Method for aggregating data in a network
a data aggregation and network technology, applied in the field of network data aggregation, can solve the problems of high cost and unreliable operation, reducing communication overhead, and providing data aggregation with end-to-end security, so as to achieve high security, reduce communication overhead, and be ready for implementation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
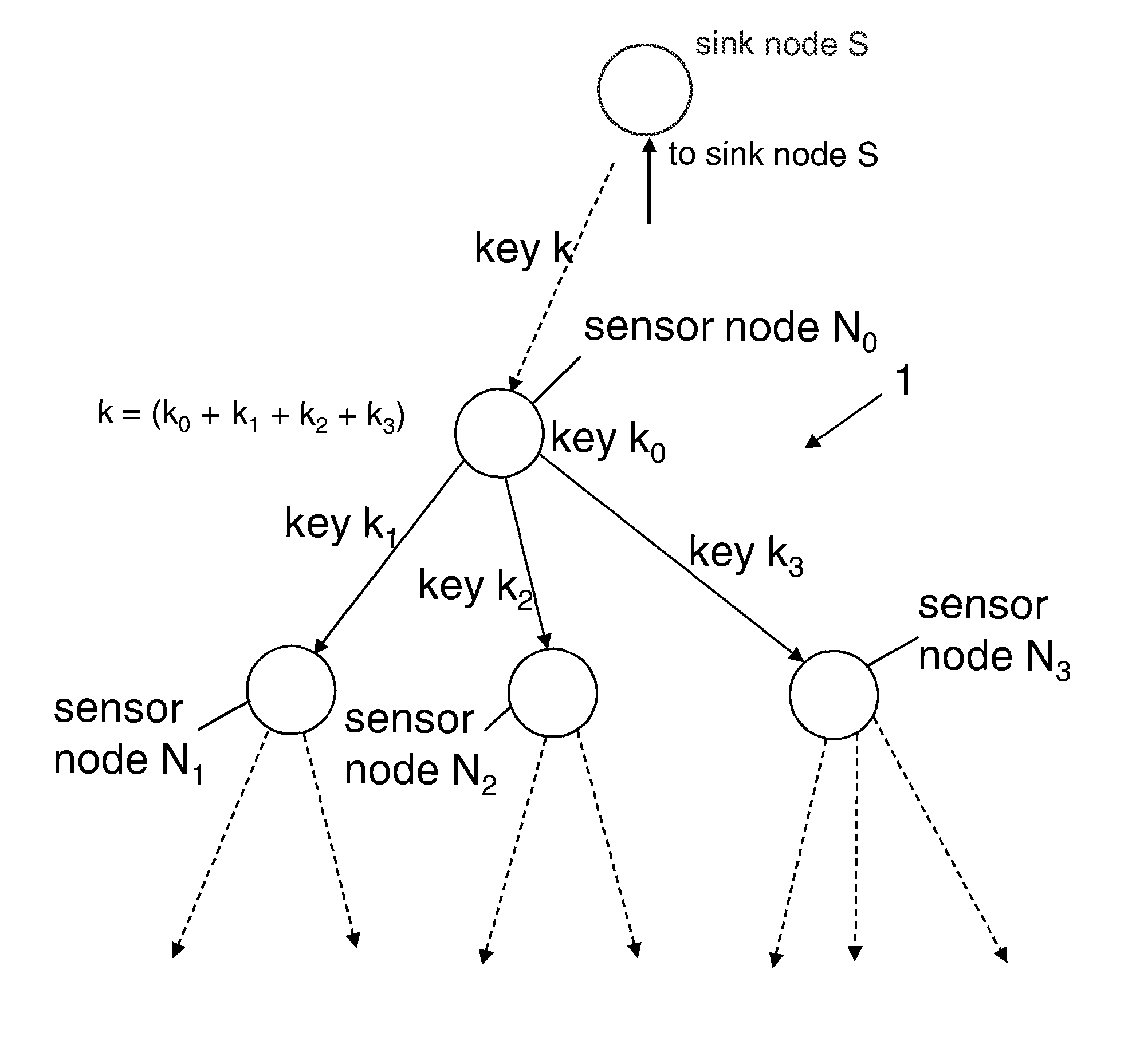
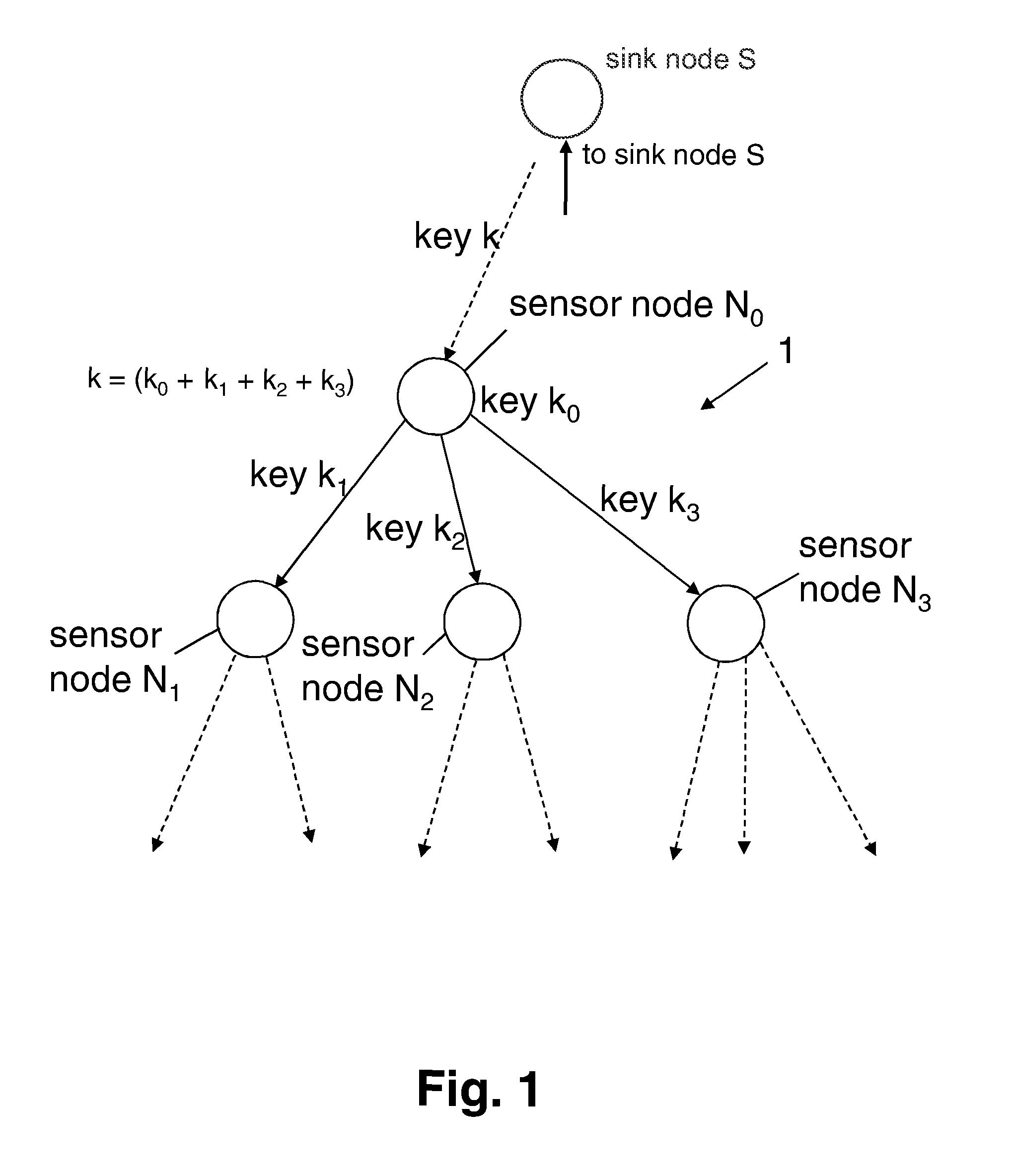
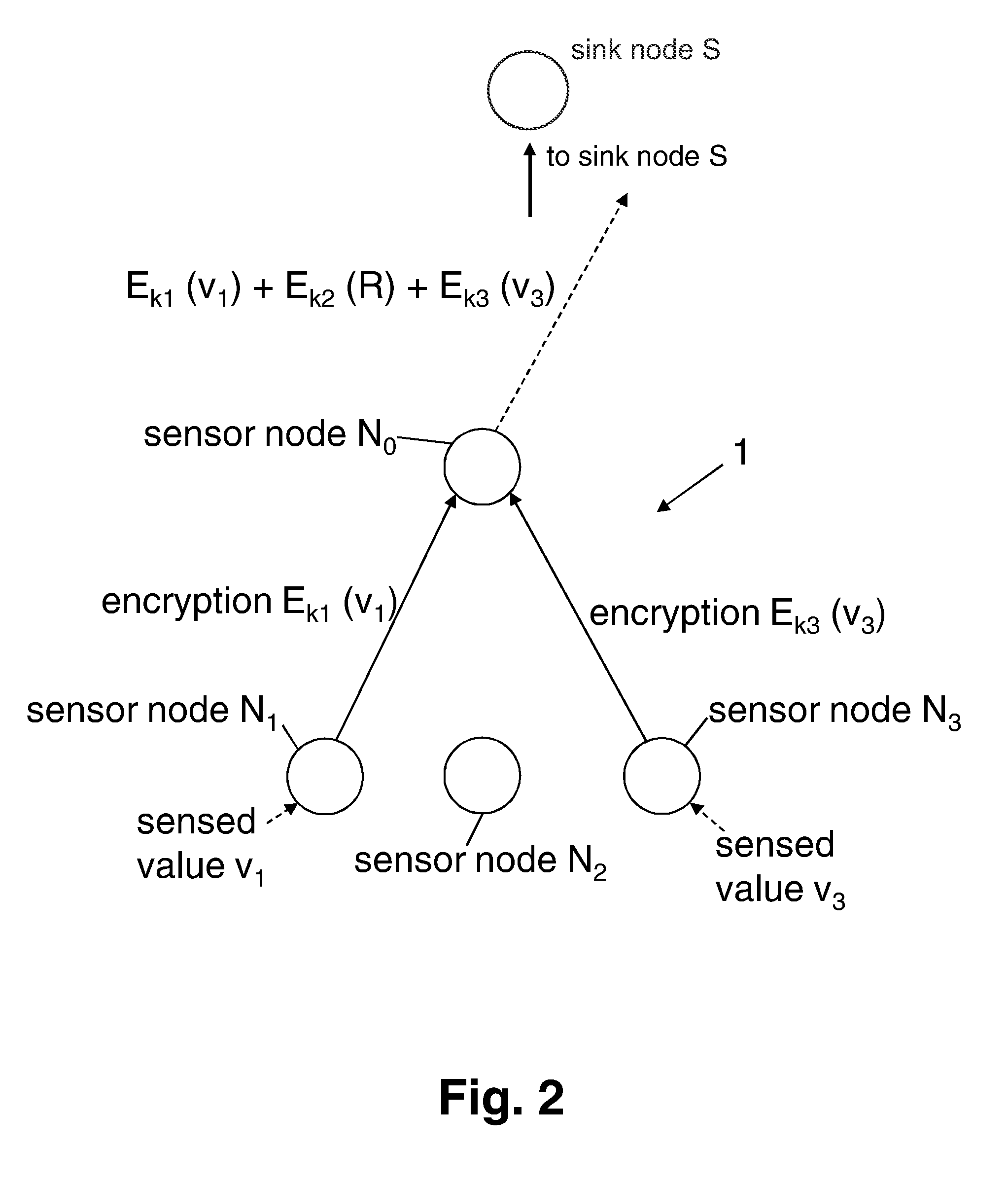
[0032]FIG. 1 illustrates schematically an embodiment of the present invention. FIG. 3 is a flow chart of the inventive method.
[0033]More precisely, the key distribution process according to the invention is shown. For the purpose of clarity and exemplary illustration, FIG. 1 only shows a very small section of a sensor network 1, the illustrated section comprising only four sensor nodes which are denominated N0, N1, N2, and N3. In practice, however, the sensor network 1 may include several thousands of sensor nodes Ni.
[0034]The initialization works top-down from the route of the sensor network 1—the sink node S—to the sensor nodes Ni. In a nutshell, every sensor node Ni receives at one point in time during the key distribution his share of the master key K which is chosen by the sink node (S100) and which is distributed to the sink nodes' successor nodes in a controlled way. In the embodiment shown in FIG. 1, sensor node N0 receives his share k of the master key K from its predecessor n
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap