Rapid microbiological inspection and quarantine method for entry and exit ports
A technology for inspection, quarantine, and microorganisms, applied in the field of molecular biology detection and identification, can solve the problems of long detection time and accuracy impact, and achieve the effect of rapid detection and accurate results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] The specific implementation steps are as follows;
[0049] 1. Sample Statistics
[0050] Collect the location, type, latitude and longitude information of the samples.
[0051] 2. Sample preparation
[0052] Sample preparation was performed using the kit EZNA Soil DNA kit, Cat. No. D5625-02 (200).
[0053] 1. Adjust the desktop high-speed refrigerated centrifuge to 4°C, adjust the temperature of the two constant temperature water baths to 65°C and 70°C respectively, and preheat the Elution Buffer in a 65°C water bath.
[0054] 2. Add 500mg glass beads and 1mL Buffer SLX MLU to the sample tube, close the centrifuge tube, place it in an amalgam blender, and mix for 20 seconds.
[0055] 3. Add 100 μL DS Buffer to the broken sample tube, mix gently, put it in a 70°C water bath for 10 minutes, and shake it intermittently during the water bath.
[0056] 4. After the water bath, take out the sample and centrifuge in a room temperature centrifuge at 3000rpm for 3min; after cen
Embodiment 2
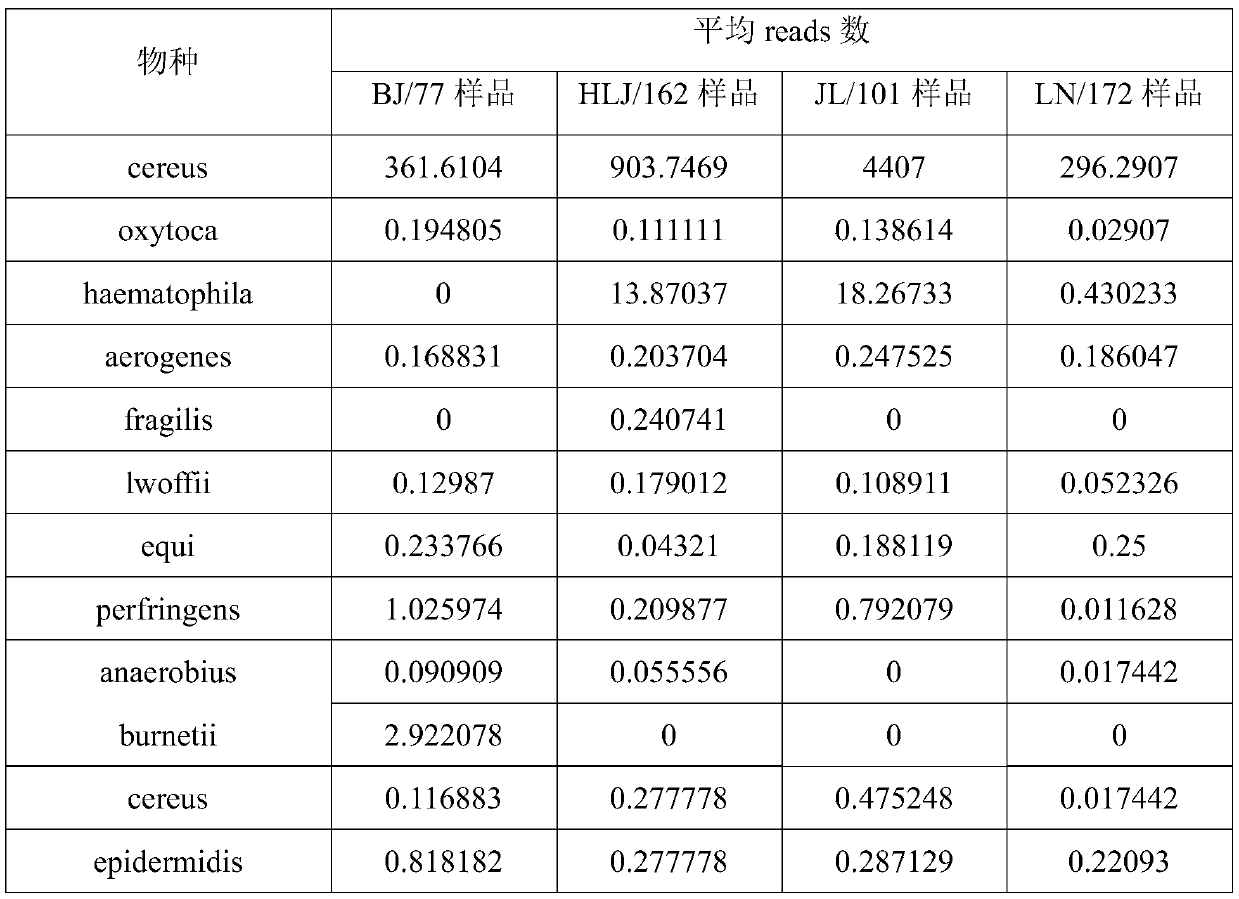
[0087] Sample source: BJ samples are soil from the wasteland in the suburbs of Beijing; HLJ, JL and LN samples are from ginseng rhizosphere soil in the three northeastern provinces.
[0088] Experimental method: the method described in Example 1 of the present invention.
[0089] Experimental results:
[0090]
[0091] The results show that the Reads distribution of the same bacteria in different locations is not uniform, and the average number of reads of some bacterial species in many samples is even less than 1. Bacteria with a relative content in this range are often difficult to detect through traditional culture methods. This explains:
[0092] 1) The method of the present invention can be detected in a state where the microbial content is extremely low, and compared with the traditional method, the detection is sensitive and the effect is better.
[0093] 2) The difference information of the flora structure of samples from different sources can be obtained through the
experiment example 1
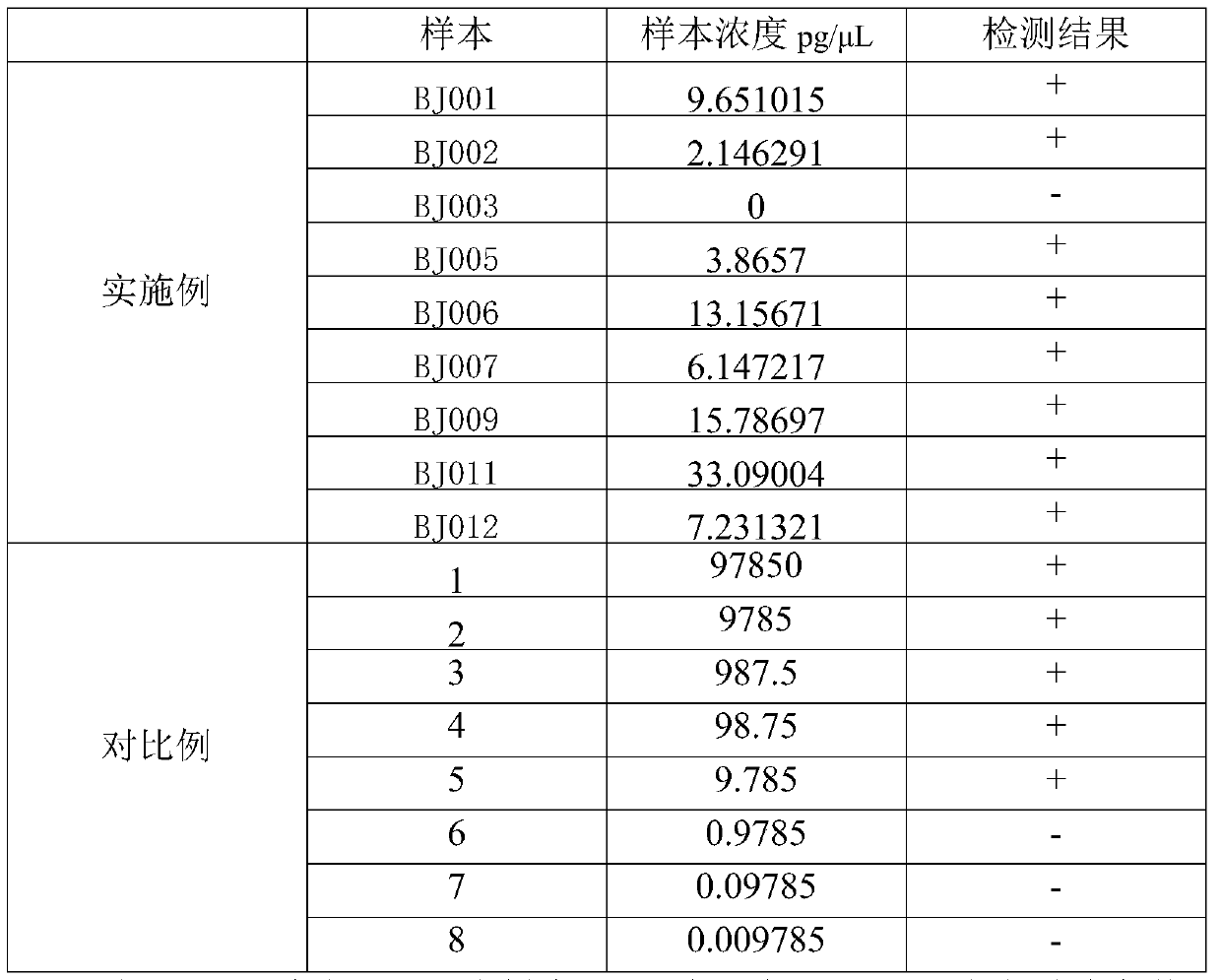
[0095] Sample size: 8-12
[0096] Experimental method: 1, the method described in the embodiment of the present invention 1;
[0097] 2. The method described in Example 3 in Chinese patent application 201710048877.1.
[0098] Experimental results:
[0099]
[0100] The results show that the present invention can be detected under the low concentration condition of sample DNA content of 2.14pg / μL, compared with 9.785pg / μL in the reference document Chinese patent application 201710048877.1, the detection method of the present invention can be detected in samples with low DNA content The bacteria in the sample can also be detected under certain circumstances, the detection is sensitive, the result is stable, and it is more suitable for the rapid detection of microorganisms, especially the inspection and quarantine of microorganisms at ports.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap