Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4 results about "Total organic carbon" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Total organic carbon (TOC) is the amount of carbon found in an organic compound and is often used as a non-specific indicator of water quality or cleanliness of pharmaceutical manufacturing equipment. TOC may also refer to the amount of organic carbon in soil, or in a geological formation, particularly the source rock for a petroleum play; 2% is a rough minimum. For marine surface sediments, average TOC content is 0.5% in the deep ocean, and 2% along the eastern margins.
Green total organic carbon steel scale and corrosion inhibitor for circulating cooling water system
InactiveCN102351328AEasy to makeEasy to useScale removal and water softeningEutrophicationCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a green total organic carbon steel scale and corrosion inhibitor for a circulating cooling water system, which comprises a scale inhibitor and a corrosion inhibitor, wherein the scale inhibitor comprises one or more of hydrolyzed polymaleic anhydride, polyacrylic acid, polymethacrylic acid, acrylic acid / hydroxypropyl acrylate copolymer, acrylic acid / hydroxypropyl acrylate / methyl acrylate terpolymer and acrylic acid / 2-acrylamido-2-methylpropane sulfonic acid copolymer; and the corrosion inhibitor comprises oxalic acid or oxalate, alpha-hydroxycarboxylic acid or salt thereof and silicate. The scale and corrosion inhibitor has excellent scale inhibition and corrosion inhibition performance, and belongs to a completely phosphorus-free metal-free environment-friendly total organic composition. Discharged waste water treated by the composition can not cause eutrophication pollution to the environment.
Owner:TIANJIN HEGUANG ELECTRICAL & MECHANICAL EQUIP CO LTD
CWB conductivity monitor
InactiveUS20120178175A1Low accuracyLow reliabilityComponent separationGeneral water supply conservationIon-exchange resinOrganic compound
This invention is a method and apparatus for monitoring the concentration of carbon dioxide dissolved in water by means of conductivity. It distinguishes between the conductivity resulting from carbon dioxide and the conductivity resulting from other constituents dissolved in water. It can be used to monitor the quality of demineralized water, boiler feedwater, steam, or condensate in electric power generation and other industrial facilities. It is constructed by adding a column containing weak base anion exchange resin and a conductivity instrument to a typical cation conductivity monitor. A sample of the water to be monitored flows first through a typical cation conductivity monitor, then through a weak base anion exchange column, and then through an additional conductivity instrument. Conductivity measured at the outlet of the weak base anion exchange column will be essentially due to whatever concentration of carbon dioxide is dissolved in the sample because other dissolved constituents that affect conductivity have been essentially removed by either the cation exchange resin that is part of a typical cation conductivity monitor, or by the weak base anion exchange resin. By subtracting the value of conductivity due to carbon dioxide (at the outlet of the weak base anion exchange column) from the value of cation conductivity (at the outlet of the cation exchange column), the value of degassed cation conductivity is obtained. In the title of the invention, CWB conductivity is an abbreviation for cation—weak base conductivity.In combination with existing methods for oxidizing organic compounds dissolved in water, this invention is also a method and apparatus for monitoring the concentration of dissolved or total organic carbon in water by means of conductivity. It distinguishes between the conductivity resulting from organic carbon and the conductivity resulting from inorganic constituents dissolved in water including carbon dioxide.
Owner:CROSMAN JAY CLIFFORD
Sodium nitrite-containing pharmaceutical compositions
Owner:HOPE MEDICAL ENTERPRISES HOPE PHARMA
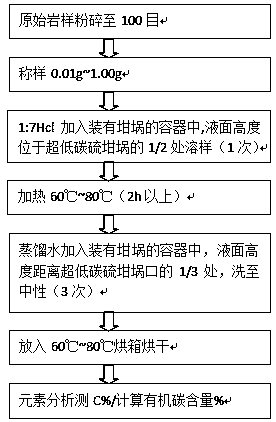
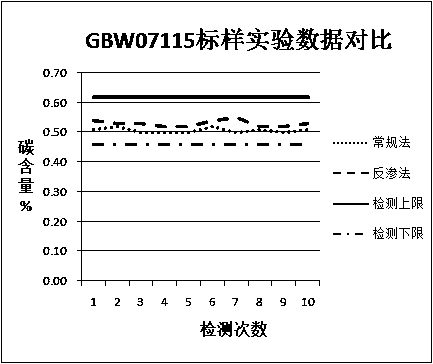
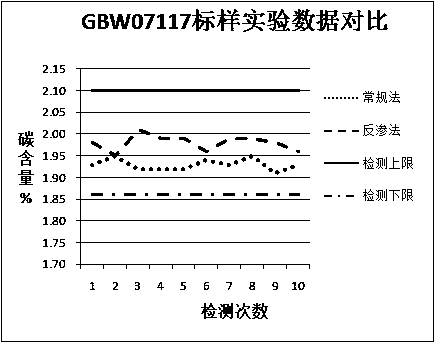
A method for the determination of total organic carbon in sedimentary rocks
InactiveCN106442096BPreparing sample for investigationEarth material testingChemistryTotal organic carbon
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap