Decoupled alignment axis for fold mirror adjustment
a technology of alignment axis and fold mirror, which is applied in the direction of optics, optical elements, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not easy to determine that the correct rotation has been achieved, time-consuming iterative process, and the need for translation and translation of scanlines
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
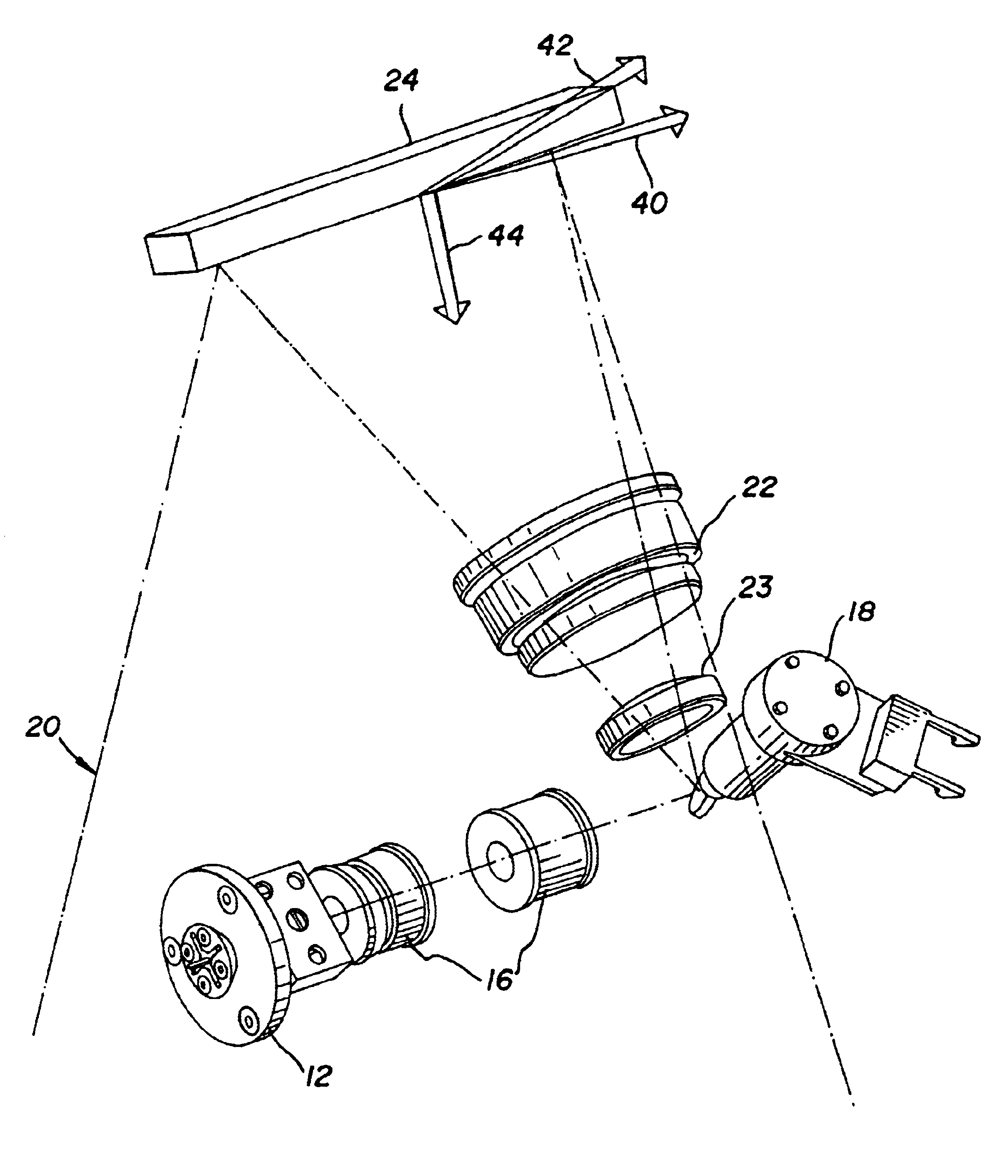
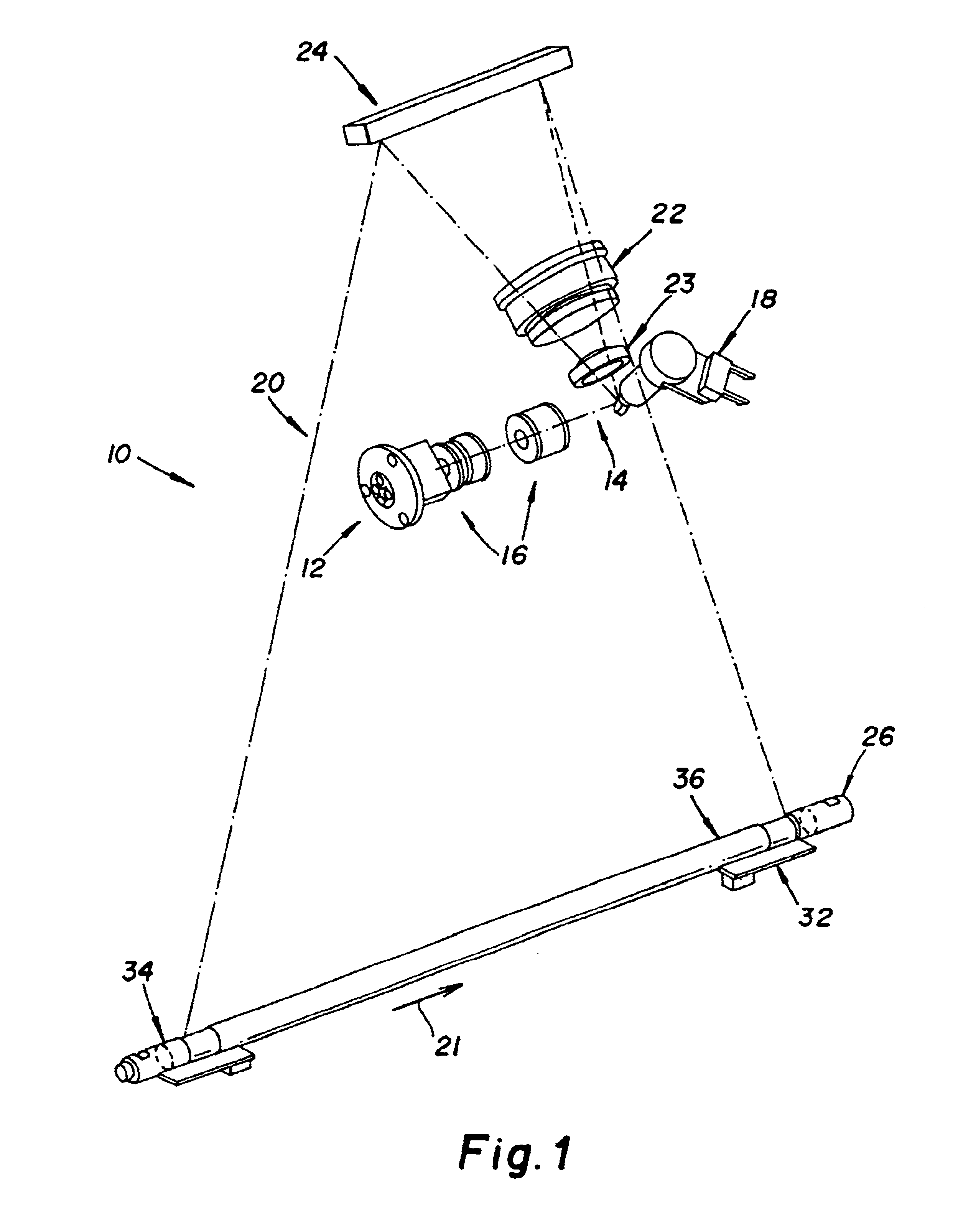
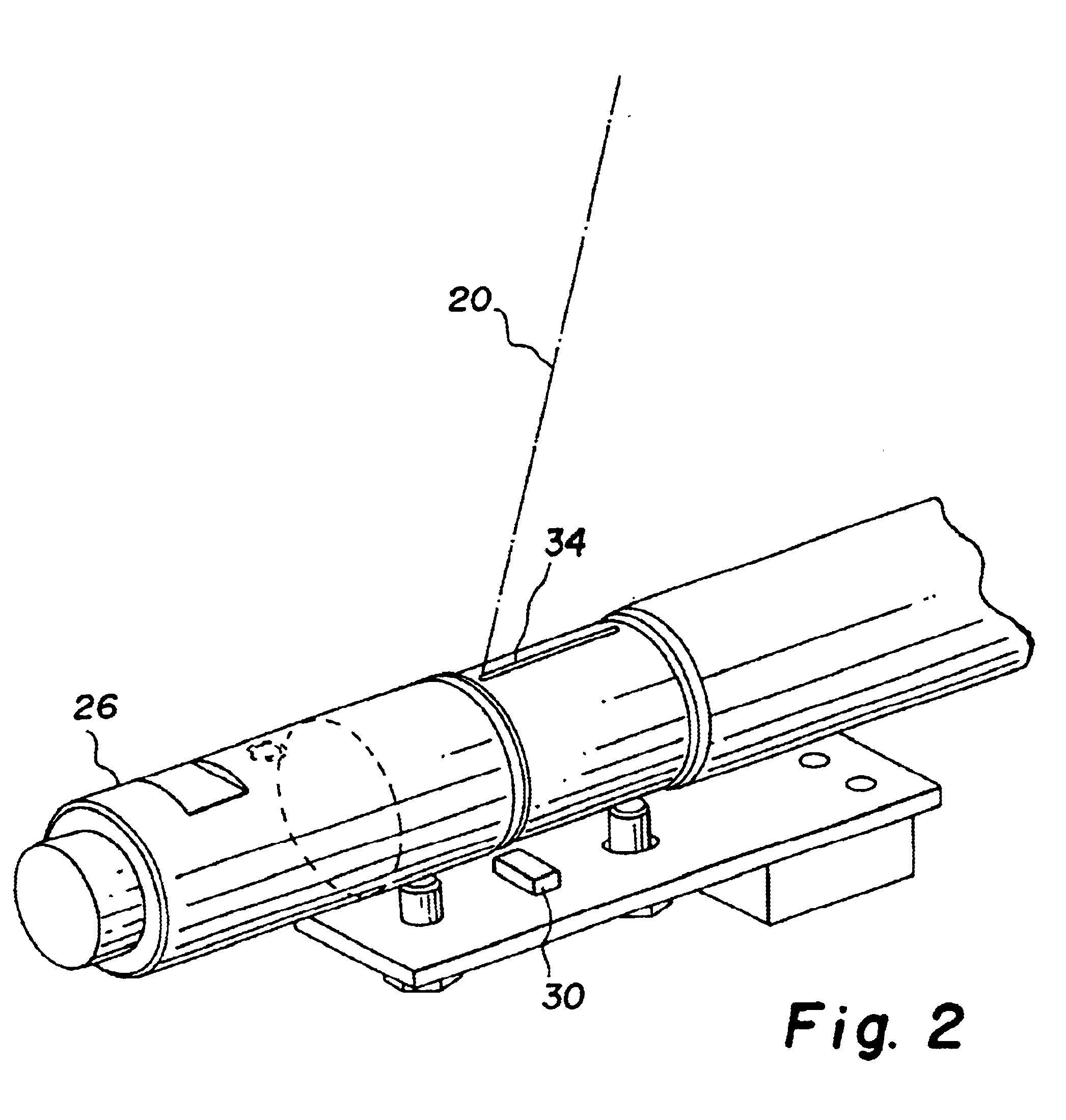
Referring now to FIGS. 1-3, there is shown a laser scanning optical system for use in a computed radiography scanning system (or any other similar scanning system) incorporating an embodiment of the present invention. As shown, laser scanning optical system 10 includes a laser diode 12 which produces a laser beam 14 shaped by shaper lens elements 16. A reciprocating galvonometer mirror 18 produces a laser beam scan line 20 in a fast scan direction 21 shaped by F-theta lens 22 and lens 23. A final fold mirror 24 directs scan line 20 onto platen 26. Platen 26 establishes an imaging region for a storage phosphor plate transported in a slow scan direction 28 over platen 26. Sensors 30 and 32 are located at the ends of scan line 20 and are activated by laser beam 14 passing through respective slits 34 and 36 in platen 26. A rotating multifaceted polygon mirror can also be used in place of the reciprocating galvonometer mirror 18 to produce laser beam scan line 20.
FIG. 3 illustrates the thre
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap