Method of Manufacturing Reference Material Using Plant Cultured Cell Lines
a cell line and plant culture technology, applied in the direction of fluorescence/phosphorescence, sugar derivates, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of protein denaturement, lack of information on the purity of a starting sample, and inferior detection rate of pcr methods, so as to improve the reliability of a reference material
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Tissue-Cultured Cell Line
[0067]Soybean from the US in which GM soybean (Glycine max) was mixed was randomly selected, germinated and grown. Thereafter, the gene analysis according to populations and tissues was performed to determine incorporation of the GM soybean.
[0068]Soybean was germinated in a dark room, and transferred and planted in the soil. Thereafter, when the soybean was grown in an incubator (dark / bright: 16 / 8 hours; 22 / 18° C., humidity of 80%) for a week, primary leaves formed. The leaves of this plant were collected, weighed, and then quenched in liquid nitrogen. Thereafter, genomic DNA was extracted, and subjected to gene amplification to determine whether the soybean was genetically modified.
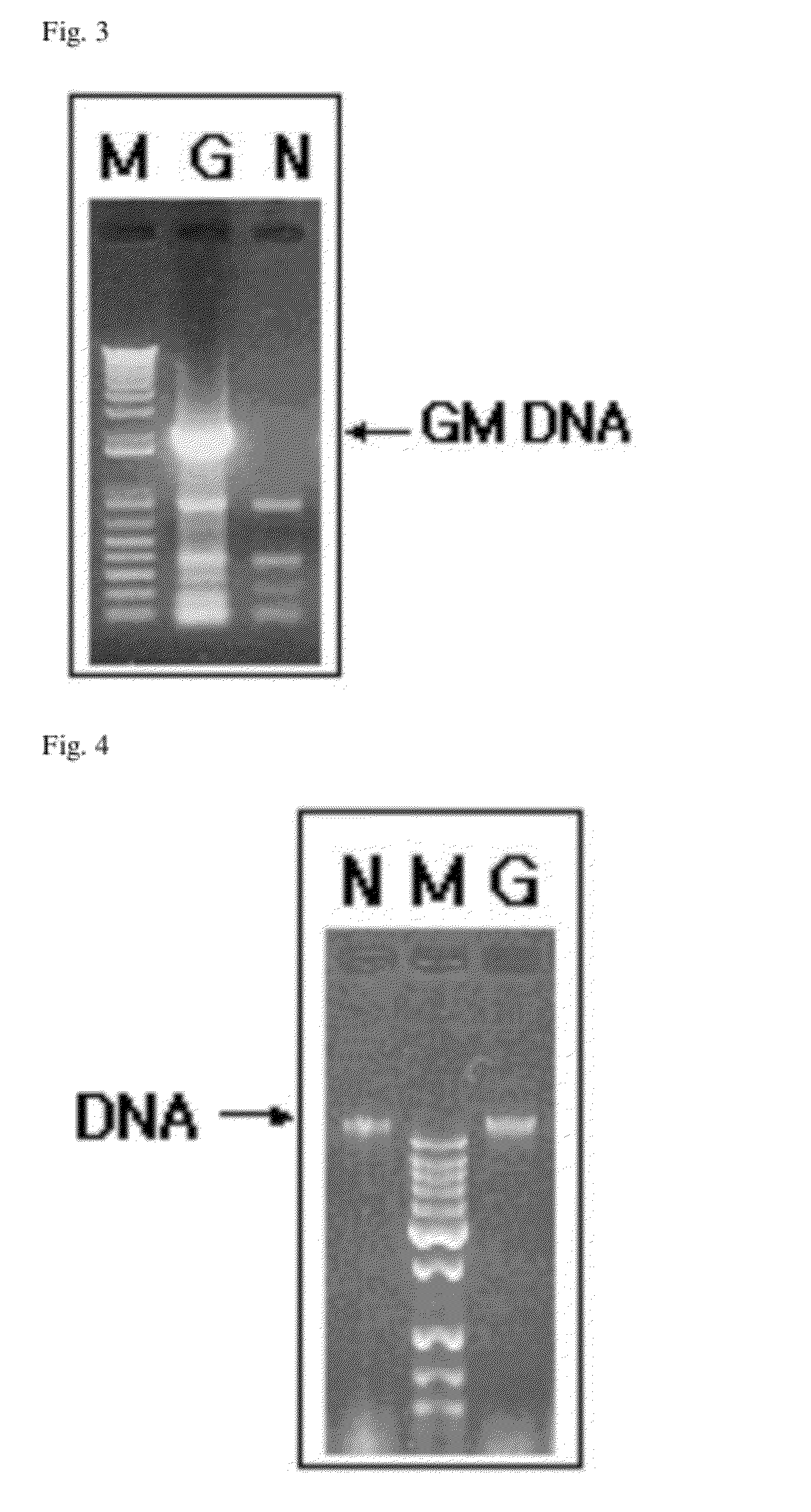
[0069]The genetic modification of the soybean was determined by PCR amplifying a DNA fragment including a modified gene of GM soybean, that is, a gene (5-enolpyruvyl shikimate-3-phosphate synthase, EPSPS) resistant to a glyphosate-based herbicide. It was confirm
example 2
Extraction of Genomic DNA From Tissue-Cultured Cell Line
[0076]The extraction of genomic DNA was performed using a variety of widely used plant DNA extraction kits according to a method proposed by the manufacturer (Qiagen, Promega, etc.) or a slightly modified method, or using a modified method from a CTAB method, in which components were used at reduced amounts, as described in “Chapter 10. Tests on Gene-Recombinant Foods in General. Methods” of “Standards and Specifications in Foods” issued by the Korea Food and Drug Administration (KFDA).
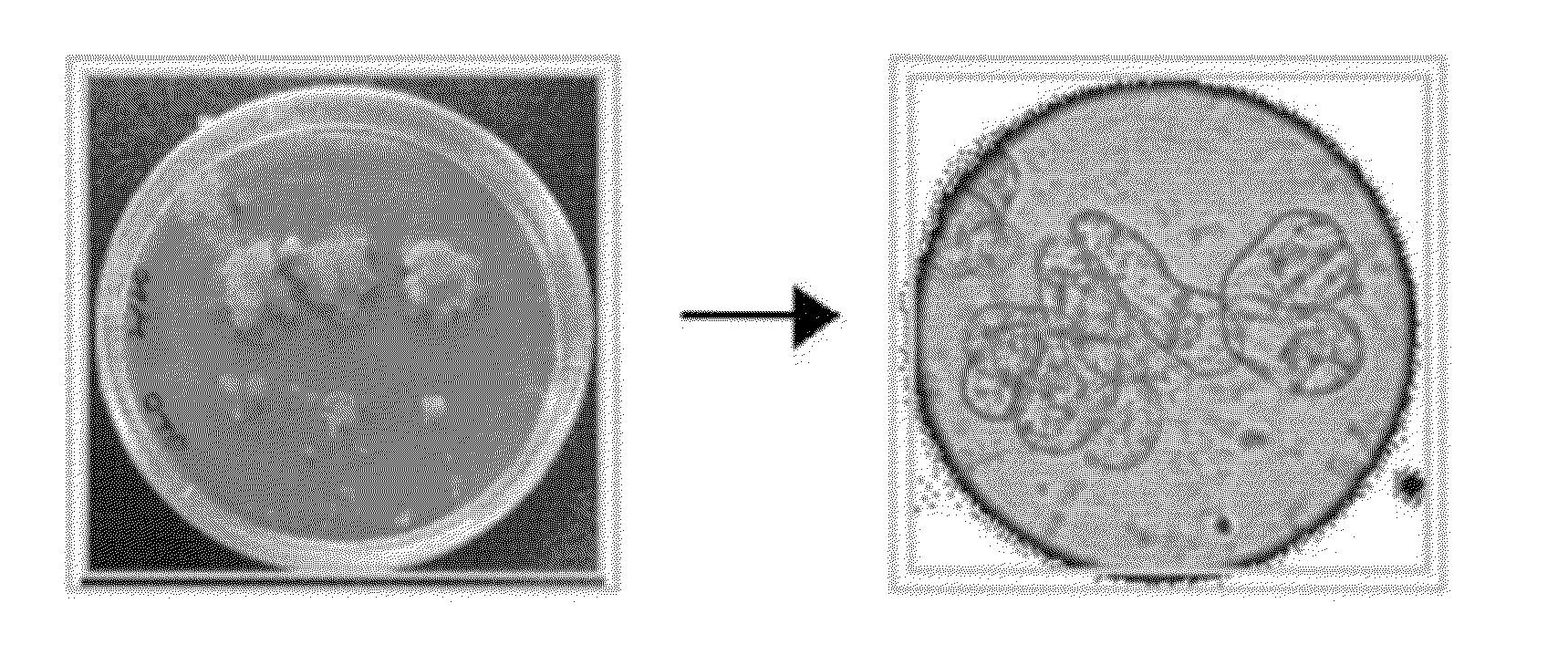
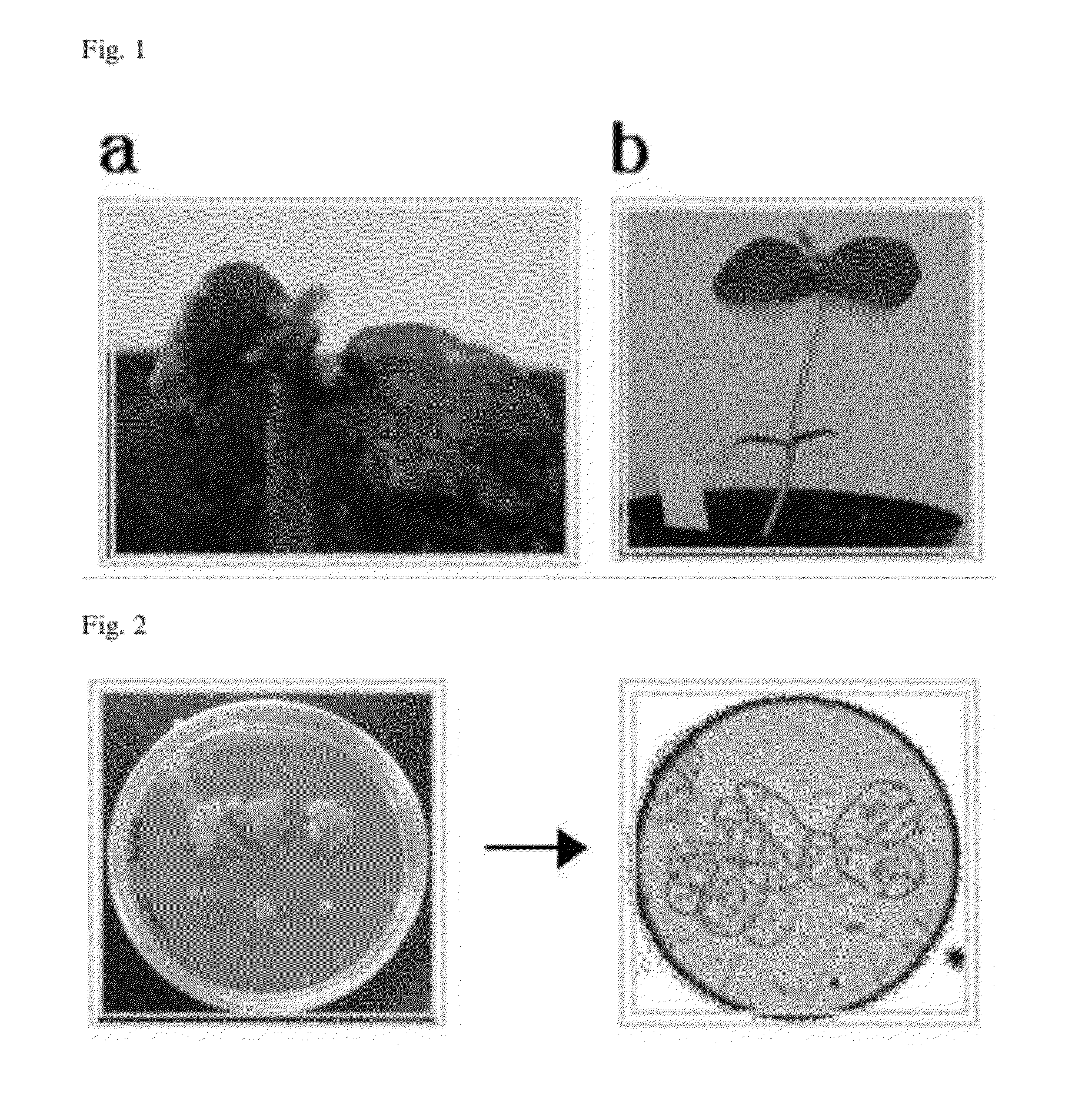
[0077]The extracted genomic DNA showed a pattern as shown in FIG. 4. The absorbance of the genomic DNA was measured under ultraviolet rays to confirm the purity, which was used later (see the KFDA's notification).
experimental example 1
Qualitative Analysis of Incorporation of GM Plant
[0078]The qualitative analysis was performed by PCR amplifying a DNA fragment including a modified gene of GM soybean, that is, a gene (i.e., EPSPS) resistant to a glyphosate-based herbicide.
[0079]The confirmation of the genetic modification of a sample through the gene amplification was performed according the method recommended by the KFDA or performed under the conditions as follows. When the genetic modification was confirmed under the following conditions, an amplified product had a size of approximately 2 kb. In addition, the genetic modification was confirmed using an endogenous gene, lectin, as the positive control.
[0080]In order to confirm the presence of an inserted gene, 2 μL of a forward primer 35S 3F (AAGATGCCTCTGCCGACA, 10 μM), 2 μL of a reverse primer NOS 3R (ATGTATAATTGCGGGACTCTAATCA, 10 μM), 2 μL of dNTP (10 mM), 2 μL of a 10× buffer, 2 μL of MgCl2 (25 mM) and 0.2 μL of Taq polymerase (5 U / μL) were put into a PCR tube,
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Ratio | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fluorescence | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap