Optical waveguide monitoring
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
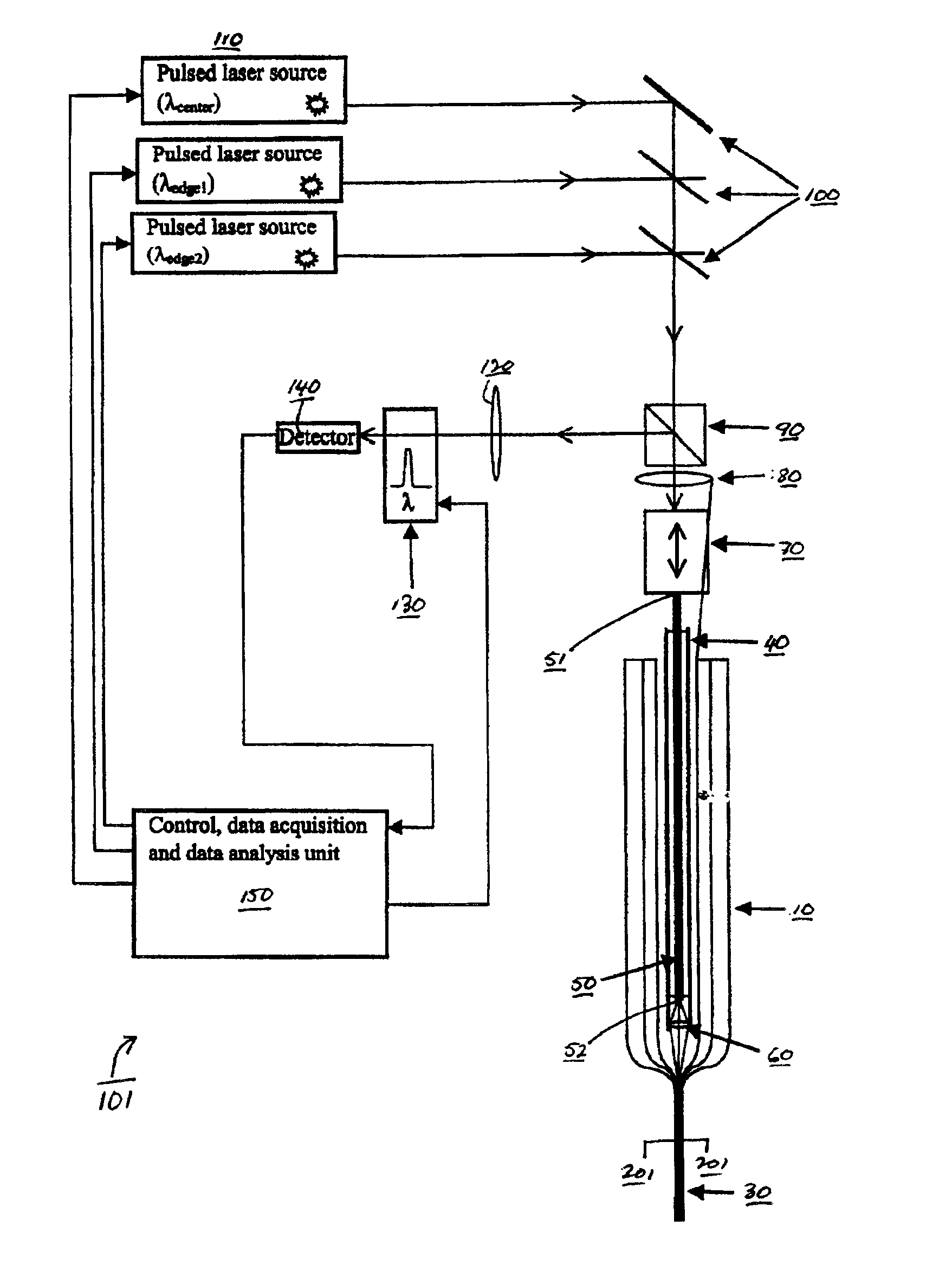
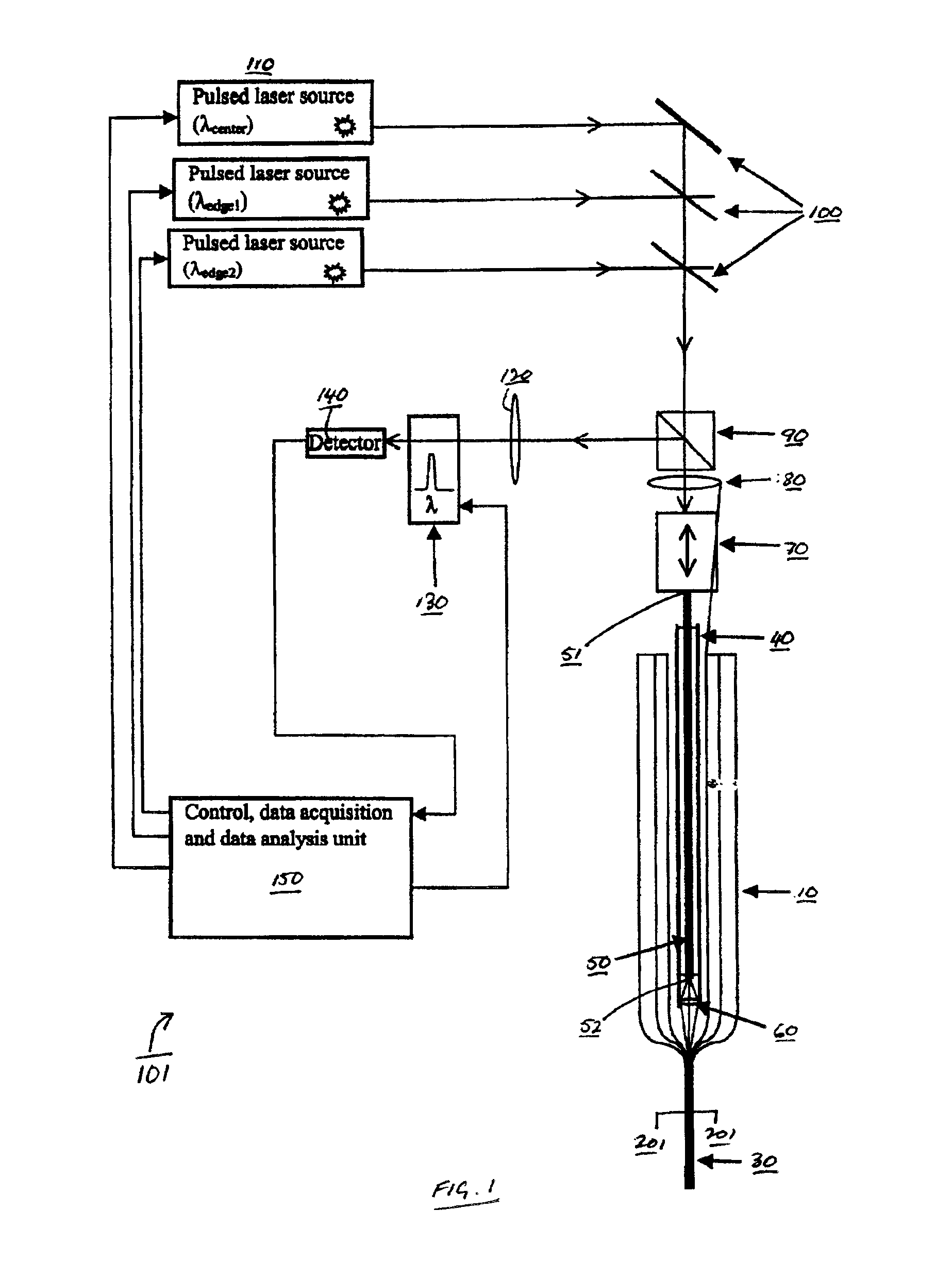
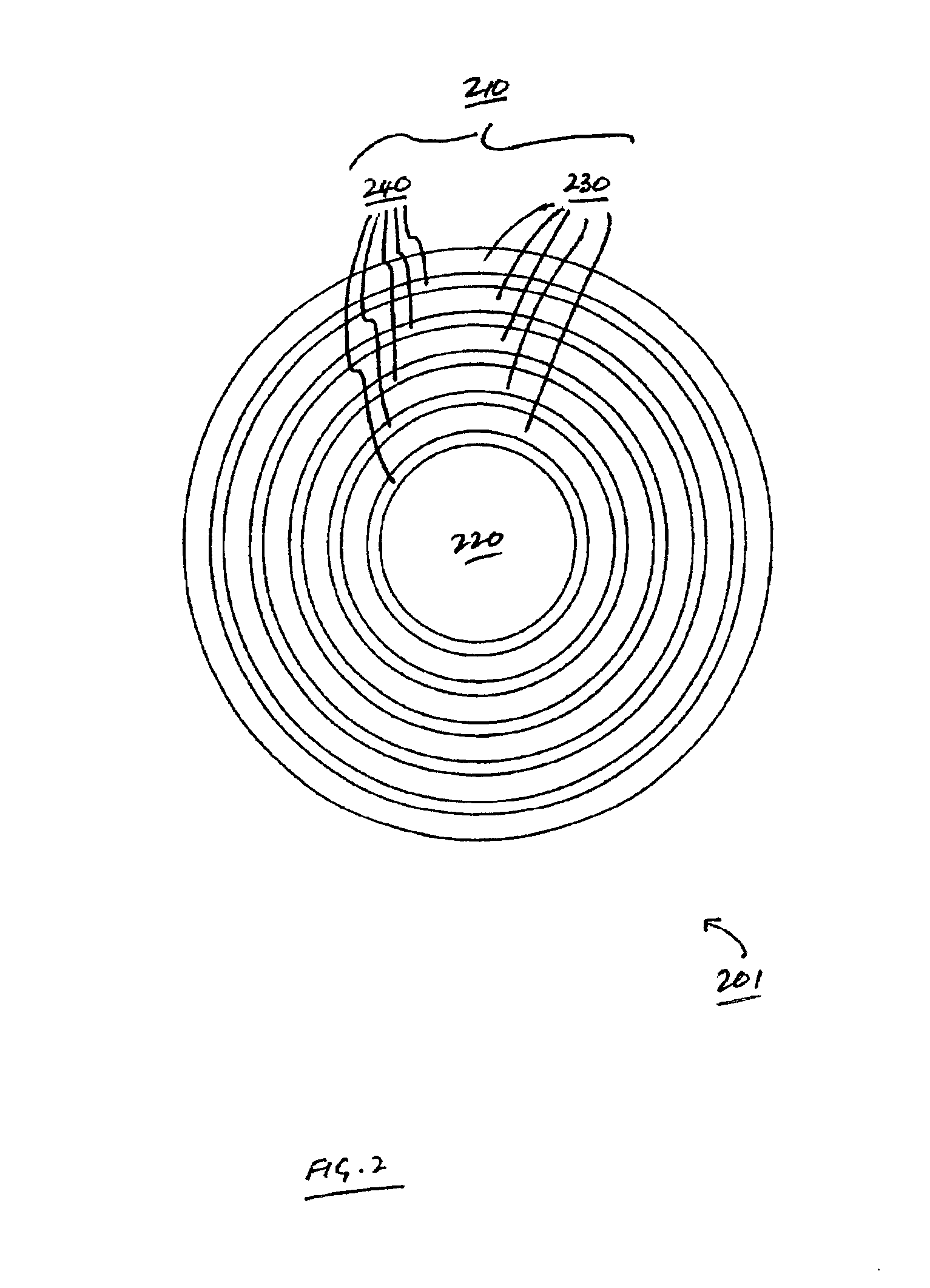
The invention features methods for detecting defects in and monitoring the transmission loss of an optical waveguide, during, for example, drawing or cabling of an optical waveguide. For example, the invention relates to monitoring the quality (e.g., monitoring transmission loss and detecting structural and compositional defects) of optical waveguides that utilize photonic bandgap confinement mechanisms for guiding light (referred to here as photonic crystal fibers), including hollow fibers. In general, defects refer to any structural, compositional or other perturbation of the fiber from its ideal design, which can affect the optical and / or mechanical performance and reliability of the fiber. Examples of defects include perturbations to core radius, perturbations to the layer thickness, delamination between layers, bubbles, particle inclusions in the core or layers, and compositional variations in the layers affecting the refractive index of the layers.
Fiber monitoring is performed
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap