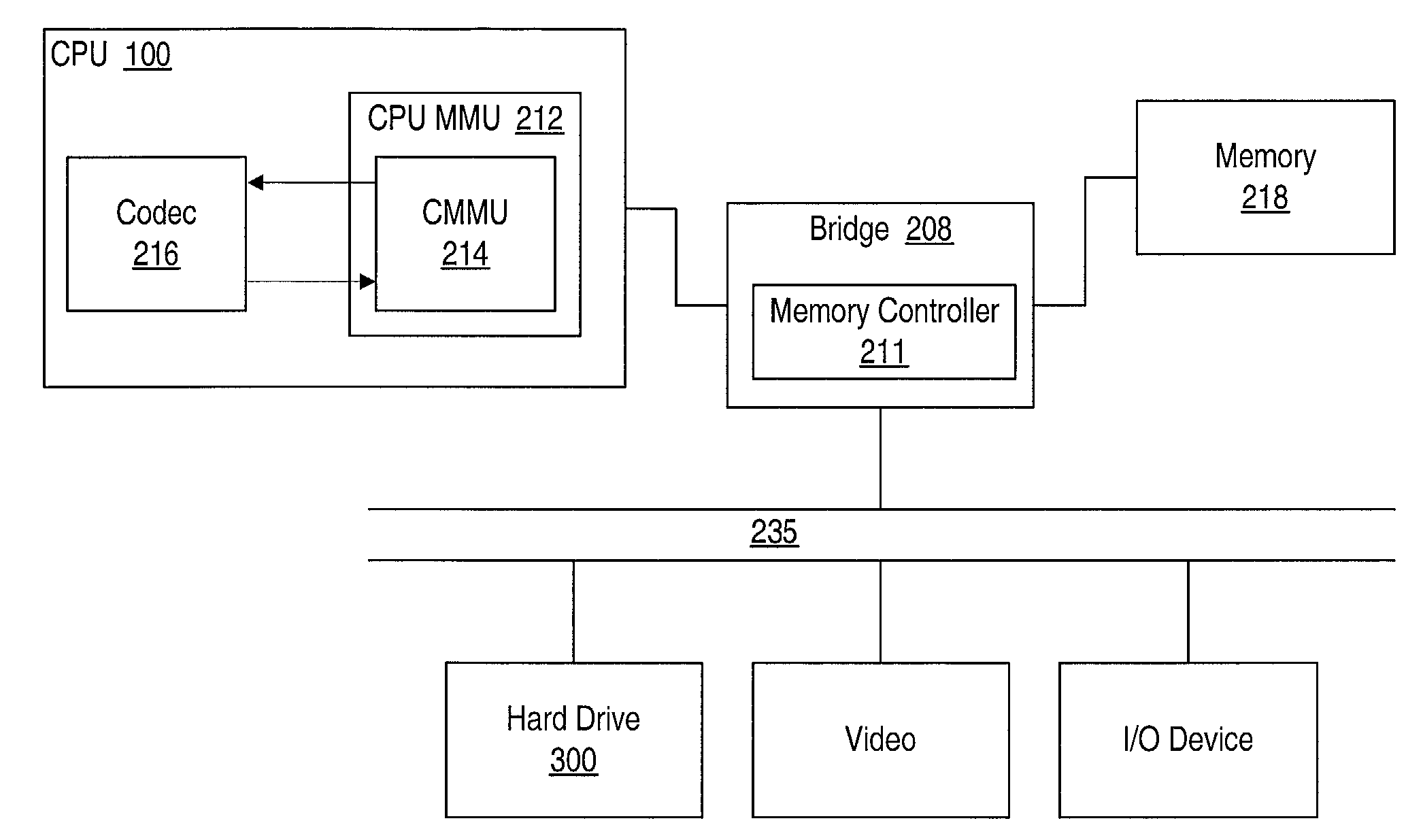
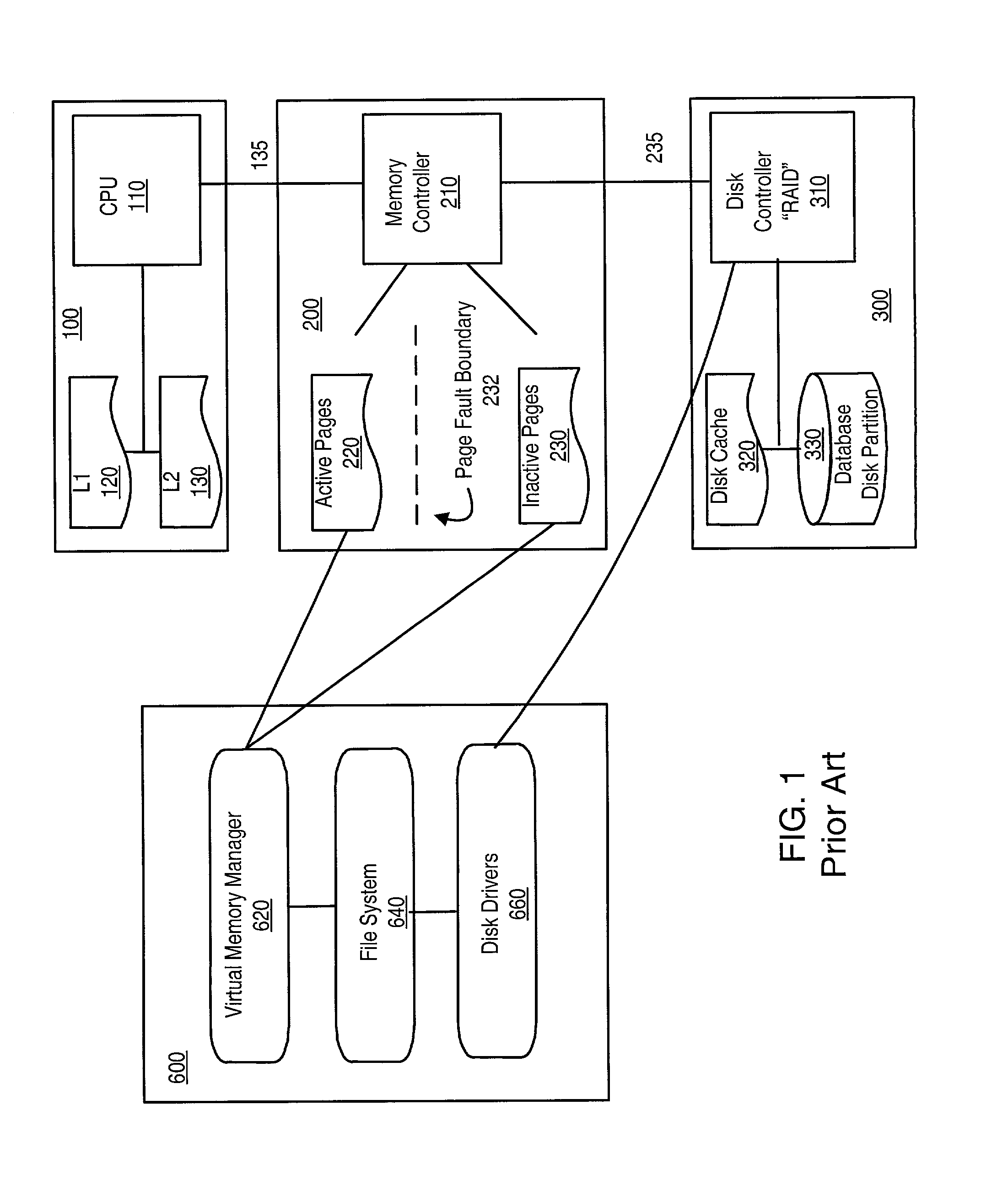
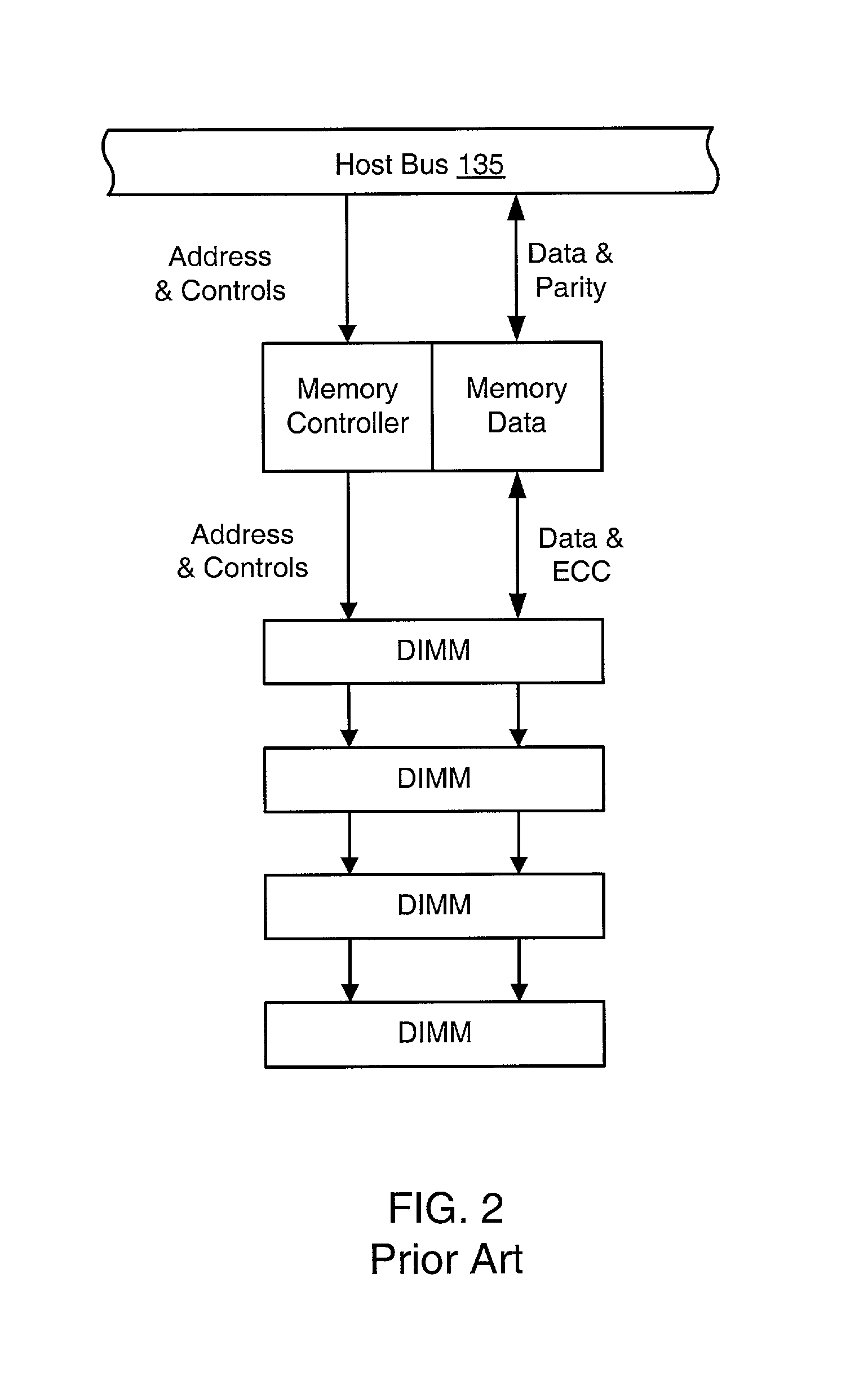
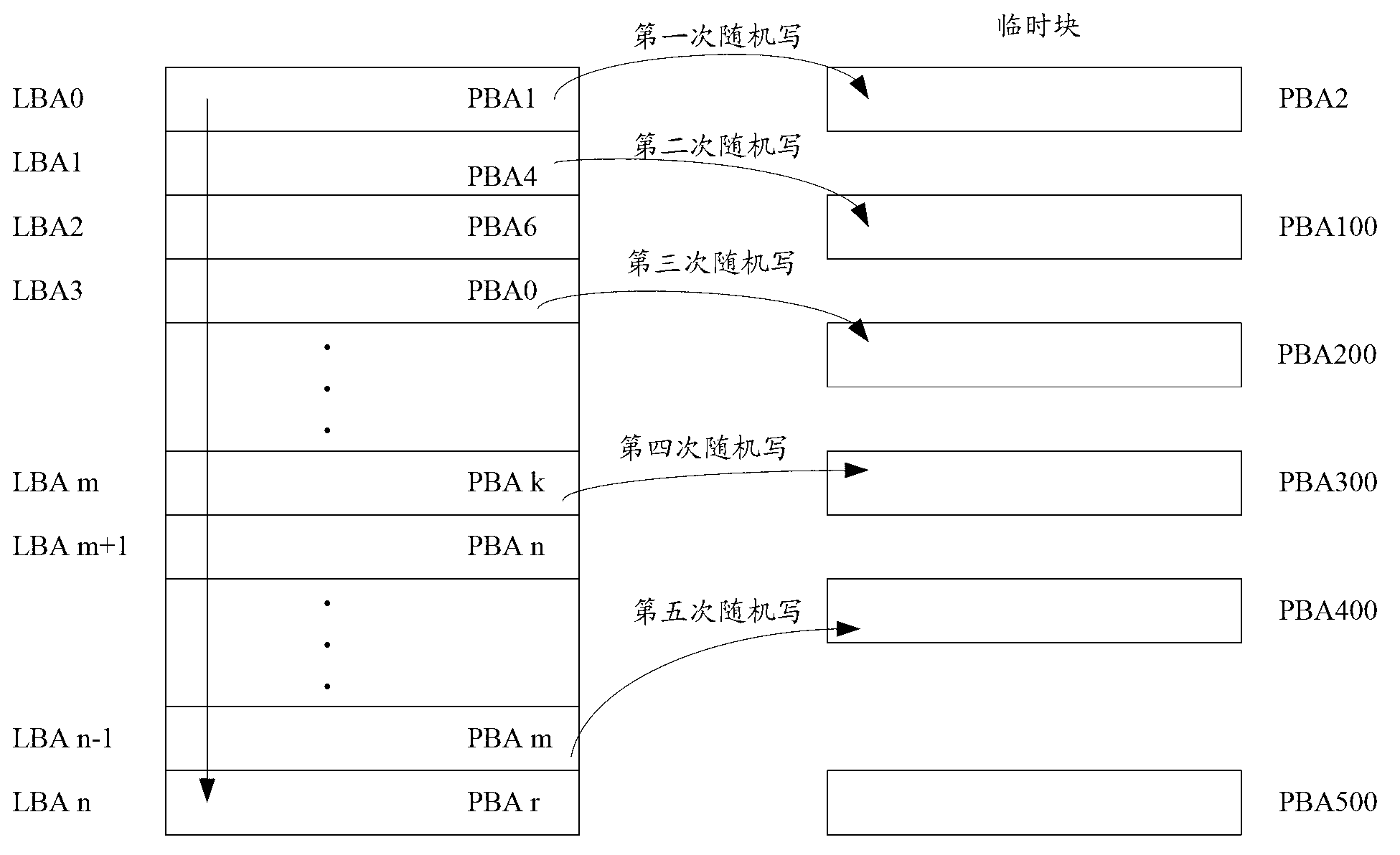
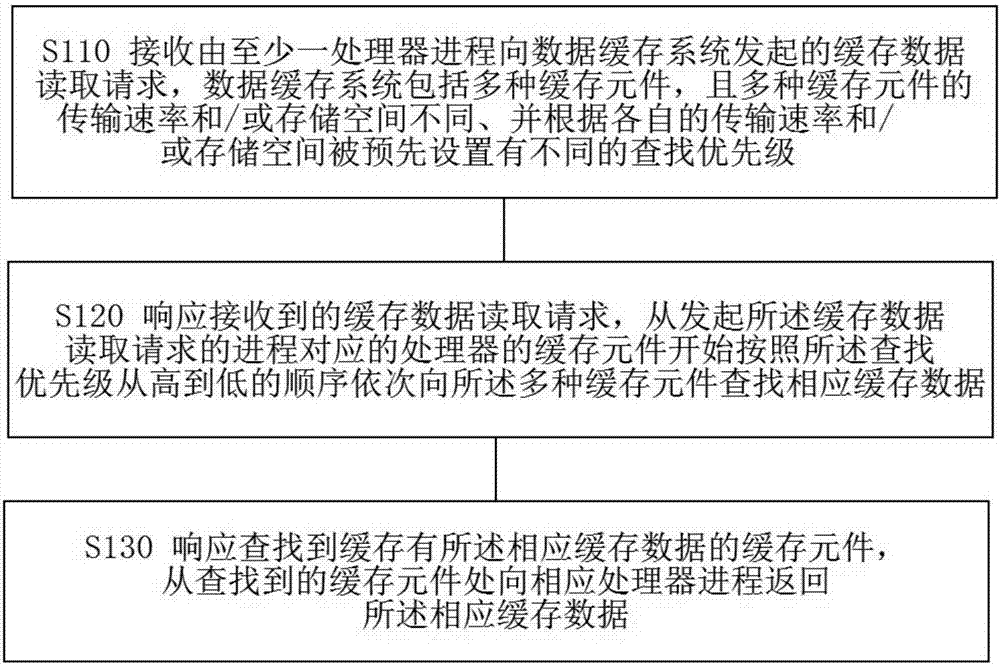
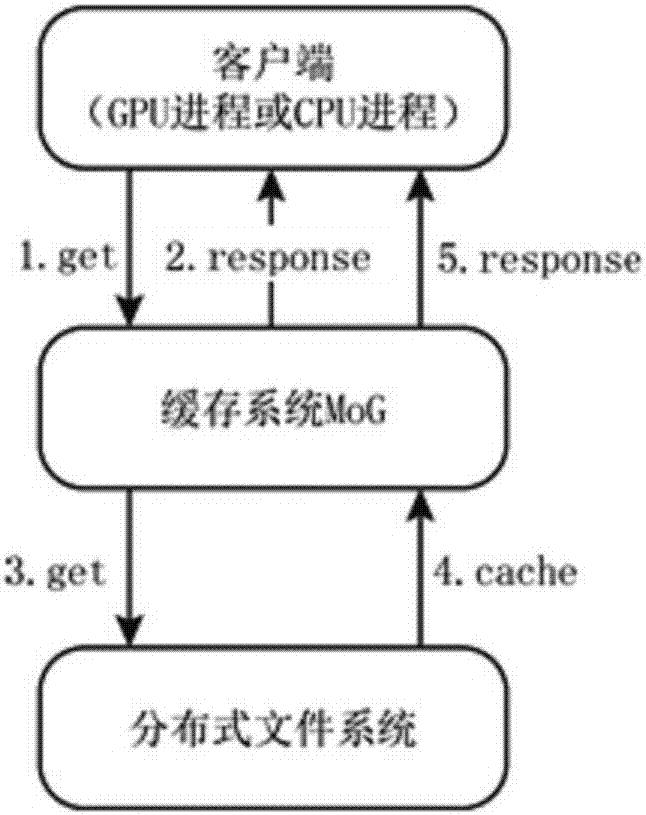
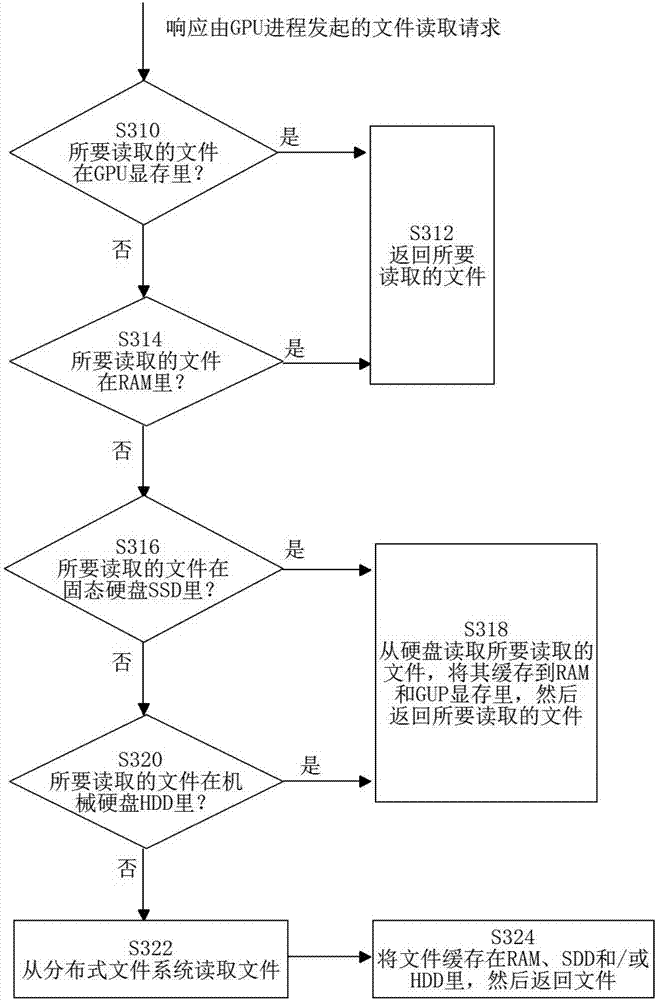
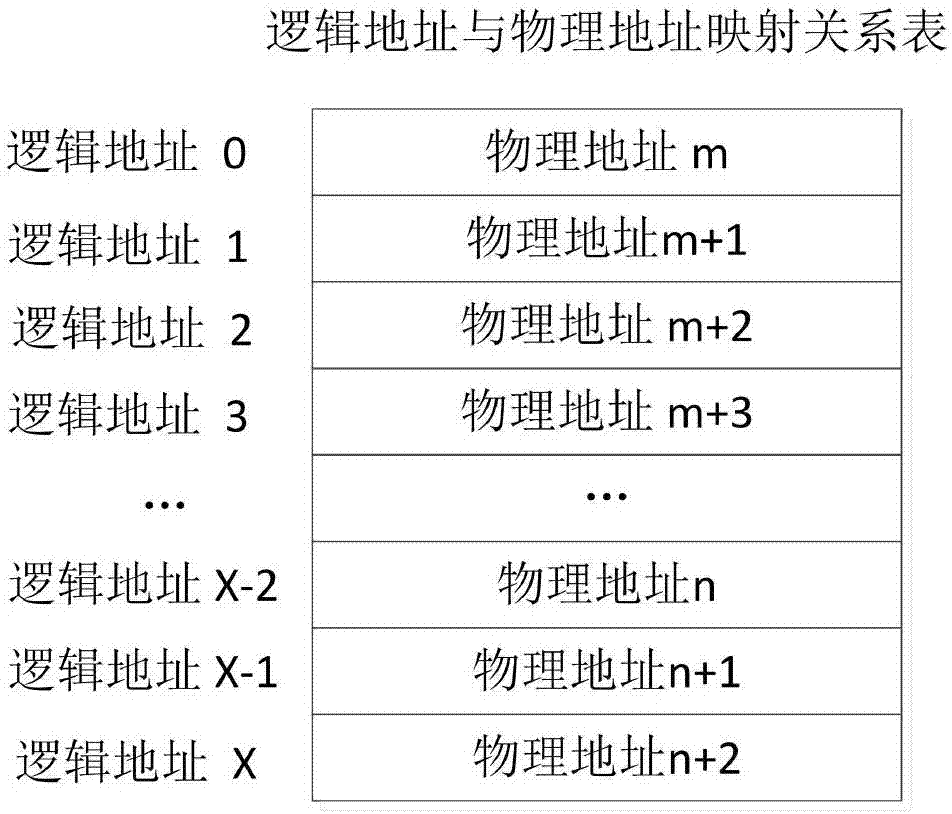
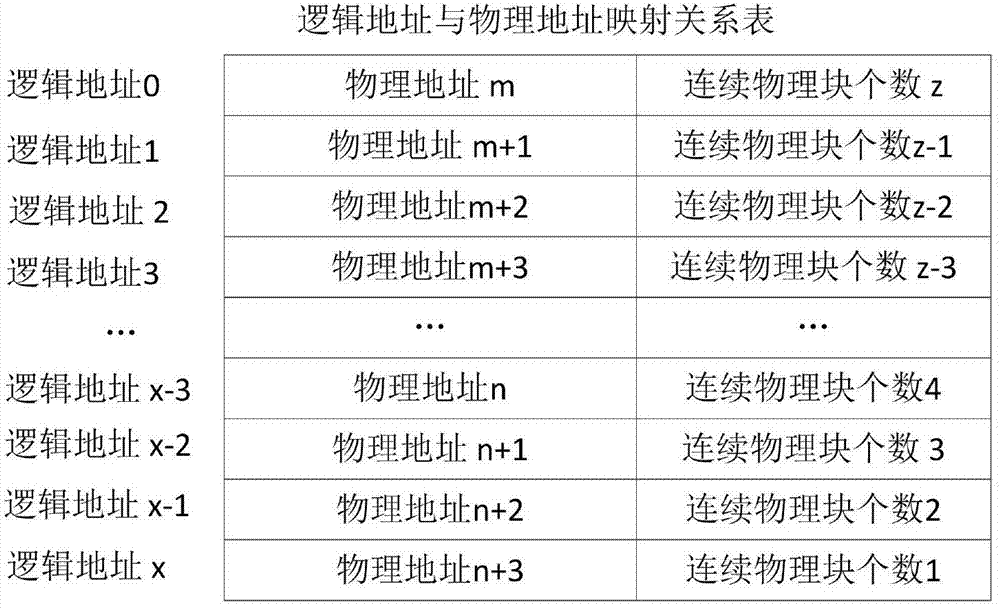
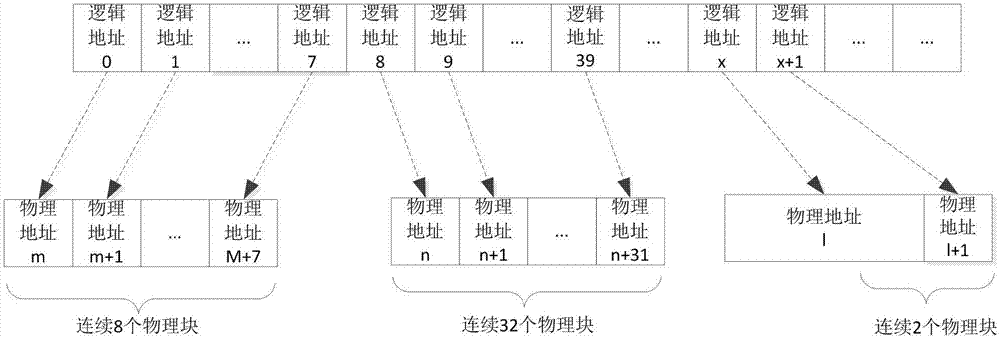
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
43results about "Memory adressing/allocation/relocation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
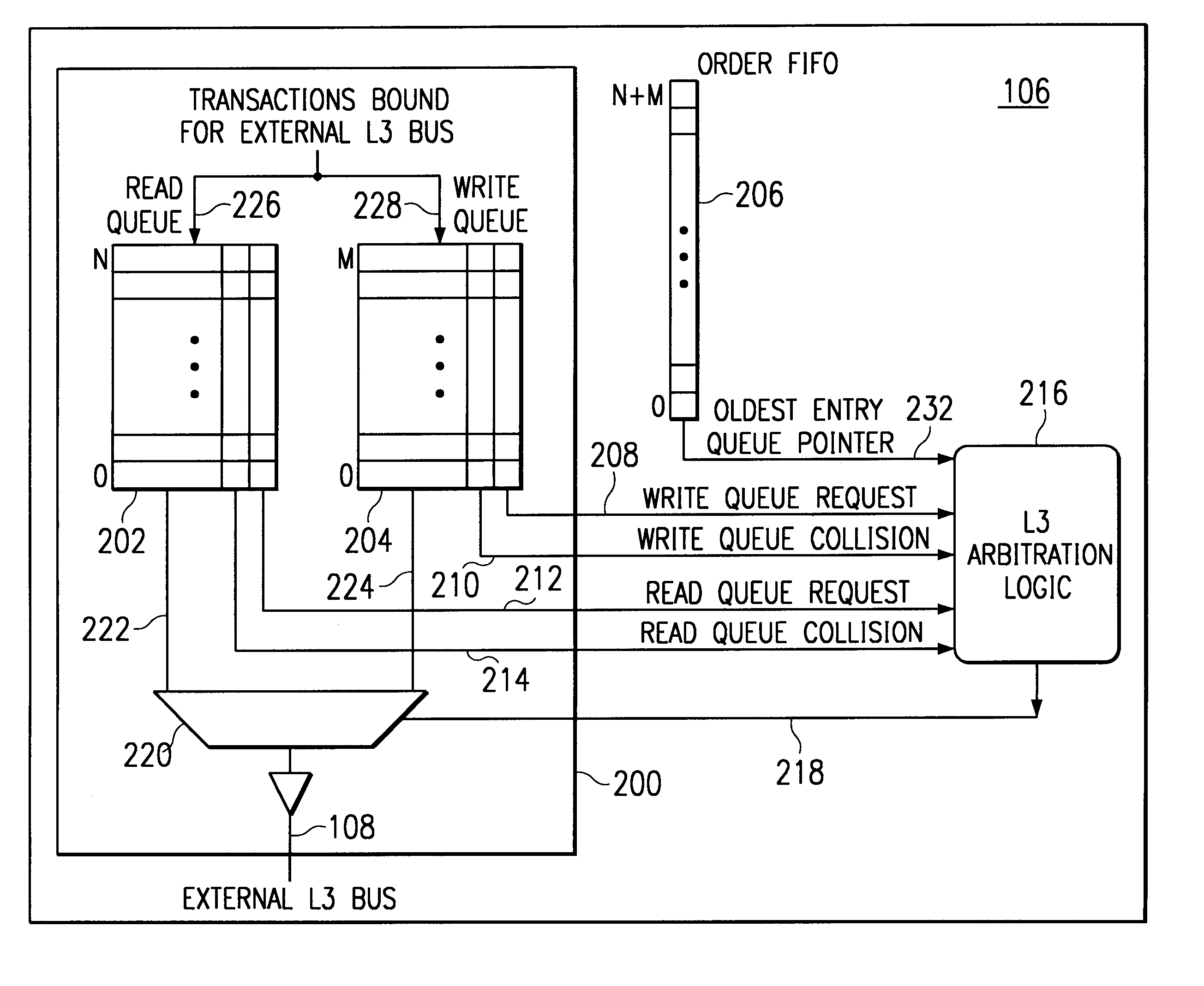
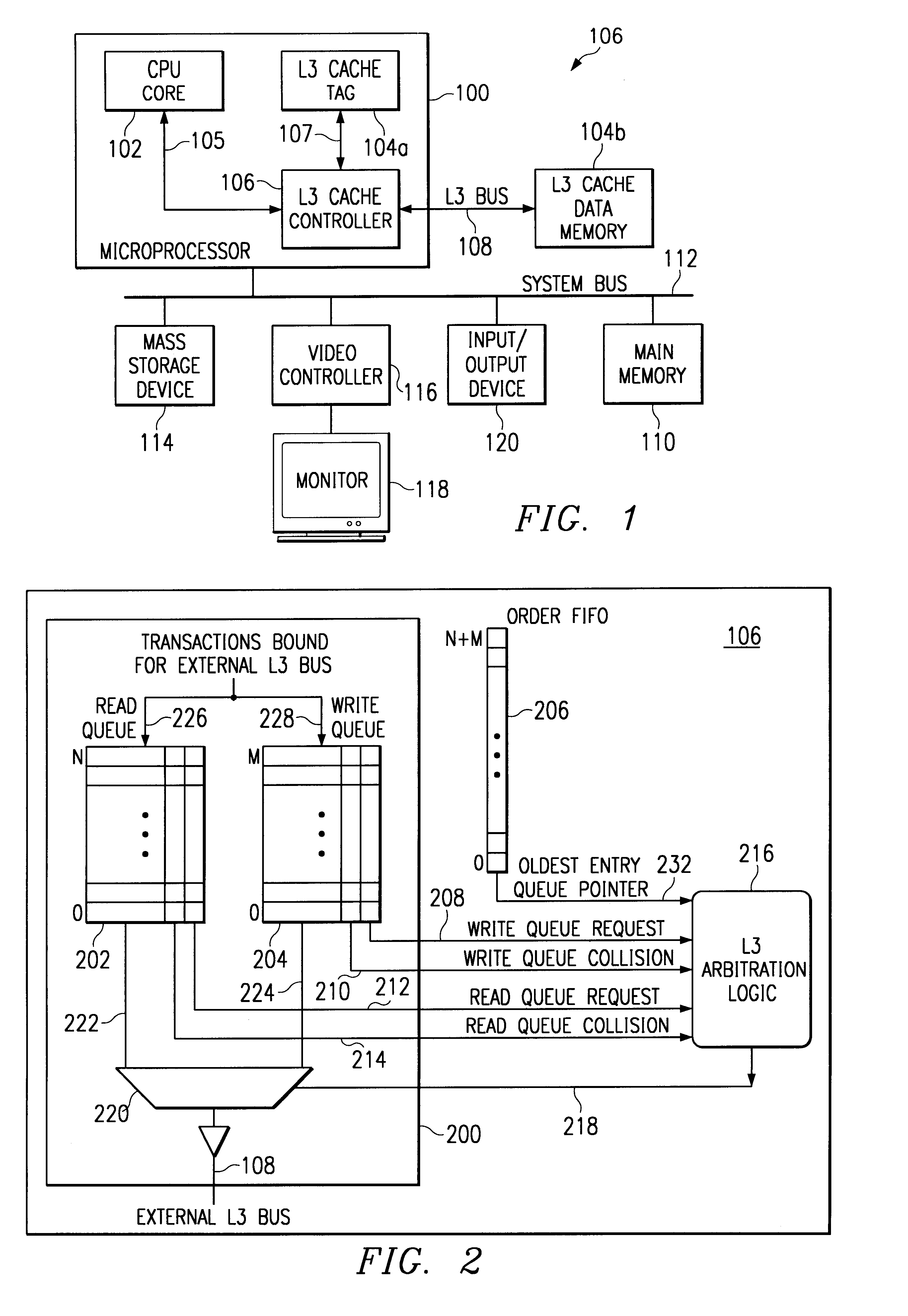
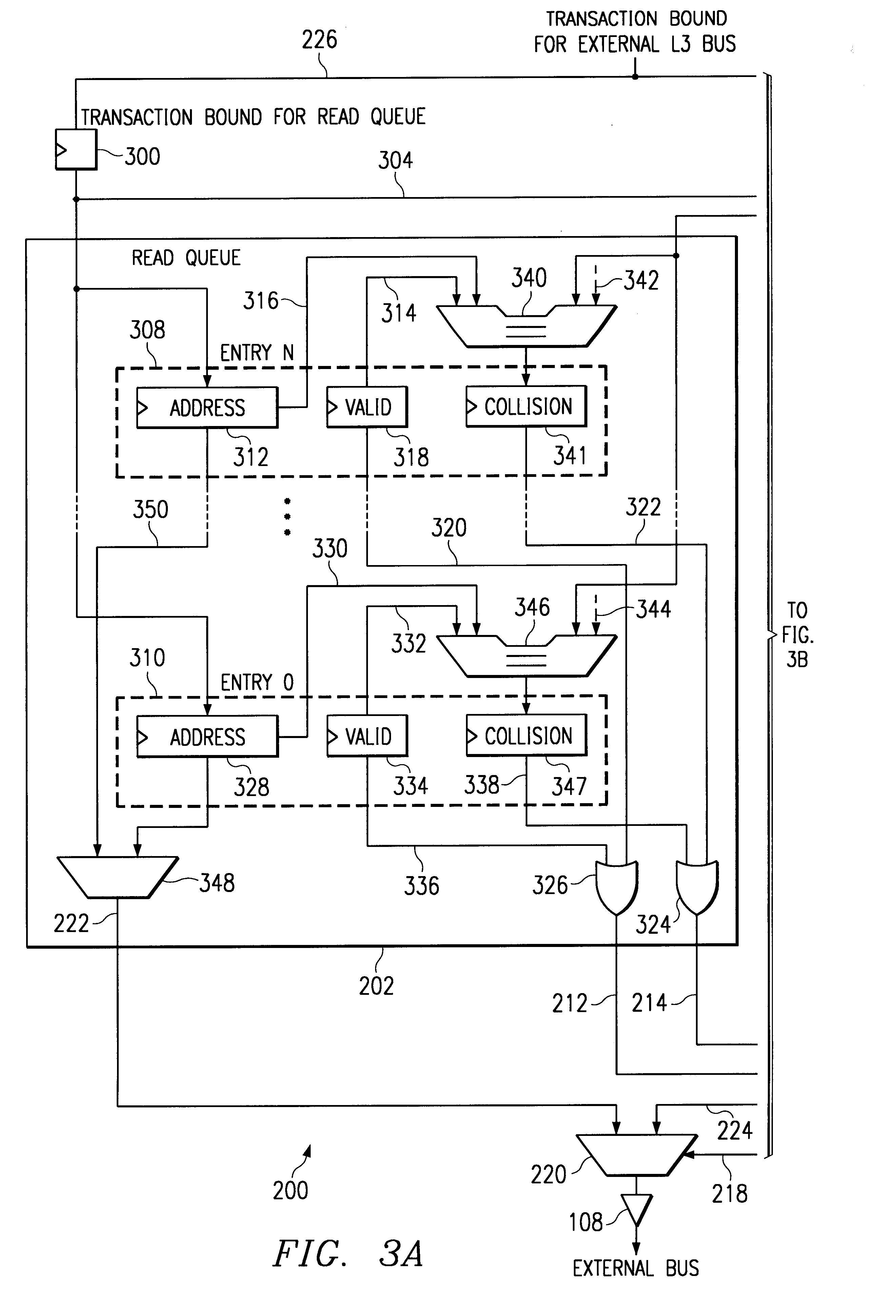
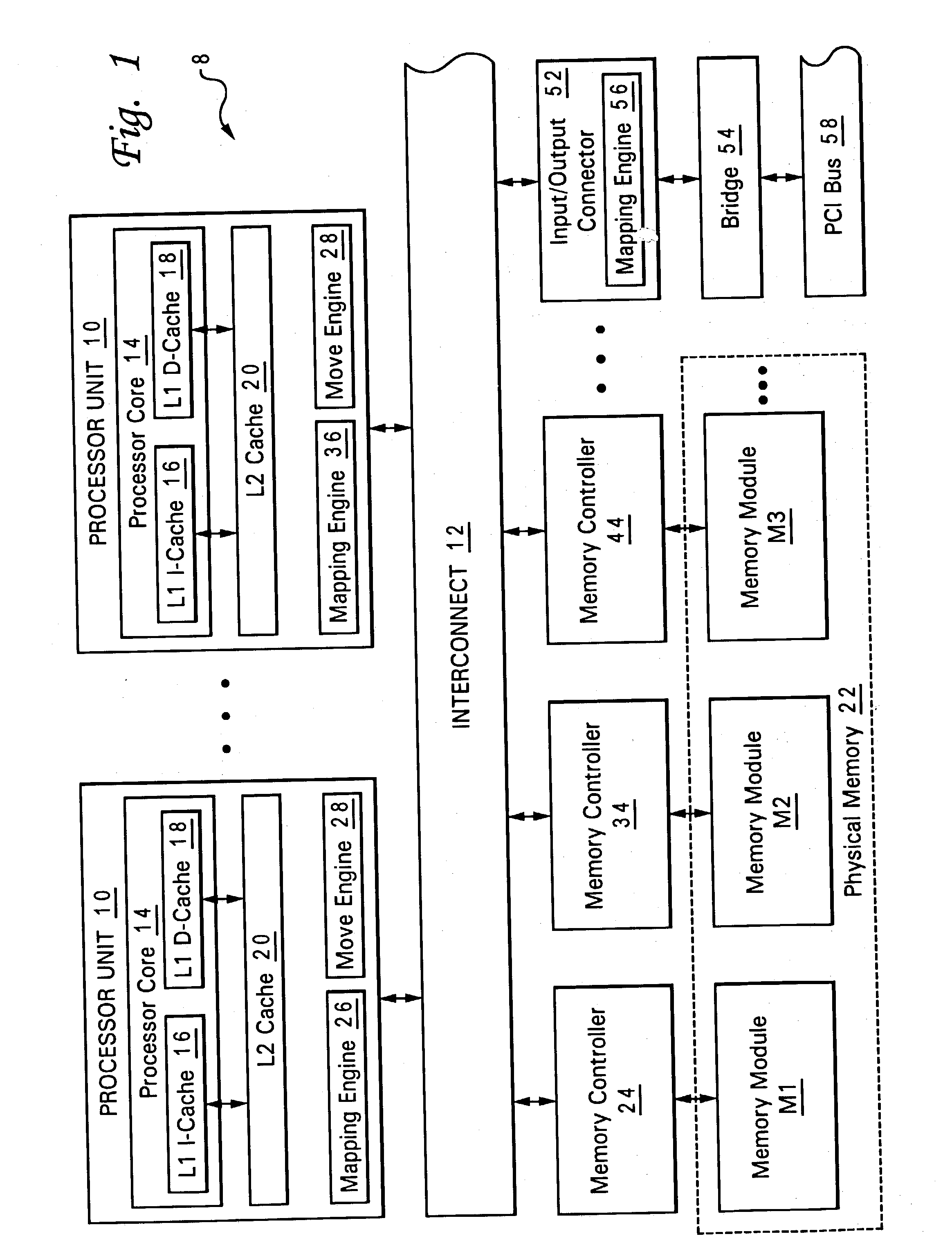
Bus optimization with read/write coherence including ordering responsive to collisions
InactiveUS6256713B1Optimizing bus utilizationMaintaining readFuel lightersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperating systemData coherency
Owner:IBM CORP +1
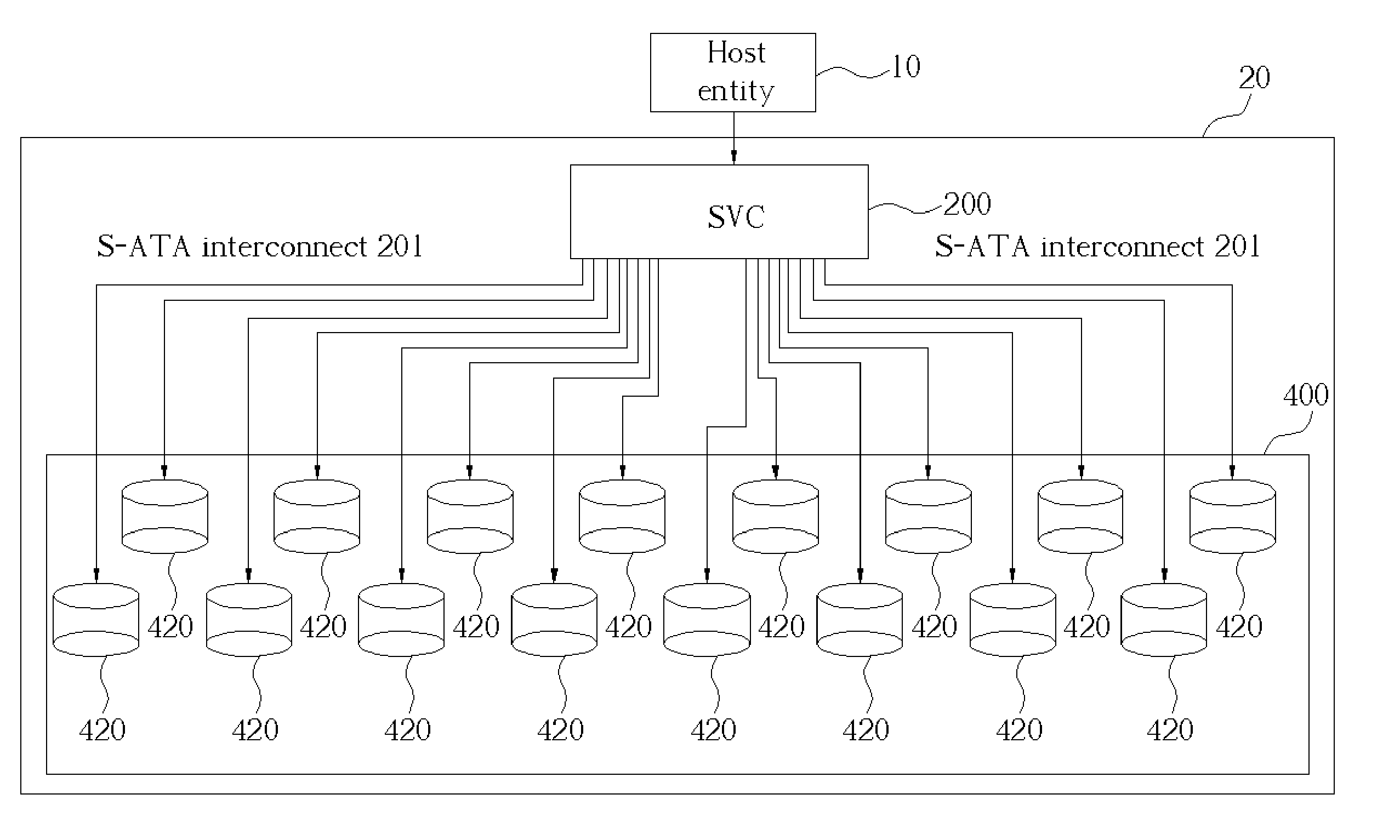
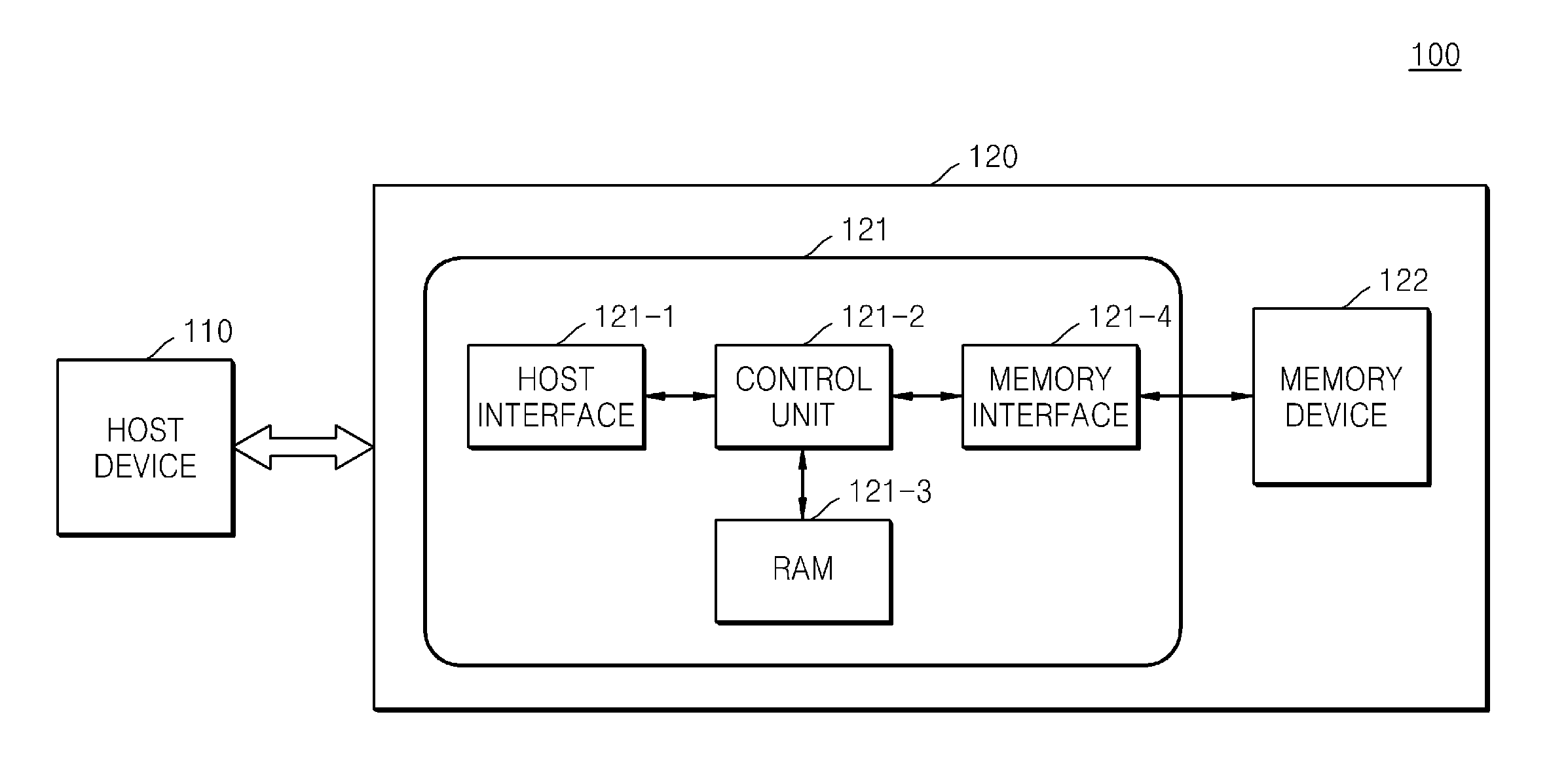
Storage virtualization computer system and external controller therefor
ActiveUS20050005044A1Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSerial ATAHost machine
Owner:INFORTREND TECH INC
Virtual address pager and method for use with a bulk erase memory
ActiveUS20120239871A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionVirtual memoryOperational system
A virtual address pager and method for use with a bulk erase memory is disclosed. The virtual address pager includes a page protection controller configured with a heap manager interface configured to receive only bulk erase memory-backed page requests for a plurality of memory pages. A RAM object cache controller is configured to store and bulk write data for a portion of the bulk erase memory. The page protection controller may have an operating system interface configured to generate a page memory access permission for each of the plurality of memory pages. The page protection controller may be configured to receive a virtual memory allocation request and generate the page memory access permission based on the virtual memory allocation request.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF PRINCETON UNIV
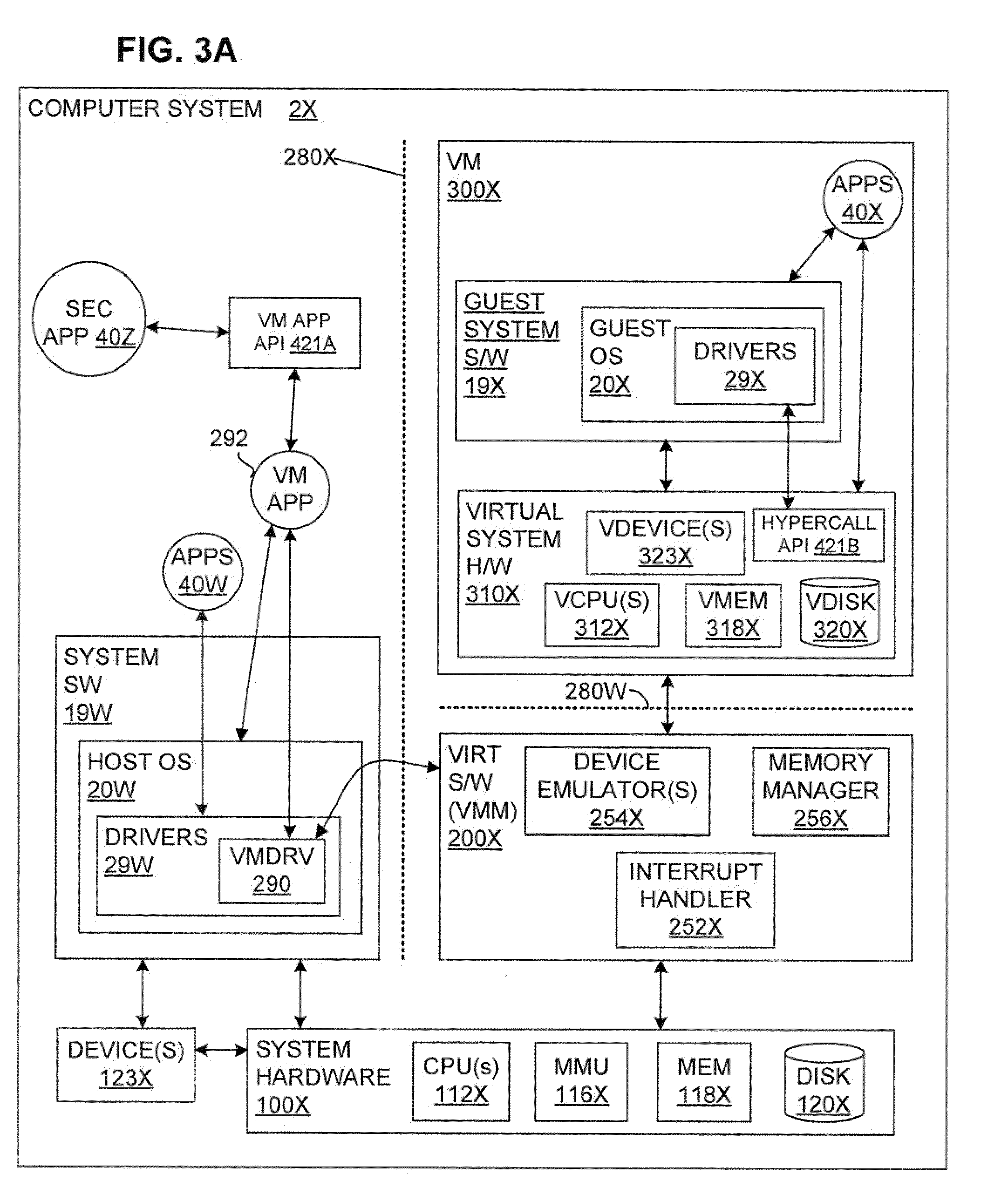
System and method to enhance memory protection for programs in a virtual machine environment
ActiveUS20110078361A1Memory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiprogramming arrangementsVirtualizationOperational system
Owner:VMWARE INC
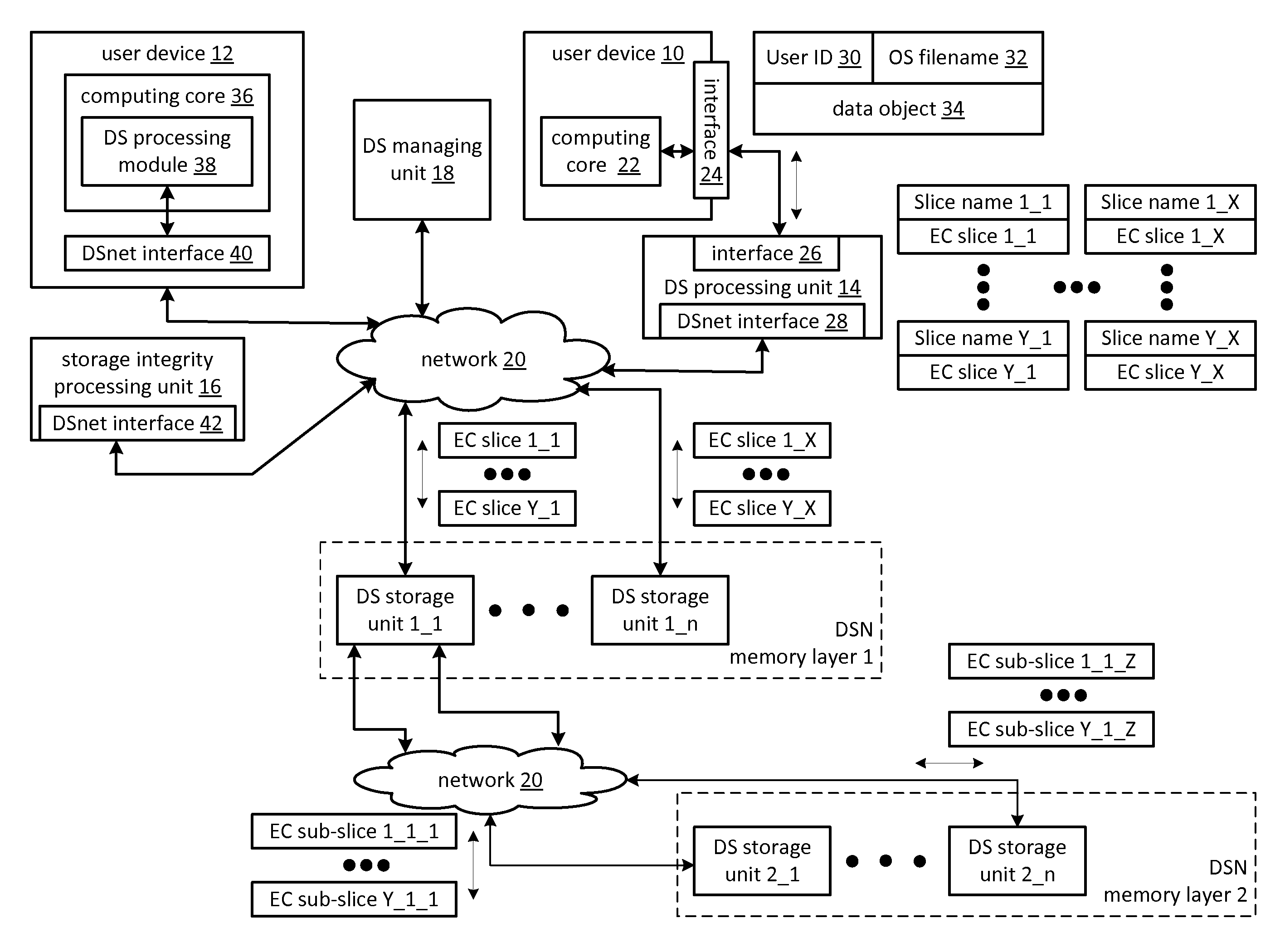
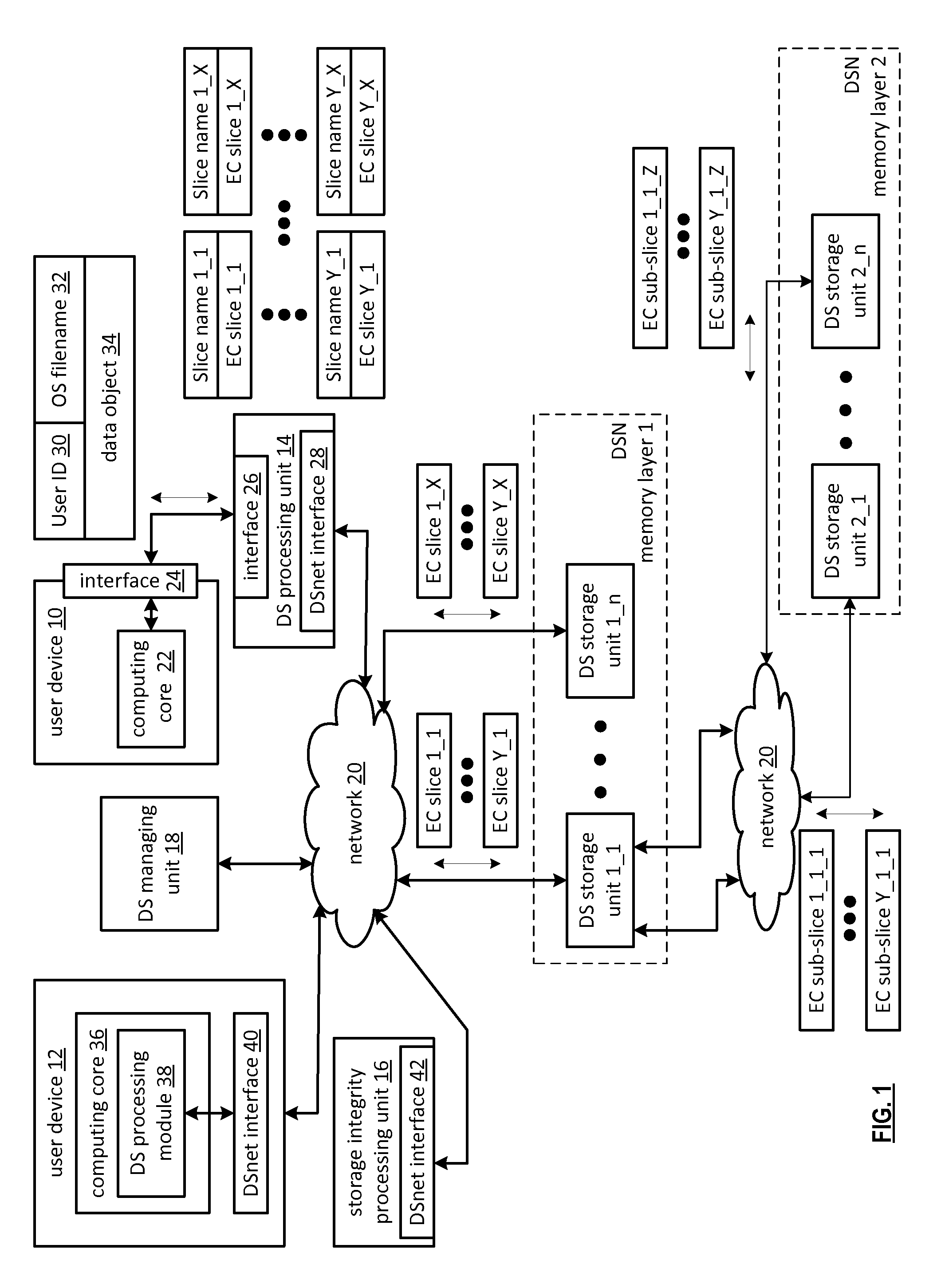
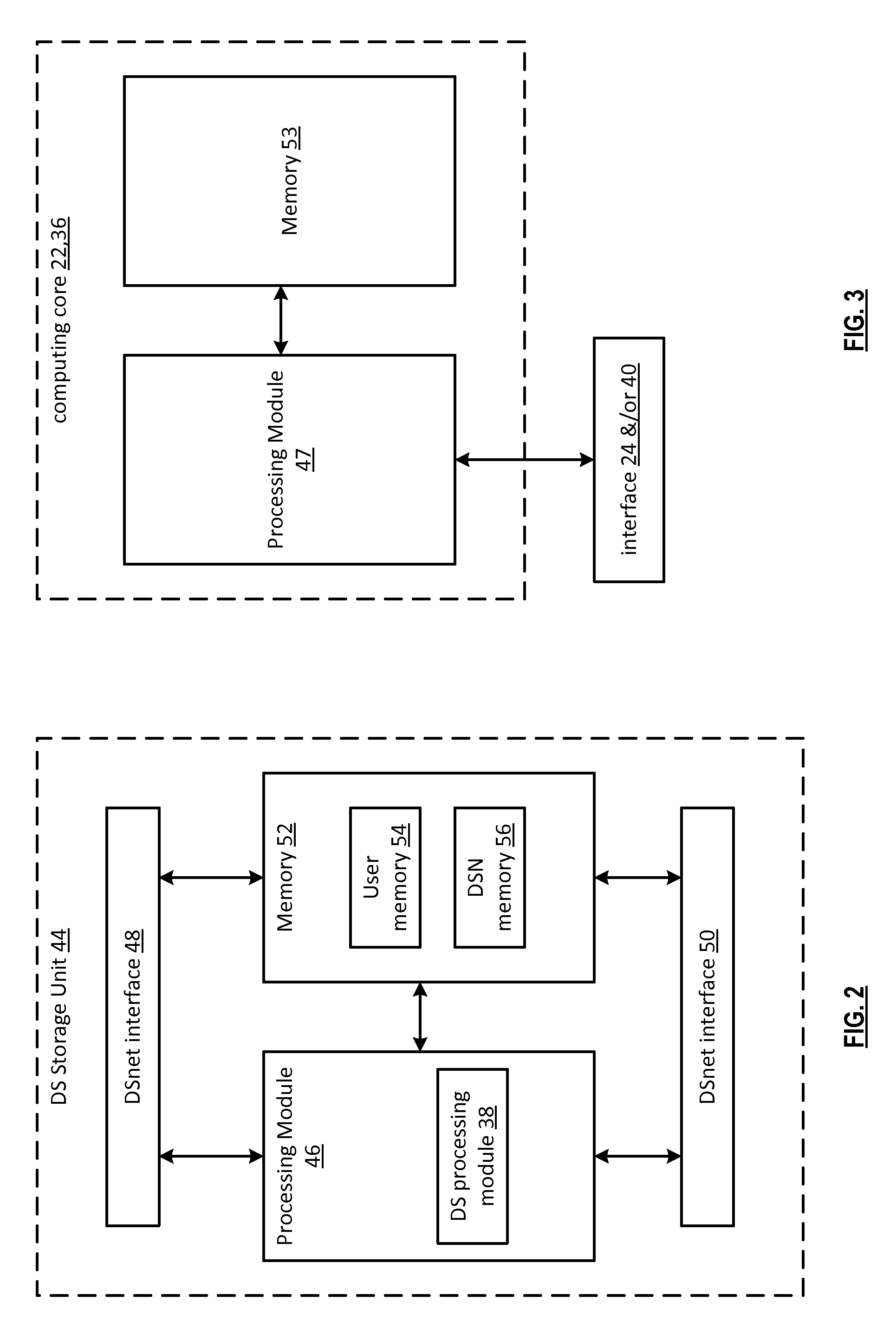
Securing data in a dispersed storage network using shared secret slices
InactiveUS20100268877A1Digital data information retrievalMemory adressing/allocation/relocationStorage cellShared secret
Owner:PURE STORAGE
System and method for managing compression and decompression and decompression of system memory in a computer system
InactiveUS7047382B2Easy to useReduce data bandwidthMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationManagement unitParallel computing
Owner:MOSSMAN HLDG
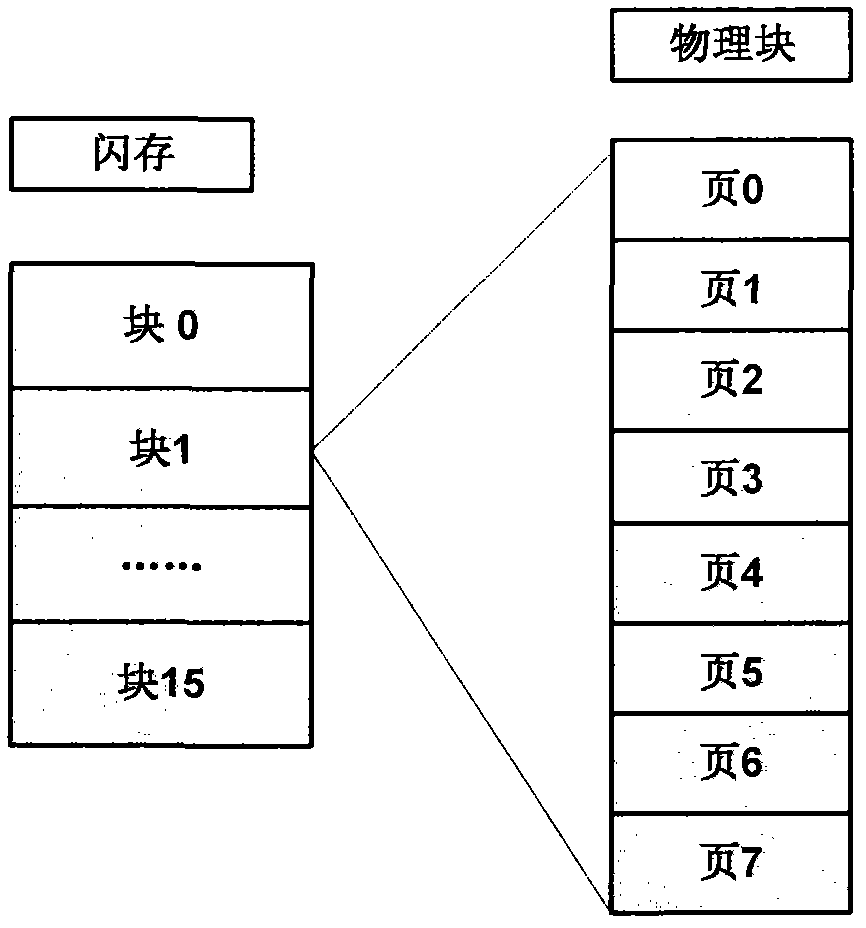
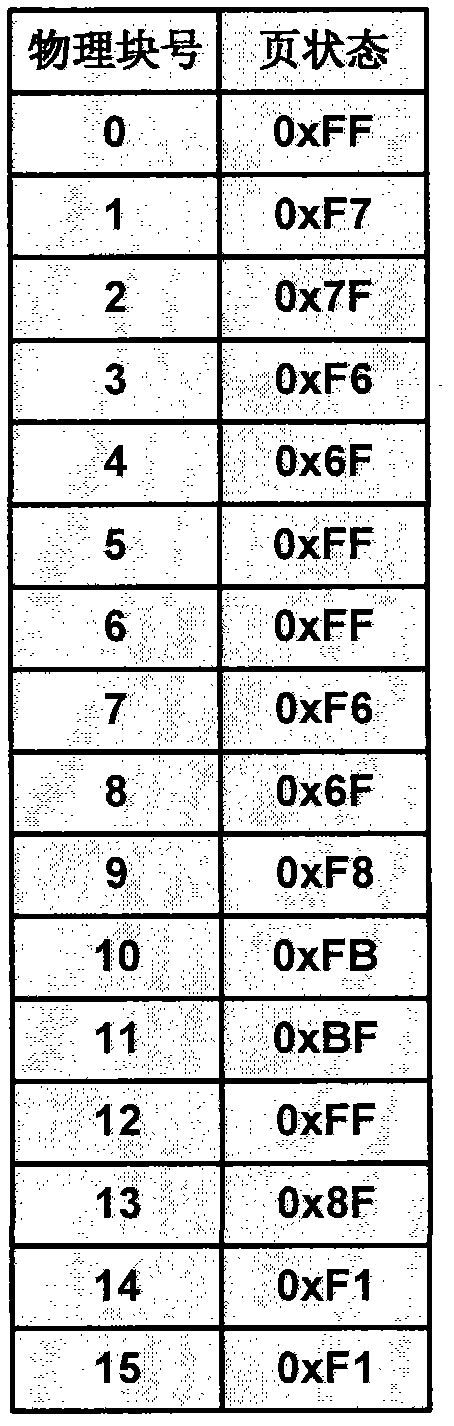
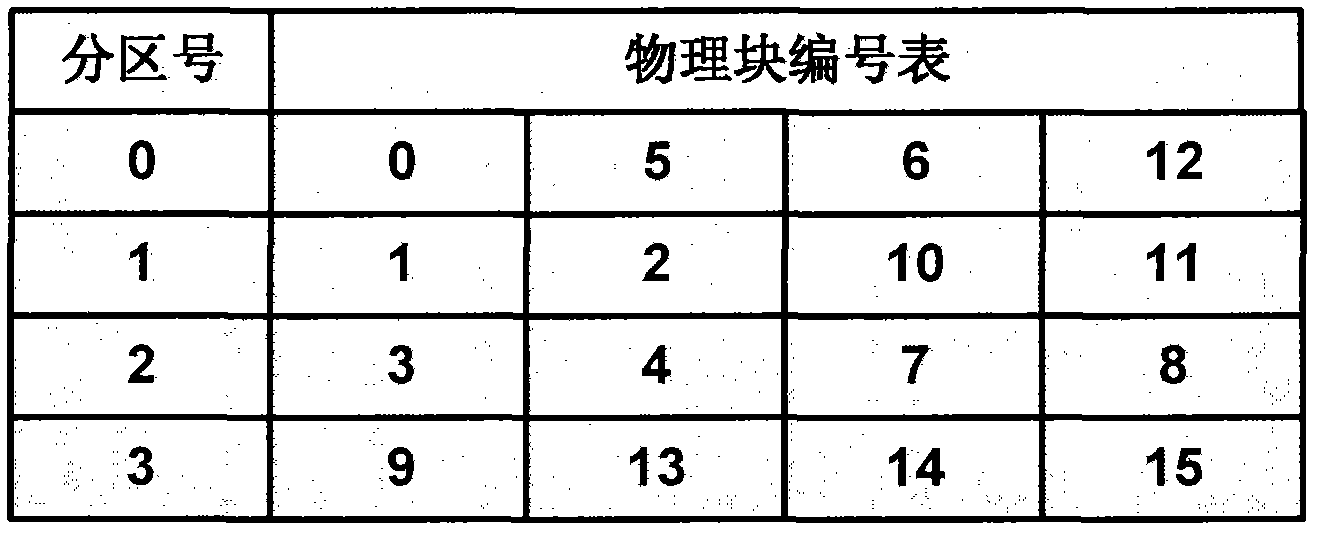
Flash memory management method and flash memory device
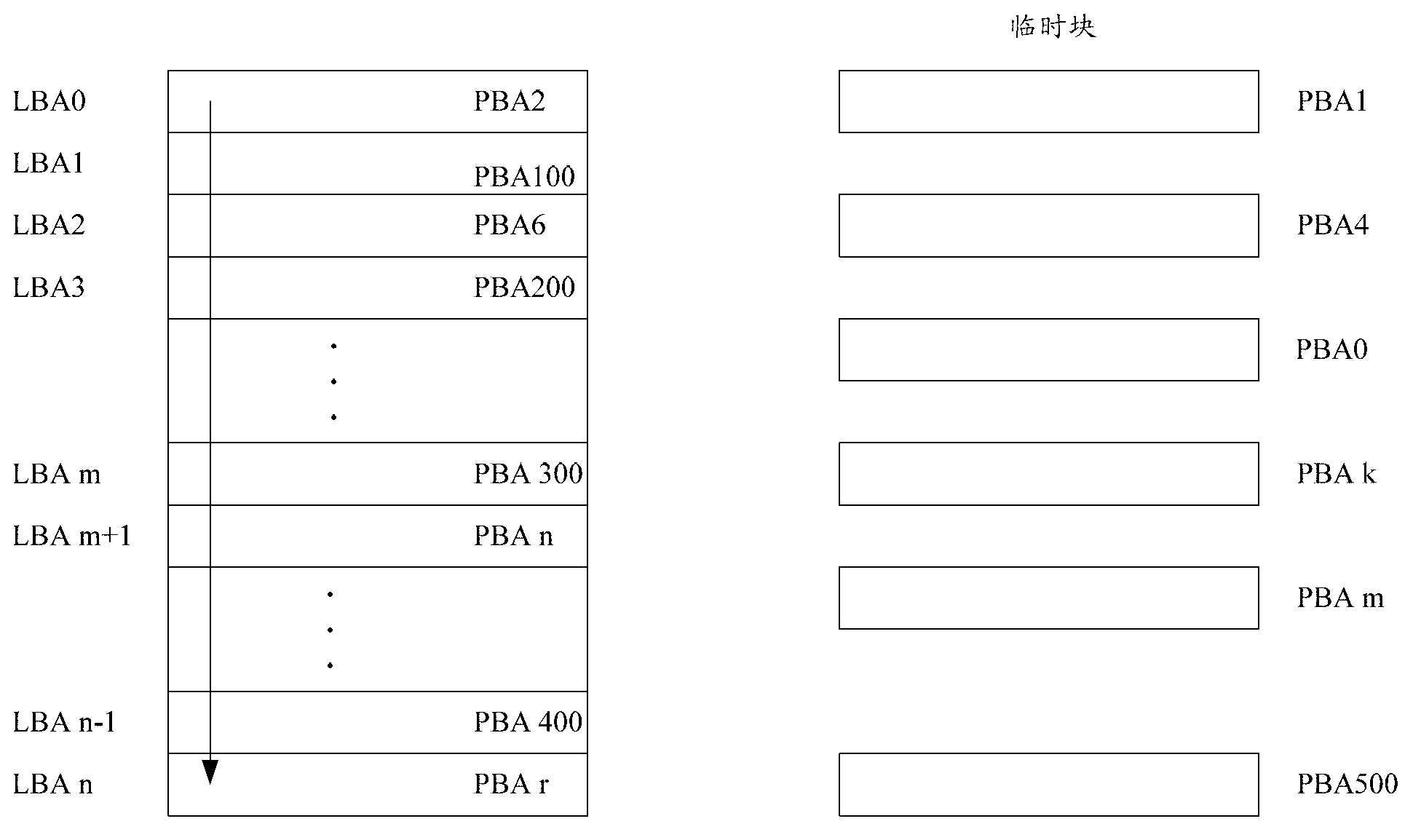
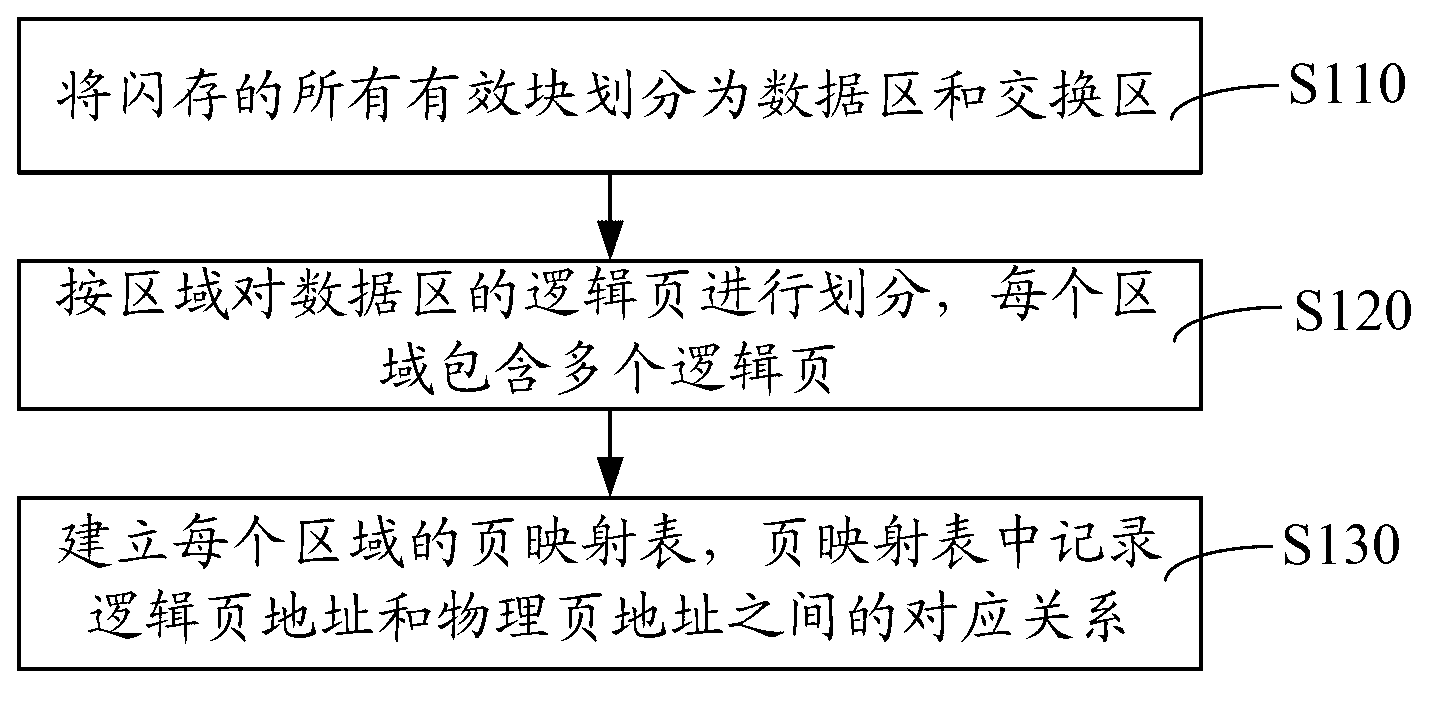
ActiveCN102841851AIncrease write speedIncrease profitMemory adressing/allocation/relocationLogical addressCopy move
The invention relates to a flash memory management method and a flash memory device. The flash memory management method comprises following steps of dividing all active blocks of a flash memory into a data area and a switching area; dividing a logical page of the data area according to the area, wherein each area comprises a plurality of logical pages; and establishing a page mapping table of each area, and recording a correspondence relation of a logical page address and a physical page address in the page mapping table. According to the flash memory management method and the flash memory device, the data area of the flash memory is divided into different areas, the page mapping table of each area is established, the correspondence relation of the logical page address and the physical page address is recorded in the page mapping table, the flash memory is managed by adopting the page as a unit, when data is written in the flash memory, the data can be written into the flash memory according to the page sequence, after multiple pages of one block are fulfilled, the data is written into a next empty block, the utilization rate of the block is improved, the copy moving operation and erasing operation of the data can be reduced, the writing-in speed of the flash memory is improved, and the occupation of an internal memory can be reduced by establishing the page mapping table according to the areas.
Owner:SHENZHEN NETCOM ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Thread-specific branch prediction by logically splitting branch history tables and predicted target address cache in a simultaneous multithreading processing environment
InactiveUS7120784B2Promote resultsAccelerates branch predictionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiprogramming arrangementsArray data structureParallel computing
Owner:IBM CORP
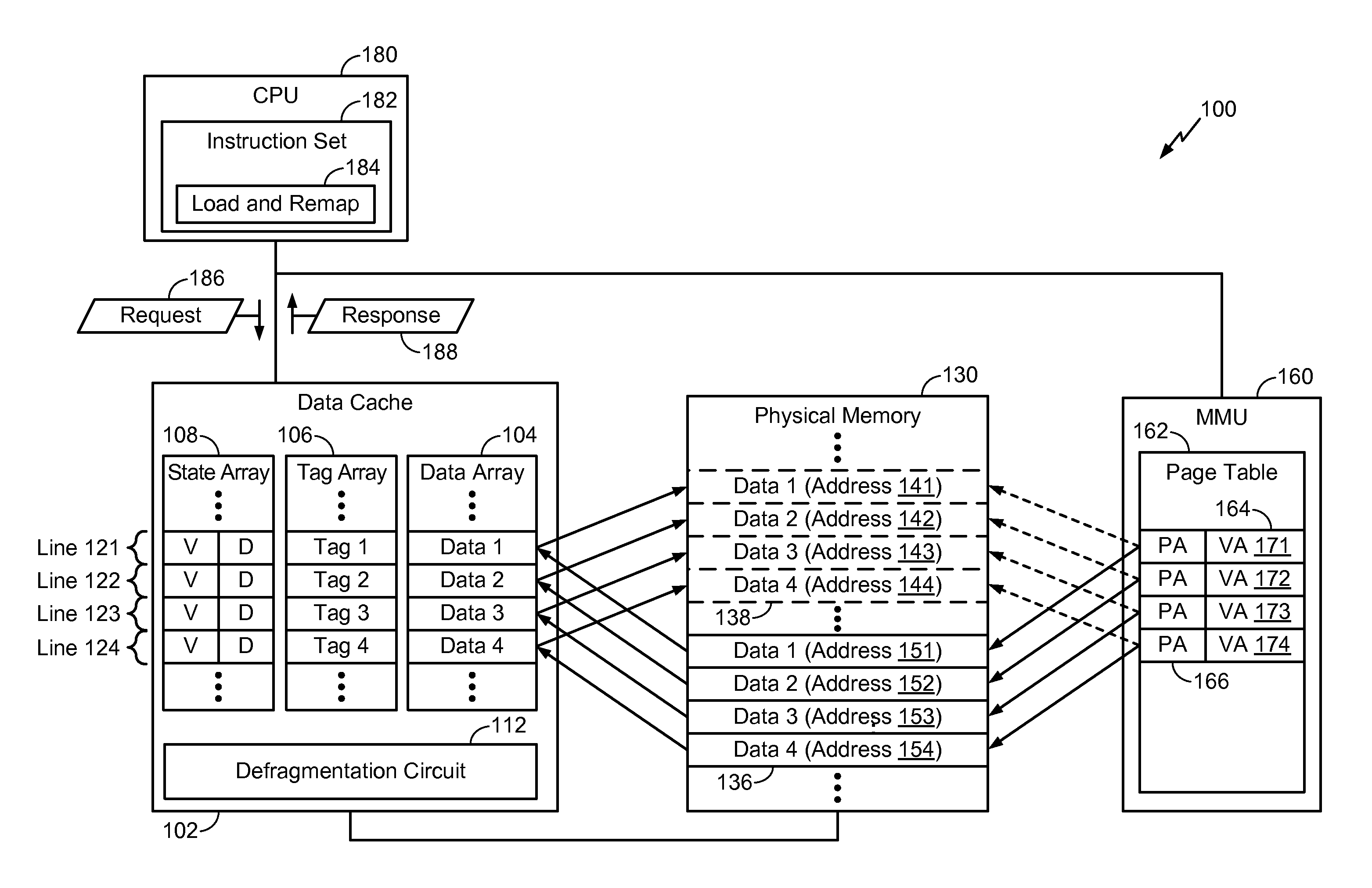
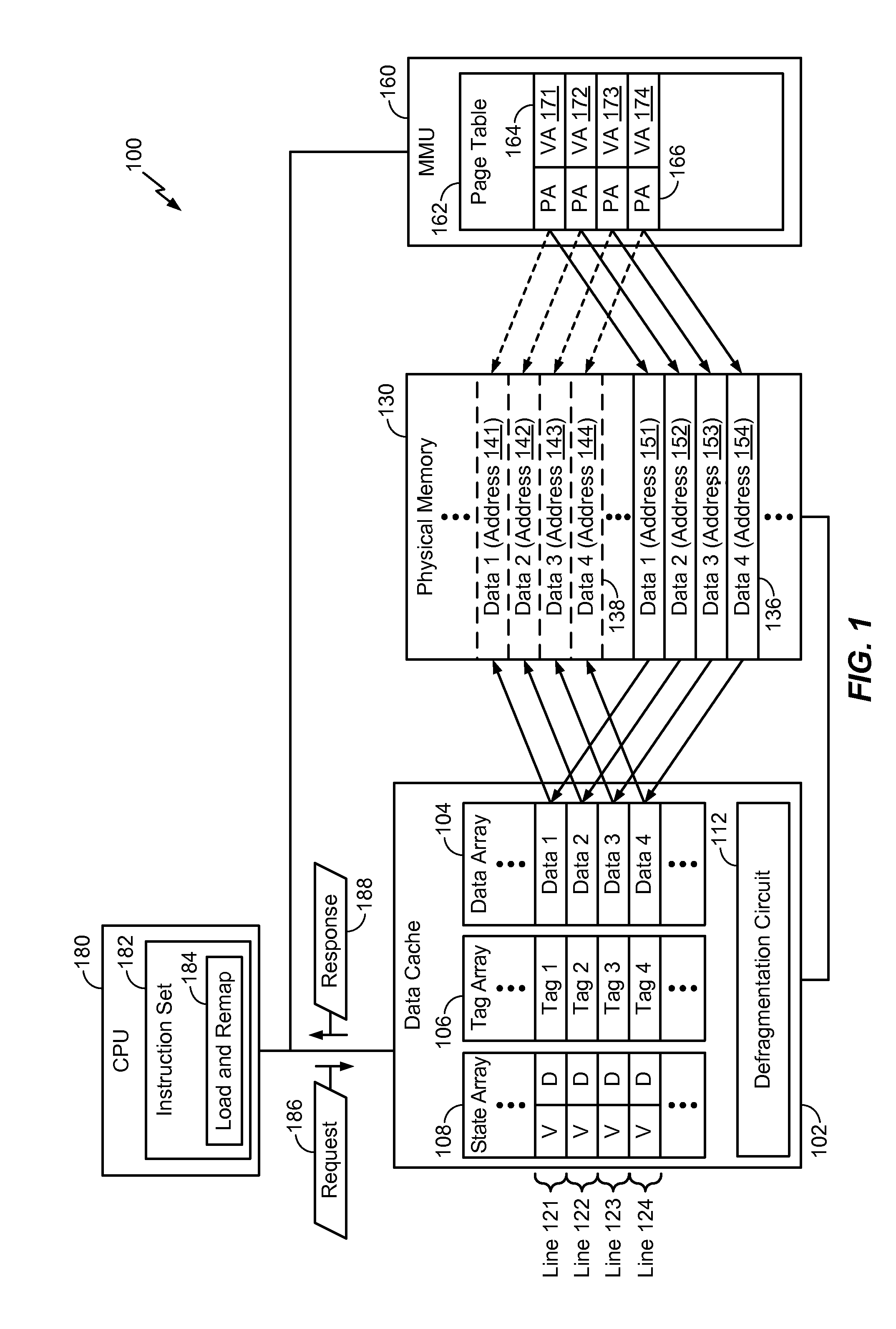
System and method to defragment a memory
ActiveUS20150186279A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMemory addressVirtual memory
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
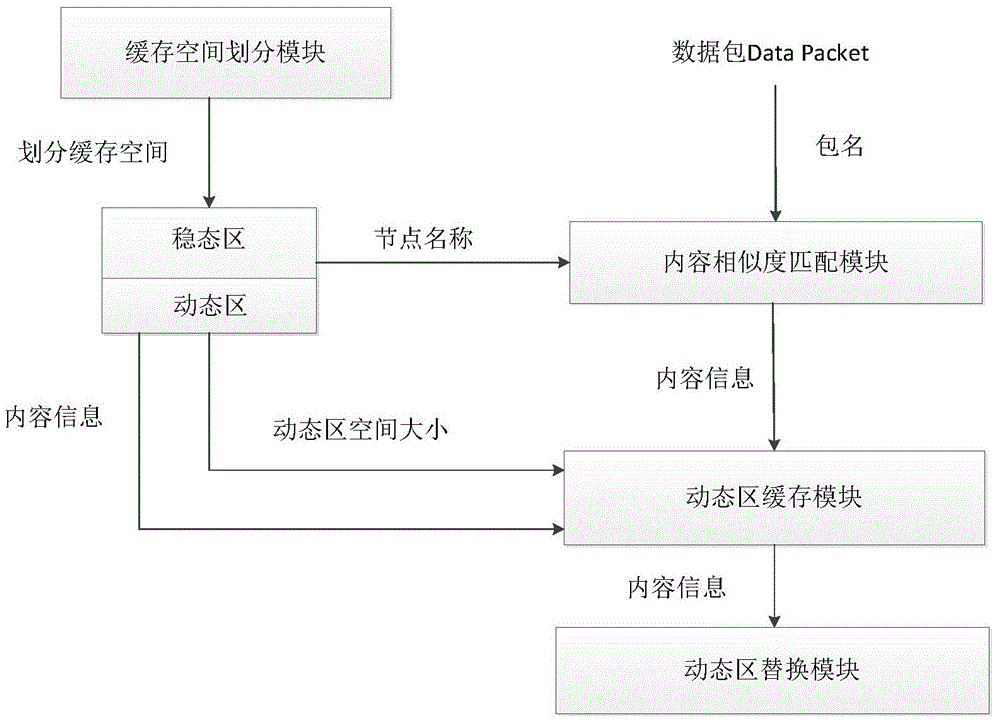
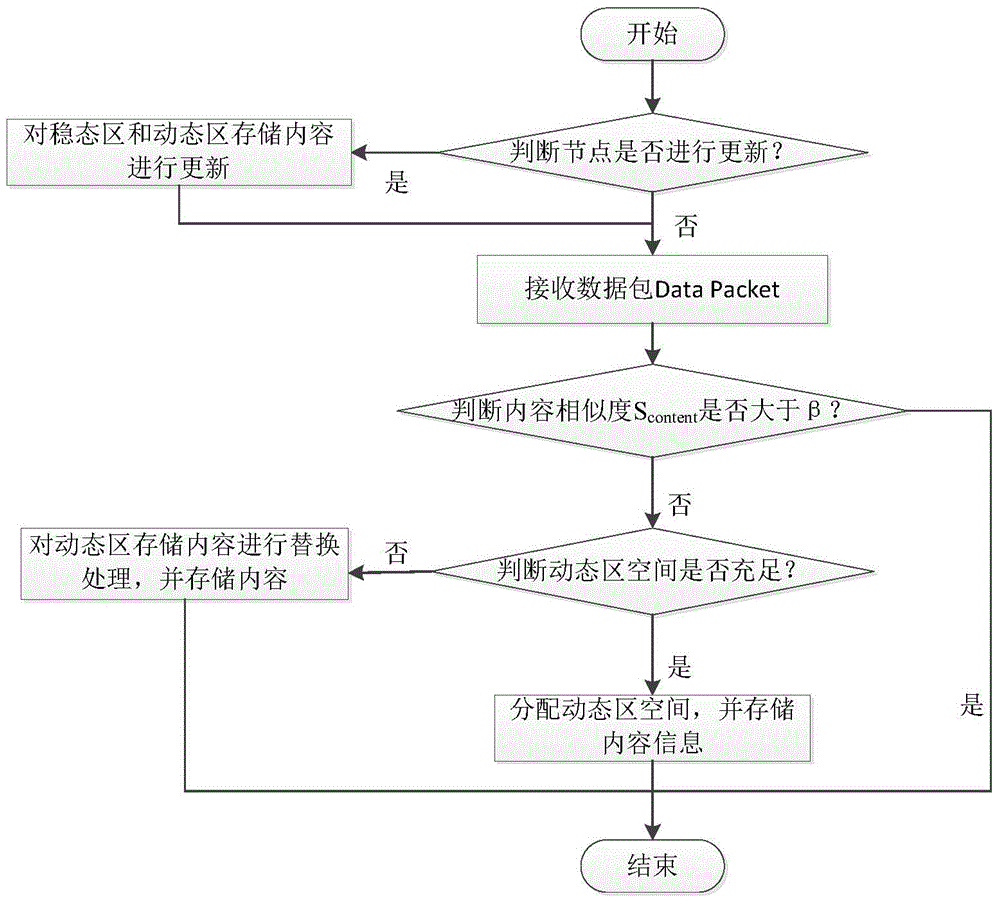
Named data network cache management system based on cache space division and content similarity and management method
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
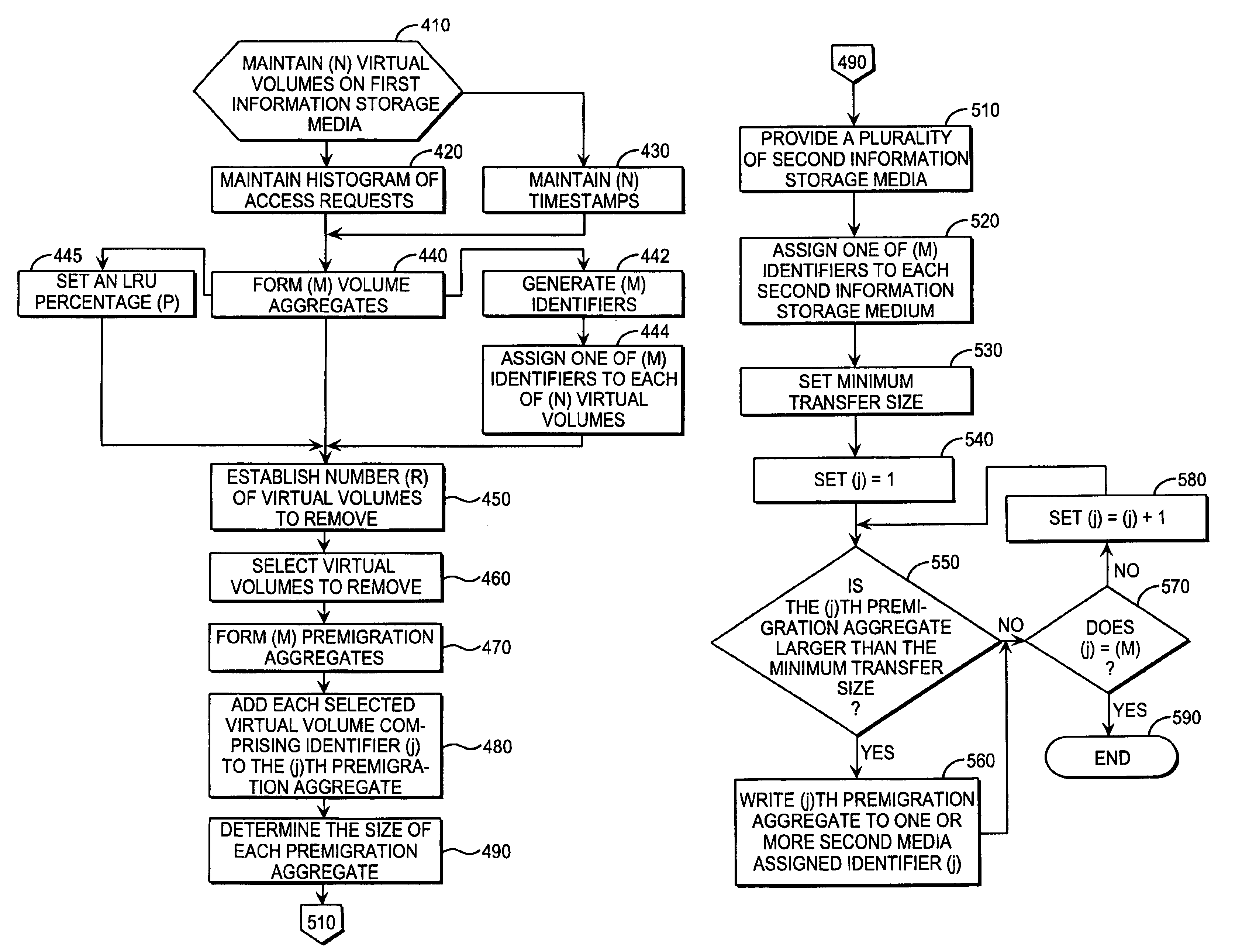
Apparatus and method to form one or more premigration aggregates comprising a plurality of least recently accessed virtual volumes
InactiveUS6938120B2Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationInformation storageComputer science
Owner:IBM CORP
System comprising storage device and related methods of operation
InactiveUS20130103893A1Improve system performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationOperating systemMemory systems
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
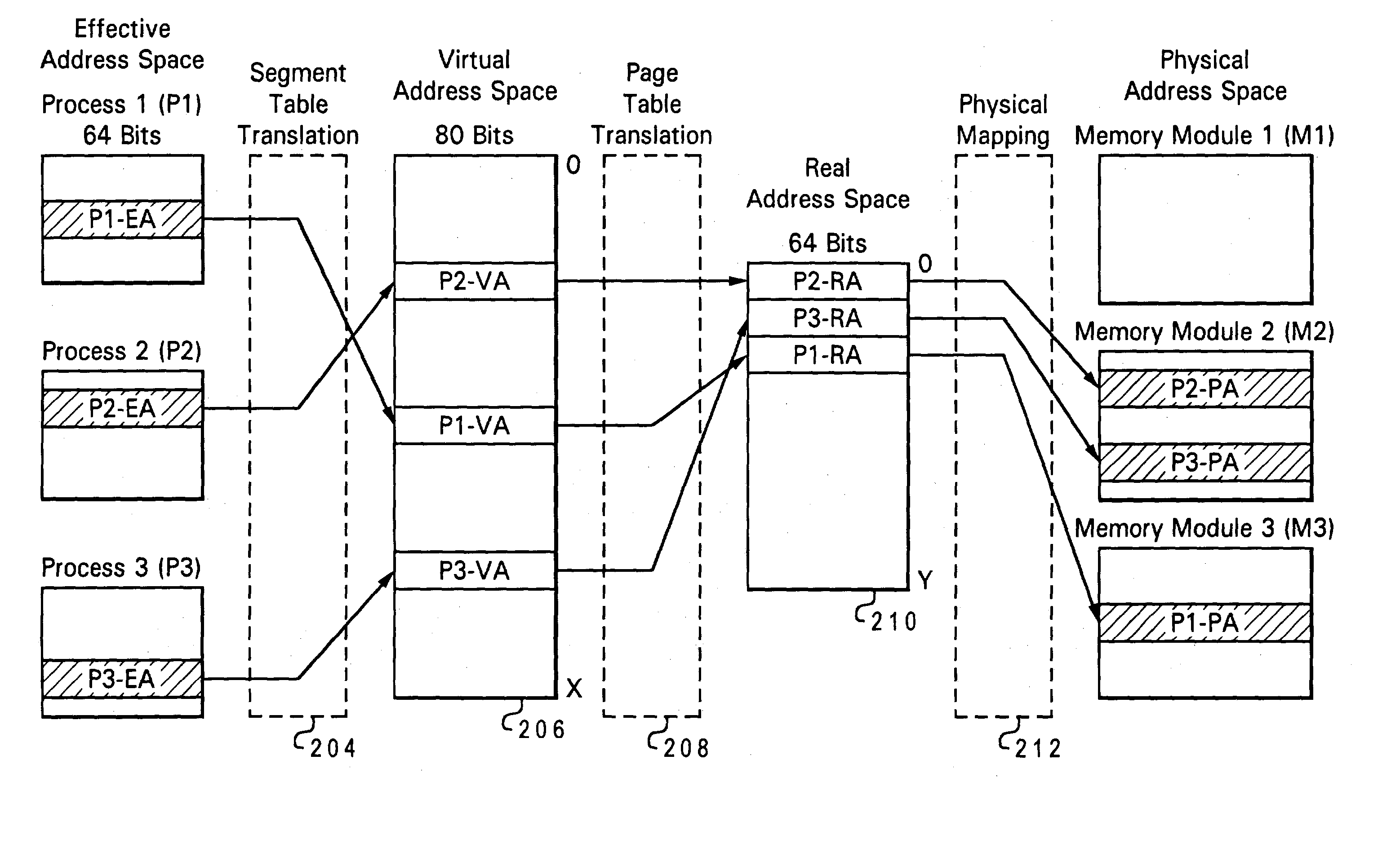
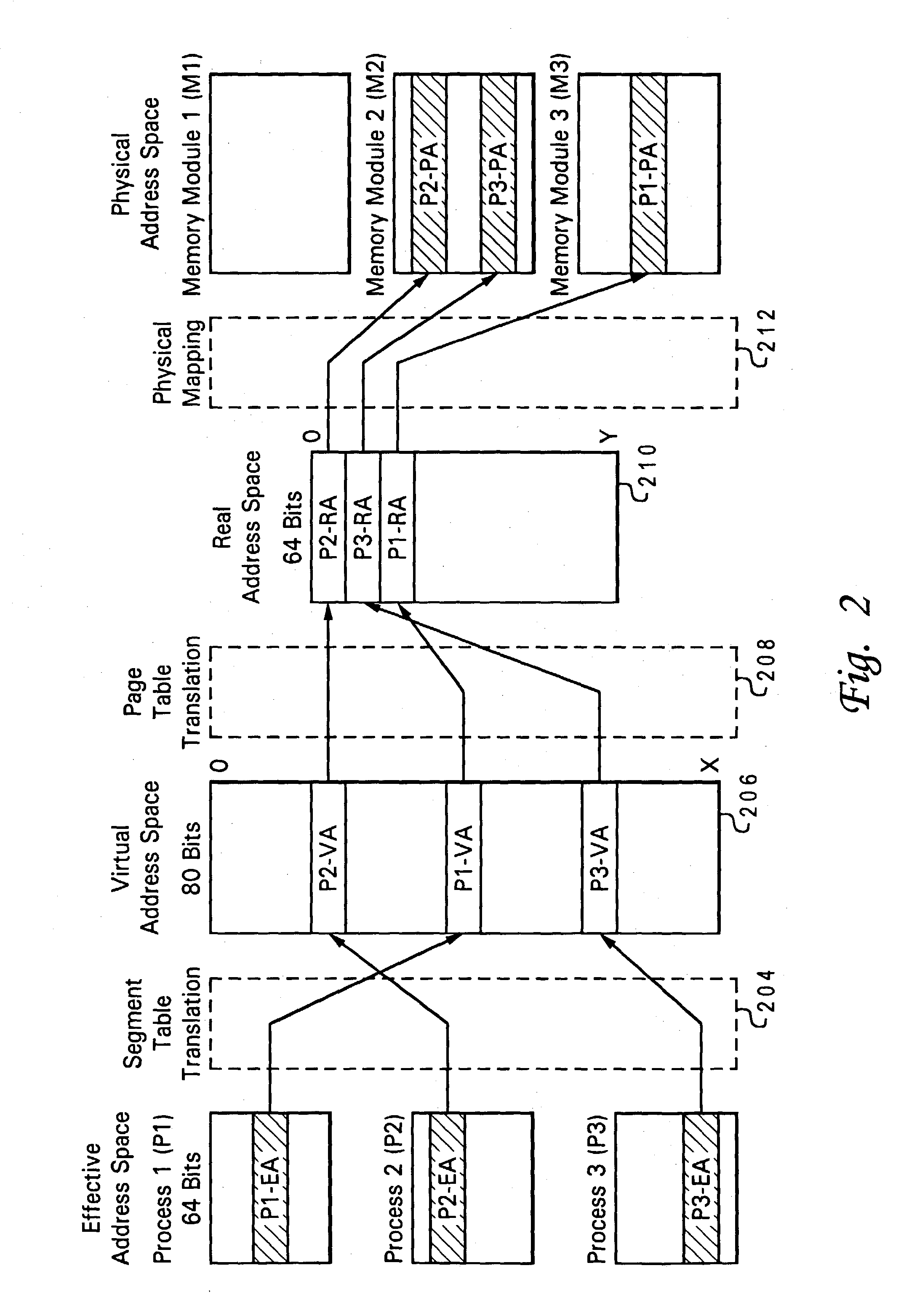
Method and system of managing virtualized physical memory in a multi-processor system
ActiveUS20040073743A1Input/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationVirtualizationAddress space
Owner:IBM CORP
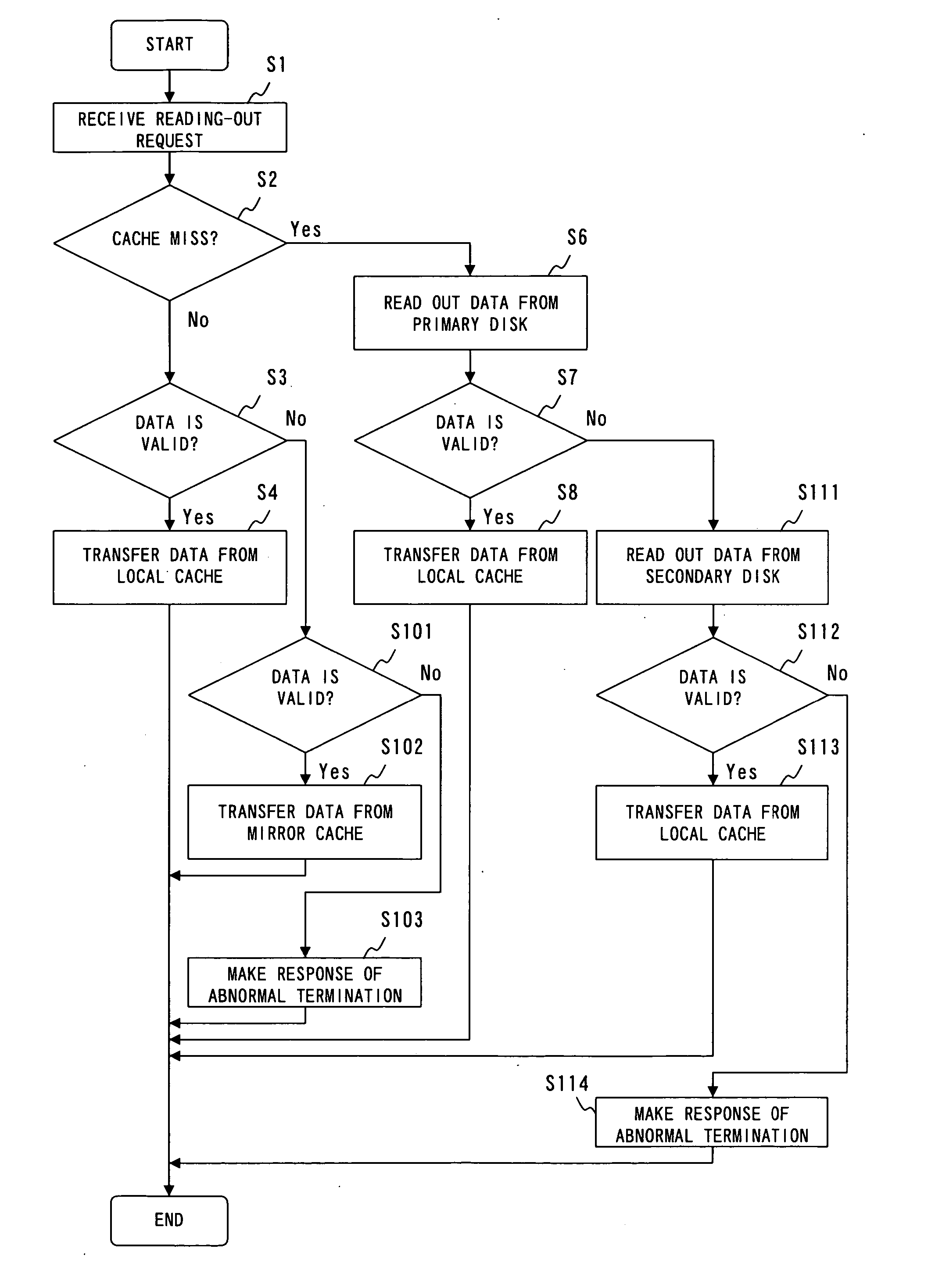
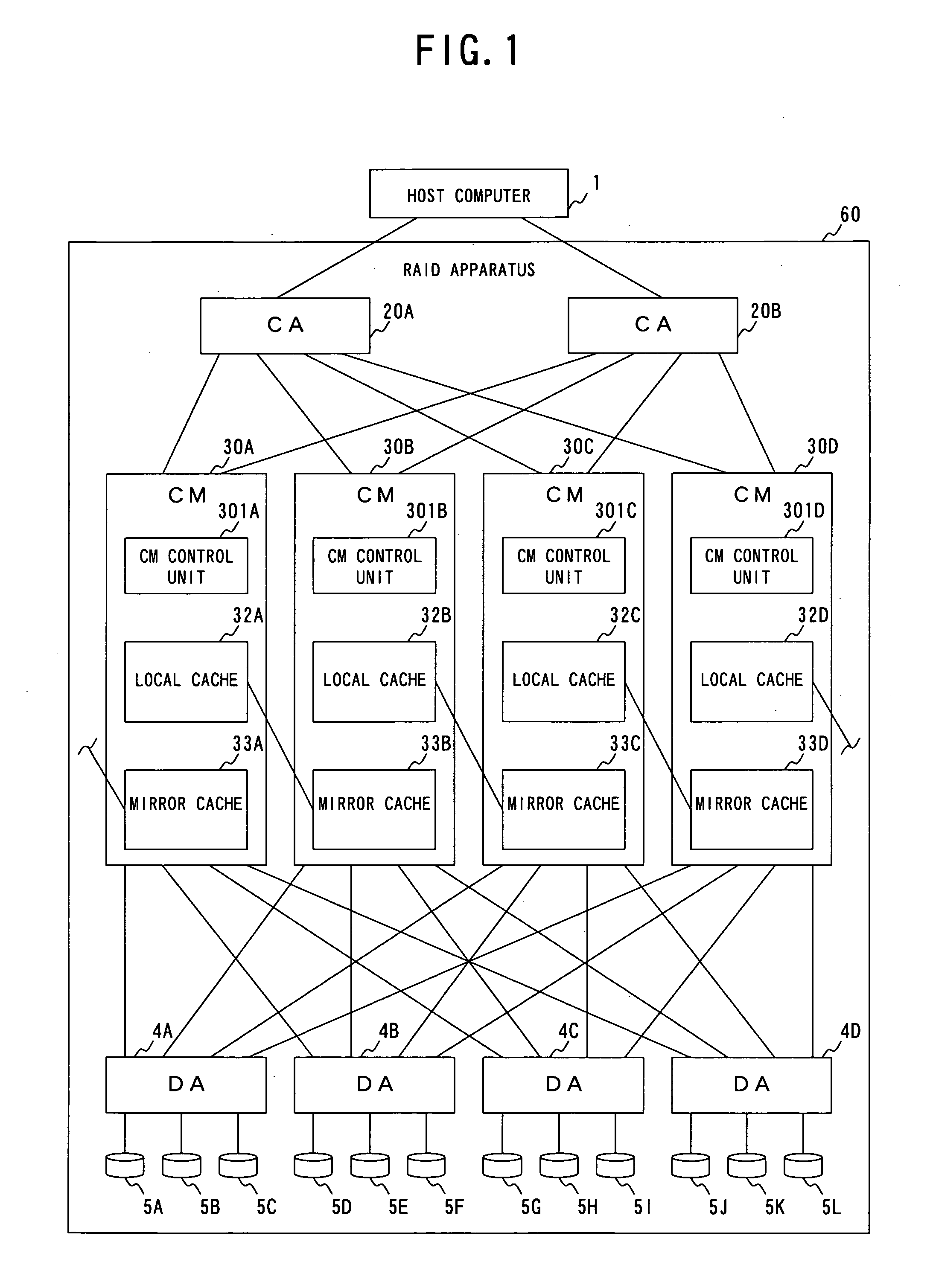
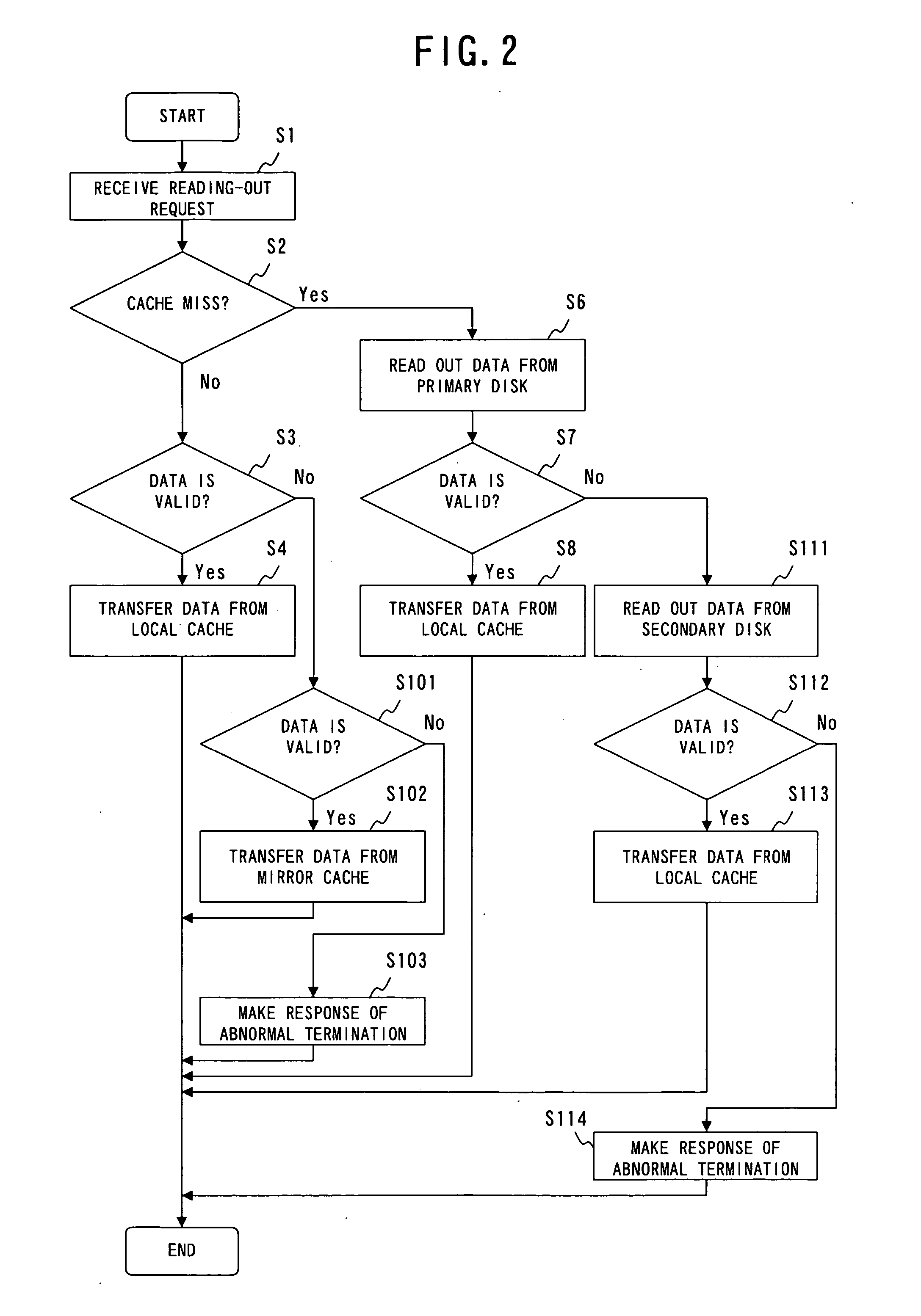
RAID apparatus, RAID control method, and RAID control program
ActiveUS20050216660A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationRAID
A RAID apparatus that at least duplicates identical data to store thus duplicated data, which, when an instruction of writing data is given, writes data to a local cache and to a mirror cache, and writes data of the local cache to a primary disk and writes data of the mirror cache to a secondary disk. When an instruction of reading out data is given, and specified data is retained in the caches, the RAID apparatus outputs valid data of the local cache or the mirror cache, while when specified data is not retained in the caches, the RAID apparatus outputs valid data of the primary disk or the secondary disk.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Block access-based flash reading and writing method
ActiveCN101930345AIncrease usage capacityInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPhysical layerProtocol Application
Owner:苏州国芯科技股份有限公司
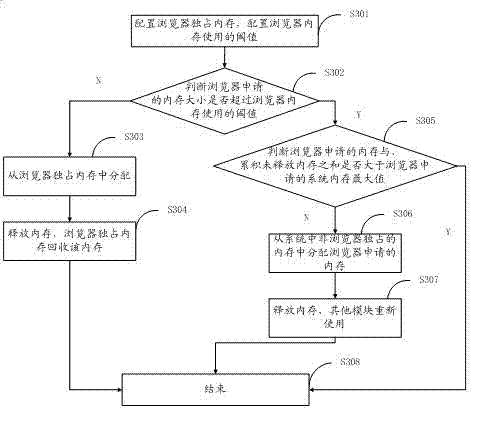
Method, system and browser for distributing hybrid memory
Owner:SHENZHEN COSHIP ELECTRONICS CO LTD
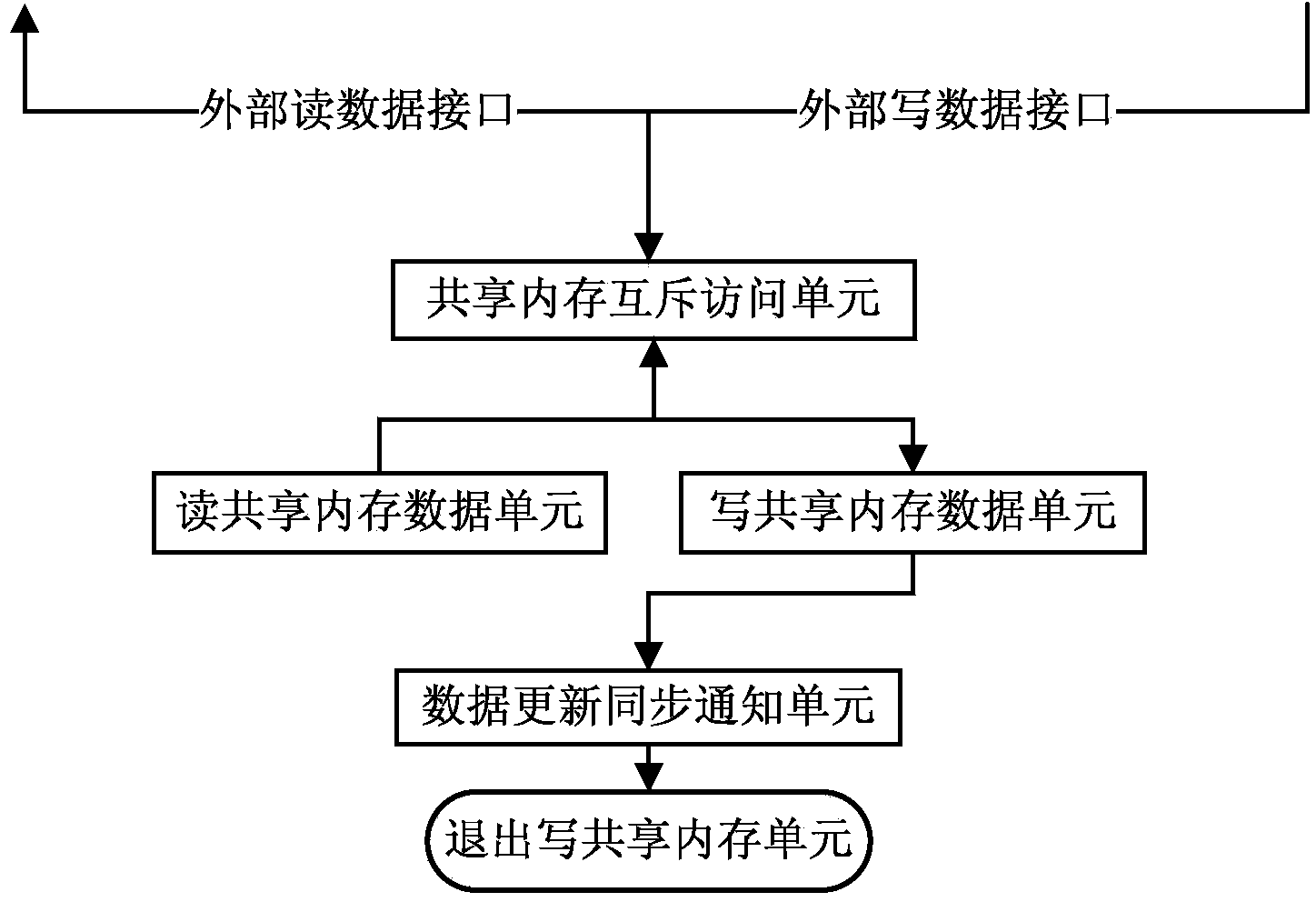
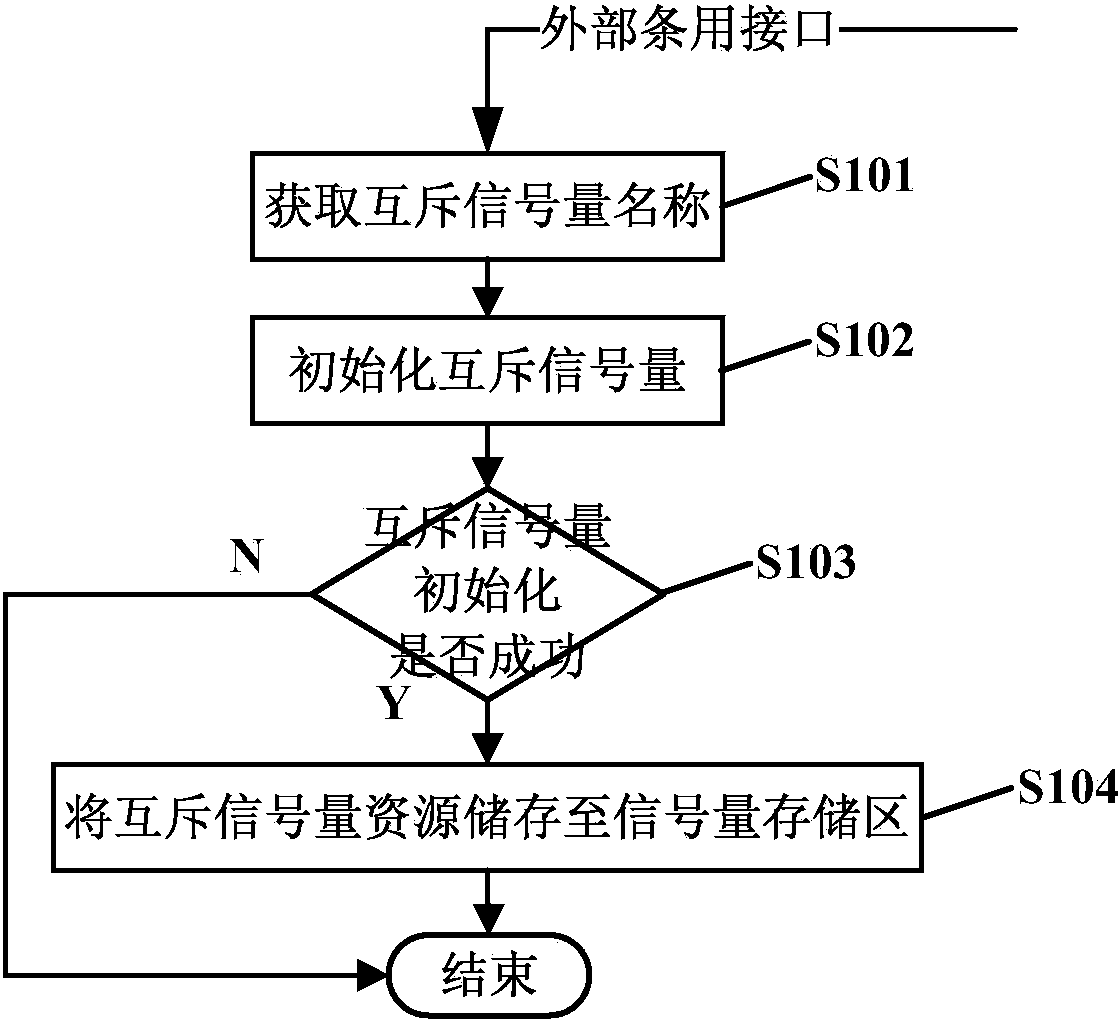
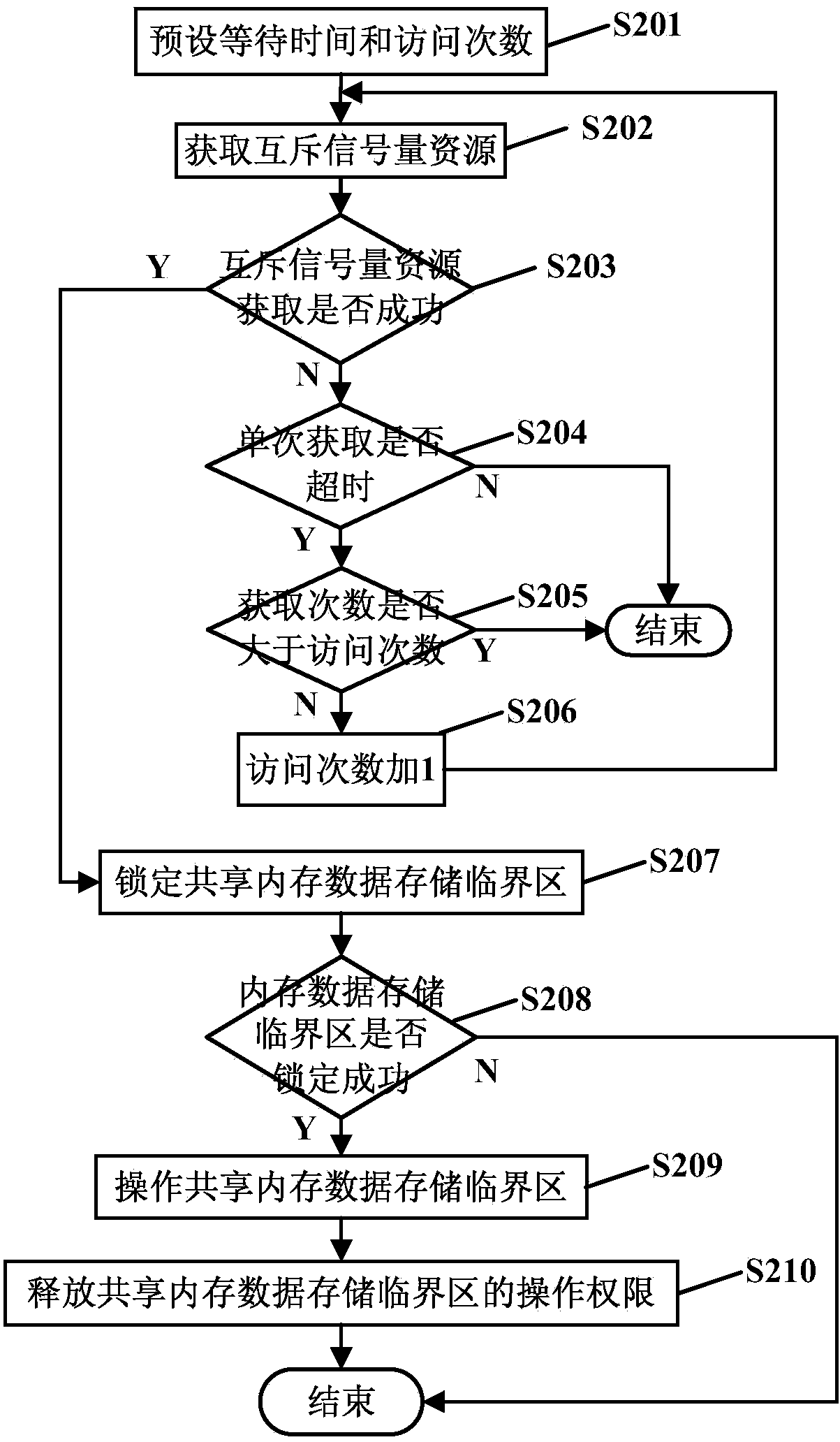
System and method for achieving home gateway data communication based on Linux shared memory
ActiveCN103731328AEffective protectionAvoid destructionMemory adressing/allocation/relocationData switching by path configurationData synchronizationGNU/Linux
Owner:FENGHUO COMM SCI & TECH CO LTD
Data processing method and system, electronic equipment
ActiveCN108009008AProgram initiation/switchingMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTransmission rateData processing
Owner:BEIJING SENSETIME TECH DEV CO LTD
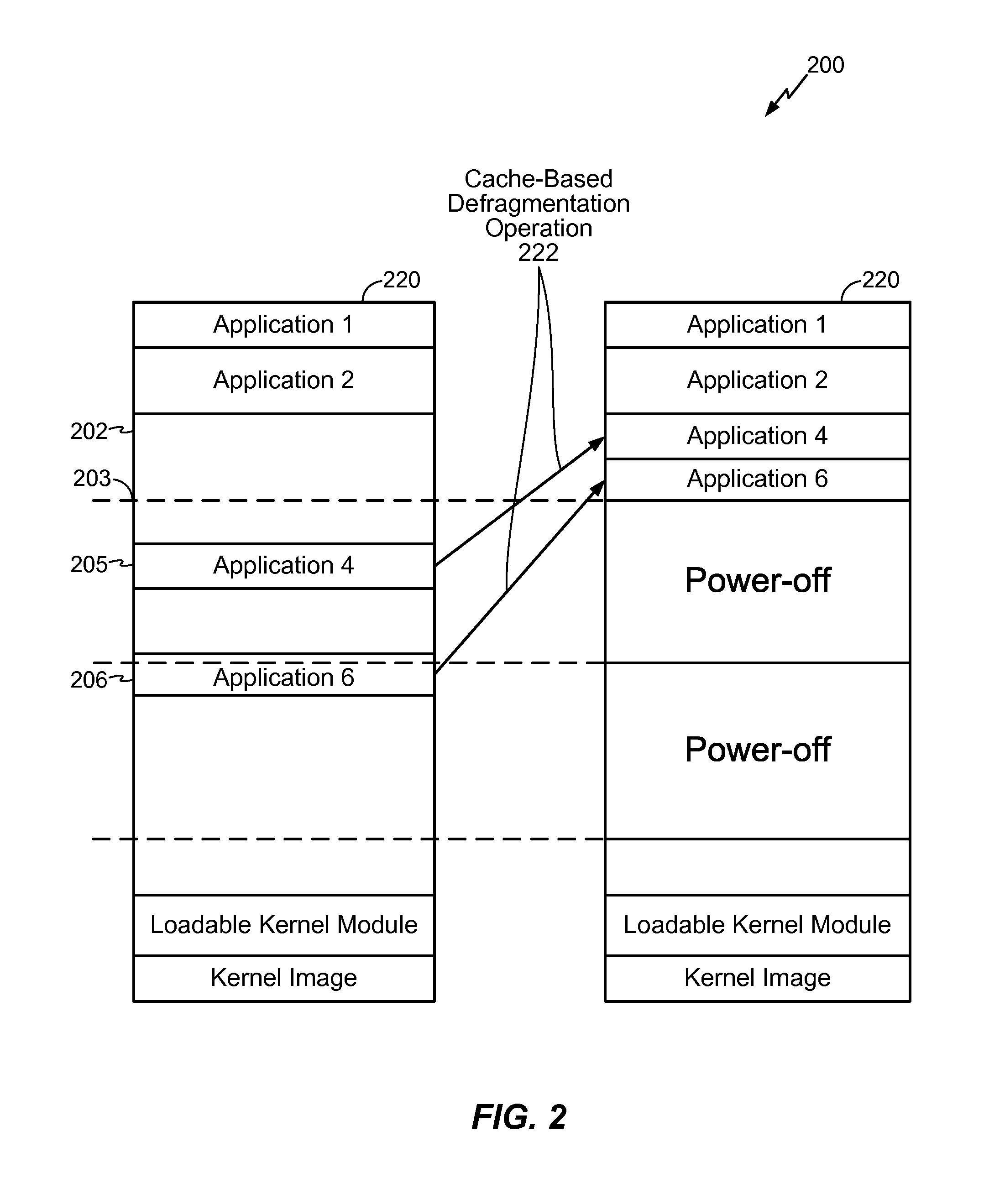
Defragmentation of digital storage media
InactiveUS20090327370A1Avoid fragmentationInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationFilter driverDefragmentation
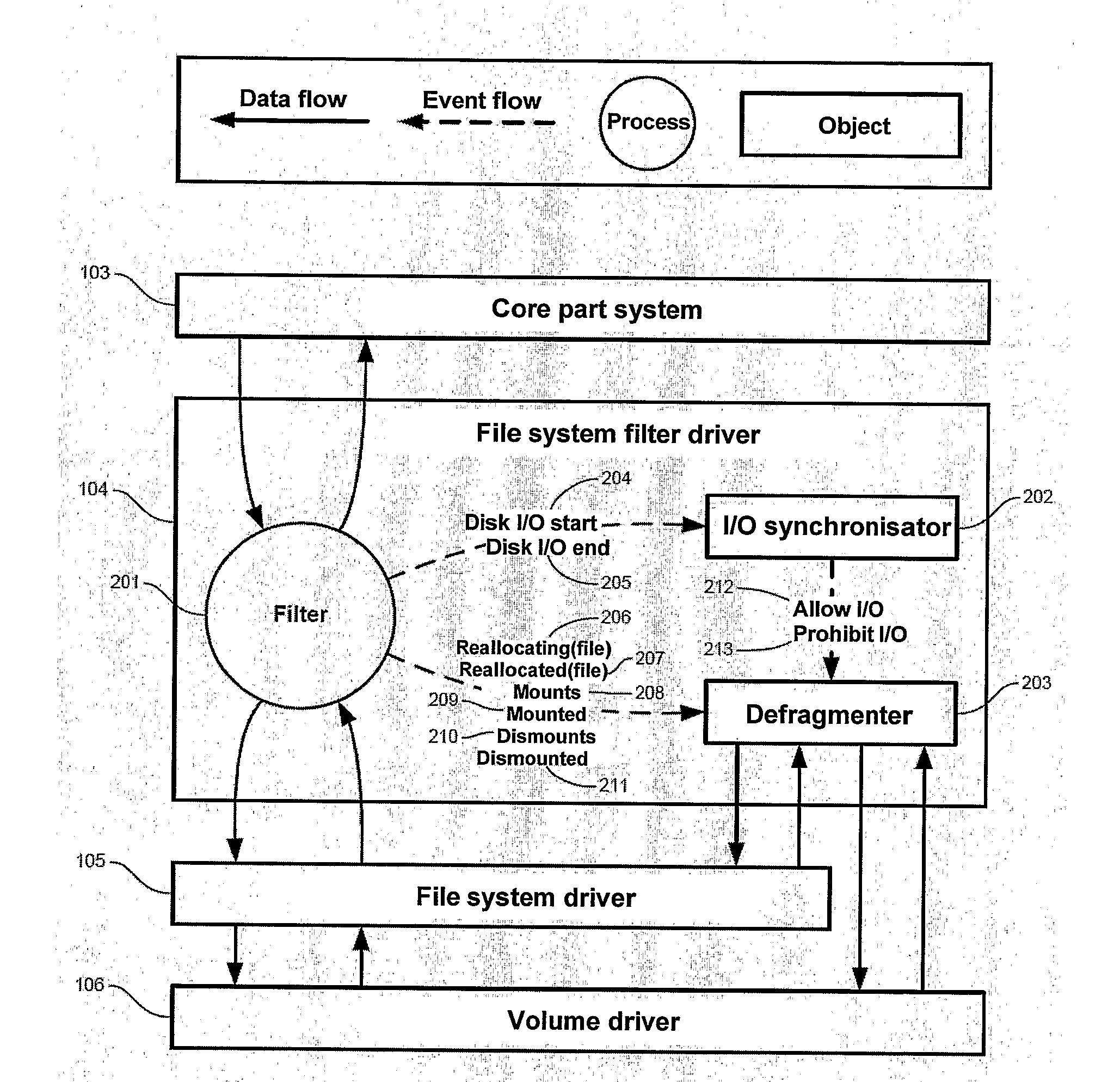
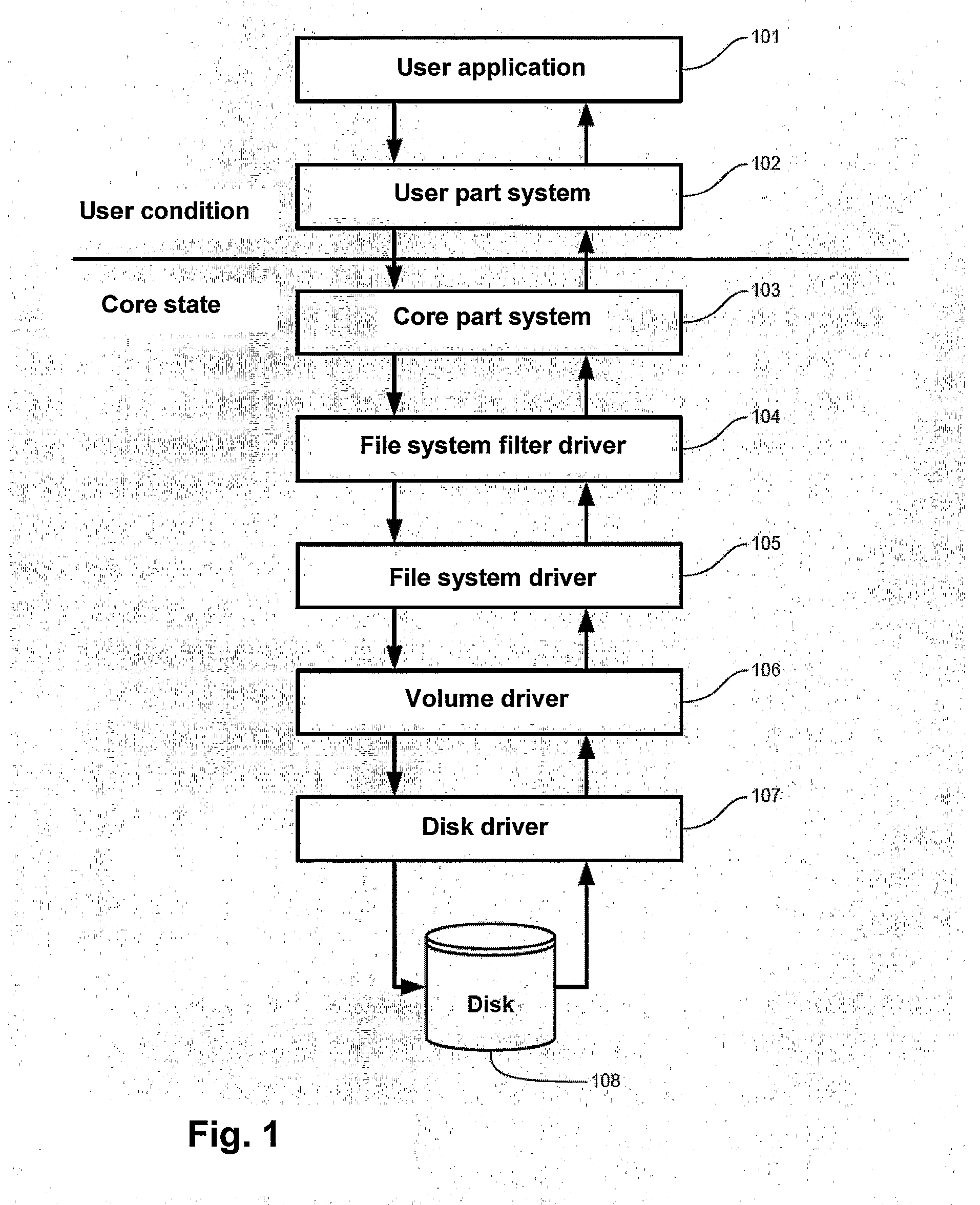
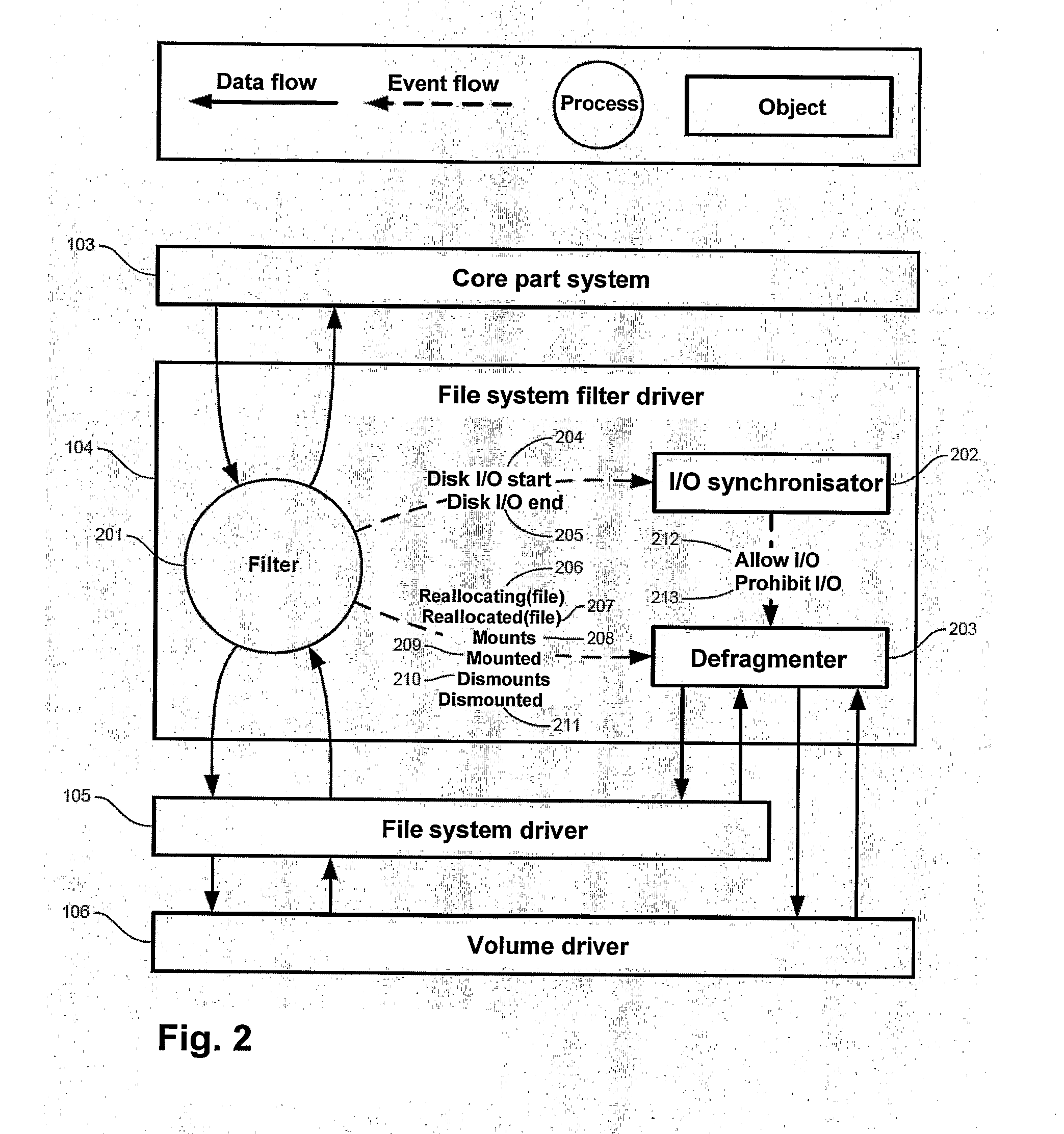
The invention concerns a technique for defragmenting digital storage media (disks). The invention is based on a filter driver or corresponding technology receiving all I / O to and / or from the file system driver, and which by itself is able to send I / O requests to the file system driver FIG. 2 illustrates the basic architecture of the invention in the form of a data flow diagram. Filter (201) receives all I / O requests to and / or from the underlying file system driver. I / O-Synchronizer (202) controls when defragmentation can be performed without interfering with external I / O requests. In Defragmenter (203) is running a separate thread that analyzes files for fragmentation received from Filter (201). Fragmented files are defragmented by sending I / O requests to the file system driver, but only when I / O-Synchronisator (202) allows it. Thereby it is immediately recognised when a files has been fragmented, and it may be defragmented momentarily without affecting in any appreciable way the remaining yield of the system.
Owner:WARP DISK SOFTWARE VCARSTEN SCHMIDT
Information processing device, information processing method and program product
InactiveUS20130091338A1Solve problemsMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTest itemDatabase
Owner:RICOH KK
Page cache device and method for efficient mapping
ActiveUS20160147670A1Efficient mappingMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSkip listPage table
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Storage device and a garbage collection method thereof
ActiveUS20210109856A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationParallel computingSoftware engineering
A memory management method of a storage device including: programming write-requested data in a memory block; counting an elapse time from a time when a last page of the memory block was programmed with the write-requested data; triggering a garbage collection of the storage device when the elapse time exceeds a threshold value; and programming valid data collected by the garbage collection at a first clean page of the memory block.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Memory resource optimization method and device
InactiveCN104572493AImplementing Collaborative Partitioning StrategiesReduce mutual interferenceMemory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionOperational systemMultilevel memory
Embodiments of the present invention relate to the field of computer. Provided are a memory resource optimization method and an apparatus, solving a mutual impact problem between existing multi-level memory resources and optimizing an existing unitary division mechanism. A specific scheme is: obtaining performance data of each program in a working set through a page coloring technology, obtaining a category of the each program by incorporating memory access frequency, selecting a page coloring division policy corresponding to the working set based on the category of the each program, inputting the page coloring division policy into an operating system kernel, and completing corresponding coloring division processing. The present invention is used for incorporating features of the working set to eliminate or reduce mutual interference of processes and threads on memory resources, improving overall performance of a computer.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +1
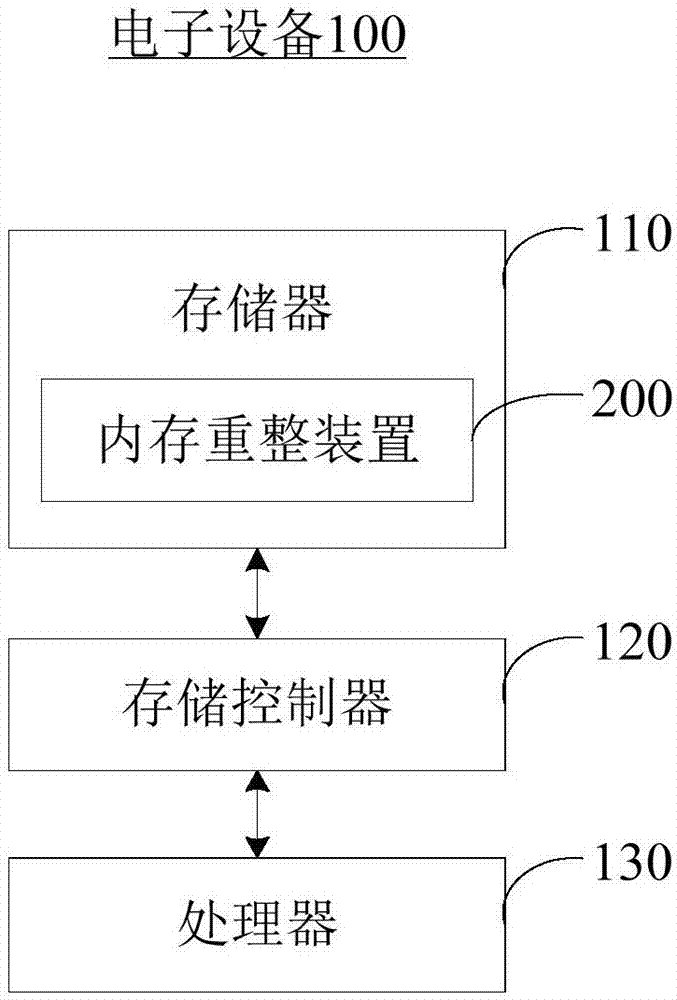
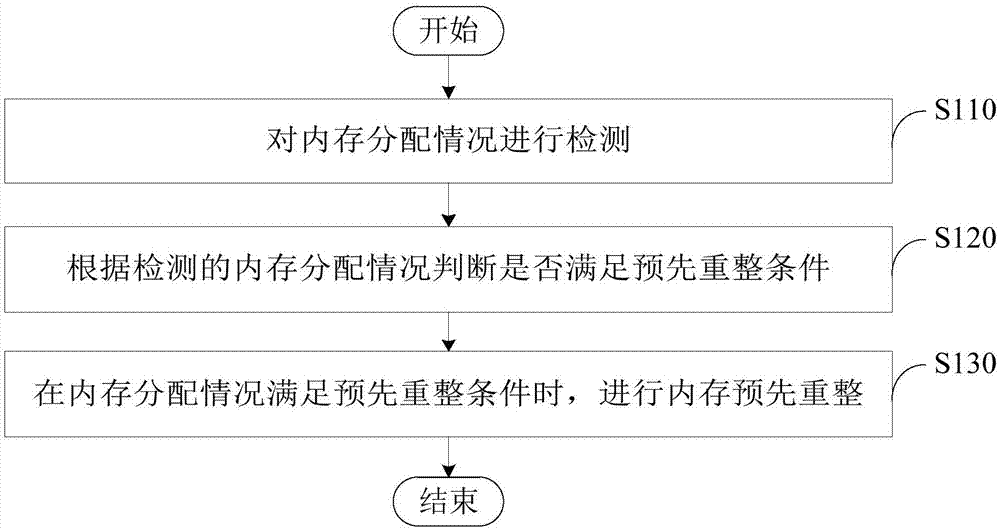
Internal memory reforming method and device, electronic equipment and readable storage medium
ActiveCN107193753AMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationElectronic equipmentComputer architecture
Owner:ONEPLUS TECH SHENZHEN
Method for enabling MLC (Multi Level Cell) to have function of SLC (Single Level Cell)
InactiveCN103870214AEfficient write performanceSLC has good stabilityInput/output to record carriersMemory adressing/allocation/relocationSingle levelMulti-level cell
Owner:AXD (ANXINDA) MEMORY TECH CO LTD
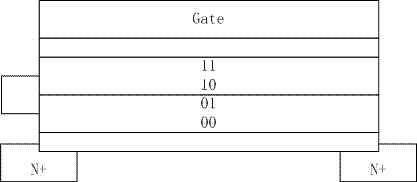
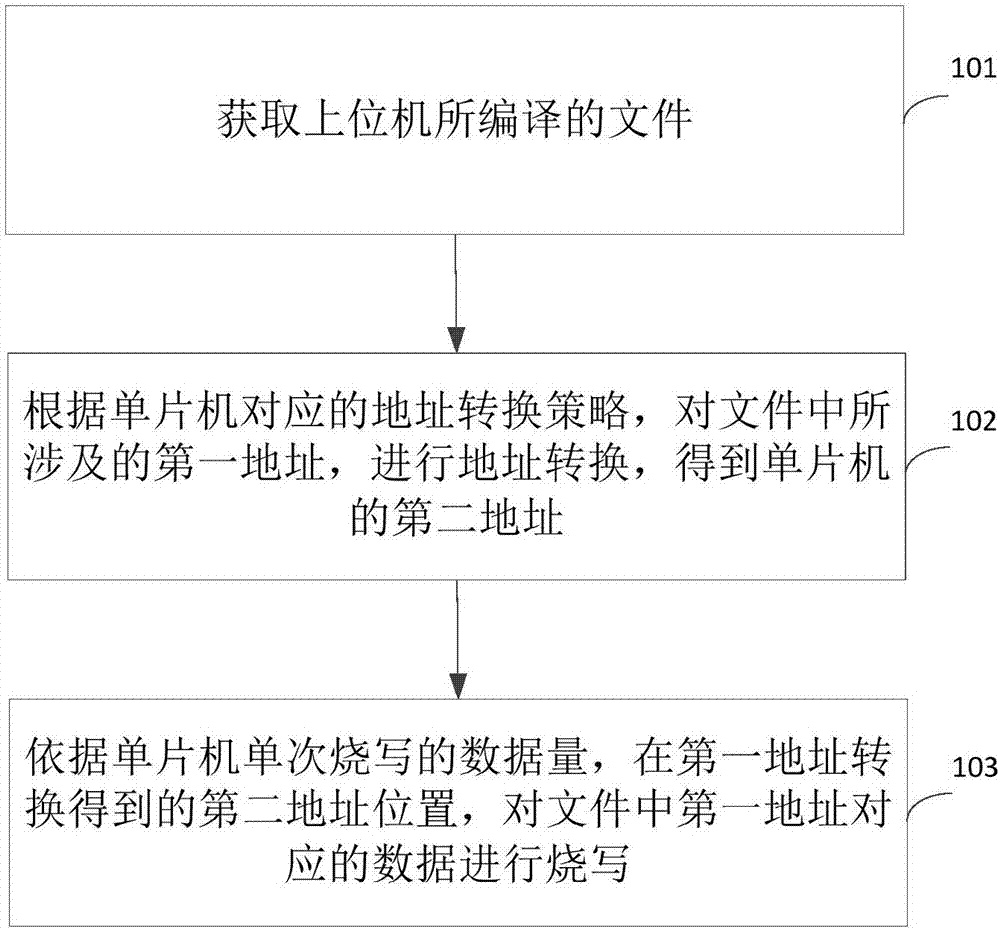
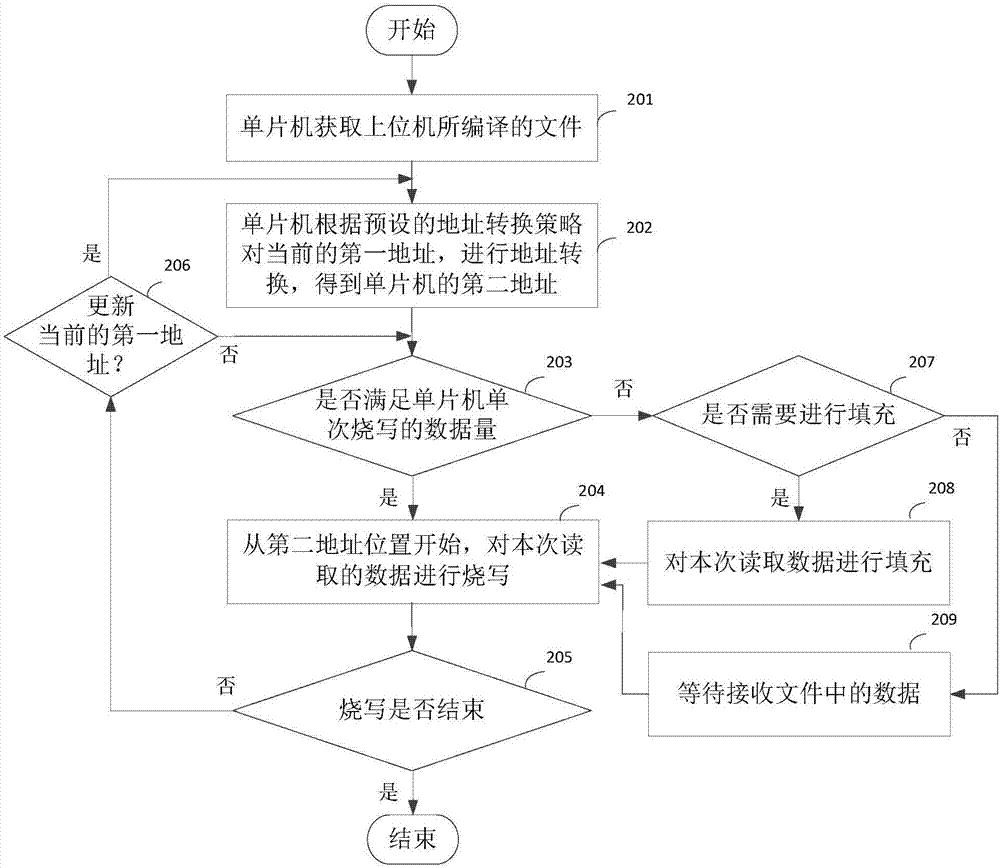
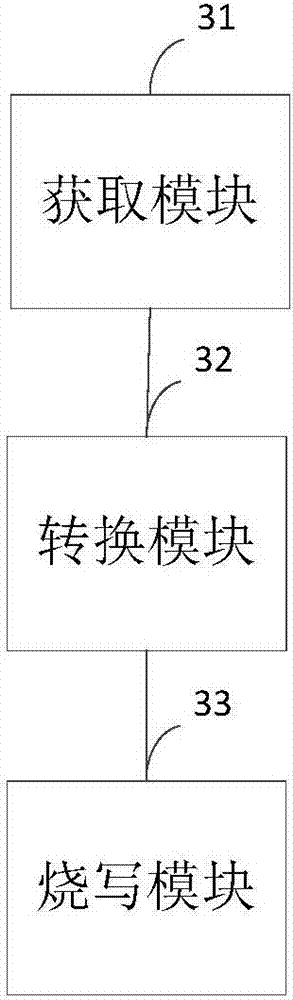
A single-chip microcomputer burn-writing method, device and system and a single-chip microcomputer
ActiveCN106990983AImprove versatilitySolve technical problems with poor versatilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProgram loading/initiatingMicrocontrollerMicrocomputer
Owner:BEIJING ELECTRIC VEHICLE
Data reading method and device
InactiveCN107329904AImprove performanceReduce the number of visits to FTLMemory adressing/allocation/relocationGranularityComputer engineering
Owner:HUNAN GOKE MICROELECTRONICS
Program execution device and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20080189507A1Short processing timeShort timeRuntime instruction translationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTheoretical computer scienceLookup table
A program execution device includes: a lookup table storage section that stores a lookup table stipulating a plurality of relations between a plurality of input data and a plurality of output data that are results of operation conducted on the plurality of input data; a program storage section that stores a program including a command directing to obtain one of the output data that is a result of the operation conducted on one of the input data, which is defined by the one of the input data and the operation; and a program execution section having a first cycle of designating the one of the input data in the command to the lookup table in the lookup table storage section, and a second cycle of receiving the one of the output data corresponding to the one of the input data from the lookup table.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Data merging method, controller and storage device for nonvolatile storage
ActiveCN103176910AShorten the timeImprove reliabilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputer scienceNon-volatile memory
Owner:PHISON ELECTRONICS
Co-operative memory management system
ActiveUS10776260B1Resource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTerm memoryComputing systems
A system for memory management that comprises: a computing system having a finite amount of memory and a physical computer readable storage memory readable by a processing circuit and storing instructions for execution by the circuit to: set, by a memory coordinator, the urgency of each memory consumer; adjust, by the memory coordinator, the memory quota of each memory consumer—such that the sum of the memory quota of each memory consumer does not exceed the memory; and adjust, by each memory consumer, its memory usage in response to a quota input and an urgency input from the memory coordinator to the memory consumer. The memory is managed by a memory coordinator and memory consumers; and consumed by the memory consumers. Each memory consumer has: a memory quota, an urgency and a memory usage. Also, the urgency of each memory consumer increases as the sum of the memory usage of the plurality of memory consumers approaches the finite amount of memory.
Owner:KINAXIS INC
Popular searches
Internal/peripheral component protection Software simulation/interpretation/emulation Code conversion Hardware monitoring Character and pattern recognition Multiple digital computer combinations Program/content distribution protection Special data processing applications Securing communication Specific program execution arrangements
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap