Nutrient switching method for culturing oleaginous microalgae
A technology of oil-producing microalgae and culture medium, which is applied in the direction of single-cell algae, biofuel, fermentation, etc., and can solve the problems of loss, long growth cycle, and low biomass production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
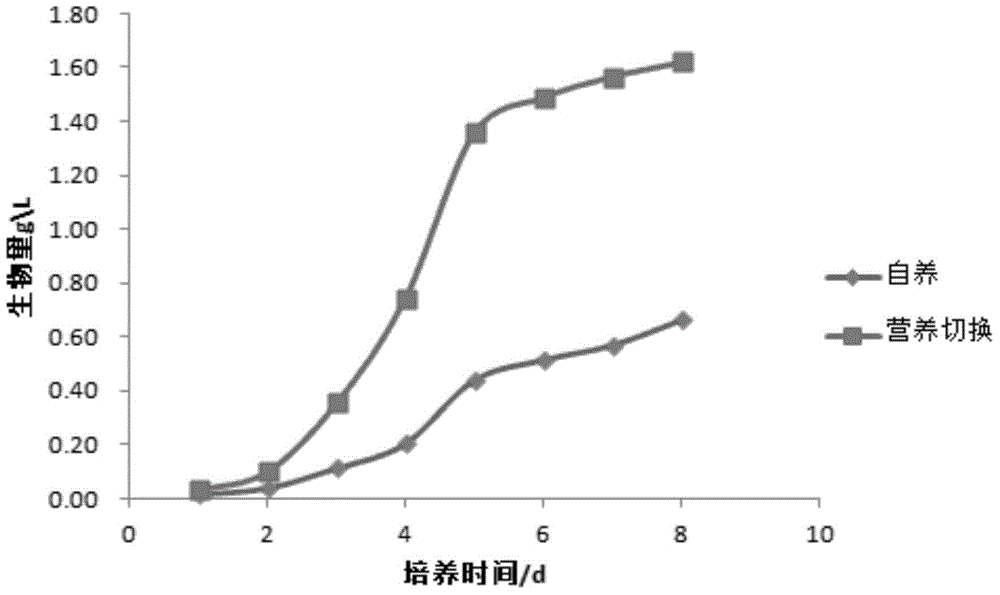
[0026] Example 1 Chlorella pyrenoidosa
[0027] (1) Activation of Chlorella pyrenoidosa: Prepare 50ml of BG11 culture medium and pour it into a conical flask. After autoclaving, pick a single colony from a solid plate for inoculation, and place it under 3000lux light intensity for 24 hours of light culture 7 days to logarithmic growth phase.
[0028] (2) Add 600ml of BG11 medium containing 5g / L glucose in a 1L aeration bottle, after autoclaving, draw 20ml of fully activated algae liquid from the Erlenmeyer flask described in step (1) for inoculation, and the initial pH value of the cultivation is 7.5, the initial inoculum concentration is 0.05g / L, the culture temperature is 25 degrees Celsius, and placed under the light intensity of 8000lux and the aeration rate of 0.3vvm for aeration culture, and the light-dark ratio is controlled at 16h:8h. Through the control of the light-dark ratio, The oleaginous microalgae in the logarithmic growth phase are switched between light and
Embodiment 2
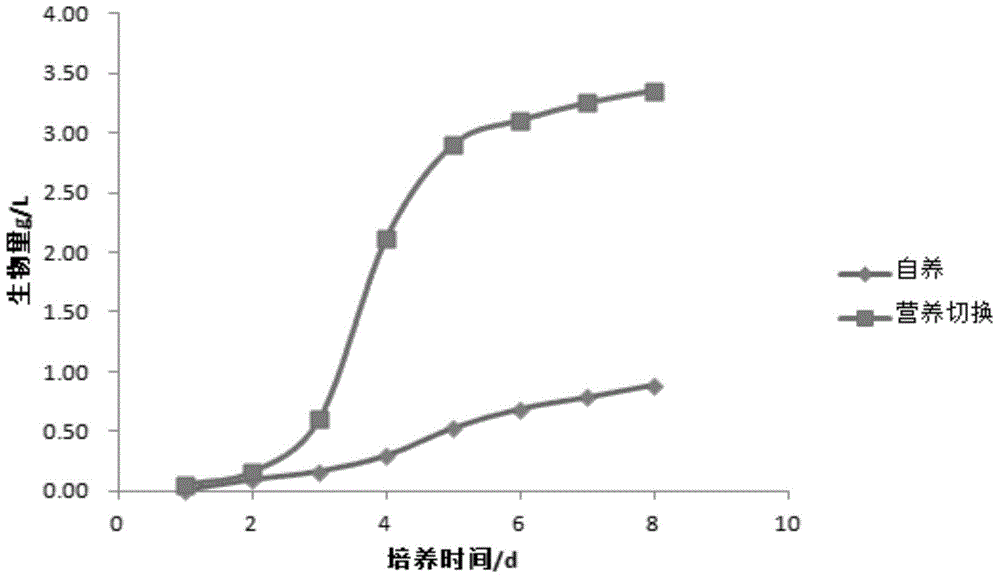
[0035] Example 2 Chlorella sorokiniana GS02
[0036] (1) Activation of Chlorella sorokiniana GS02: Prepare 50ml of BG11 medium and pour it into a conical flask. After autoclaving, pick a single colony from a solid plate for inoculation, and place it under 4000lux light intensity for 24 hours of light culture 7 days to logarithmic growth phase.
[0037](2) Add 500ml of BG11 medium containing 10g / L glucose in a 1L aeration bottle, after autoclaving, draw 35ml of fully activated algae liquid from the Erlenmeyer flask described in step (1) for inoculation, and the initial pH of the cultivation is 8.0, the initial inoculum concentration is 0.1g / L, the culture temperature is 30 degrees Celsius, and placed under the light intensity of 10000lux with 0.5vvm ventilation rate for aeration culture, the control light-dark ratio is 12h:12h, through the control of light-dark ratio, The oleaginous microalgae in the logarithmic growth phase are switched between light and no light environment
Embodiment 3
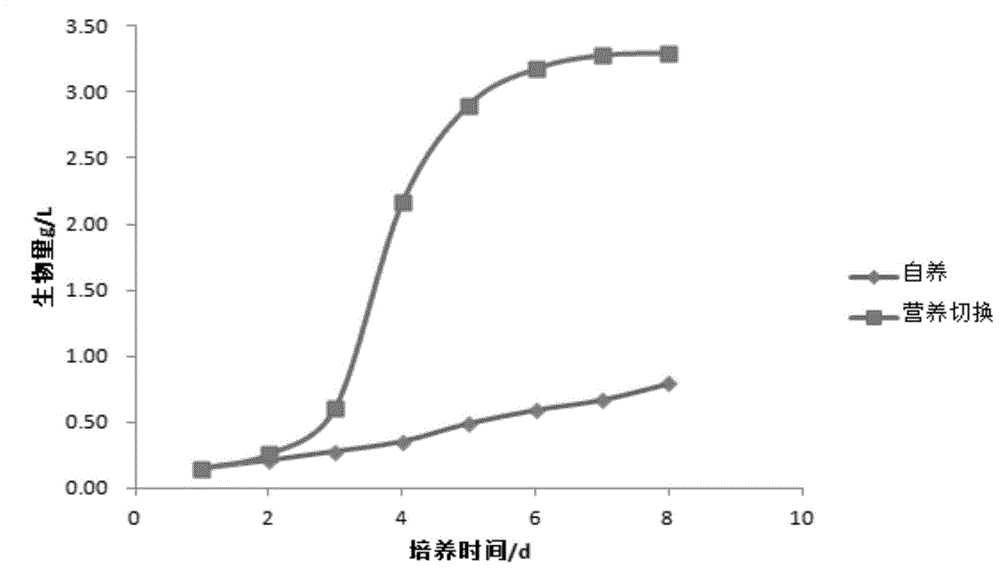
[0043] Example 3 Chlorella sorokiniana GS02
[0044] (1) Activation of Chlorella sorokiniana GS02: Prepare 60ml of BG11 medium and pour it into a conical flask. After autoclaving, pick a single colony from a solid plate for inoculation, and place it under 4000lux light intensity for 24 hours of light culture 7 days to logarithmic growth phase.
[0045] (2) Add 500ml of BG11 medium containing 10g / L glucose in a 1L aeration bottle, after autoclaving, draw 50ml of fully activated algae liquid from the Erlenmeyer flask described in step (1) for inoculation, and the initial pH of the cultivation is 8.5, the initial inoculum concentration is 0.15g / L, the culture temperature is 28 degrees Celsius, and it is placed under the light intensity of 6000lux and the aeration rate is 0.7vvm for aeration culture, and the light-dark ratio is controlled to be 8h:16h. By controlling the light-dark ratio, The oleaginous microalgae in the logarithmic growth phase are switched between light and no
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap