Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7 results about "Varistor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A varistor is an electronic component with an electrical resistance that varies with the applied voltage. Also known as a voltage-dependent resistor (VDR), it has a nonlinear, non-ohmic current–voltage characteristic that is similar to that of a diode. In contrast to a diode however, it has the same characteristic for both directions of traversing current. Traditionally, varistors were indeed constructed by connecting two rectifiers, such as the copper-oxide or germanium-oxide rectifier in anti-parallel configuration. At low voltage the varistor has a high electrical resistance which decreases as the voltage is raised. Modern varistors are primarily based on sintered ceramic metal-oxide materials which exhibit directional behavior only on a microscopic scale. This type is commonly known as the metal-oxide varistor (MOV).
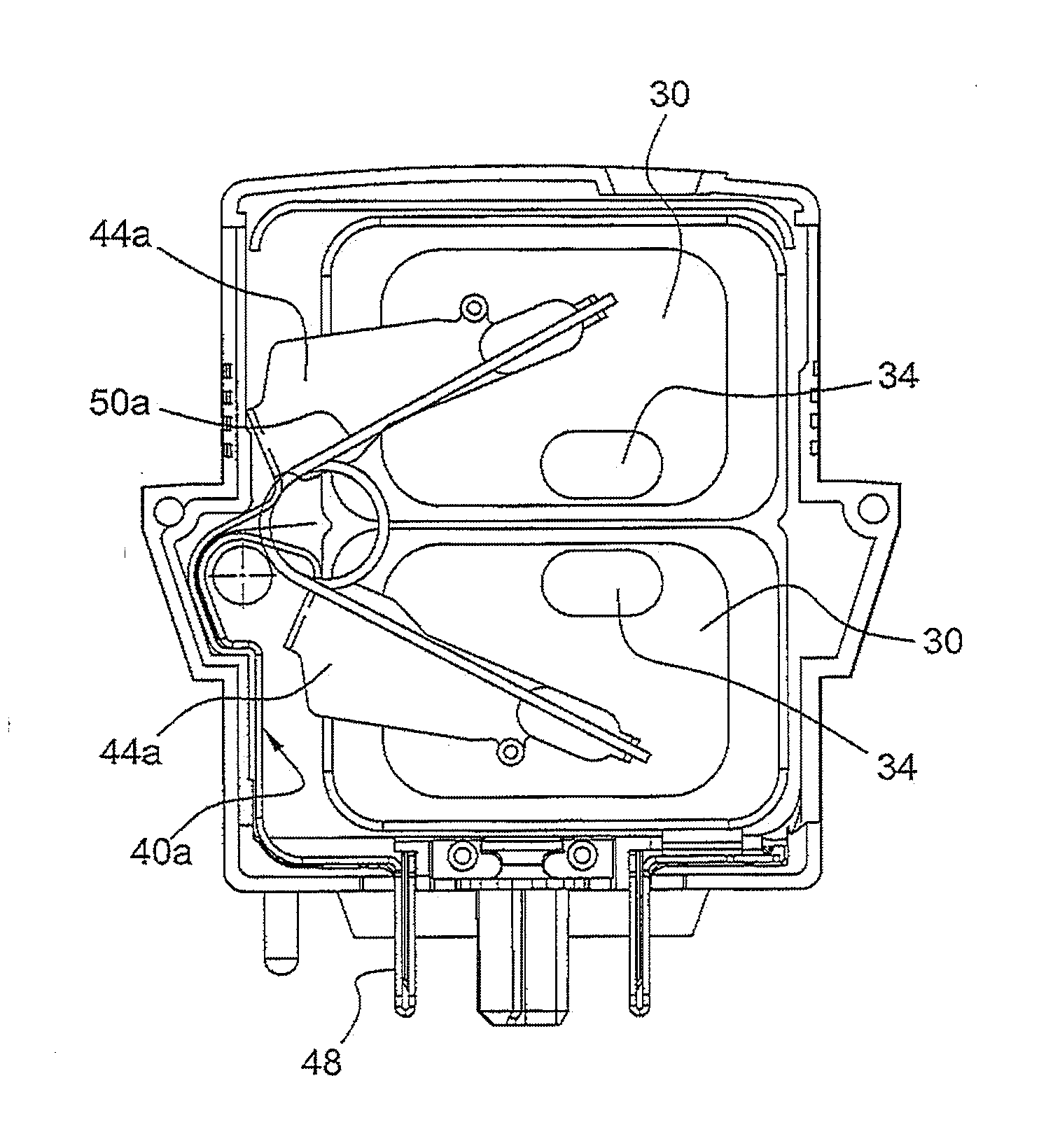
Varistor comprising an electrode having a protruding portion forming a pole and protection device comprising such a varistor
ActiveUS20110248816A1Current responsive resistorsEmergency protective arrangement detailsVaristorElectrical and Electronics engineering
Owner:ABB FRANCE SAS
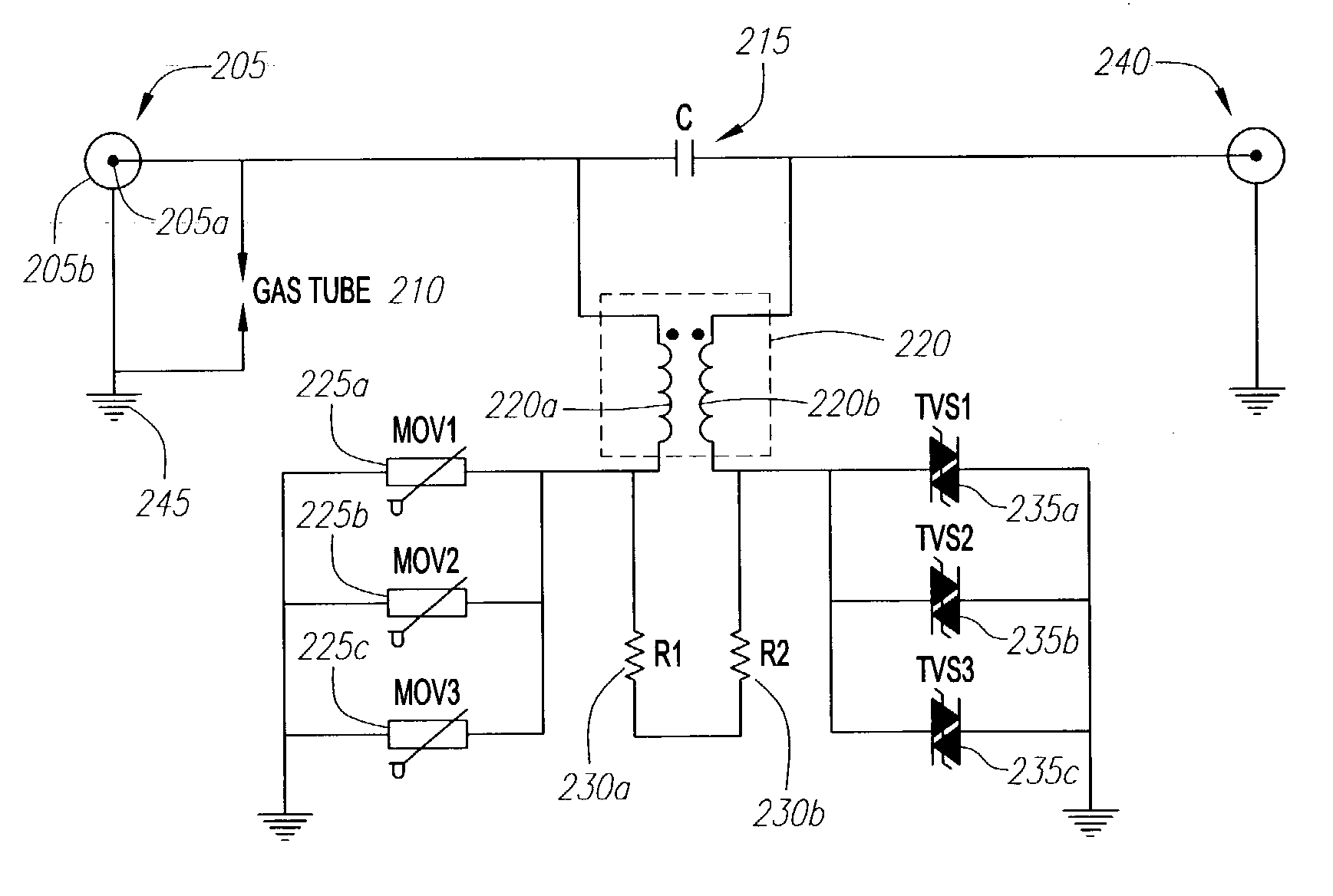
Circuit for diverting surges and transient impulses
InactiveUS20050259376A1High bandwidthSmall sizeCoupling device detailsEmergency protective arrangement detailsElectrical conductorTransformer
Owner:INFINITE ELECTRONICS INT INC
Laminated varistor, mounting structure of laminated varistor, and varistor module
InactiveUS20060061449A1Improve Radiation PerformanceCurrent responsive resistorsResistor electrostatic/electromagnetic shieldingElectrical conductorHeat generation
A laminated varistor having excellent radiation capability is provided. A heat conductor portion is disposed on the top surface of a rectangular parallelepiped laminated chip including a plurality of first conductor layers and a plurality of second conductor layers disposed alternately in a lateral direction with varistor layers therebetween, and the heat conductor portion is connected to a top end of each second conductor layer. Therefore, when the heat from an exothermic device, e.g., an IC, disposed in the vicinity is transferred to each of the first conductor layers and the second conductor layers via a first electrode portion and a second electrode portion or when heat generation occurs as a current passes through the varistor layers, the heat is directly and highly efficiently transferred from each second conductor layer to the heat conductor portion, and is effectively released to the outside from the heat conductor portion.
Owner:TAIYO YUDEN KK
Large magnetic field system capable of being controlled at high precision and turned off quickly
PendingCN113078889AExperimental structure is simpleEasy to operateElectronic switchingHelmholtz coilField-effect transistor
The invention discloses a large magnetic field system capable of being controlled with high precision and turned off quickly. An IGBT switch module comprises an insulated gate bipolar transistor, a first piezoresistor and a second piezoresistor, the drain electrode of a field effect transistor is connected with the emitter electrode of the insulated gate bipolar transistor, the drain electrode and the source electrode of the field effect transistor are connected with a third piezoresistor in parallel, The Feshbach coil comprises a first Helmholtz coil and a second Helmholtz coil, both the first Helmholtz coil and the second Helmholtz coil are formed by winding copper pipes, and both the first Helmholtz coil and the second Helmholtz coil are provided with water inlet holes and water outlet holes. According to the invention, the piezoresistor is used for dissipation, and the insulated gate bipolar transistor is combined to realize rapid turn-off of a large magnetic field; a PID controller is used for feeding back the current in the Feshbach coil so as to control the current; and the output voltage of the current source is externally controlled, so that two or more parallel current sources output different voltages under different currents.
Owner:INNOVATION ACAD FOR PRECISION MEASUREMENT SCI & TECH CAS
Insulating blocking head with sensing function
InactiveCN107782922AElectrical measurement instrument detailsElectrical testingVaristorHigh pressure
Owner:江苏科兴电器有限公司
Tripping type lightning protection piezoresistor
InactiveCN113314281AResistor cooling/heating/ventillationNon-adjustable resistorsVaristorEngineering
Owner:户壮
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap