Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
2 results about "Binding energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physics, binding energy (also called separation energy) is the minimum energy required to disassemble a system of particles into separate parts. This energy is equal to the mass defect minus the amount of energy, or mass, that is released when a bound system (which typically has a lower potential energy than the sum of its constituent parts) is created, and is what keeps the system together.
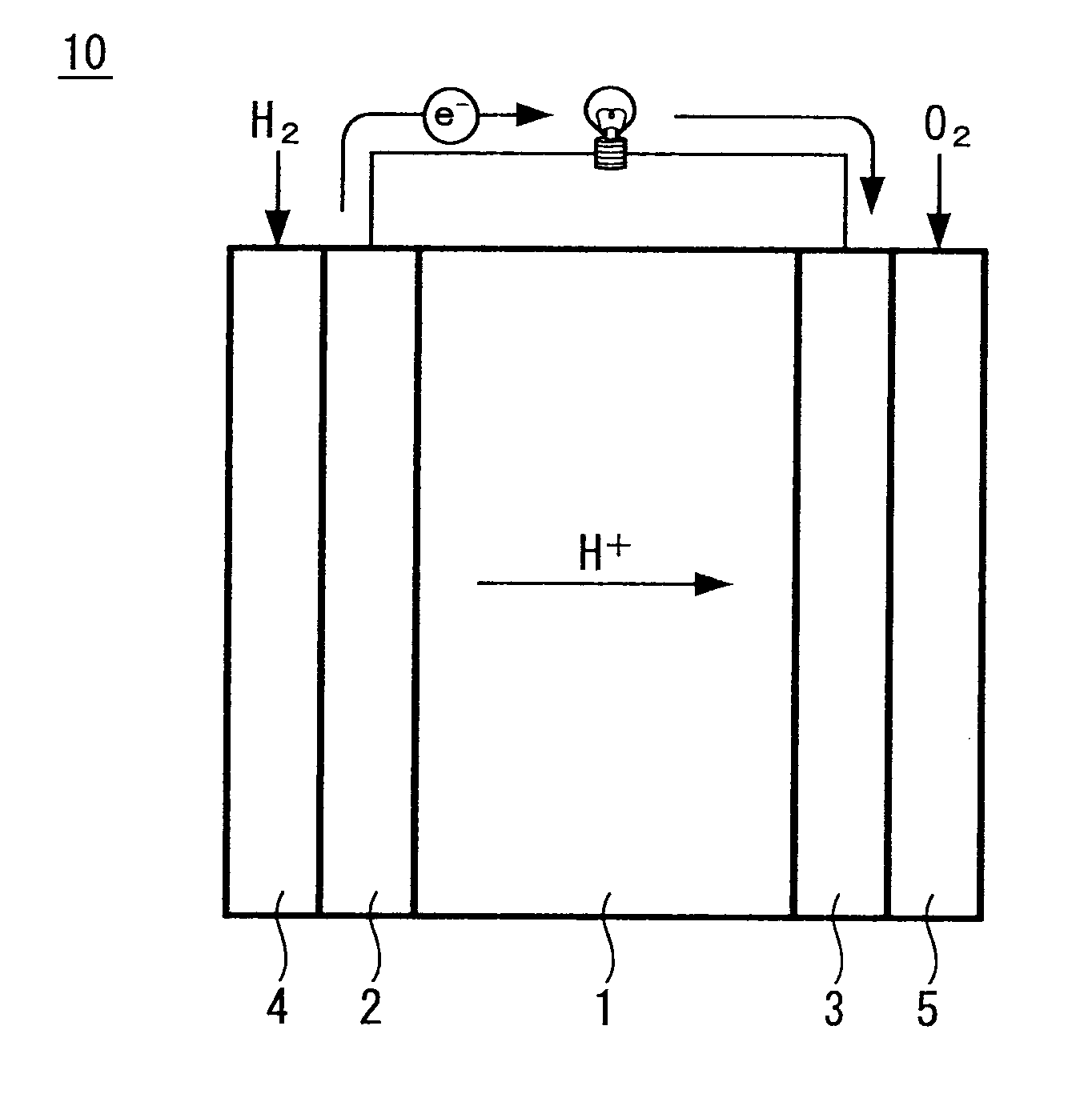
Carbon catalyst, method for producing carbon catalyst, fuel cell, electricity storage device, and use of carbon catalyst
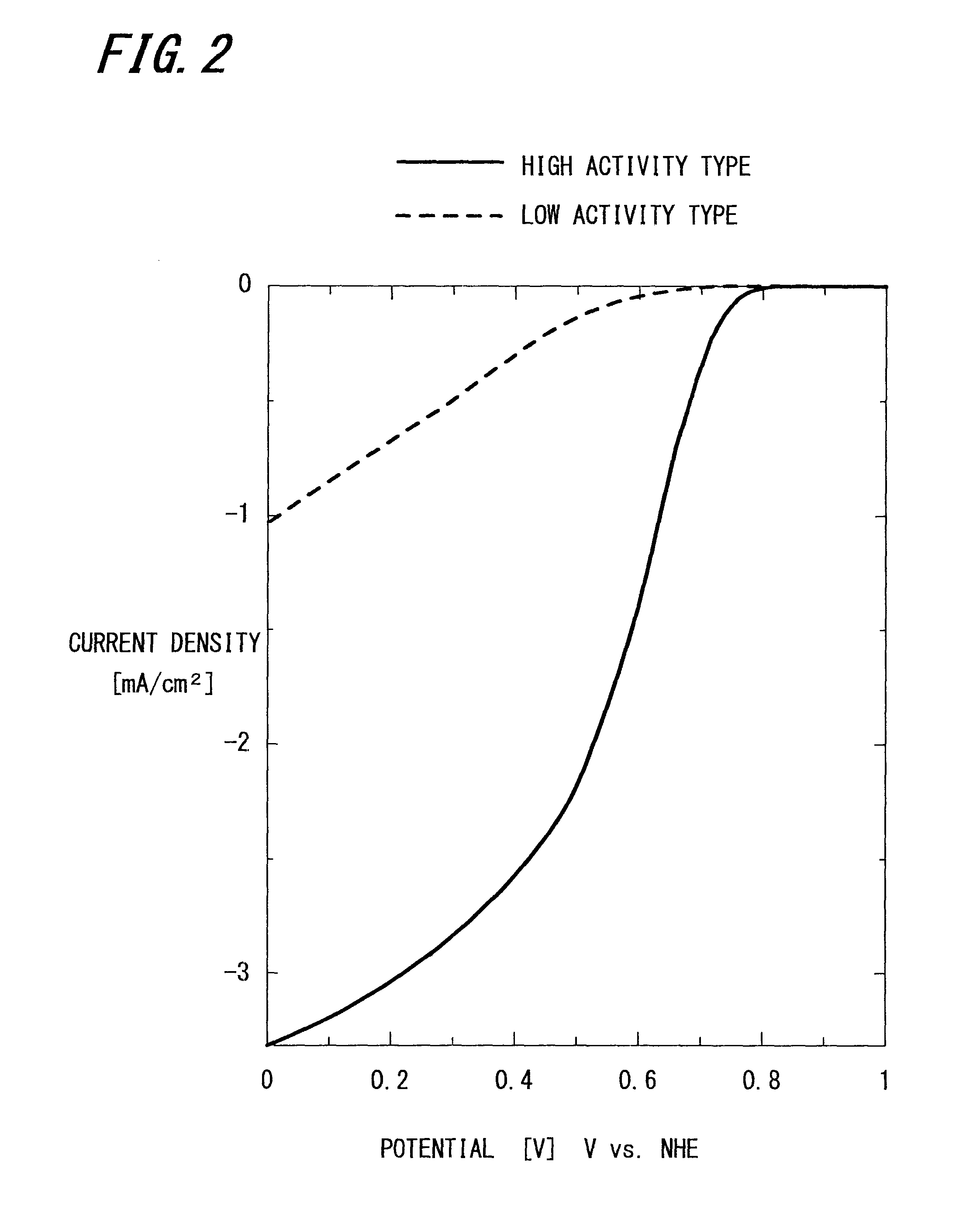
ActiveUS20130288888A1High activitySpeed up chemical reactionsCell electrodesHybrid capacitor electrodesElectricityBinding energy
Owner:ROWANWOOD IP
Electrode, nonaqueous electrolyte battery, battery pack and vehicle
ActiveCN108630908AImprove life characteristicsAlkali titanatesNegative electrodesBinding energyX-ray
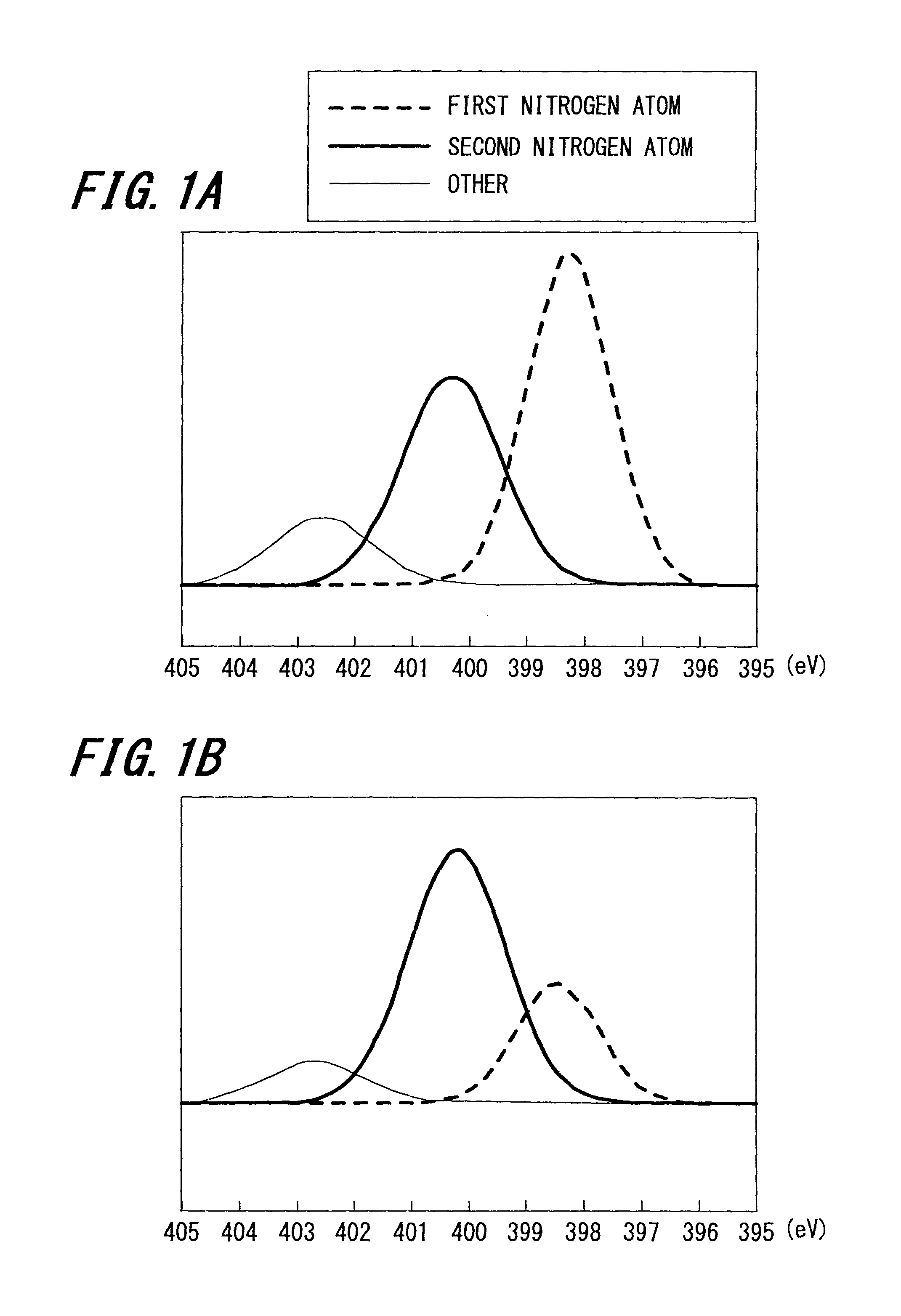
The invention relates to an electrode, a nonaqueous electrolyte battery, a battery pack and a vehicle. The invention provides an electrode excellent in service performance. According to one approach,an electrode (3) is provided. The electrode (3) includes an active material-containing layer (3b). The active material-containing layer (3b) includes a Na-containing niobium-titanium composite oxide having an orthorhombic crystal structure. The active material-containing layer (3b) satisfies I2 / I1>=1. I1 is an intensity of a peak P1 appearing in a binding energy range of 289 eV to 292 eV in an X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy spectrum of the active material-containing layer (3b). I2 is an intensity of a peak P2 appearing in a binding energy range of 283 eV to 285 eV in the X-ray photoelectronspectroscopy spectrum of the active material-containing layer (3b).
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap