Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
7 results about "Moment of inertia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the angular mass or rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis; similar to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration. It depends on the body's mass distribution and the axis chosen, with larger moments requiring more torque to change the body's rotation rate. It is an extensive (additive) property: for a point mass the moment of inertia is just the mass times the square of the perpendicular distance to the rotation axis. The moment of inertia of a rigid composite system is the sum of the moments of inertia of its component subsystems (all taken about the same axis). Its simplest definition is the second moment of mass with respect to distance from an axis. For bodies constrained to rotate in a plane, only their moment of inertia about an axis perpendicular to the plane, a scalar value, matters. For bodies free to rotate in three dimensions, their moments can be described by a symmetric 3 × 3 matrix, with a set of mutually perpendicular principal axes for which this matrix is diagonal and torques around the axes act independently of each other.
Golf club head with peripheral weighting
InactiveUS6860818B2Increase moment of inertiaVariable distributionOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingWound drainsEngineeringMoment of inertia
A golf club head with low peripheral and rearward weighting includes C-shaped and annular weights connected with at least one of the rear and bottom surfaces, respectively, of the head. The weighting within the peripheral weights is adjustable between the heel, rear, and toe portions of the head to customize the weight distribution of the head in accordance with a golfer's swing. The added weight and its orientation increases the moment of inertia of the head and reduces the rotation thereof.
Owner:TOPGOLF CALLAWAY BRANDS CORP
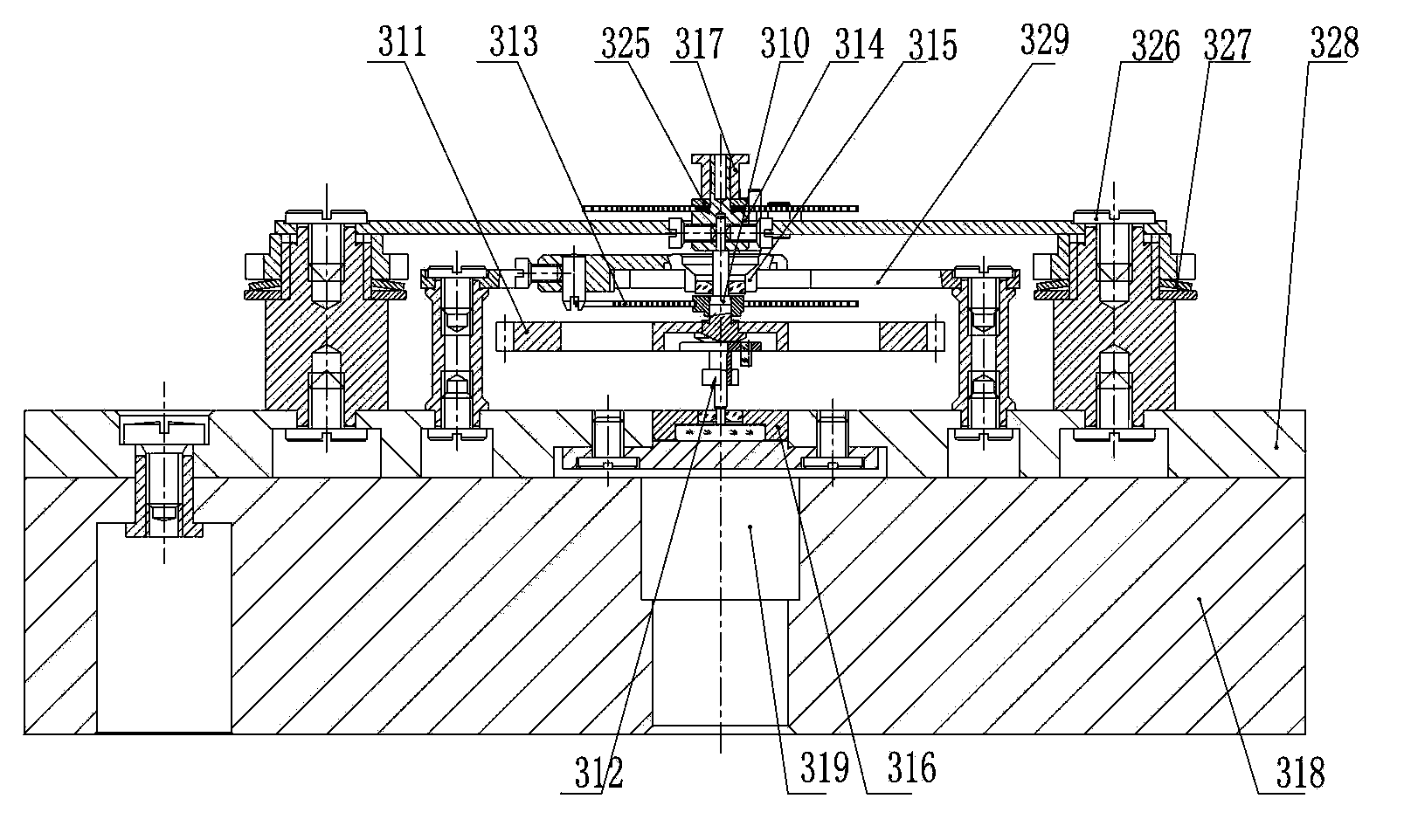
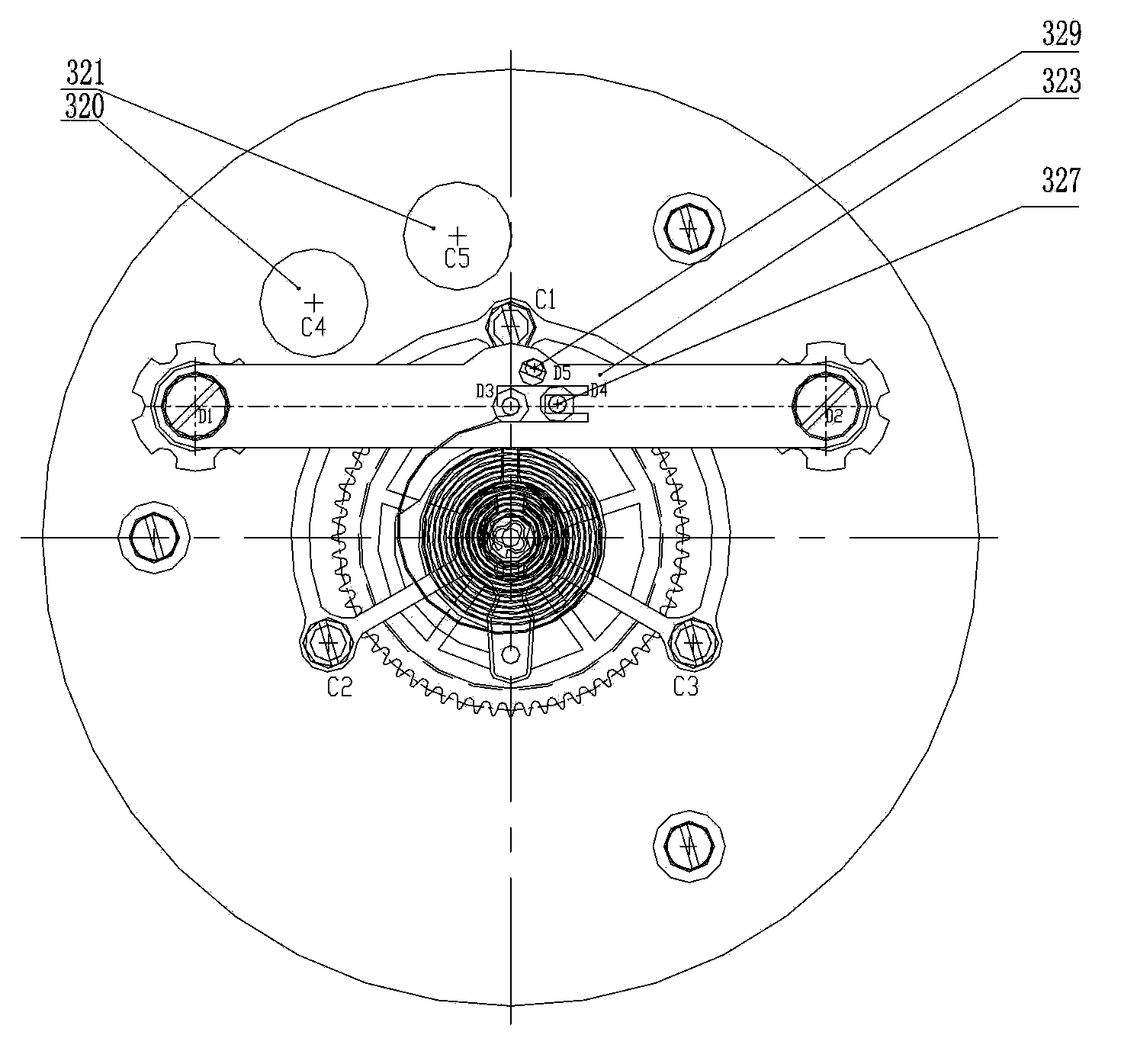
Rotatory inertia piezoelectric actuator comprising dual-rhombic series driving mechanism and actuation method
ActiveCN106208806AChange the status quo of power-off unlockingReduce assembly requirementsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesInterference fitPiezoelectric actuators
The invention discloses a rotatory inertia piezoelectric actuator comprising a dual-rhombic series driving mechanism and an actuation method. The actuator consists of an upper baffle, a lower baffle, a bearing, a rotary output shaft, the dual-rhombic series driving mechanism and piezoelectric stacks, wherein the dual-rhombic series driving mechanism comprises series dual-rhombic rings; the piezoelectric stacks are in interference fit inside the series dual-rhombic rings; a friction block is arranged at a series joint of the piezoelectric stacks; the rotary output shaft of the actuator is connected with the upper baffle and the lower baffle through the bearing respectively; and the dual-rhombic series driving mechanism is fixedly assembled between the upper baffle and the lower baffle. After finish of assembly, a side face of the friction block is in close contact with the rotary output shaft, and the actuator can drive a load to output bidirectional rotary motion by control of voltage time sequences and amplitudes of the piezoelectric stacks. The rotatory inertia piezoelectric actuator has the characteristics of easiness in assembly, quick response and accurate action.
Owner:XIAN LONGWEI TECH CO LTD
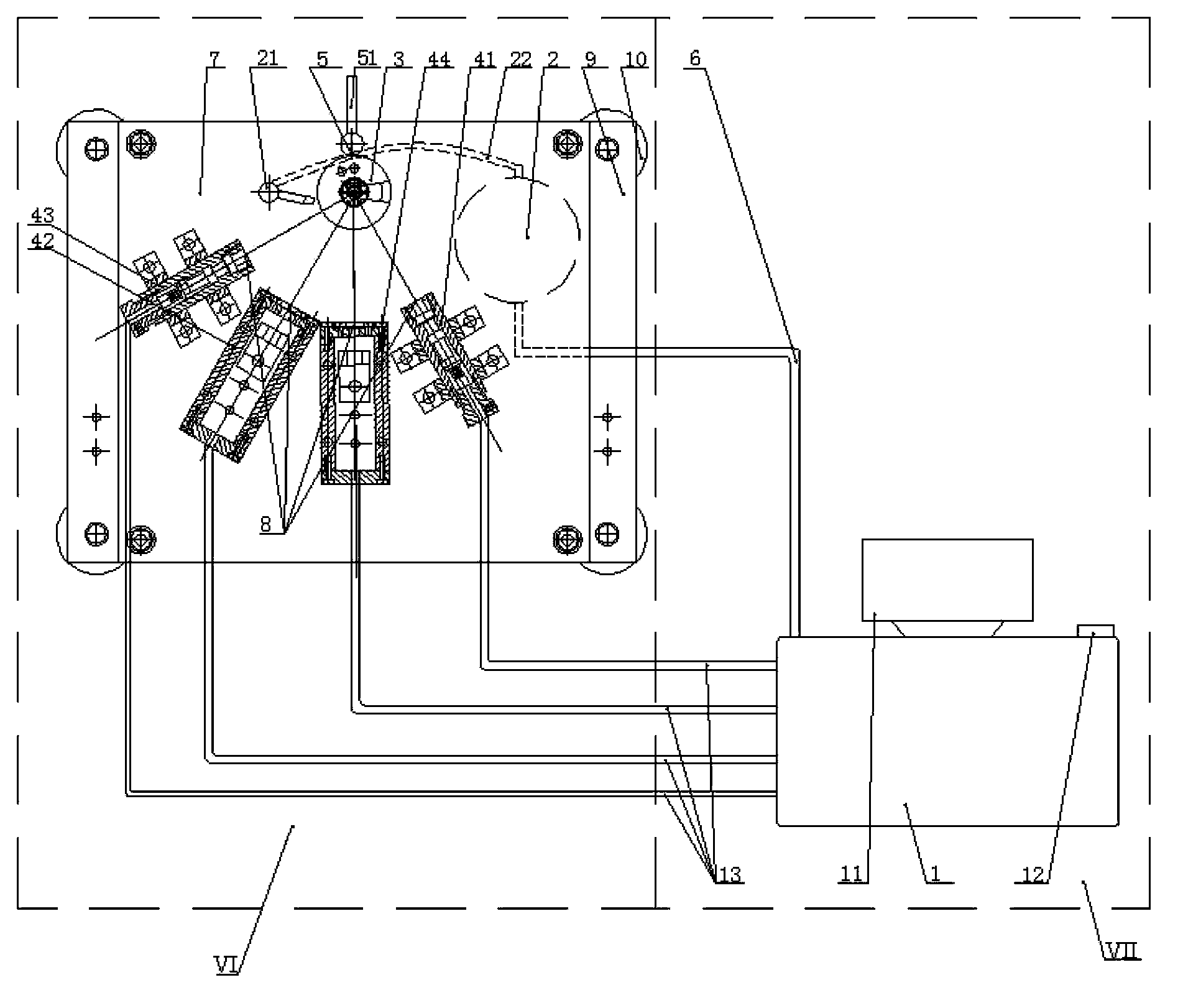
Method for dynamically measuring rigidity of silicon balance spring and rotational inertia of balance wheel and measurement device
ActiveCN103674742AEliminate measurement effectsFast measurementStatic/dynamic balance measurementMaterial strength using repeated/pulsating forcesMeasurement deviceMoment of inertia
Owner:TIANJIN SEAGULL WATCH CO LTD
Permanent magnet double-stator synchronous machine
InactiveCN101154863AReduce volumeReduced responseCooling/ventillation arrangementSupports/enclosures/casingsEngineeringMoment of inertia
A permanent magnetism double-stator synchronous machine is provided, wherein, a rotor is a multipolar drag cup rotor consisting of a tegular permanent magnetic steel, a non-magnetic bracket and a rotating shaft; the inner annulus and the outer annulus of the magnetic steel of the rotor are respectively provided with a bushing and a lantern ring; the single end of the drag cup rotor is fixed on the rotating shaft, and a fan is arranged on the rotor; an air passage is arranged on the bracket and between the bushing and the rotating shaft; the four corners of a square housing fixing an outer stator core are provided with air chutes; a left end closure and a right end closure are provided with vents correspondingly. The invention has the advantages of small cubage of the machine, minimal armature reaction and moment of inertia, convenient manufacturing and simple structure.
Owner:TIANJIN DEXIN ELECTRIC MACHINERY
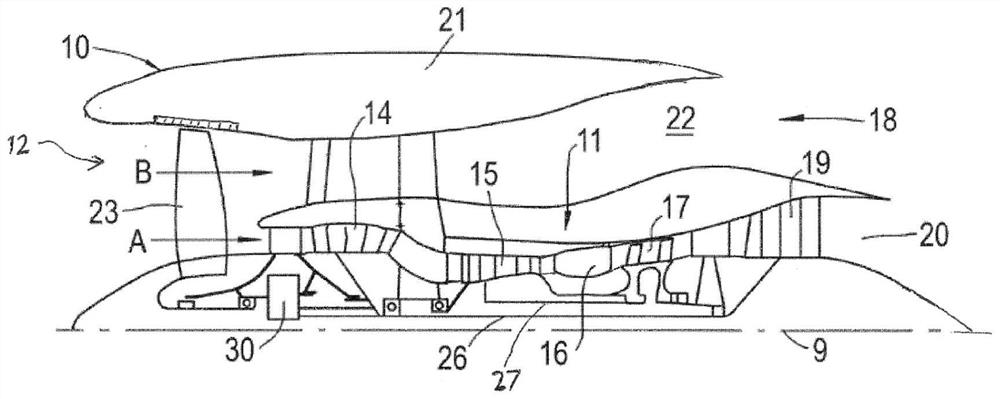
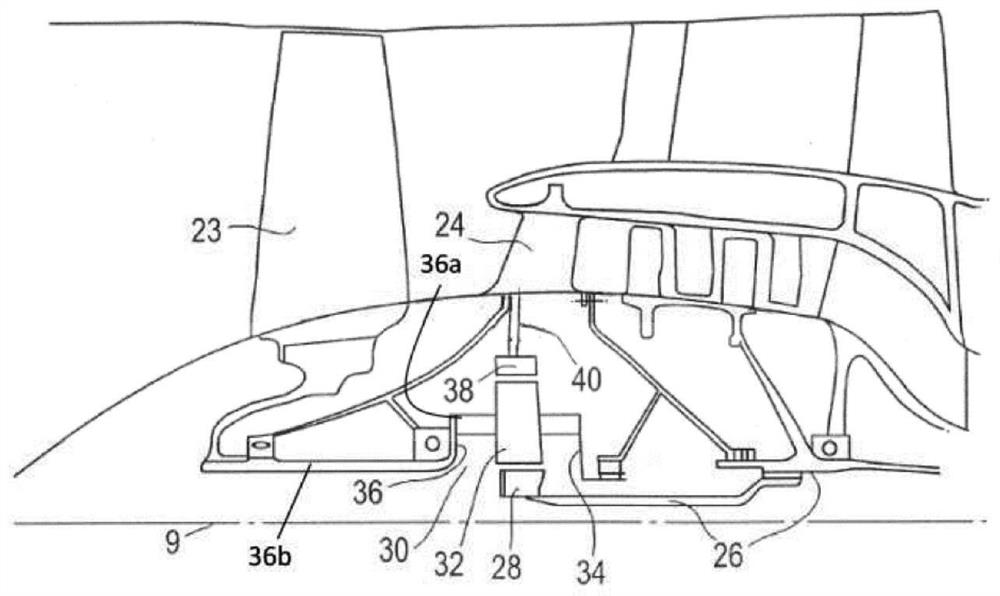
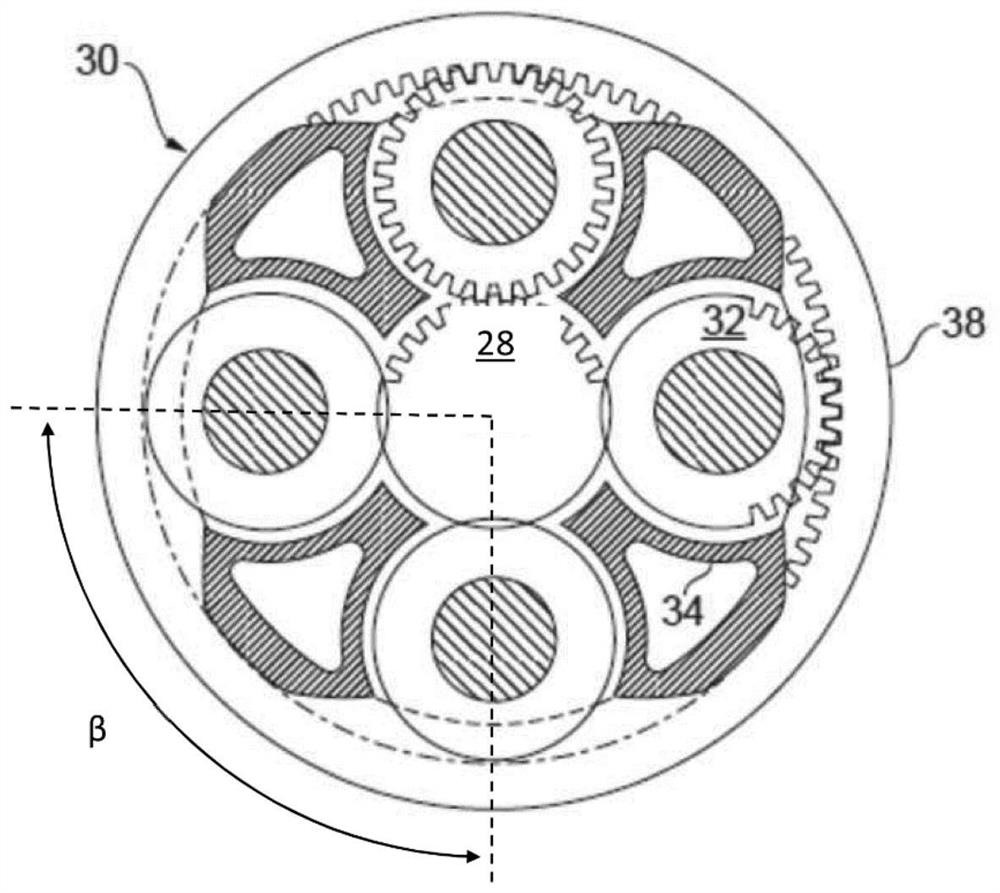
High power epicyclic gearbox and operation thereof
InactiveCN112923026ASmall diameterReduce rotation input speedGas turbine type power plantsEngine fuctionsFlight vehicleGear wheel
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Popular searches
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap