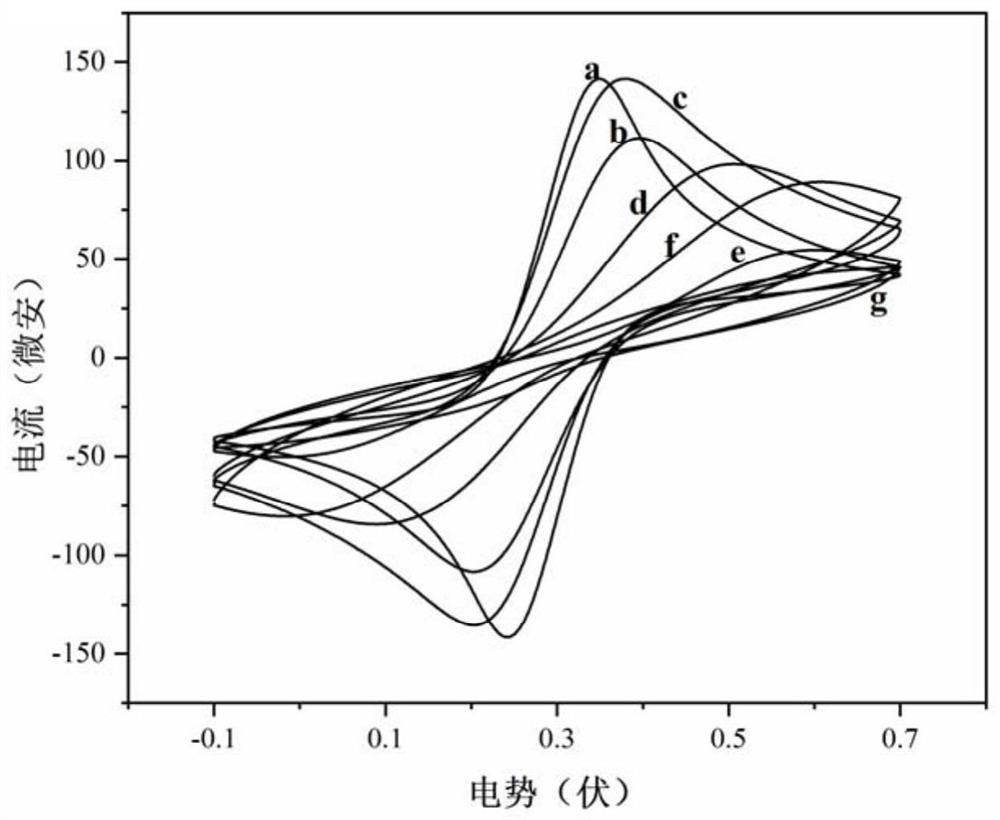
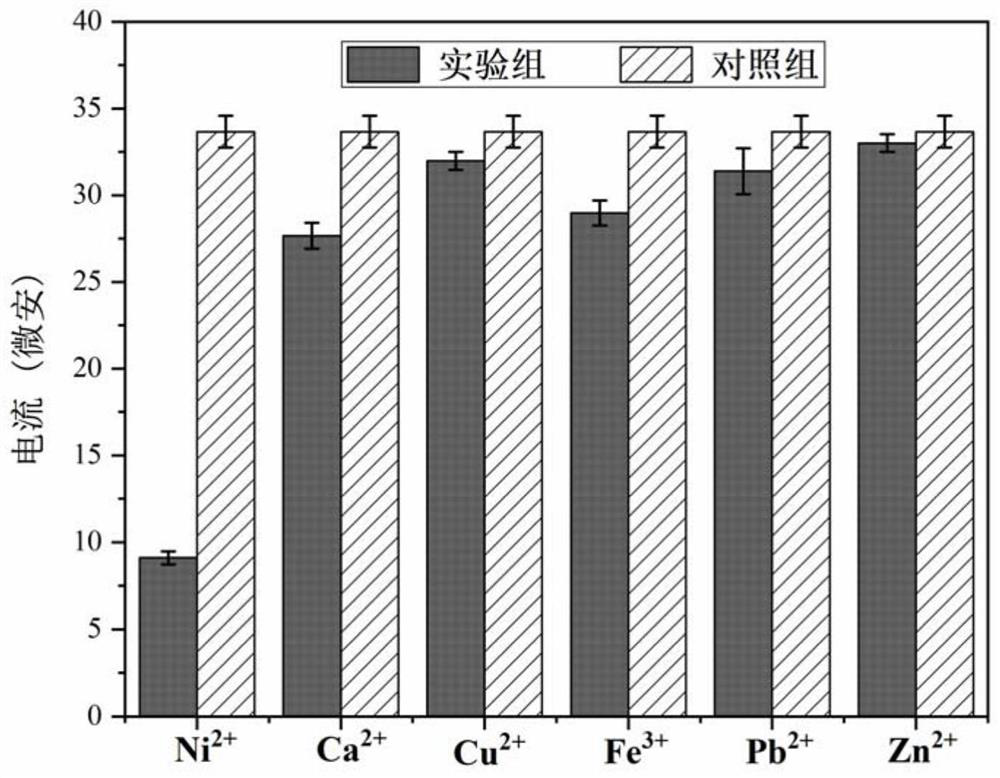
Magnetically-induced self-assembled electrochemical biosensor for sensitively detecting trace nickel ions and application of magnetically-induced self-assembled electrochemical biosensor
A biosensor and sensitive detection technology, which is applied in the field of electrochemical biosensing, can solve the problems of unstable current signal and easy detachment of substrate materials from the electrode surface, etc., and achieve the effects of fast operation, simple and rapid electrode regeneration, and convenient portability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0056] A method for sensitively detecting trace Ni of the present invention 2+ The magnetically induced self-assembled electrochemical biosensor, the construction process is as follows:
[0057] 1) The magnetic glassy carbon electrode (MGCE) is sequentially made of 0.3 μm and 0.05 μm Al 2 o 3 The powder is polished to the mirror surface, and then ultrasonically cleaned in ultrapure water, absolute ethanol, and ultrapure water in turn, and the clean MGCE is obtained after drying;
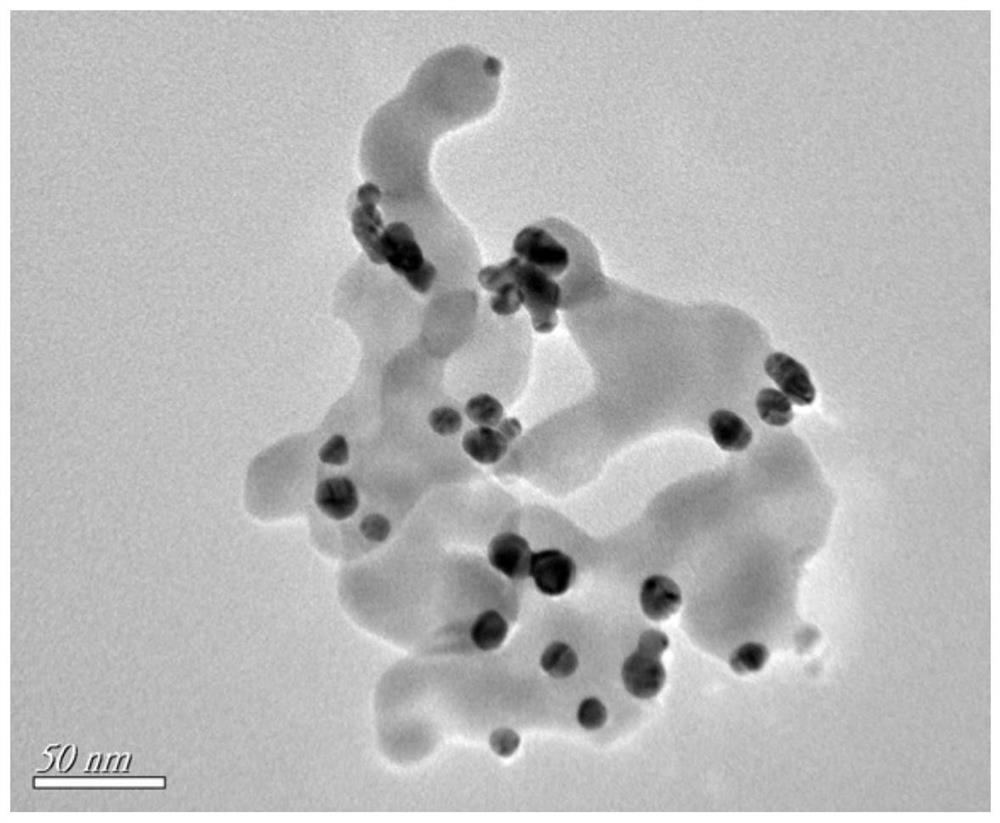
[0058] 2) The α-Fe prepared by the preparation example 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 - Ultrasonic dispersion of Au nanocomposites in ultrapure water to prepare α-Fe at a concentration of 20mg / mL 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 -Au nanocomposite suspension, for subsequent use;
[0059] 3) Add 8μL of 20mg / mLα-Fe 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 -Au nanocomposite suspension was added dropwise to the clean MGCE surface, and after the liquid was dried at room temperature, MGCE / α-Fe 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 -Au modified electrode, s
Embodiment 2
[0099] A method for sensitively detecting trace Ni of the present invention 2+ The magnetically induced self-assembled electrochemical biosensor, the construction method is as follows:
[0100] 1) The magnetic glassy carbon electrode (MGCE) is sequentially made of 0.3 μm and 0.05 μm Al 2 o 3 The powder is polished to the mirror surface, and then ultrasonically cleaned in ultrapure water, absolute ethanol, and ultrapure water for 1 min, and then dried to obtain a clean MGCE for use;
[0101] 2) The α-Fe prepared by the preparation example 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 -Au nanocomposites were ultrasonically dispersed in ultrapure water and prepared as α-Fe at a concentration of 5 mg / mL 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 -Au nanocomposite suspension, for subsequent use;
[0102] 3) Dispense 8 μL with a concentration of 5mg / mLα-Fe 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 -Au nanocomposite suspension is added dropwise to the clean MGCE surface, and after the liquid is dried, MGCE / α-Fe 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 -Au modif
Embodiment 3
[0110] A method for sensitively detecting trace Ni of the present invention 2+ The magnetically induced self-assembled electrochemical biosensor, its construction method:
[0111] 1) The magnetic glassy carbon electrode (MGCE) is sequentially made of 0.3 μm and 0.05 μm Al 2 o 3 The powder is polished to the mirror surface, and then ultrasonically cleaned in ultrapure water, absolute ethanol, and ultrapure water in turn, and the clean MGCE is obtained after drying;
[0112] 2) The α-Fe prepared by the preparation example 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 - Ultrasonic dispersion of Au nanocomposites in ultrapure water to prepare α-Fe at a concentration of 25mg / mL 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 -Au nanocomposite suspension, for subsequent use;
[0113] 3) Dispense 8μL of 25mg / mLα-Fe 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 -Au nanocomposite suspension was added dropwise to the clean MGCE surface, and after the liquid was dried, MGCE / α-Fe 2 o 3 / Fe 3 o 4 -Au modified electrode, spare.
[0114] 4) Add an equa
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Peak current | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap