Method of switching an optical signal in an optical flex grid network
A flexible grid, optical signal technology, applied in multiplexing communications, optical multiplexing systems, selection devices for multiplexing systems, etc., can solve the problem of not being able to offset signal impairments
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
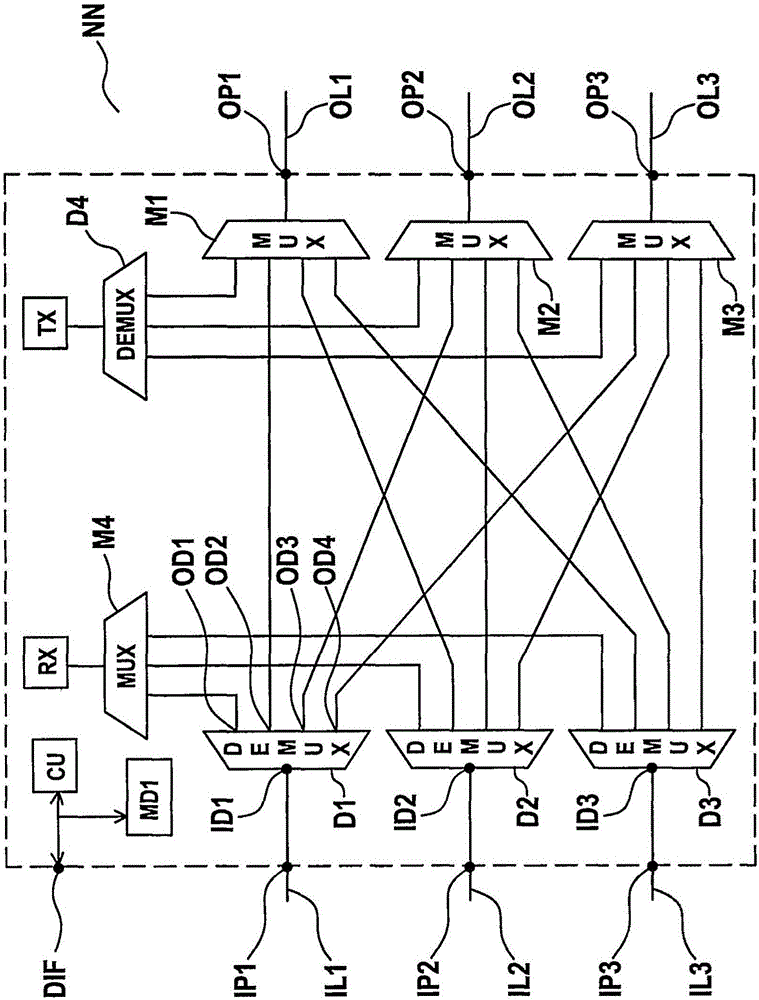
[0037] figure 1 A mesh network MN is shown in which different optical network nodes N1 , N2 , N3 , N4 are connected by different optical links such as eg optical link OL12 or optical link OL21 . At the optical link, the transmission direction is in figure 1 Inside is indicated by different arrows pointing in the corresponding transport direction.
[0038] Preferably, node N1 and node N3 are add-drop multiplexing nodes, while node N2 and node N4 are cross-connect nodes. The network nodes additionally mentioned below in this document may be add / drop multiplex nodes or cross-connect nodes.
[0039] An optical connection from one of these nodes (e.g. node N1) to another of these nodes (e.g. node N3) can be established by a so-called optical path, which goes from Node N1 to node N2 and then travels from node N2 to node N3 via the optical link with index 23 . It can be assumed that the wavelength of the optical signal transmitted at node N1 in the direction towards node N3 along...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap