A microwave or millimeter wave RF part realized by die-forming
a technology of die-forming and microstrip lines, applied in waveguides, antennas, domestic articles, etc., can solve the problems of large losses in dielectric and conductive parts of microstrip networks, conductive losses are very high due to the miniaturization, and microstrip lines can only be made wider, so as to achieve cost-effective production and good performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0096]In the following detailed description, preferred embodiments of the present invention will be described. However, it is to be understood that features of the different embodiments are exchangeable between the embodiments and may be combined in different ways, unless anything else is specifically indicated. Even though in the following description, numerous specific details are set forth to provide a more thorough understanding of e present invention, it will be apparent to one skilled in the art that the present invention may be practiced without these specific details. In other instances, well-known constructions or functions are not described in detail, so as not to obscure the present invention.
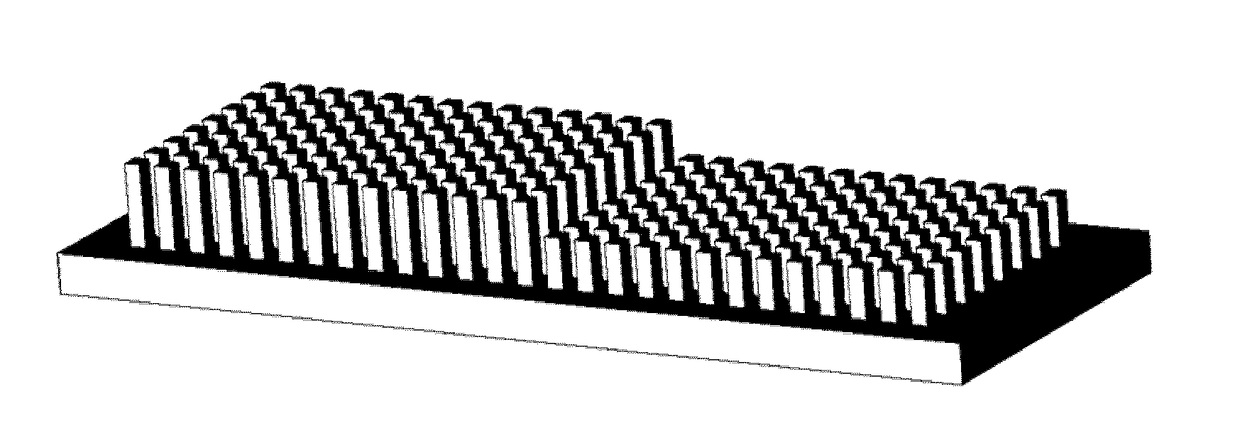
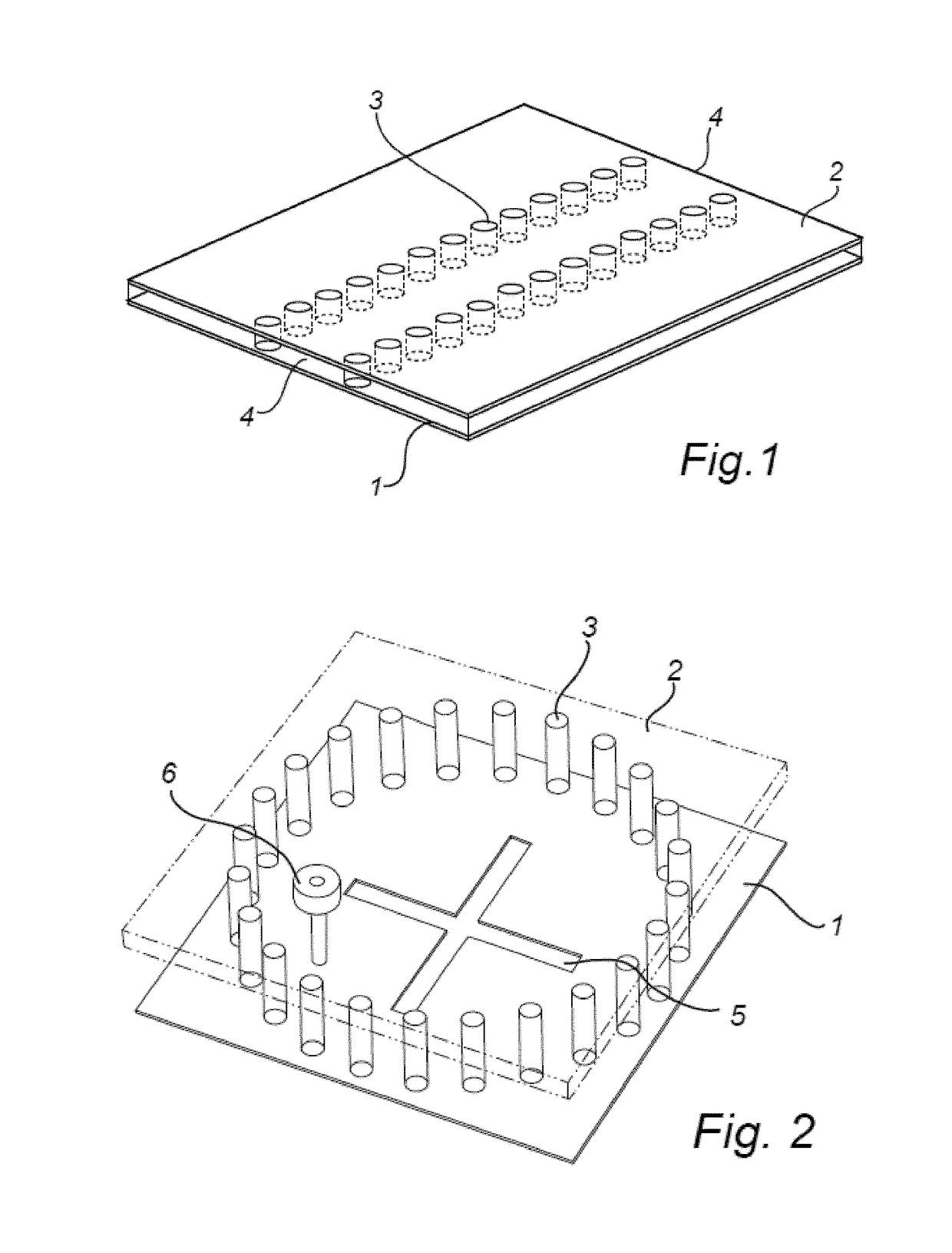
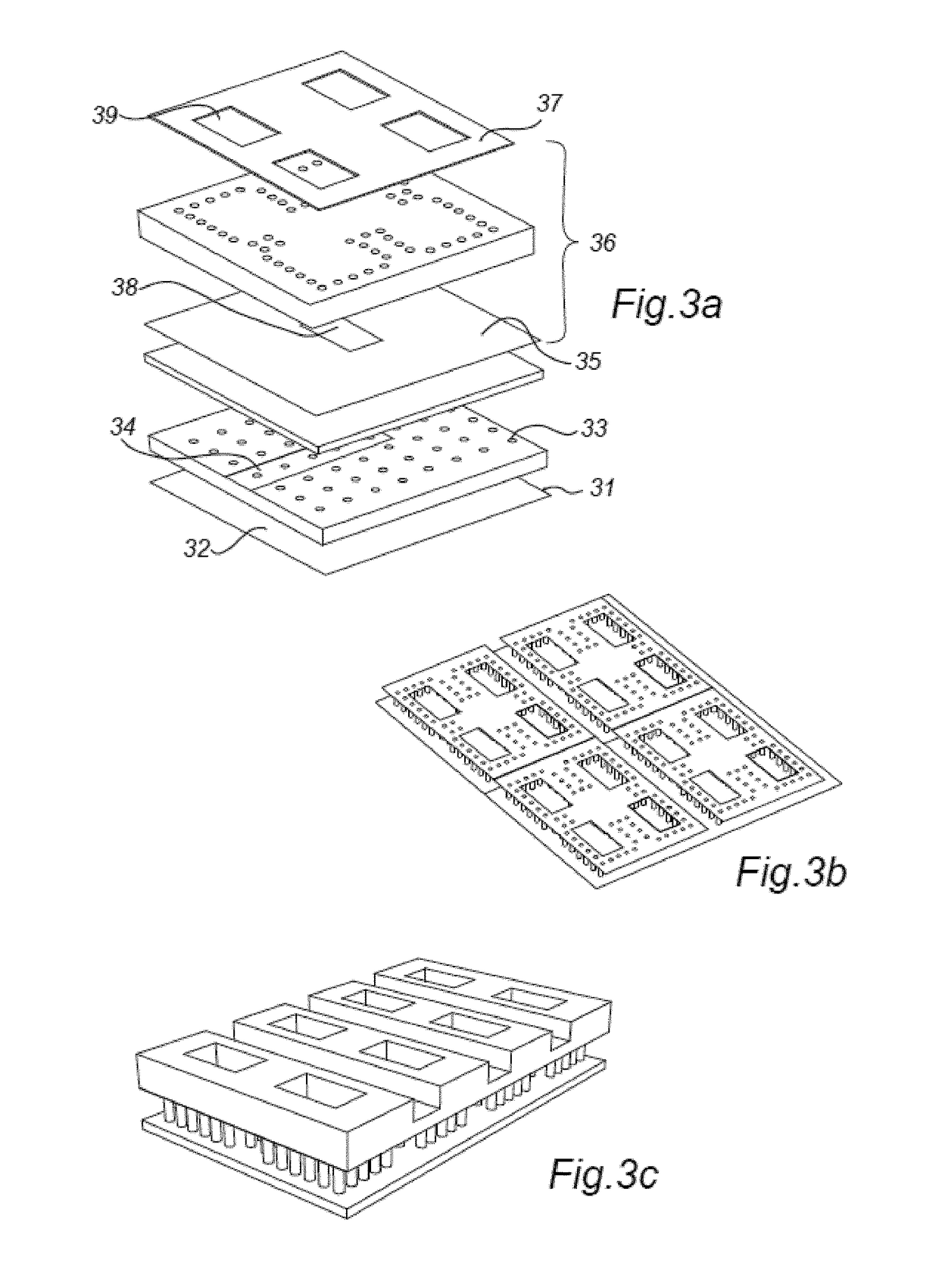
[0097]In a first embodiment, as illustrated in FIG. 1, an example of a rectangular waveguide is illustrated. The waveguide comprises a first conducting layer 1, and a second conducting layer 2 (here made semi-transparent, for increased visibility). The conducting layers are arranged at
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap