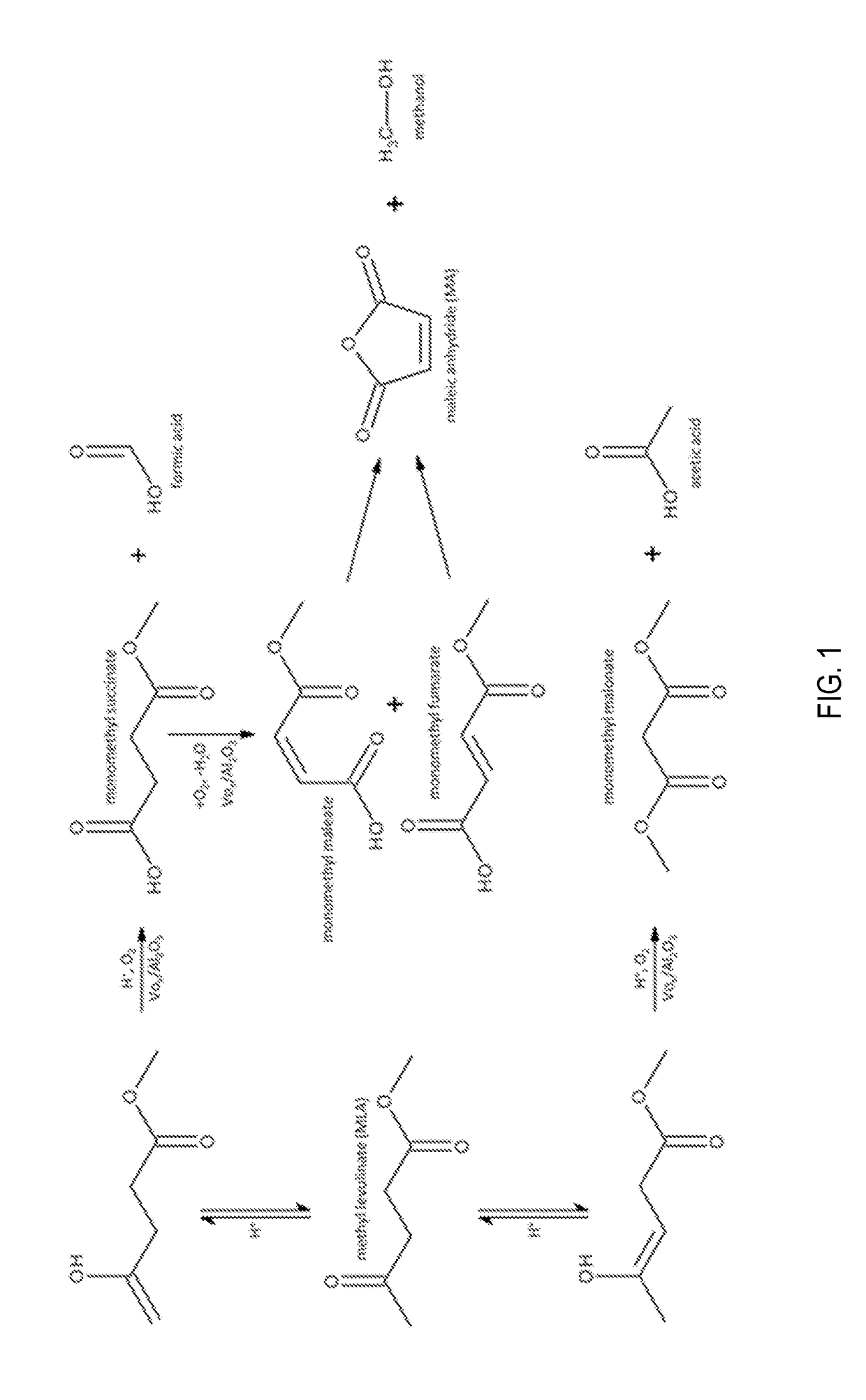
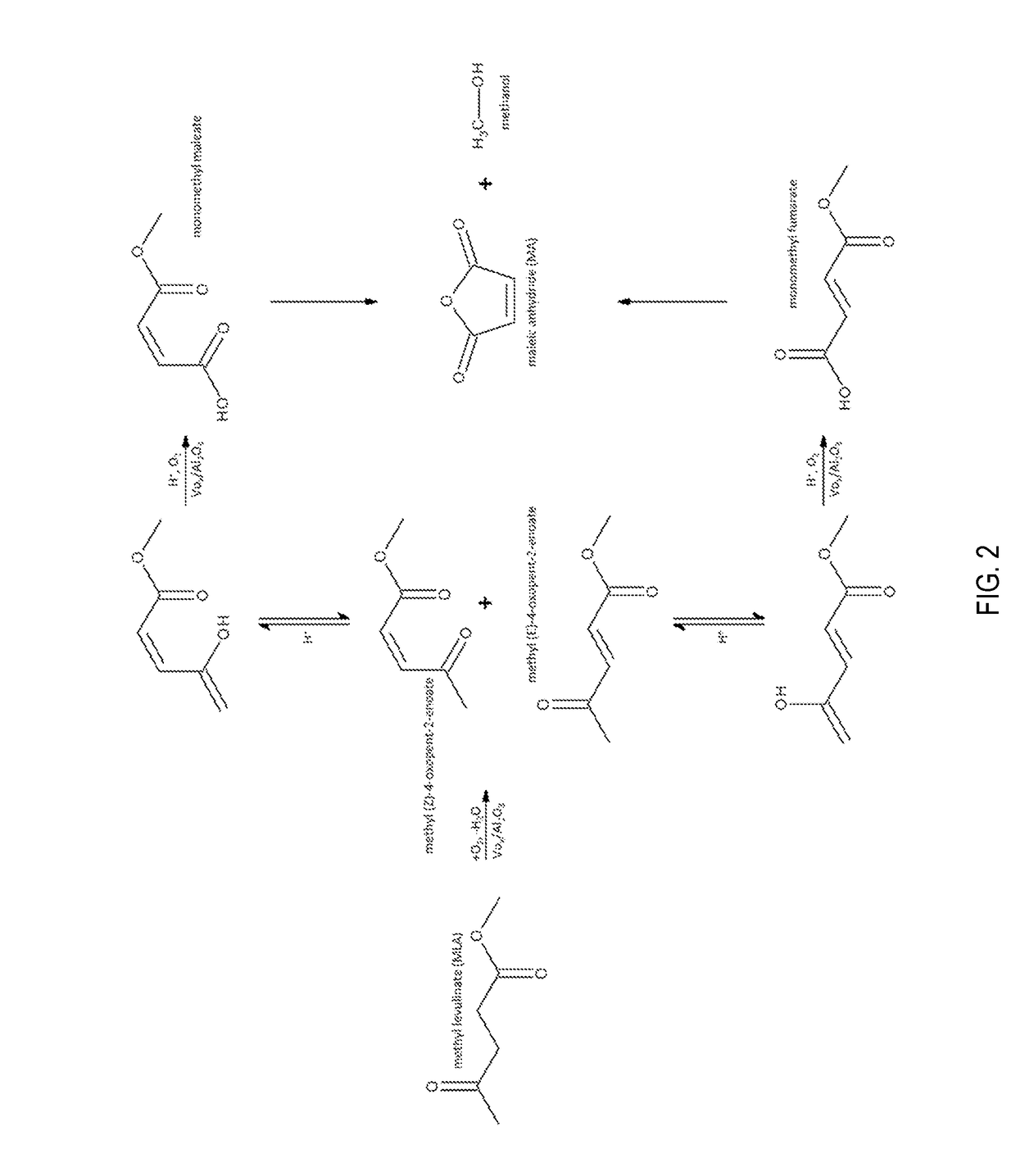
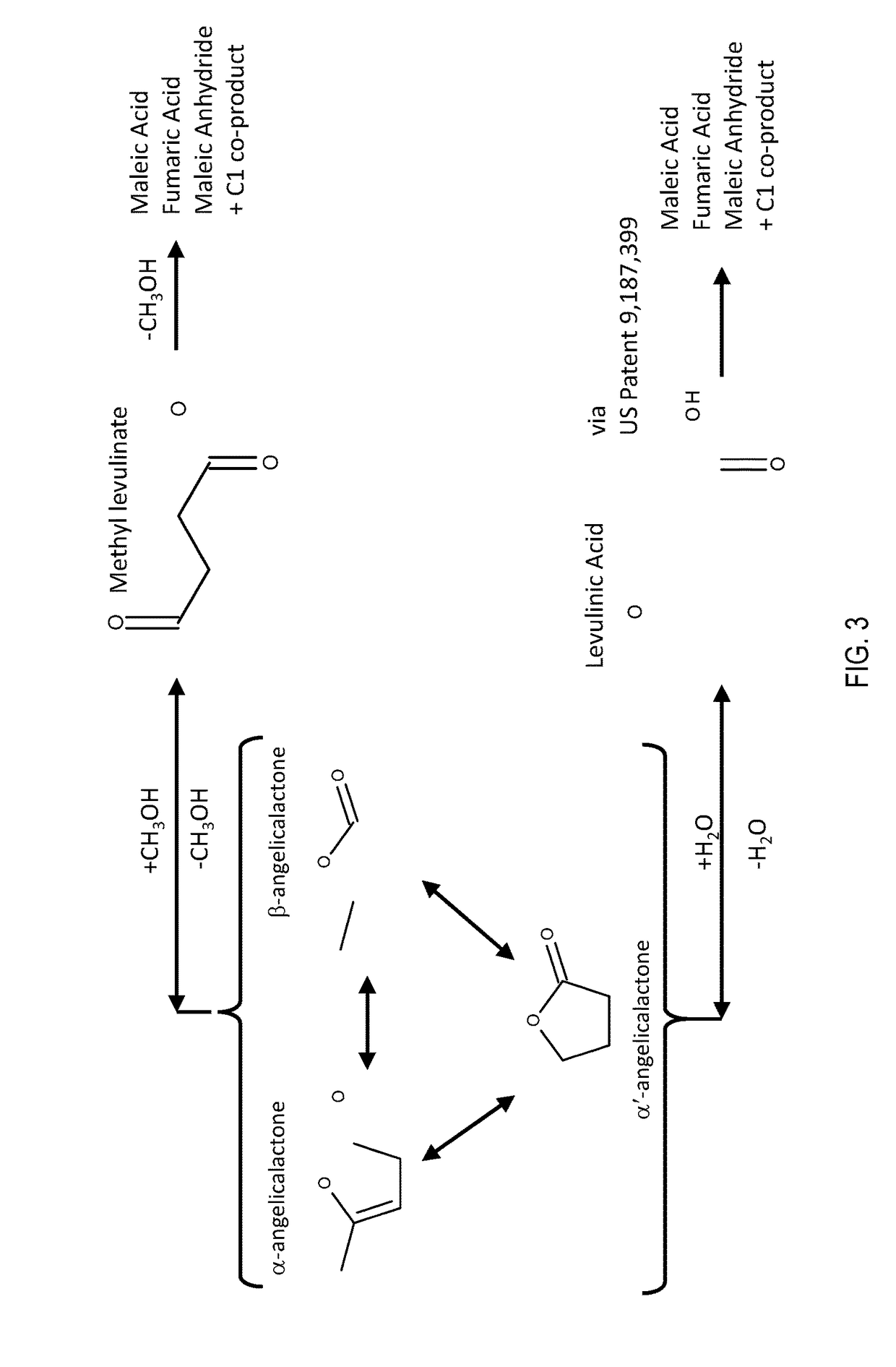
Production of maleic acid, fumaric acid, or maleic anhydride from levulinic acid analogs
a technology of fumaric acid and maleic anhydride, which is applied in the direction of catalyst activation/preparation, metal/metal-oxide/metal-hydroxide catalyst, physical/chemical process catalyst, etc. it can solve the problems of high viscosity, low vapor pressure, and high reactive ions of levulinic acid, so as to facilitate the formation of maleic anhydride and lower melting points , the effect of increasing the vapor pressur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0012]The reducible oxide catalyst used in this study was a vanadium oxide (VOx) supported at monolayer loading on γ-Al2O3. The catalyst was prepared by incipient wetness impregnation of vanadium oxalate onto γ-Al2O3. A solution of oxalic acid and ammonium metavanadate at a molar ratio of 2:1 was used to wet the surface of the alumina. The resulting powder was crushed and sieved to achieve uniform particle size and was activated by a stream of air (Airgas Ultra Zero) for 4 hours at 723 K.
[0013]The VOx / Al2O3 sample was then loaded into a catalytic packed bed reactor into which methyl levulinate and molecular oxygen was introduced in a helium diluent. ML was delivered into the system as a liquid using a Cole Parmer syringe pump (Model 100), while O2 (Airgas UHP) and He (Airgas UHP) were supplied by two Brooks 5850S mass flow controllers. ML, O2 and He were preheated to 403 K and mixed in a ½″ vessel field filled with quartz chips, which served to vaporize the ML. The gaseous mixture of
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap