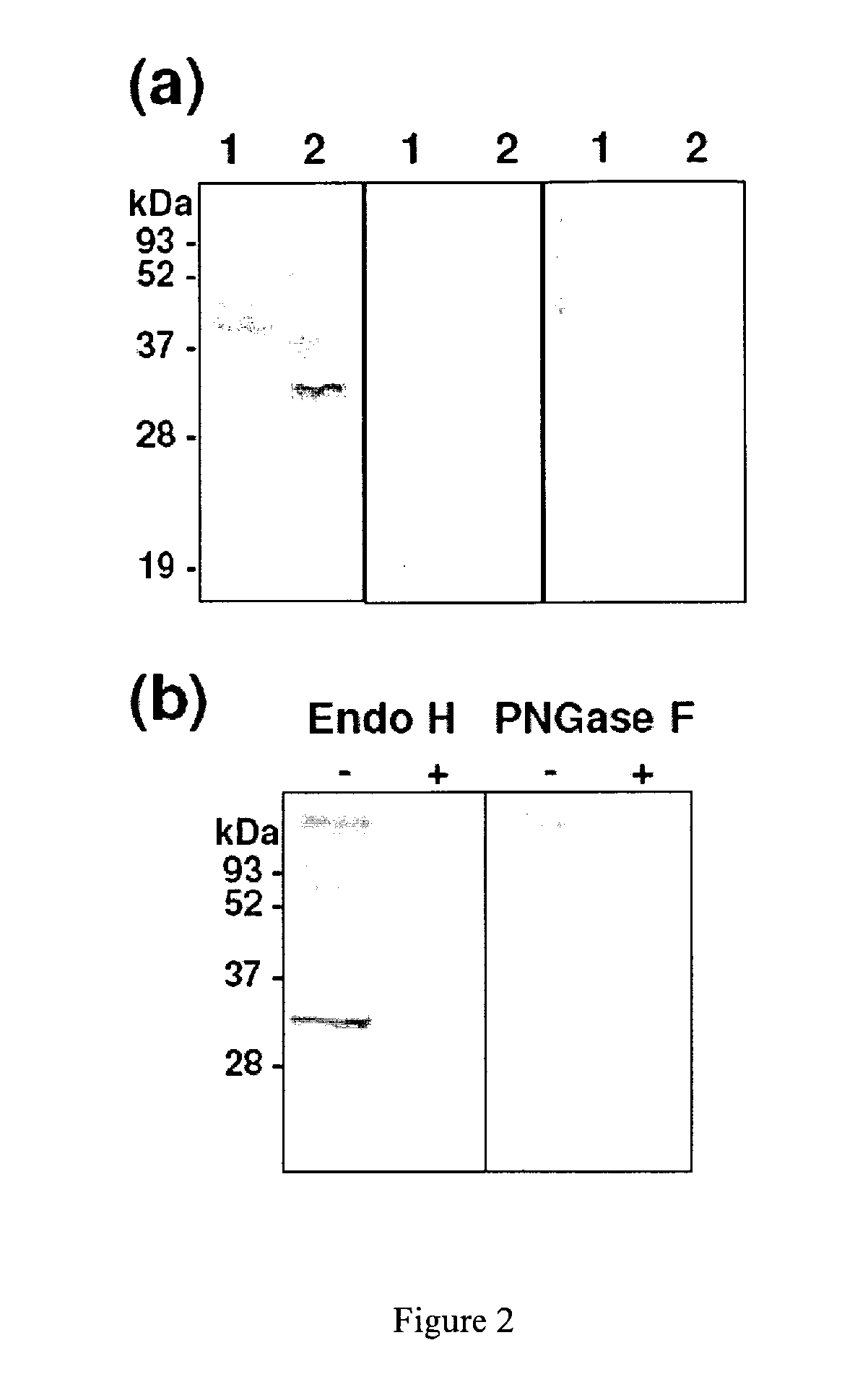
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4 results about "Glycosylation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glycosylation (see also chemical glycosylation) is the reaction in which a carbohydrate, i.e. a glycosyl donor, is attached to a hydroxyl or other functional group of another molecule (a glycosyl acceptor). In biology, glycosylation mainly refers in particular to the enzymatic process that attaches glycans to proteins, or other organic molecules. This enzymatic process produces one of the fundamental biopolymers found in cells (along with DNA, RNA, and proteins). Glycosylation is a form of co-translational and post-translational modification. Glycans serve a variety of structural and functional roles in membrane and secreted proteins. The majority of proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum undergo glycosylation. It is an enzyme-directed site-specific process, as opposed to the non-enzymatic chemical reaction of glycation. Glycosylation is also present in the cytoplasm and nucleus as the O-GlcNAc modification. Aglycosylation is a feature of engineered antibodies to bypass glycosylation. Five classes of glycans are produced...
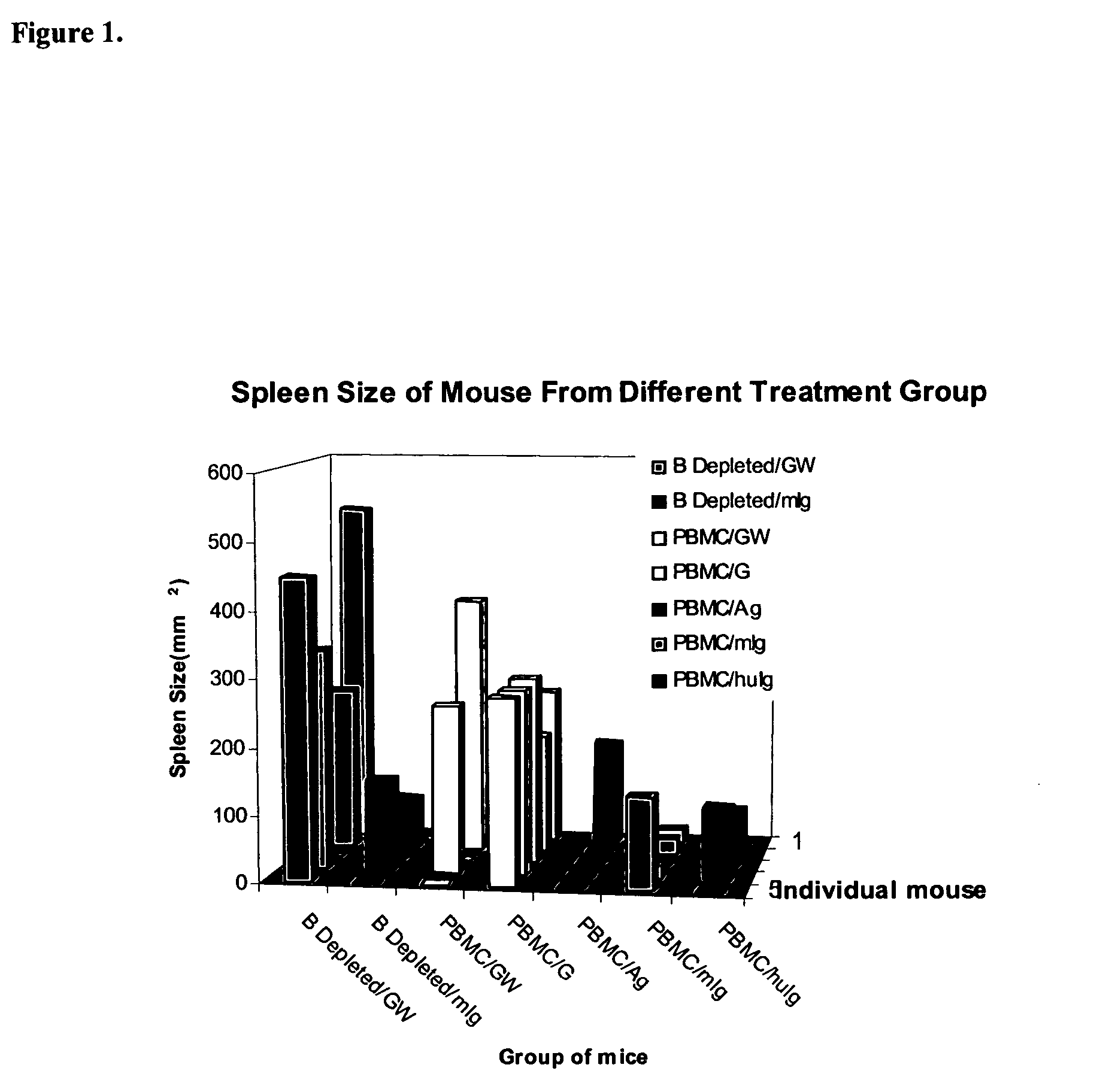
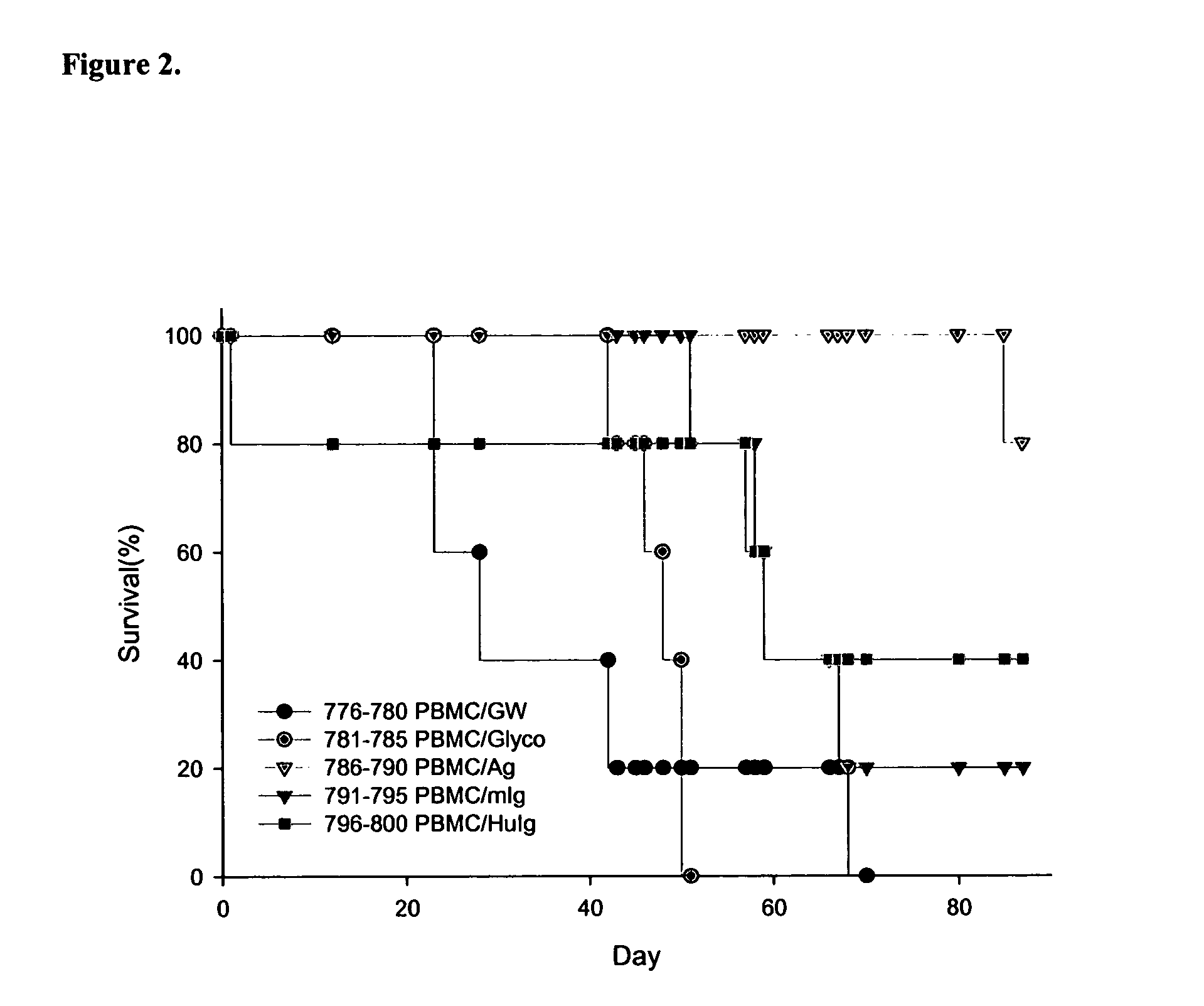
Anti-CD137 antibody as an agent in the treatment of cancer and glycosylation variants thereof
InactiveUS20060182744A1Reduce and prevent inactivationEasy to manufactureImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsAnticarcinogenCD137
Owner:GTC BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC
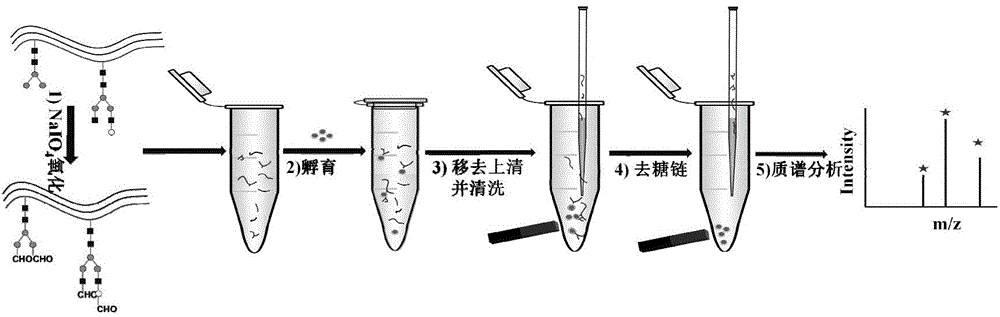
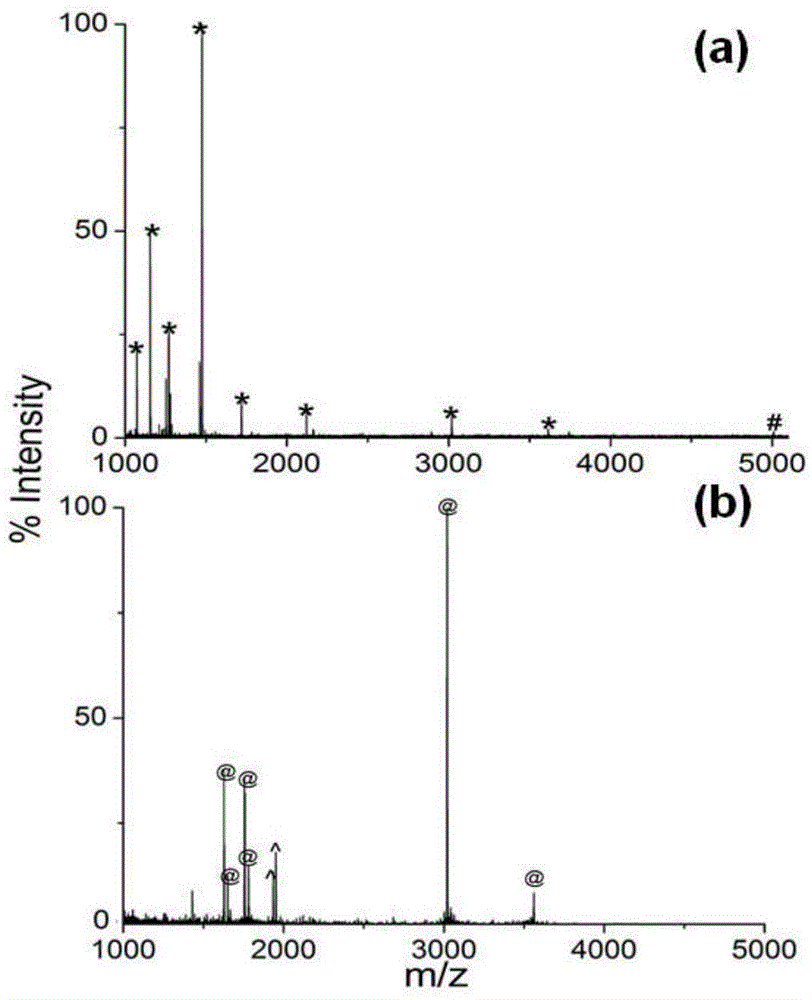
Method for solid-phase enrichment and mass spectrographic analysis of glycosylated peptide fragment
ActiveCN105300783AImprove Analytical Mass Spectrometry SelectivityHigh reaction specificityPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansGlycopeptideMass spectrometric
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Production of glycosylated polypeptides in micro algae
Owner:INSTITUT FR DE RES & DEV POUR LEXPL DE LA MER IFREMER +2
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap