Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4 results about "Single-nucleotide polymorphism" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP; /snɪp/; plural /snɪps/) is a substitution of a single nucleotide that occurs at a specific position in the genome, where each variation is present at a level of <1% in the population.
Method for breeding Ili horses, and kit employed in method
InactiveCN103181361AImprove body size traitsAccelerate cultivationMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnimal husbandryBody sizeBiology
Owner:新疆维吾尔自治区畜牧科学院中国-澳大利亚绵羊育种研究中心
Molecular marker related to feed conversion efficiency characters of meat ducks and application thereof
ActiveCN108165639AReduce manufacturing costSpeed up genetic progressMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationSingle-nucleotide polymorphismZoology
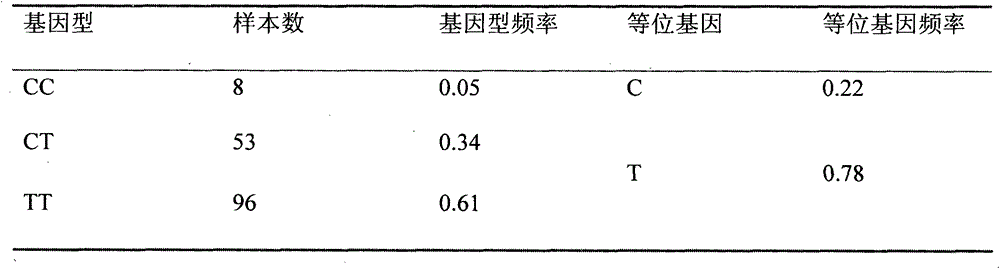
The invention discloses a molecular marker related to the feed conversion efficiency character of meat ducks and application thereof. The invention provides a method for detecting the feed conversionefficiency characters of ducks to be detected. The method comprises the following steps: the genotype based on a specific SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) of the duck to be detected, the feed conversion efficiency of the AA genotype duck to be detected is higher than that of the AC genotype duck to be detected, and the feed conversion efficiency of the AC genotype duck to be detected is higherthan that of the CC genotype duck to be detected. On the basis of the genotype of the SNP site, the selection of the feed conversion efficiency characters can be realized, the feed conversion efficiency of the AA genotype duck is superior to that of the AC genotype duck and the CC genotype duck, and the feed conversion efficiency of the AC genotype duck is superior to that of the CC genotype duck. The molecular marker disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that early selection for the feed conversion efficiency characters can be realized, the production cost can be saved, the genetic progress can be accelerated, the breeding of the ducks can be better served and the economic application value and the scientific research are very large.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI CAAS
Methods and kits for predicting the risk of diabetes associated complications using genetic markers and arrays
InactiveUS20130209447A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiabetic kidneyGenetics predisposition
A method for diagnosing a genetic predisposition in a subject for diseases, disorders or conditions including a diabetic kidney complication such as kidney disease of type 2 diabetes or type 1 diabetes, end stage renal disease (ESRD) due to type 2 diabetes, ESRD due to hypertension in type 2 diabetes, ESRD due to type 1 diabetes; cardiovascular diseases due to type 2 diabetes or type 1 diabetes such as atherosclerotic peripheral vascular disease, hypertension, ischemic cardiomyopathy, and myocardial infarction due to type 2 diabetes or type 1 diabetes; and cerebrovascular accident due to type 2 diabetes. At least one polynucleotide is analyzed to detect a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), in which the presence of the single nucleotide polymorphism indicates that the subject is suffering from, at risk for, or suspected of suffering from the diseases, disorders or conditions. Also provided is an array or kit for diagnosing the genetic predisposition.
Owner:THE CHINESE UNIVERSITY OF HONG KONG
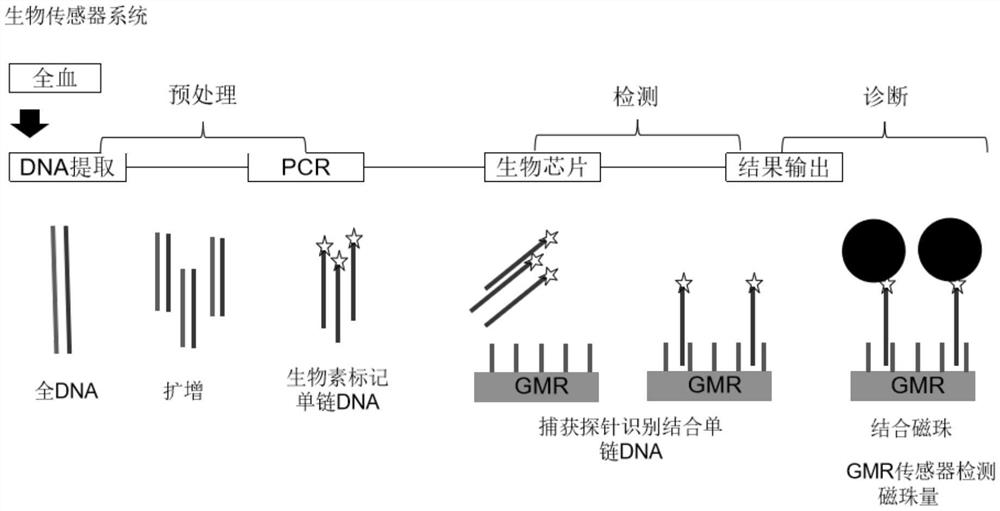
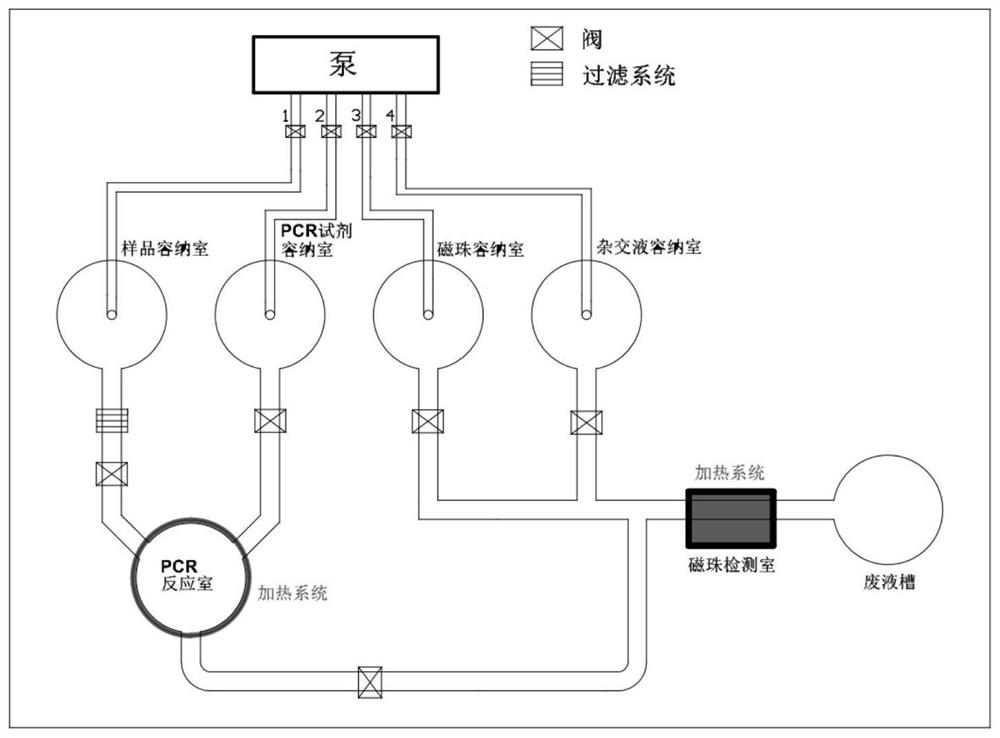
Method and device for detecting target gene or SNP (Single Nucleotide Polymorphism) site of target gene by combining asymmetric PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) and magnetic sensitive detector
PendingCN114107438AShort reaction timeSimple designBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsHybridization reactionSingle strand
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap