Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
9 results about "Microarray" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A microarray is a multiplex lab-on-a-chip. It is a two-dimensional array on a solid substrate (usually a glass slide or silicon thin-film cell) that assays (tests) large amounts of biological material using high-throughput screening miniaturized, multiplexed and parallel processing and detection methods. The concept and methodology of microarrays was first introduced and illustrated in antibody microarrays (also referred to as antibody matrix) by Tse Wen Chang in 1983 in a scientific publication and a series of patents. The "gene chip" industry started to grow significantly after the 1995 Science Paper by the Ron Davis and Pat Brown labs at Stanford University. With the establishment of companies, such as Affymetrix, Agilent, Applied Microarrays, Arrayjet, Illumina, and others, the technology of DNA microarrays has become the most sophisticated and the most widely used, while the use of protein, peptide and carbohydrate microarrays is expanding.
Compound biochip based on photon crystal
InactiveCN101358242AImprove performanceEnhanced signal selectivityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosphereComposite substrate
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method of making and using hybrid polymeric thin films for bio-microarray applications
InactiveUS20050048554A1Peptide librariesBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPolyelectrolyteCost effectiveness
Platforms for easy and cost-effective fabrication of bio-microarrays are disclosed. In one embodiment, the platform contains a substrate having a surface coated with a film of alternating polycationic and polyanionic polymers. In another embodiment, the platform contains a substrate having a surface coated with a polyelectrolyte-silica sol-gel film. Also disclosed are bio-microarrays fabricated using the above platforms and methods of making the platforms and the microarrays.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Microfluidic chip system for culture and multiplication behavior research of marine microalgae
InactiveCN102876562AImprove throughputSimple and fast operationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProcess integrationBiology
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Test composition for screening cancers
InactiveUS20150337386A1Nucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementScreening cancerNucleotide
Owner:ISTAT BIOMEDICAL
Identification of silkworm hemocyte specific expressed gene cathepsin O regulation element
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Preparation and application of probe liquid chip for hypersensitive detection of miRNA
InactiveCN108103148AHigh detection sensitivityThe detection process is fastMicrobiological testing/measurementDisulfide ReductionPlasma resonance
Owner:清水湾生物材料(深圳)有限公司
Kit of peripheral blood free-nucleotide miRNAs-based ultrasensitive detection device and detection method of kit
ActiveCN108660216AHigh sensitivityIncrease the difficultyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicrosphereNucleotide
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF ARMY MEDICAL UNIV
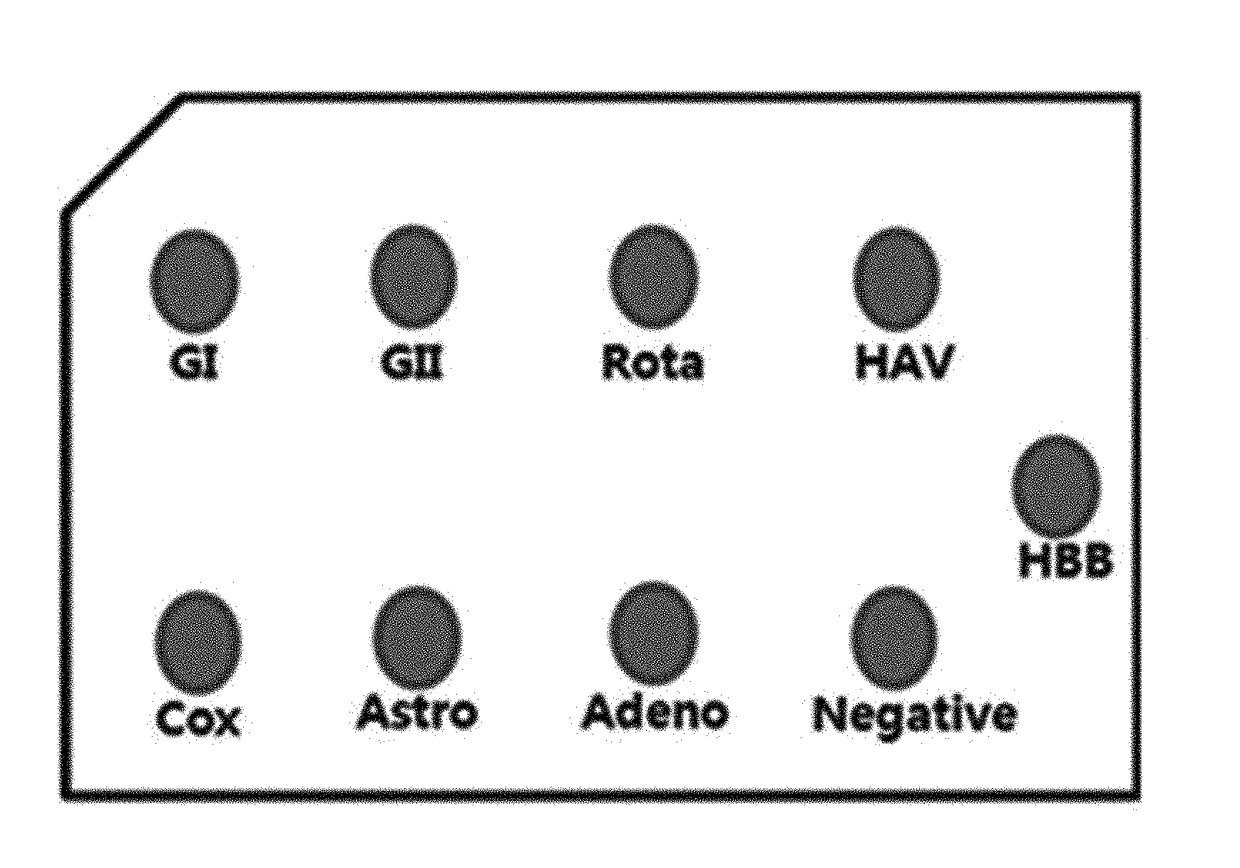
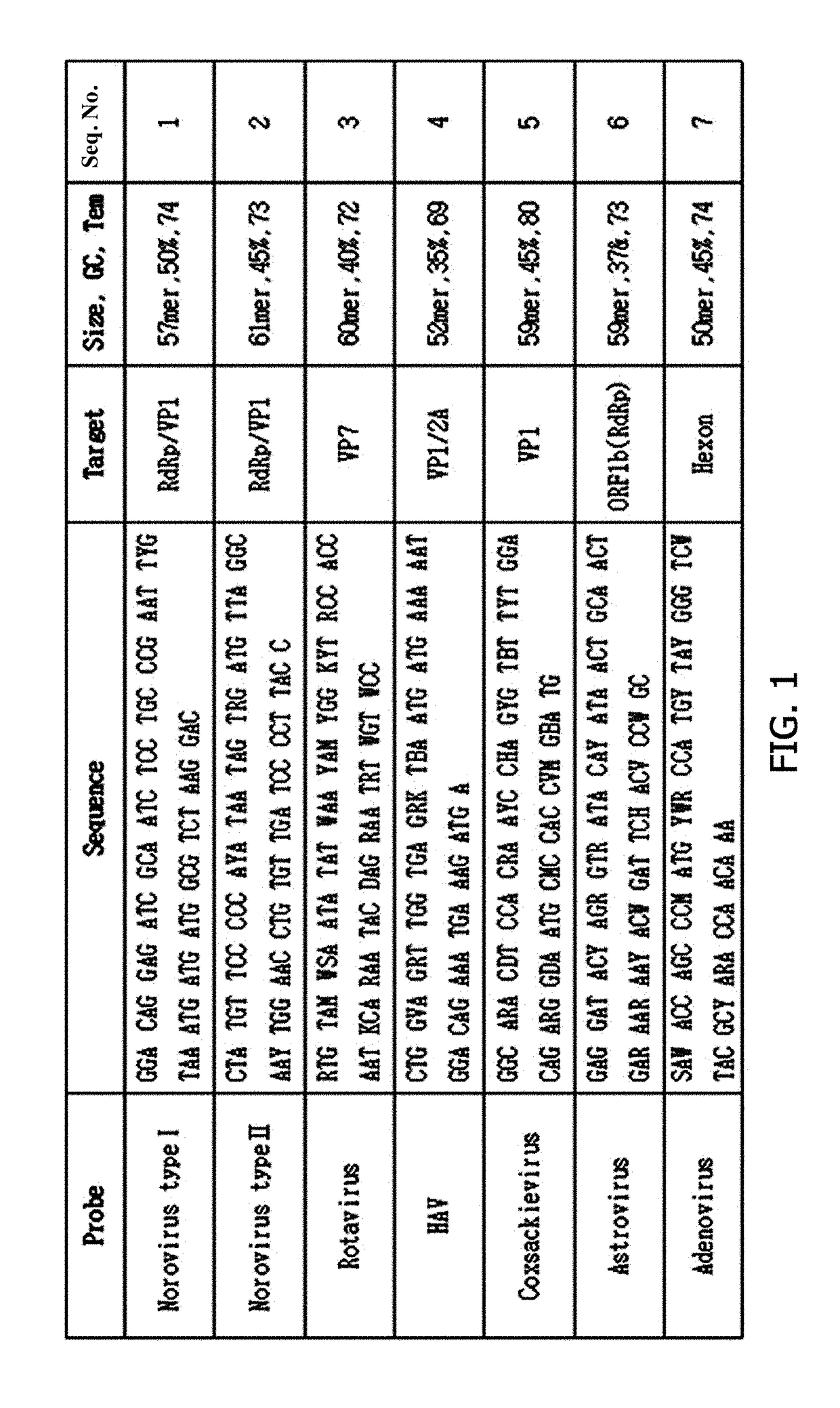
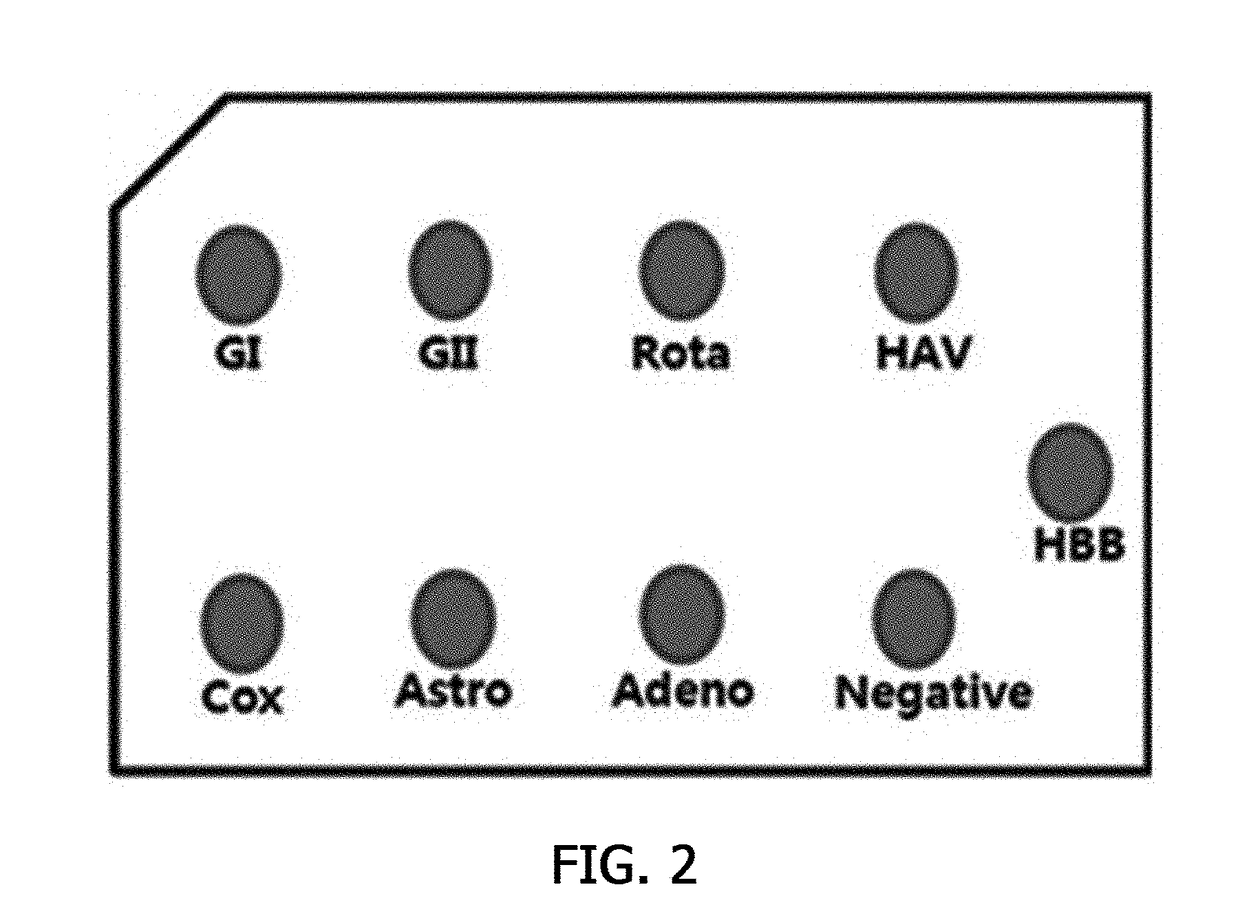
Probe for detecting virus
ActiveUS20170356912A1Low costSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA microarrayCoxsackievirus
Owner:THE CATHOLIC UNIV OF KOREA IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND
Gene chip for detecting transgenic plant and products containing screened gene NOS and application thereof
InactiveCN101824473AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescencePositive controlSpecific detection
Owner:山东鲁保科技开发有限公司
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap