Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7 results about "RAID" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
RAID (Redundant Array of Inexpensive Disks or Drives, or Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a data storage virtualization technology that combines multiple physical disk drive components into one or more logical units for the purposes of data redundancy, performance improvement, or both. This was in contrast to the previous concept of highly reliable mainframe disk drives referred to as "single large expensive disk" (SLED).
Systems and Methods for Optimizing Host Reads and Cache Destages in a Raid System
InactiveUS20100199039A1Minimize host read response timeLarge throughputMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionRAIDCoupling
Owner:IBM CORP
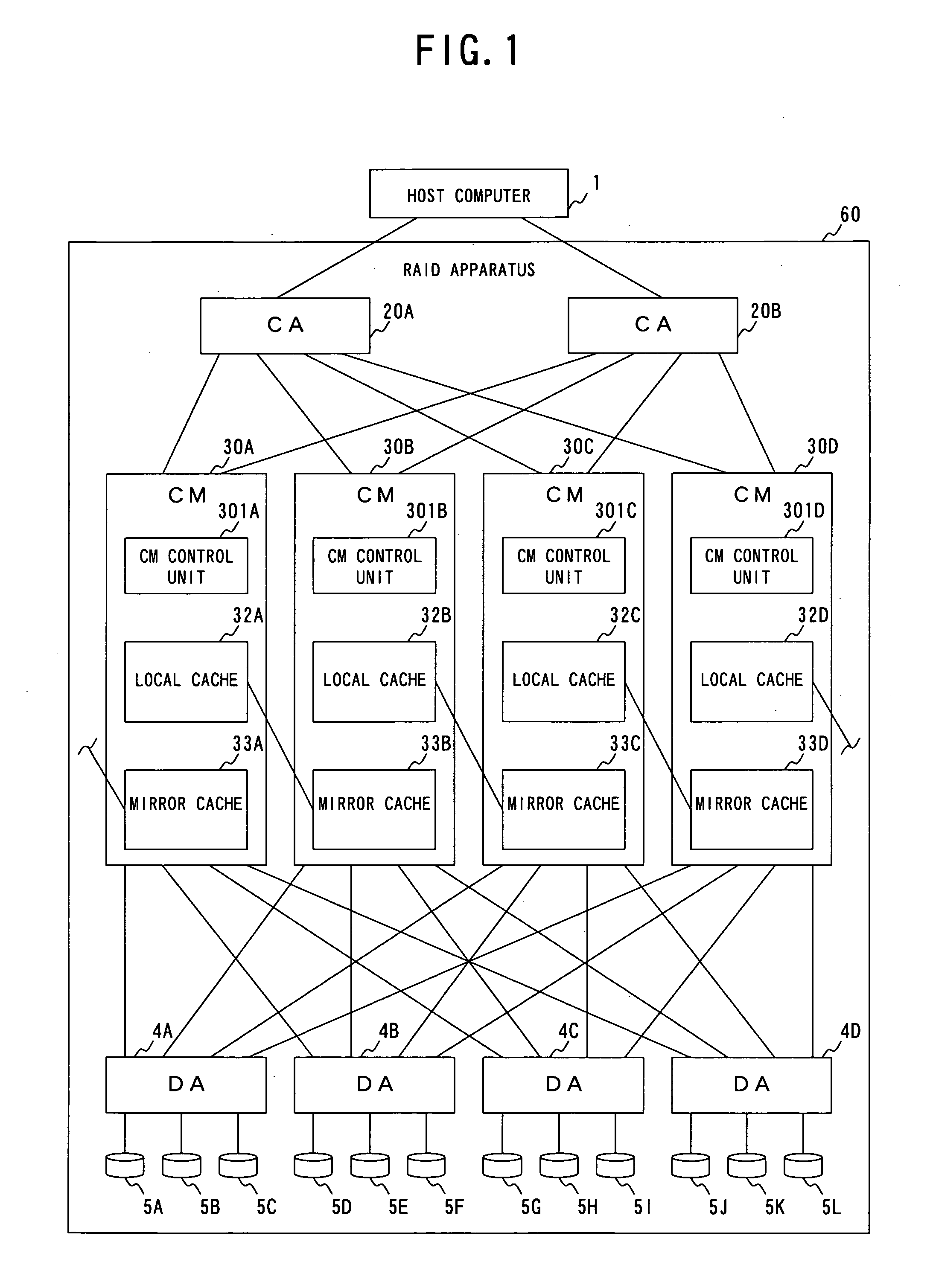
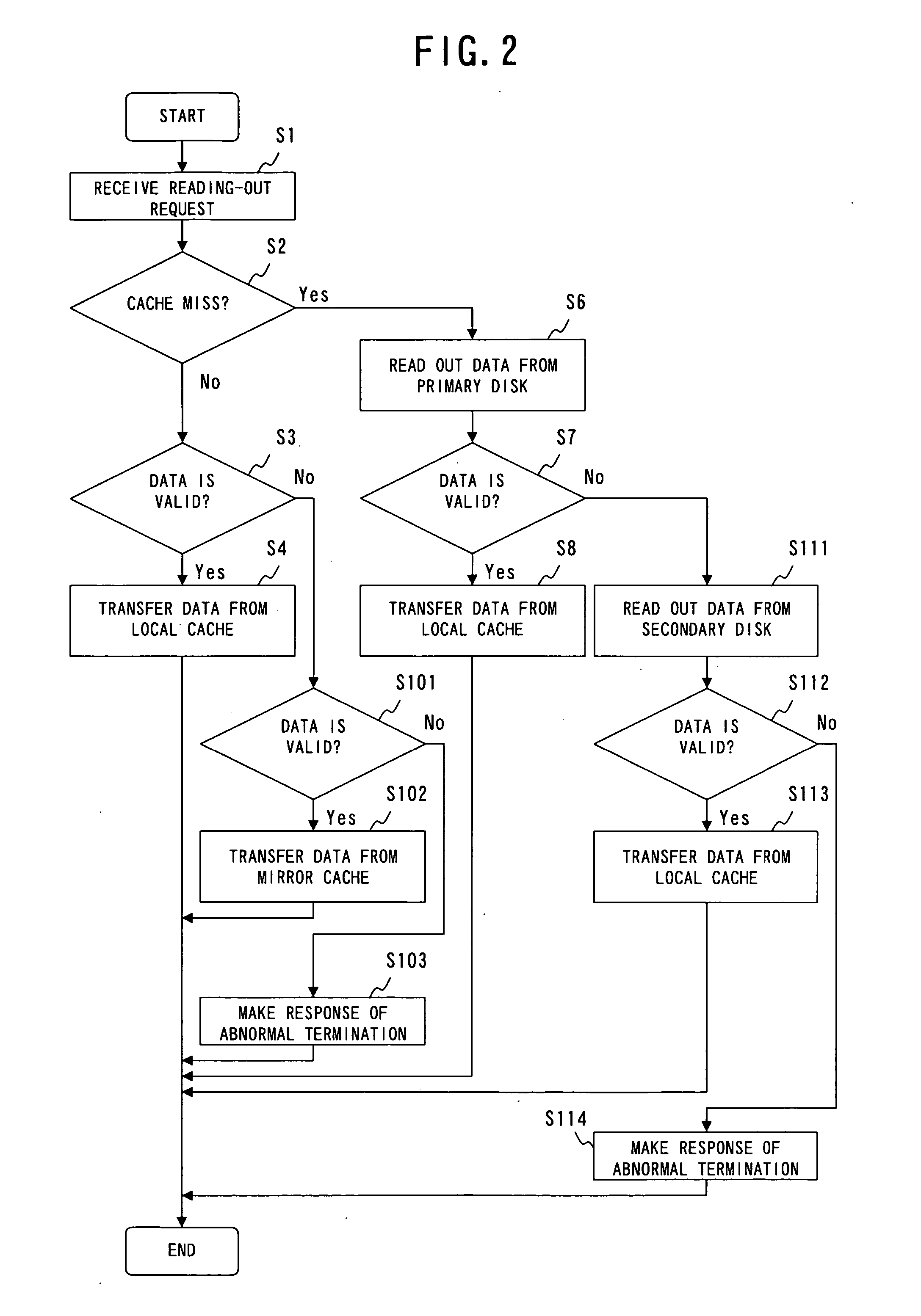
RAID apparatus, RAID control method, and RAID control program
ActiveUS20050216660A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAID
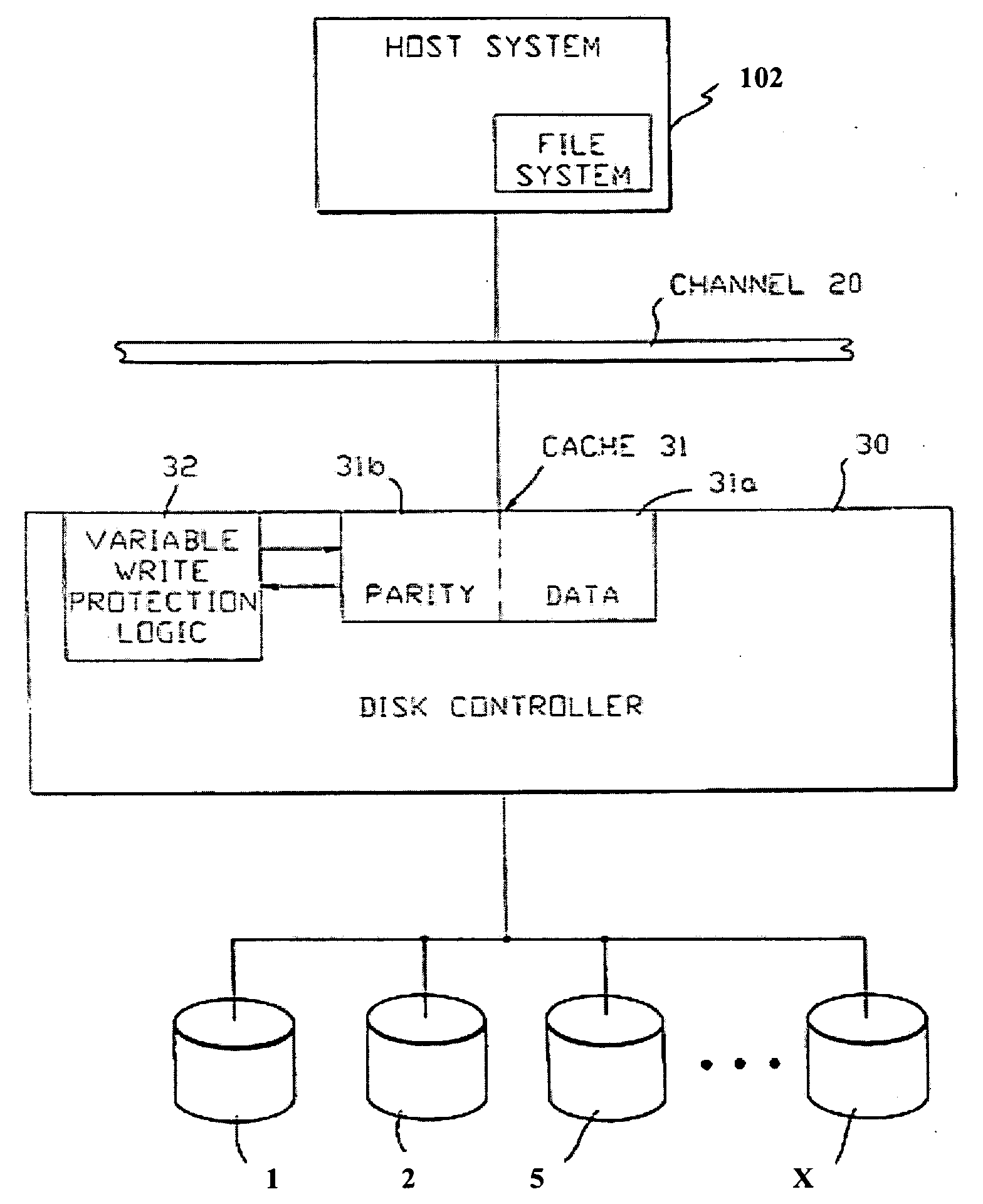
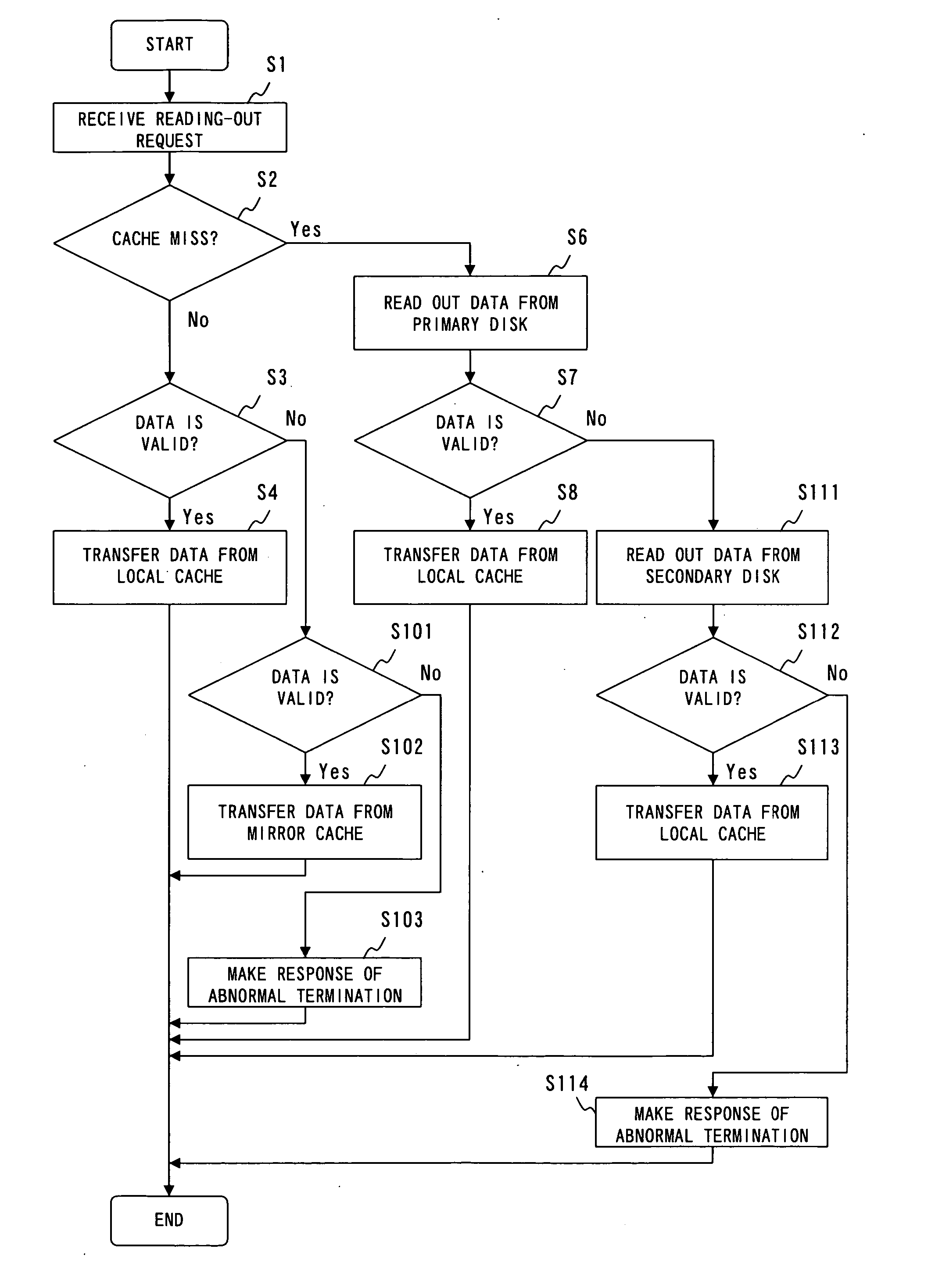
A RAID apparatus that at least duplicates identical data to store thus duplicated data, which, when an instruction of writing data is given, writes data to a local cache and to a mirror cache, and writes data of the local cache to a primary disk and writes data of the mirror cache to a secondary disk. When an instruction of reading out data is given, and specified data is retained in the caches, the RAID apparatus outputs valid data of the local cache or the mirror cache, while when specified data is not retained in the caches, the RAID apparatus outputs valid data of the primary disk or the secondary disk.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
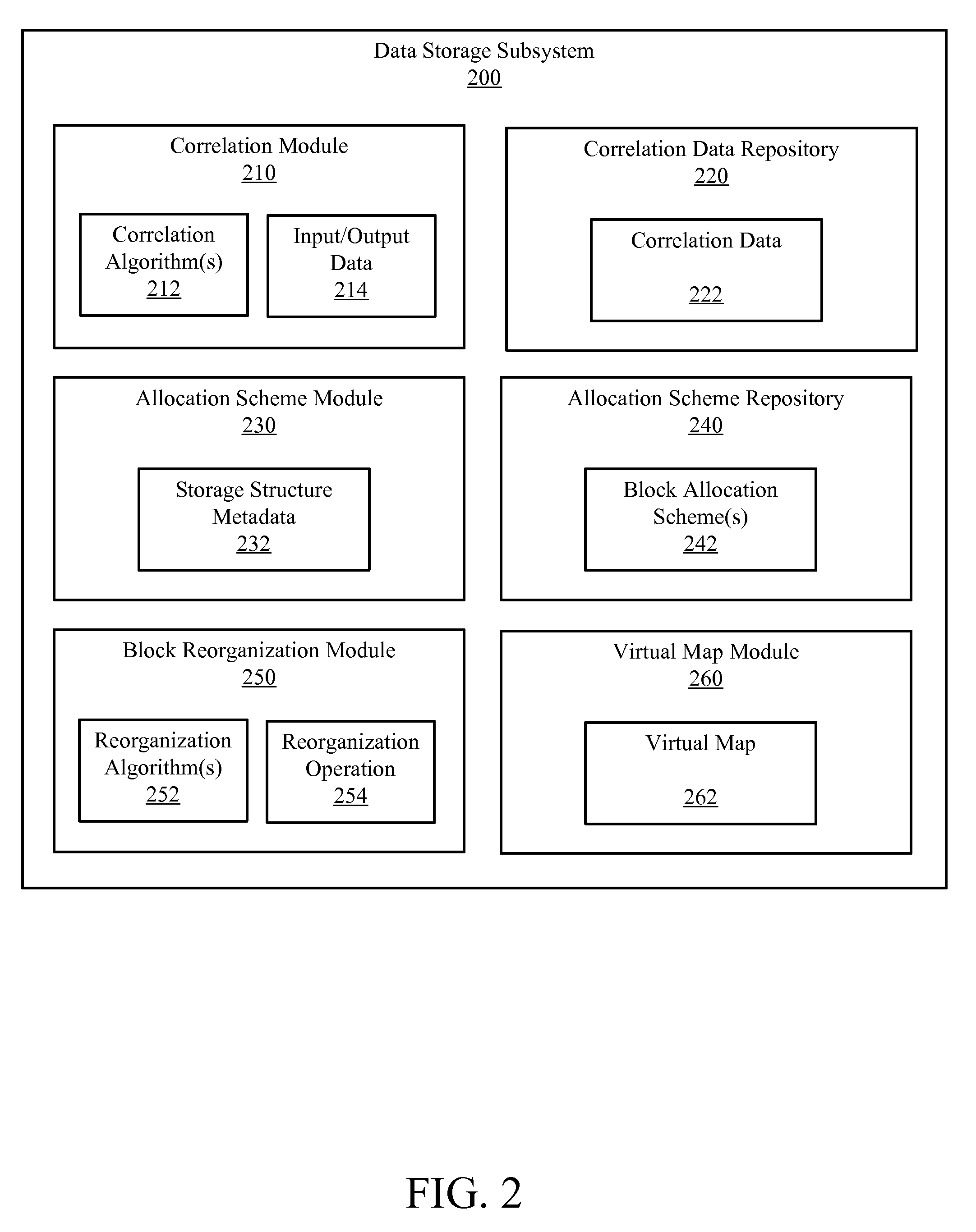
System and method for storage structure reorganization
InactiveUS20080270742A1Minimize data access timeError detection/correctionMemory systemsRAIDData store
Owner:IBM CORP
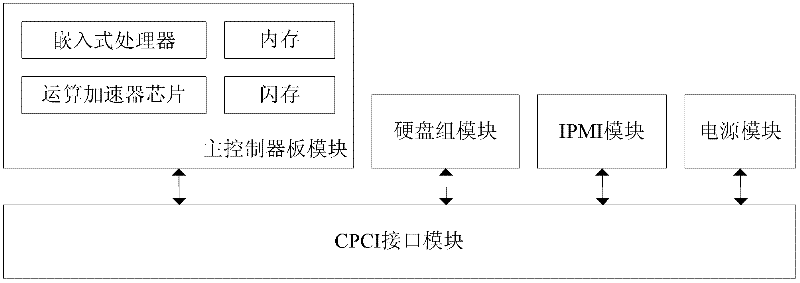
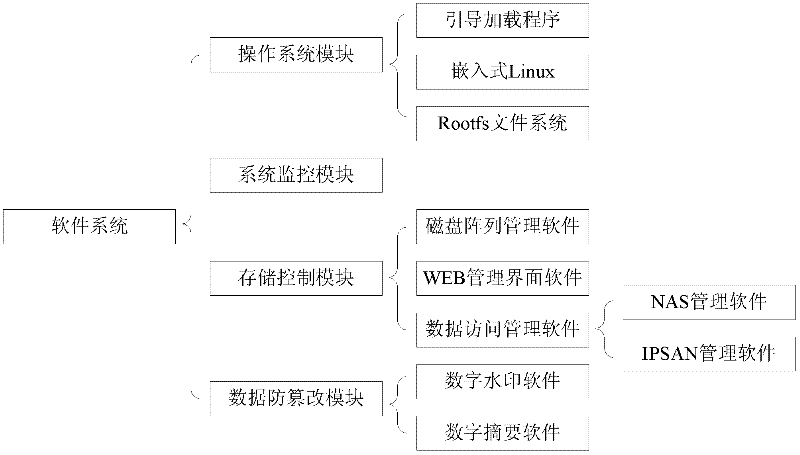
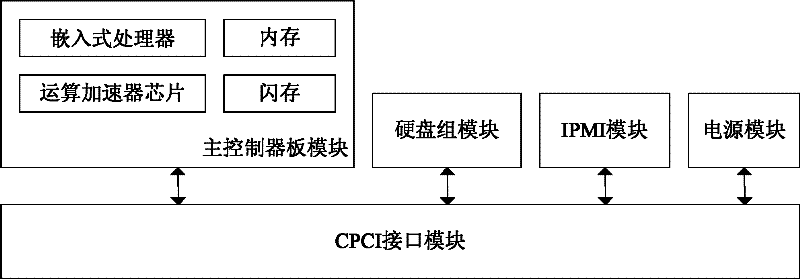
Storage system for network communication recording device of digital substation
InactiveCN102650933AReduce volumeReduce power consumptionInput/output to record carriersStorage area networkSoftware system
Owner:北京信而泰科技股份有限公司
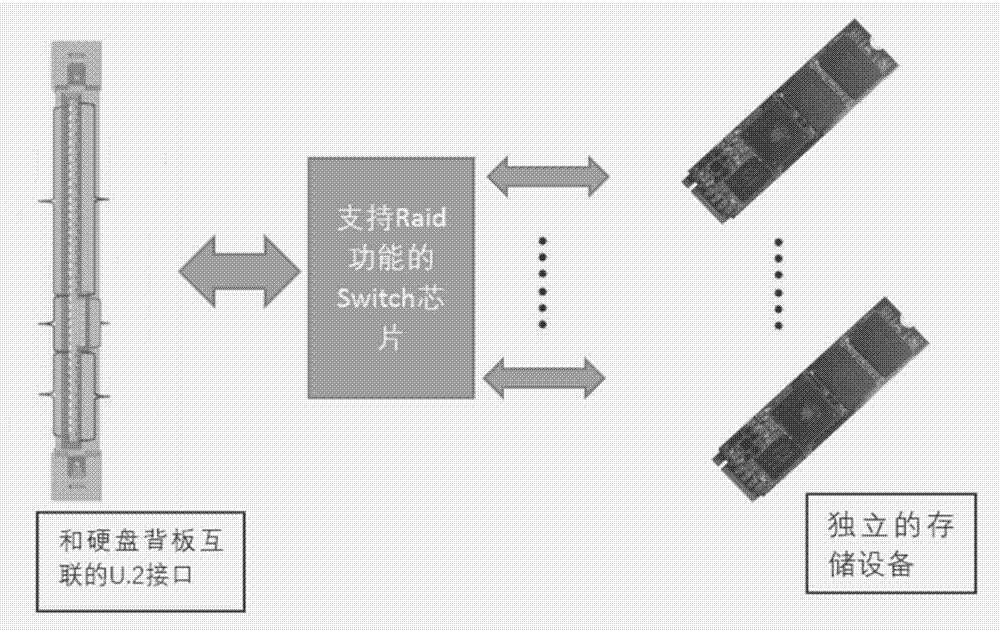
PCIE storage device supporting self-Raid function based on U.2 interface
Owner:ZHENGZHOU YUNHAI INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
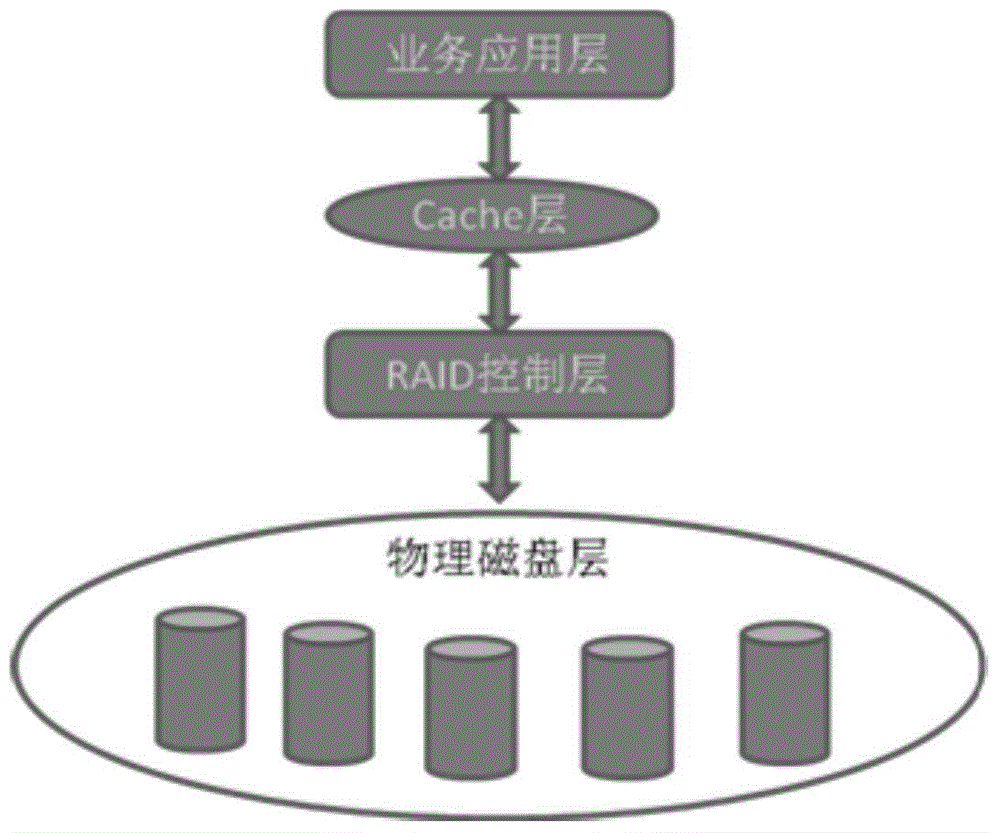
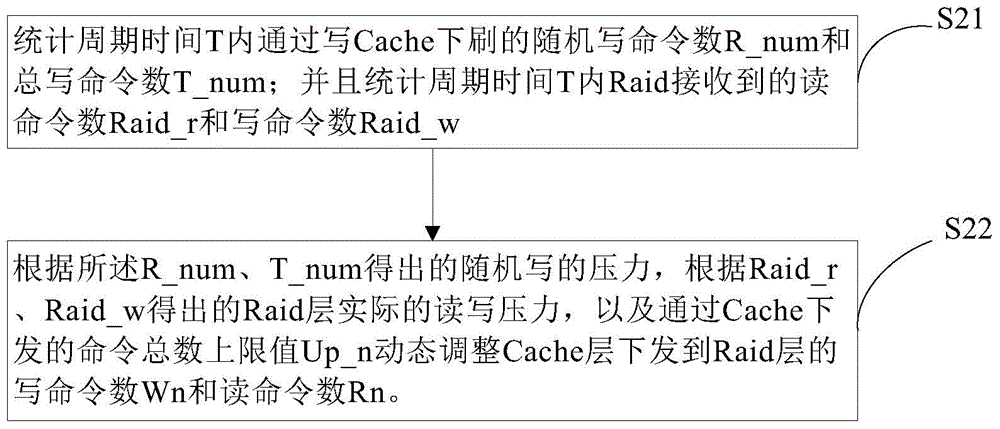
Method and device for dynamically adjusting reading order number and writing order number in storage device Cache
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIVIEW TECH
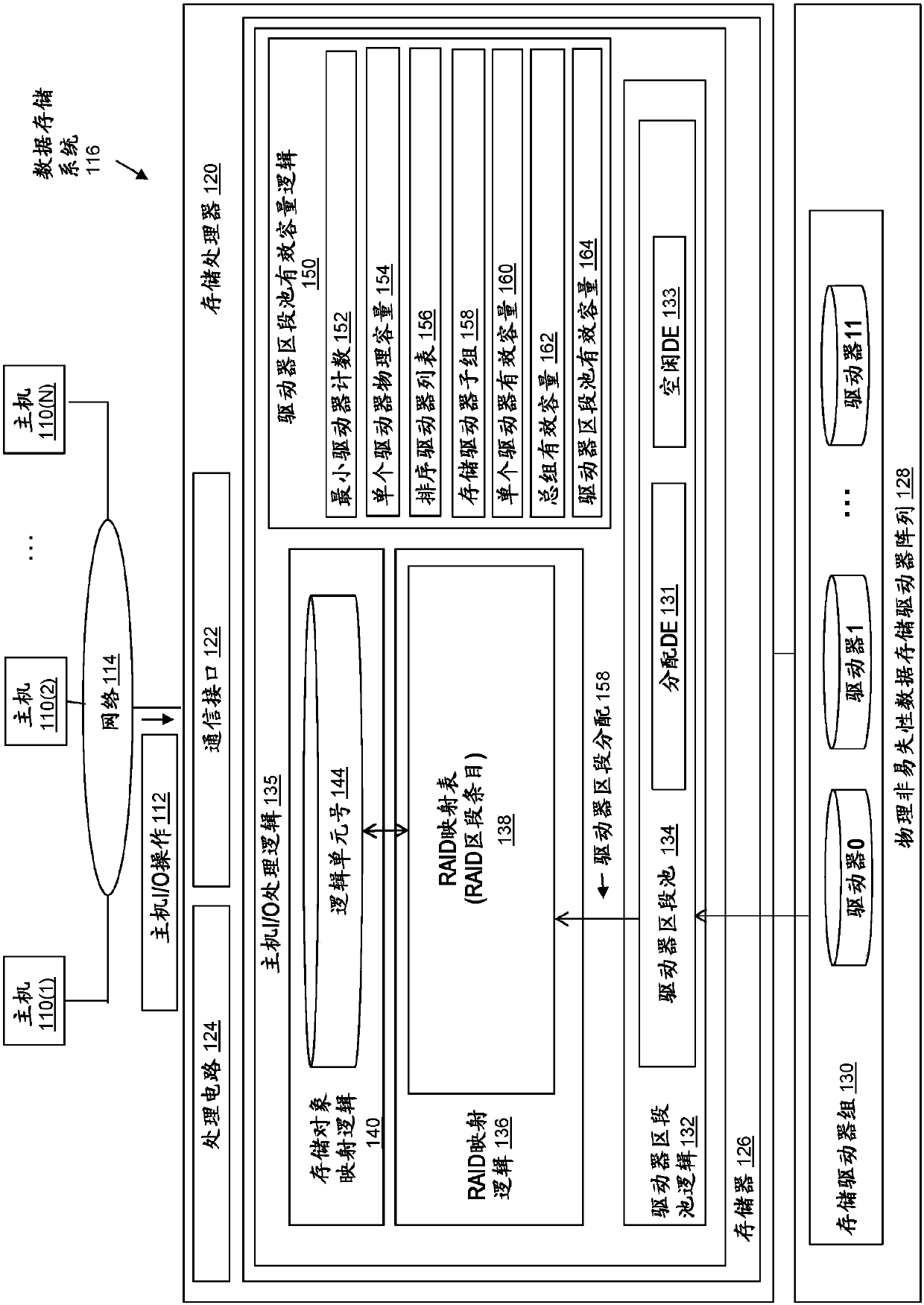
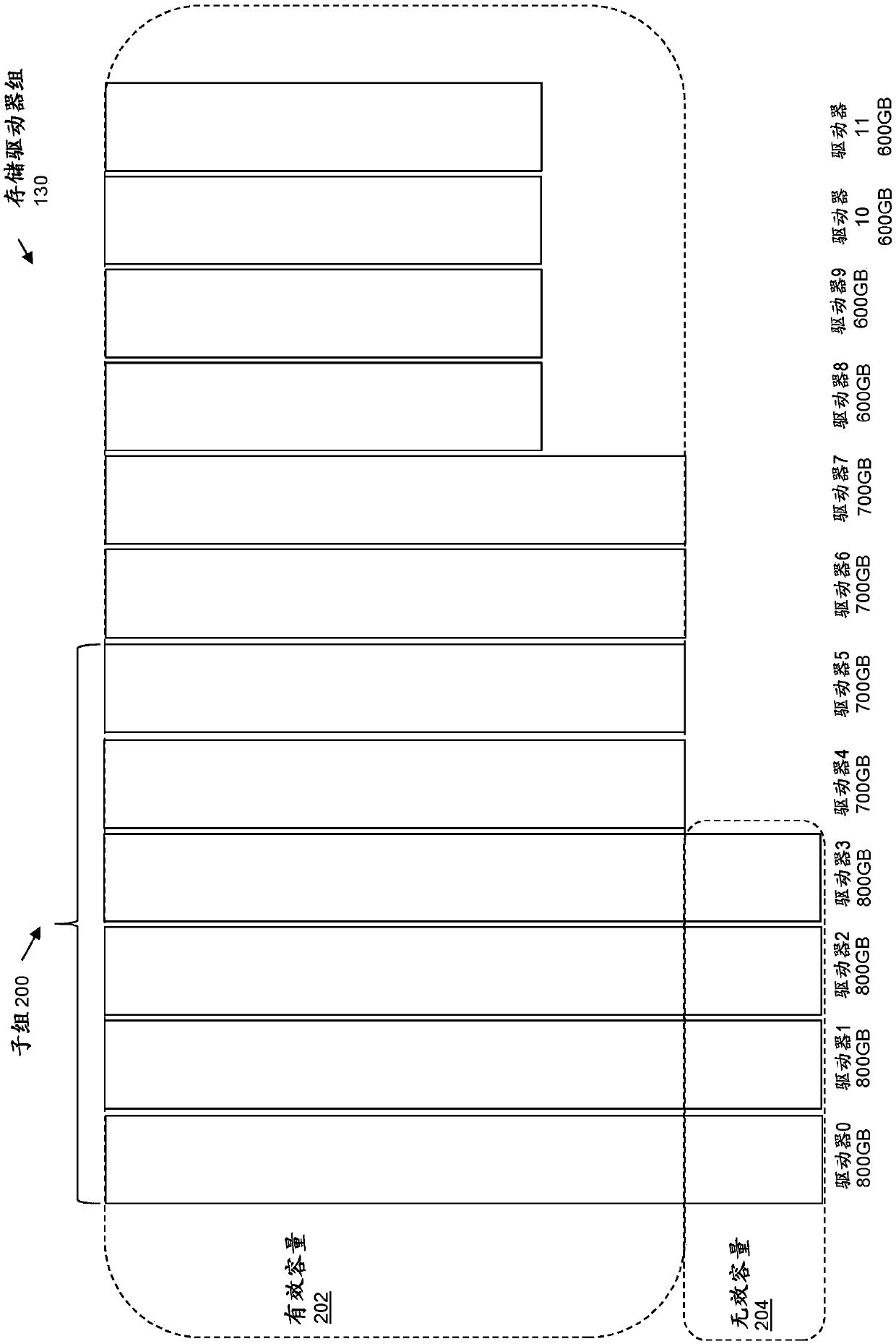
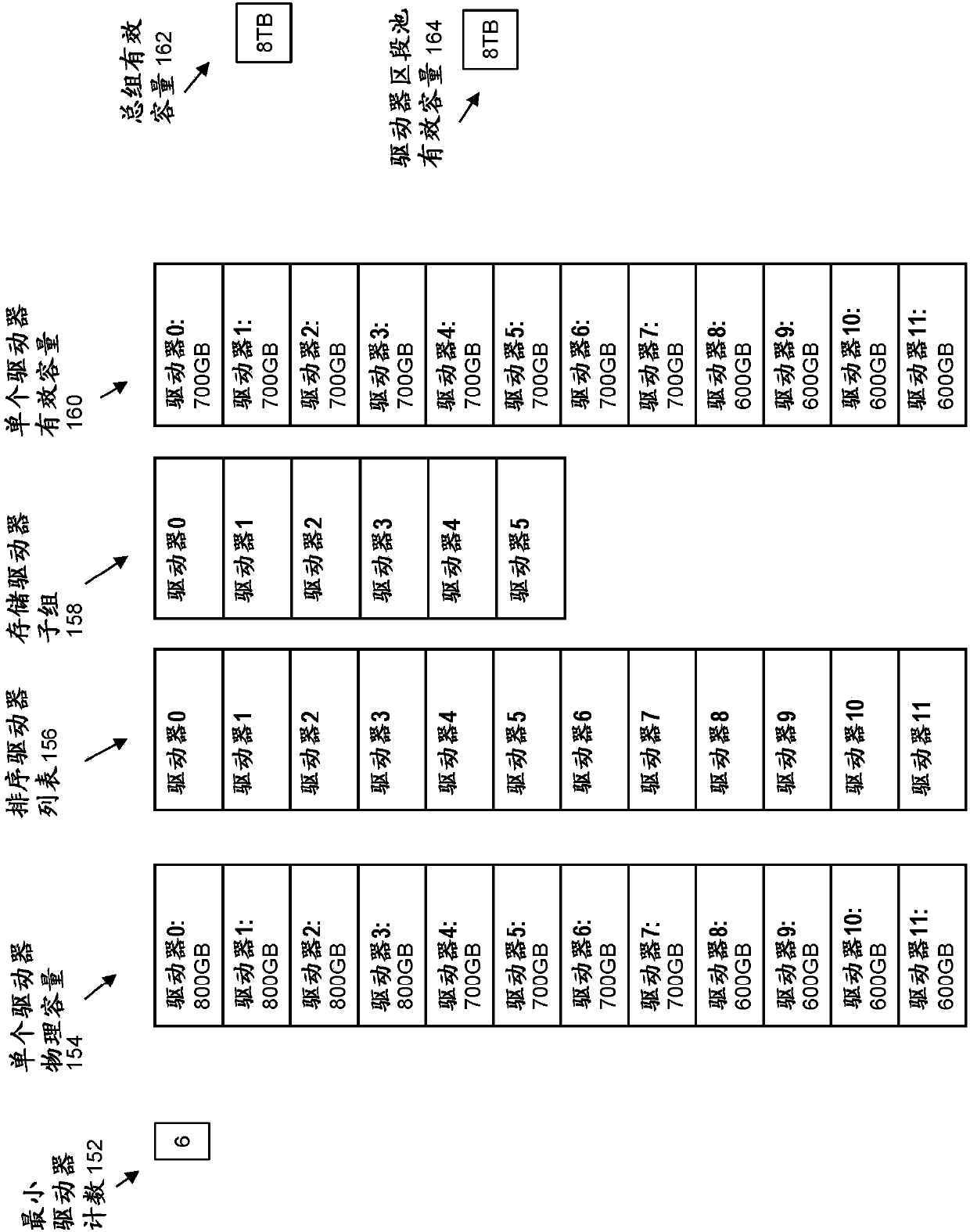
Effective capacity of driver segment pool generated from driver set
ActiveCN110096219AReduce rebuild timeEasy to replaceInput/output to record carriersError detection/correctionRAIDEmbedded system
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap