Liver bud stem cell, preparation method and application thereof
A technology of stem cells and liver buds, applied in the field of biomedicine
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1. Isolation and culture of liver bud stem cells from human embryonic liver bud tissue
[0036] 1.1 Pretreatment of the culture vessel: Cover the bottom wall of the culture bottle / dish / plate with 0.2% gelatin, leave it at room temperature for 30 minutes, suck out the 0.2% gelatin, dry it at room temperature and set aside.
[0037] 1.2 Preparation of culture medium:
[0038] Improved IF medium:
[0039]
[0040] Among them, IMDM and HAM F12 medium, NEAA, GlutamaxTM, penicillin / streptomycin are products of GibcolBRL, FBS are products of Hyclone Company, insulin and EGF are products of Sigma Company.
[0041] Preparation of frozen stock solution:
[0042]
[0043] Mix well and store at 4°C for later use.
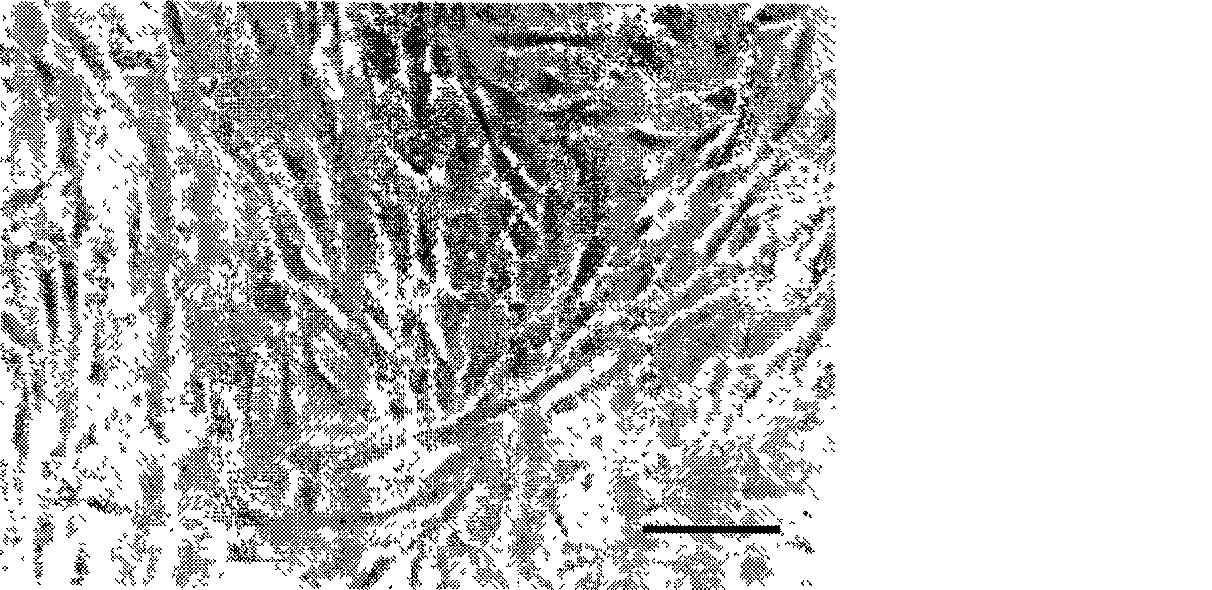
[0044] 1.3 Isolation, inoculation and culture of human fetal liver cells: Aborted human embryos with a gestational age of 4.5 weeks were placed under a dissecting microscope ( figure 1 ), it can be seen that the liver bud is located on the ventral si
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: Identification of biological characteristics of human liver bud stem cell line:
[0051] 2.1 Analysis of proliferation kinetics
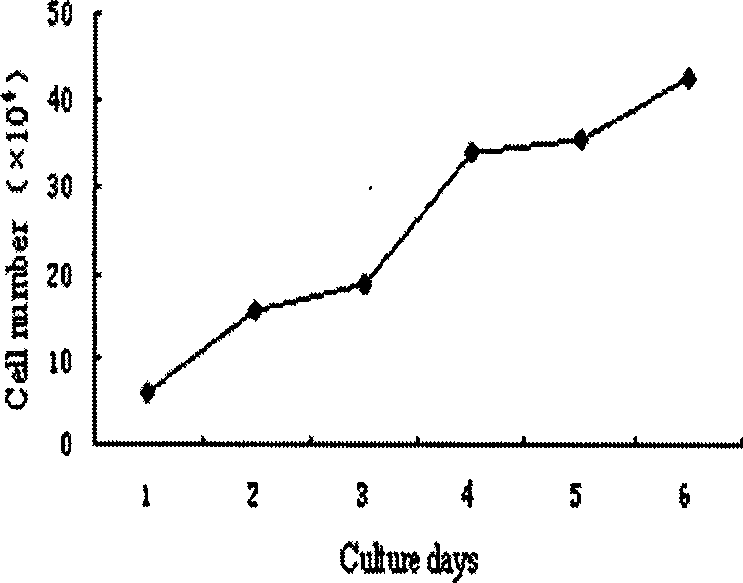
[0052] Refer to "Cell Culture" (World Book Publishing Company, edited by Situ Zhenqiang and Wu Junzheng) to draw the growth curve as follows image 3 shown. The doubling time was calculated as 28.1 hours according to the formula TD=tlog2 / log(N / N0). Take 1×10 4 / cm 2 Cells were inoculated at a certain density and subcultured approximately every 4-5 days. At present, it has been cultured in vitro for more than one year, and the cell proliferation has remained stable for more than 25 passages (about 90 doubling times).
[0053] 2.2 Cell tumorigenicity analysis:
[0054] Will 2×10 7 hLBSC cells were transplanted into SCID mice (n=4) subcutaneously, observed once a week, no tumor was observed for a total of 14 weeks. It proves that hLBSC has no transformation and no tumorigenicity.
[0055] 2.3 Molecular phenotype detection
Embodiment 3
[0069] Example 3. Induced differentiation of liver bud stem cells into hepatocytes
[0070] 3.1 Preparation of induction solution:
[0071] D-10-SB Medium
[0072]
[0073] 3.2 Induction to liver cells:
[0074] Place the coverslip in a 60mm culture dish and inoculate 2×10 cells 4 / CM 2 , when the cells on the coverslip grow to 60% confluence, change the induction medium D-10-SB medium to continue the culture.
[0075] 3.3 Morphological observation of the differentiation process:
[0076] Cell morphology and growth were observed daily under an inverted phase-contrast microscope and recorded by photomicrography. Under the light microscope, it can be seen that the short fusiform or triangular cells become flattened and hypertrophic after adding sodium butyrate for 24 hours, and the ratio of nucleus to cytoplasm is obviously reduced. Hypertrophic binuclear cells were seen under the microscope 48 hours after induction. After 10 days, about 10-15% of the cells became binuc
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap