Spintronics element and magnetic memory device
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example
[0025]Exemplary embodiments of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. The same reference signs are used to designate the same or similar components throughout the drawings.
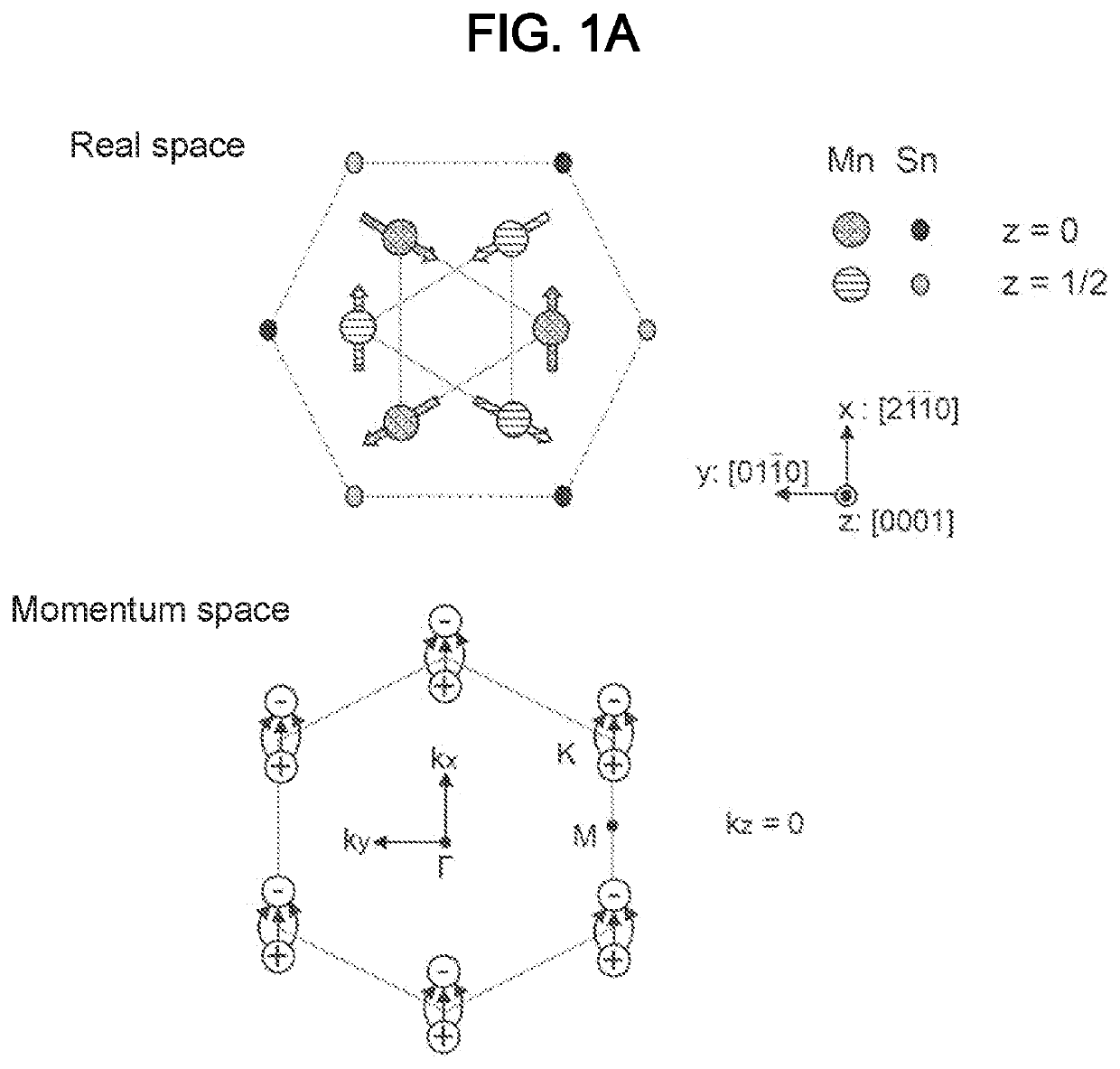
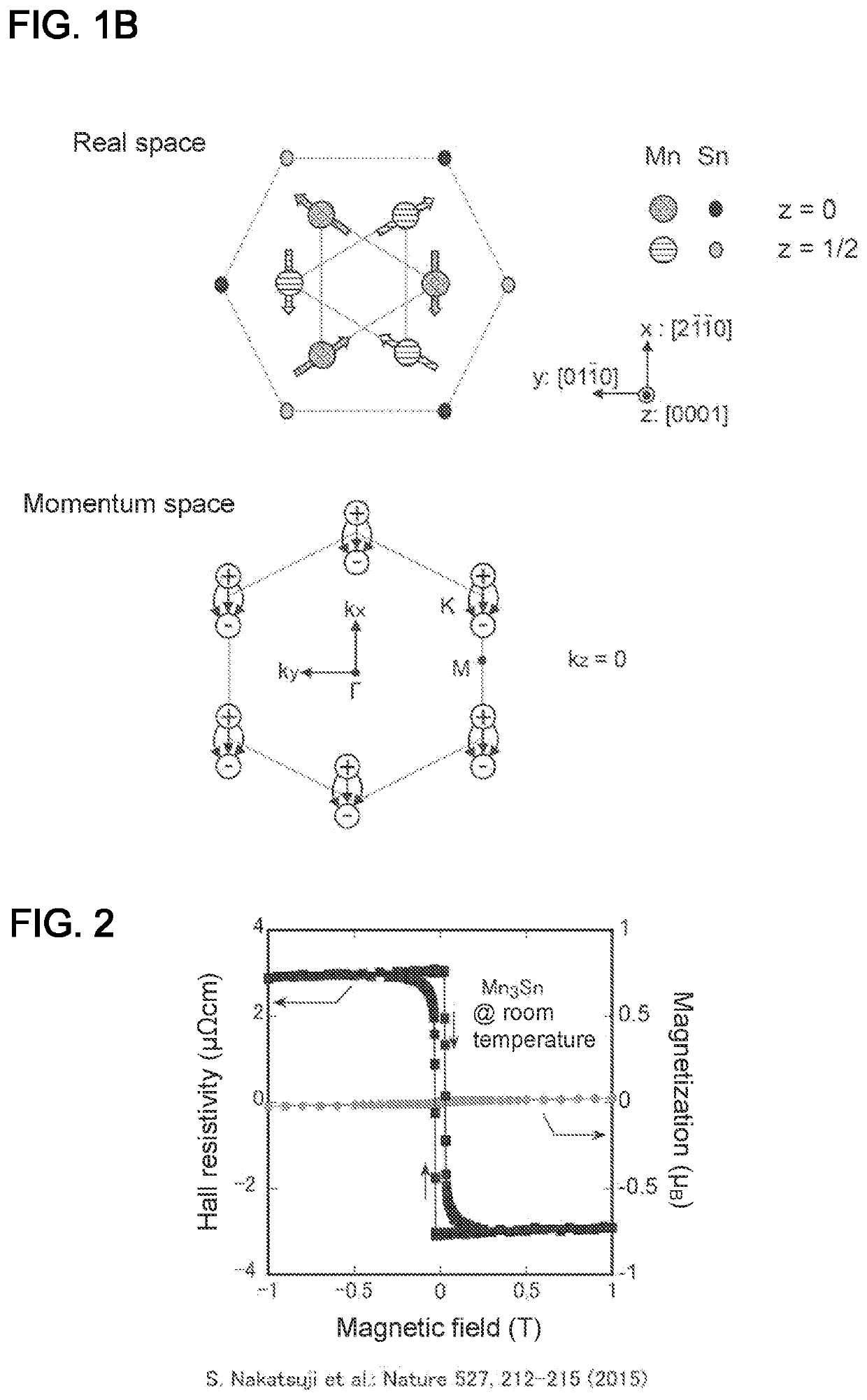
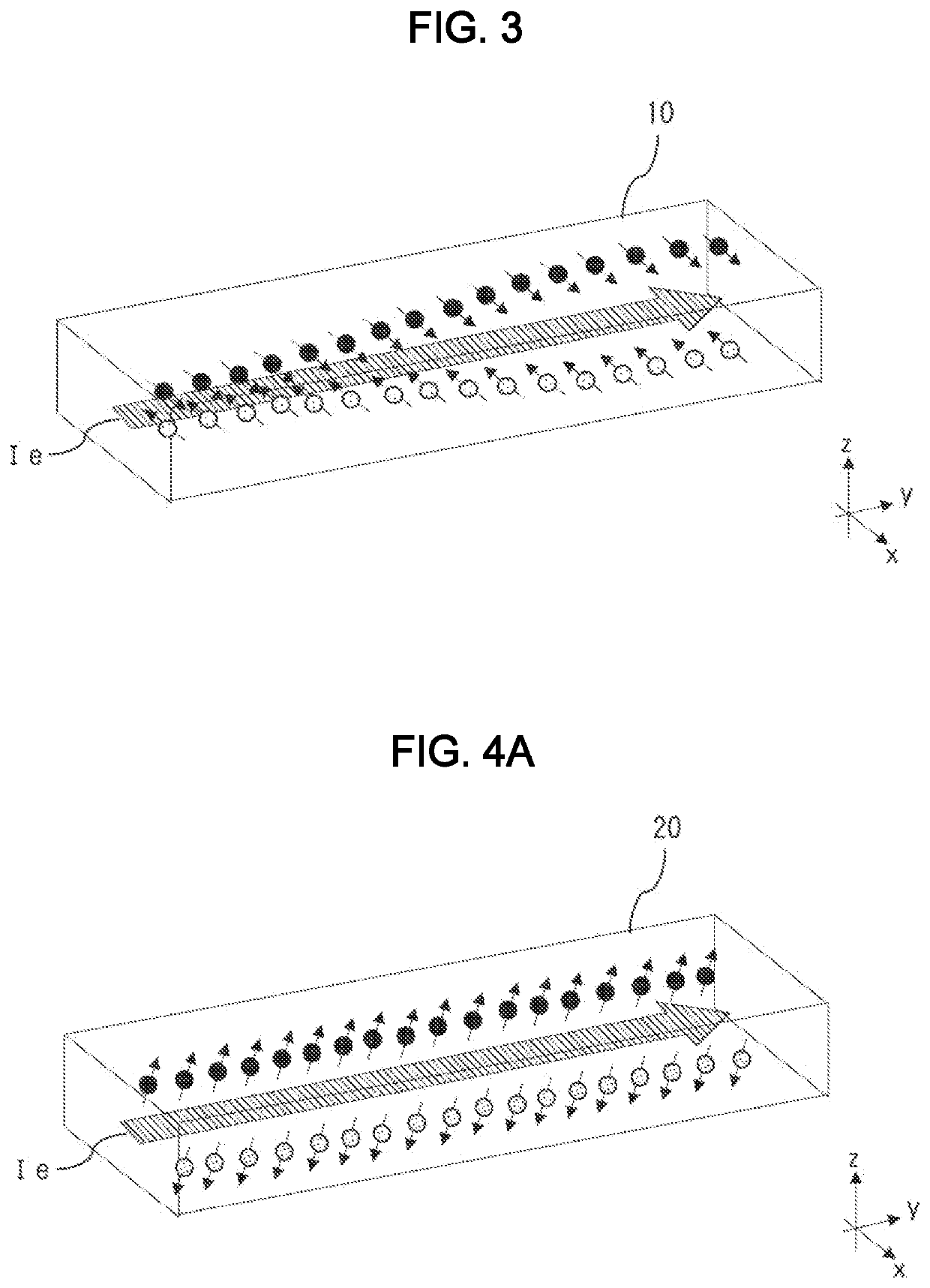
[0026]Ferromagnets exhibit a relatively large magnetization, and thus have been used extensively as key components of various devices including motors, power generators, magnetic sensors, and magnetic memories. Antiferromagnets, on the other hand, exhibit a very tiny magnetization, show an extremely small response, and are hard to control as opposed to ferromagnets, which leads to limited applications.
[0027]In recent years, spintronics for magnetic memories has required high density and high-speed processing. A memory cell with an antiferromagnetic component produces almost no stray fields because of a tiny magnetization described above. Therefore, antiferromagnets would be suitable for use in high-density magnetic memories. Moreover, antiferromagnets typically have a resonant f
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap