Spatial filtering device
A technology of spatial filtering and filtering small holes, which is applied in the direction of optical components, optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the difficulty of small hole processing, alignment accuracy, sparking, etc., to increase misalignment tolerance, improve safety performance, Improve the effect of filtering effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
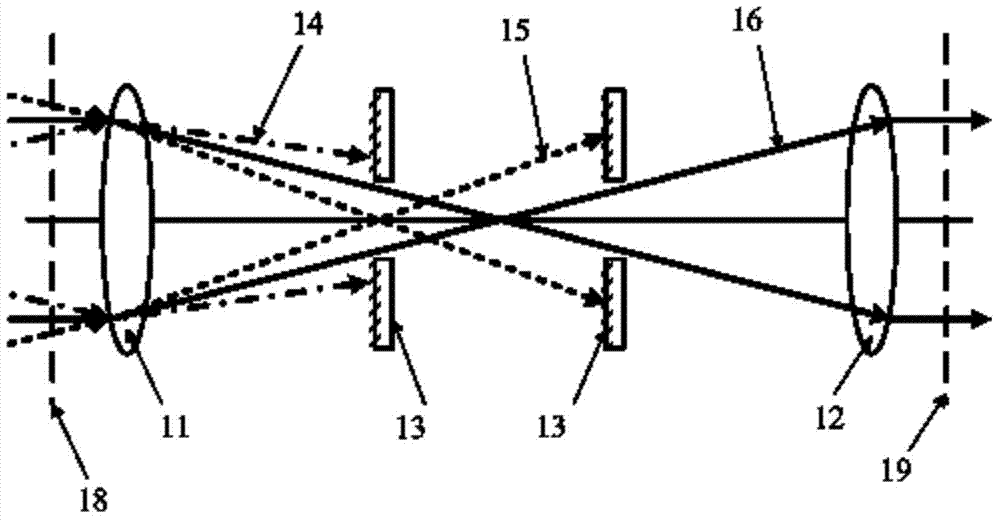
[0026] Such as figure 1 As shown, a spatial filter device provided by Embodiment 1 of the present invention includes a frequency division lens 11, a restoration lens 12, and at least two filter pinholes 13. The frequency division lens 11 and the restoration lens 12 constitute a confocal optical system, that is, The frequency lens 11 and the restoration lens 12 are arranged on the same optical axis, and the image focus of the frequency division lens 11 coincides with the object focus of the restoration lens 12; at least two filter apertures 13 are arranged on the focus of the confocal optical system and 11 and / or between the restoration lens 12, that is, at least two filter apertures 13 can be arranged between the focus of the confocal optical system and the frequency division lens 11, or both are arranged between the focus of the confocal optical system and the restoration lens 12 In between, one or more filter apertures 13 may also be provided on both sides of the focal point
Embodiment 2
[0031] The spatial filtering device provided in Embodiment 2 is basically the same in structure as Embodiment 1, and the similarities will not be described again. The difference lies in:
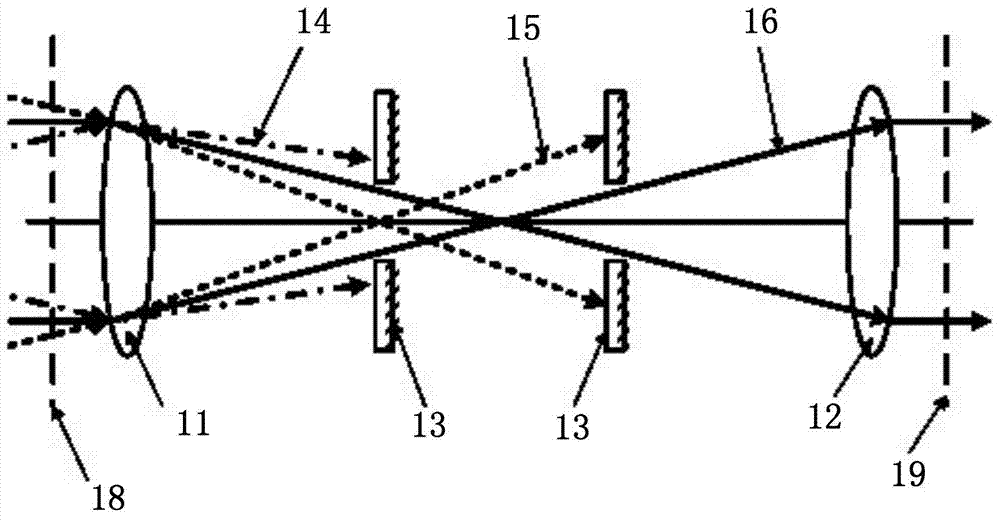
[0032] Such as figure 2 As shown, in the direction of light propagation, the rear surface of the filter hole 13 is a textured surface, and the matrix material of the filter hole 13 is undoped yttrium aluminum garnet. At the front and rear positions of the focal point of the confocal optical system, the front and rear surfaces perpendicular to the incident laser beam are textured surfaces, and the different high-frequency components 14 in the incident laser beam are filtered by the surfaces of different filter pinholes 13 to achieve low-pass filter function.
Embodiment 3
[0034] The spatial filtering device provided in the third embodiment has basically the same structure as that in the second embodiment, and the similarities will not be repeated, but the difference is:
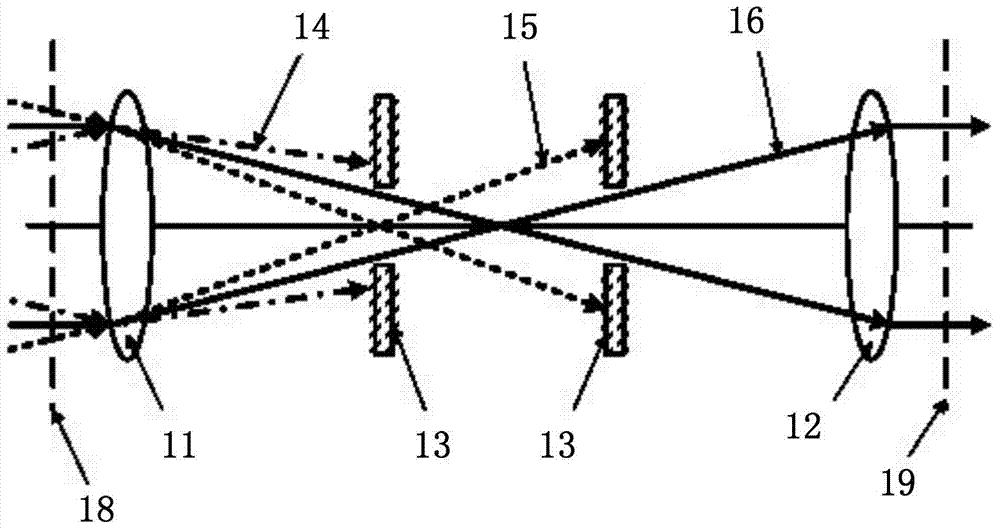
[0035] Such as image 3 As shown, in the light propagation direction, the front and rear surfaces of the filter hole 13 are textured surfaces, and the matrix material of the filter hole 13 is sapphire. Located at the front and back of the focal point of the confocal optical system, the front and rear surfaces perpendicular to the laser incident are textured surfaces, relying on the double textured surface of different filter holes 13 to filter out different high-frequency components 14 in the incident laser beam, Realize the low-pass filter function.
[0036] In summary, the spatial filter device of the present invention uses the confocal frequency division lens 11 and the restoration lens 12 combined with different focal lengths, at least two filter holes 13 of low-absorption mat
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap