Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
81 results about "Turbine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
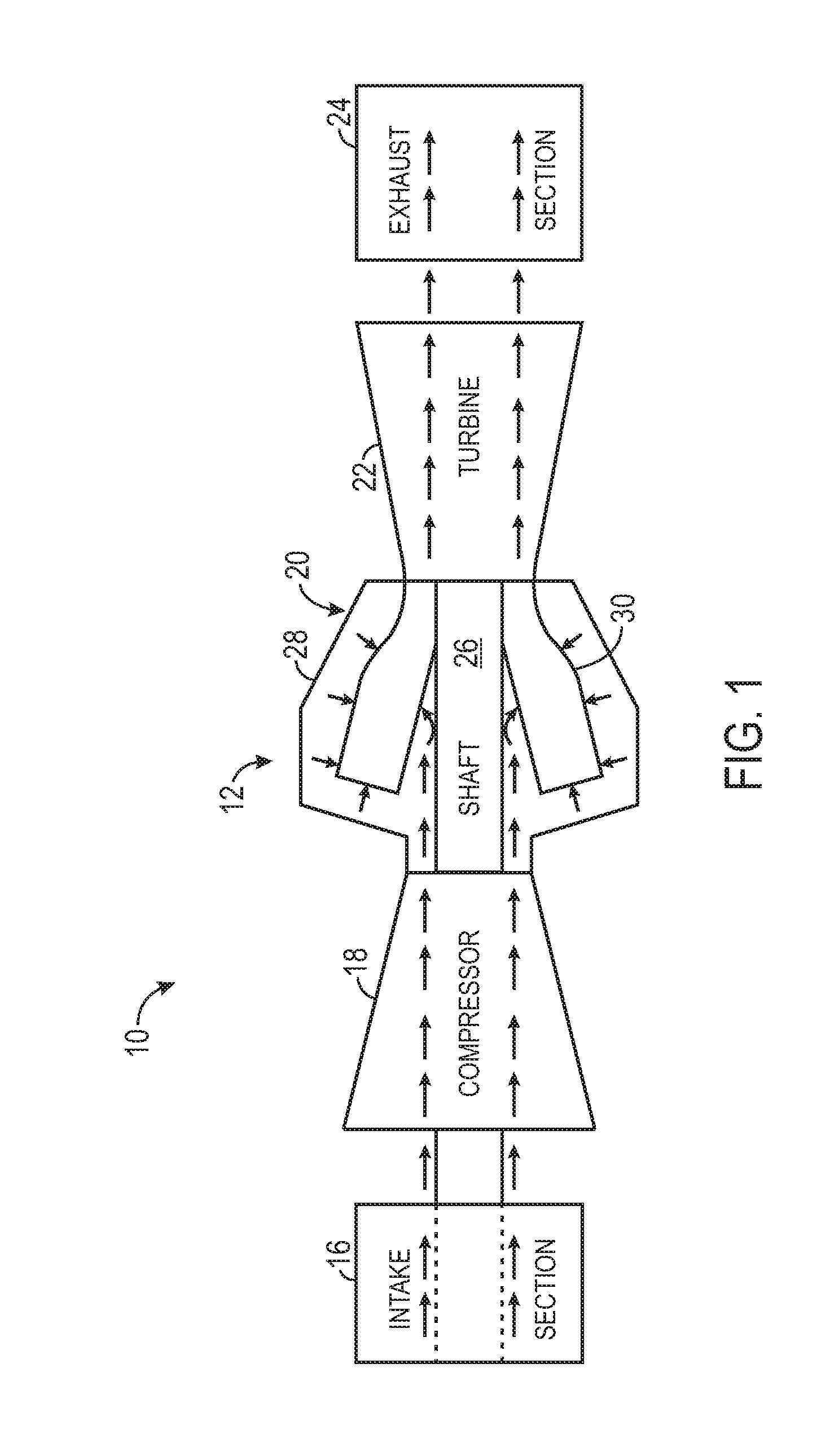
A turbine (from the Latin turbo, a vortex, related to the Greek τύρβη, tyrbē, meaning "turbulence") is a rotary mechanical device that extracts energy from a fluid flow and converts it into useful work. The work produced by a turbine can be used for generating electrical power when combined with a generator. A turbine is a turbomachine with at least one moving part called a rotor assembly, which is a shaft or drum with blades attached. Moving fluid acts on the blades so that they move and impart rotational energy to the rotor. Early turbine examples are windmills and waterwheels.
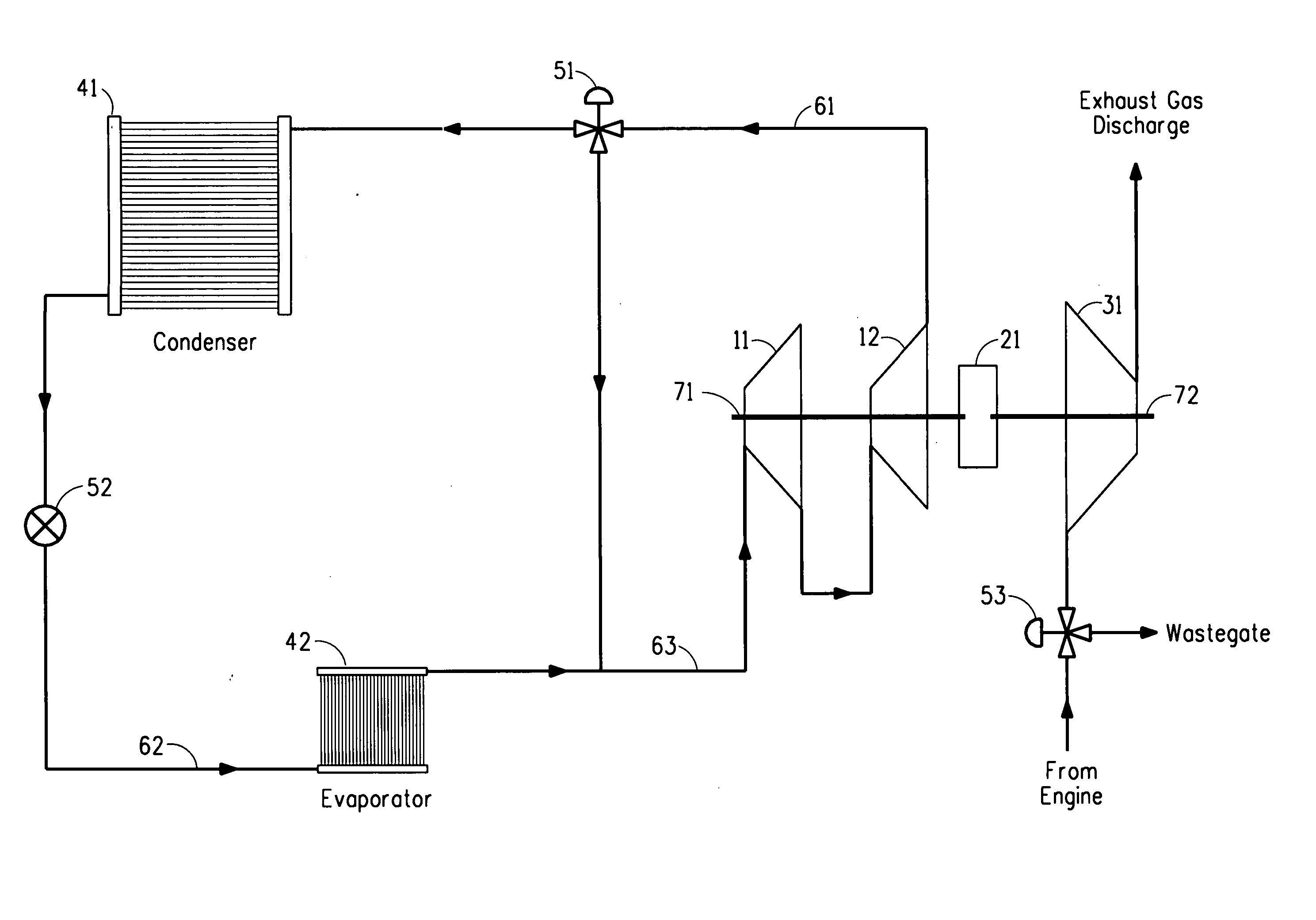
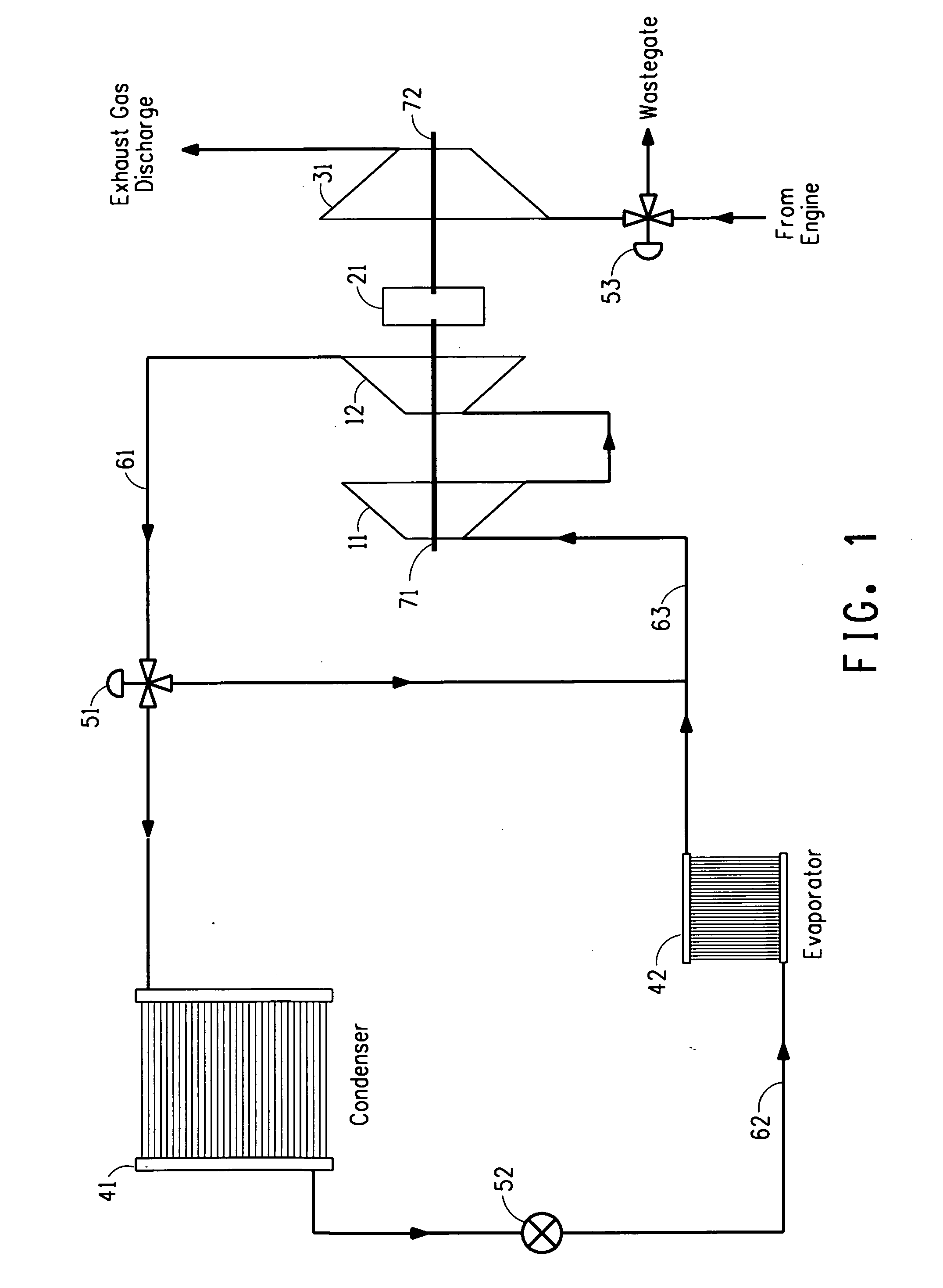
Refrigeration/air-conditioning apparatus powered by an engine exhaust gas driven turbine
InactiveUS20060242985A1Vary amountCompression machines with non-reversible cycleClimate change adaptationAir conditioningRefrigeration
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Air Flow Cooking Appliance
ActiveUS20170360254A1Easy extractionReduce in quantityDomestic stoves or rangesLighting and heating apparatusEngineeringTurbine
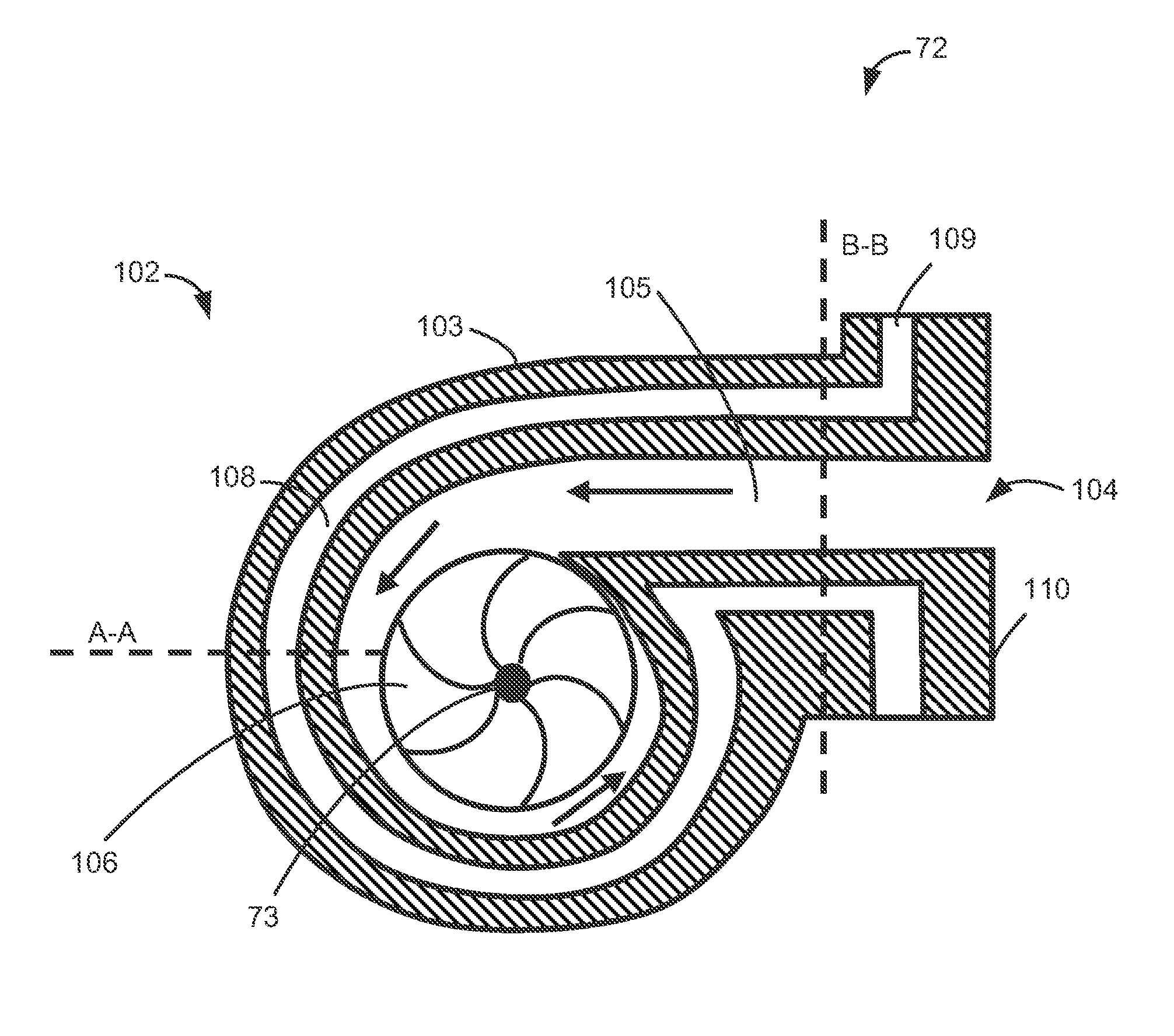
Food cooking appliance comprising: a centrifugal turbine arranged to create an air flow inside a cooking space, a steam extraction window arranged so as to extract, toward the exterior of the appliance, steam present inside the cooking space, wherein the extraction window has, at every point on its passageway surface, a normal direction with at least one non-zero component along a tangential direction to a circle centered on the centrifugal turbine and passing to the center of the extraction window.
Owner:SEB SA
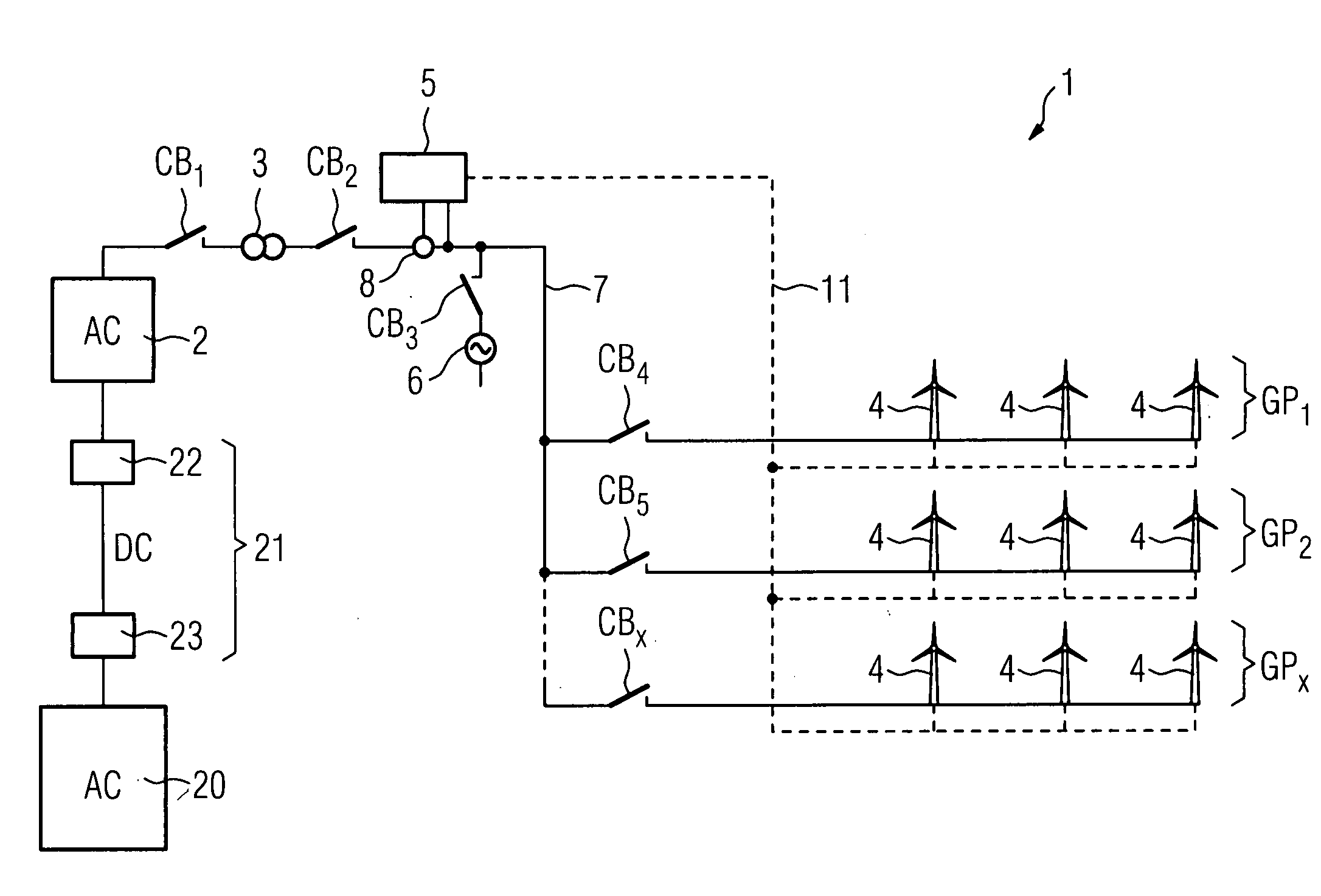
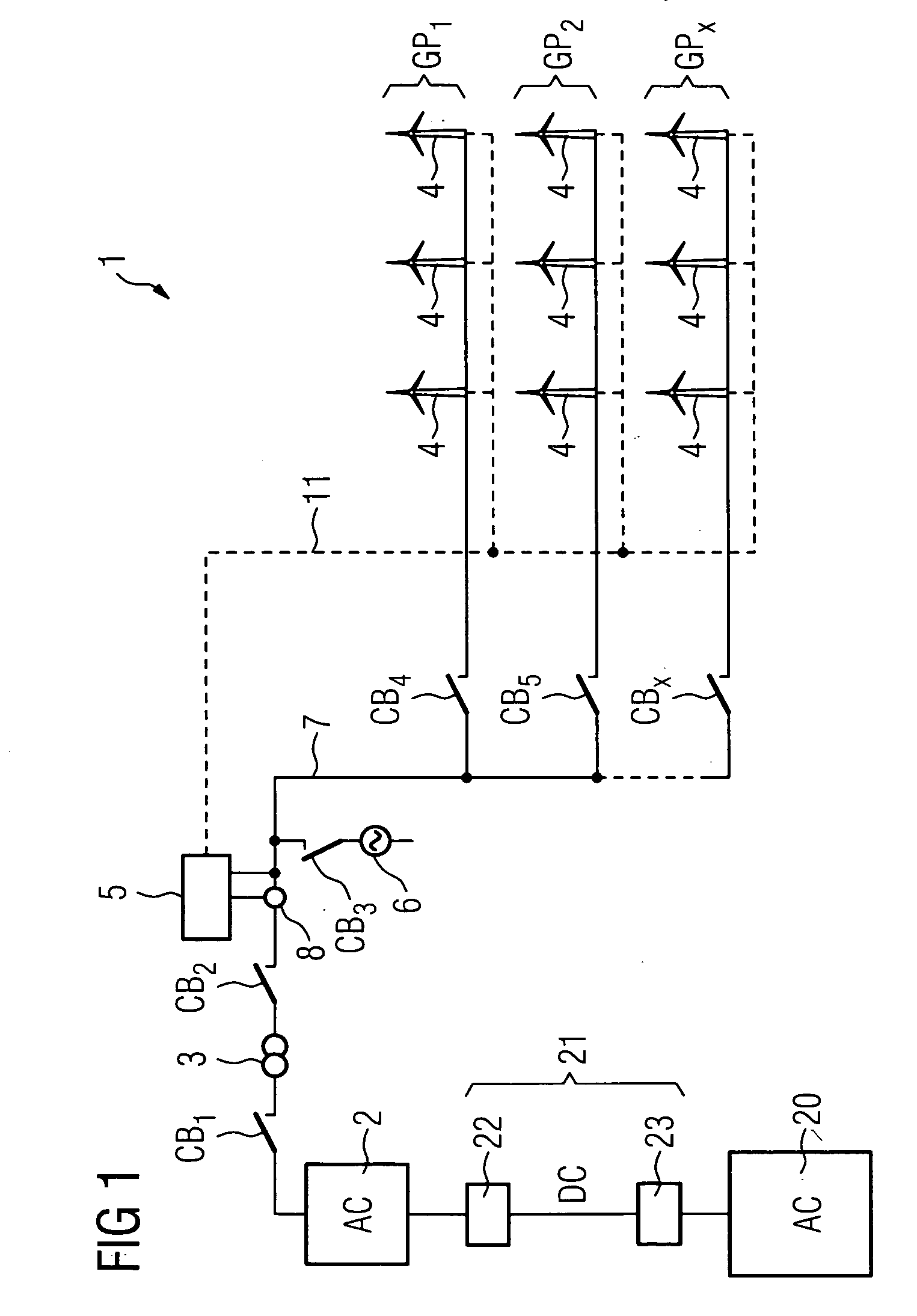
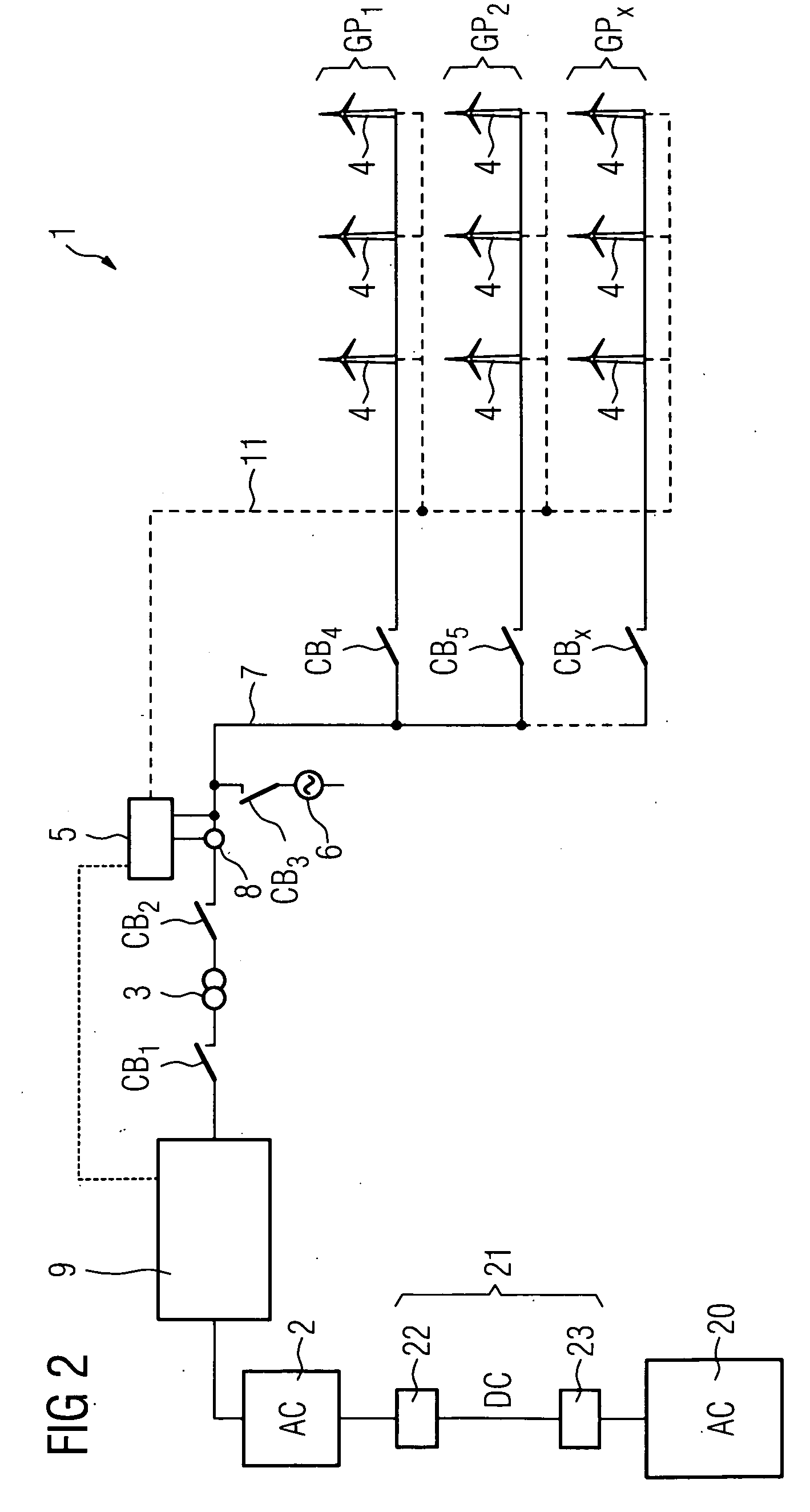
Method of start up at least a part of a wind power plant, wind power plant and use of the wind power plant
ActiveUS20080284172A1Guaranteed uptimeWind motor controlSingle network parallel feeding arrangementsPeaking power plantPower station
Owner:SIEMENS GAMESA RENEWABLE ENERGY AS
Novel megawatt wind generating set testing system and testing method thereof
InactiveCN101881814ASave electricityFlexible configurationDynamo-electric machine testingDistribution transformerMotor drive
The invention provides a novel megawatt wind generating set testing system and a testing method thereof. Energy provided by a power system provides electric energy for a double shaft-extension dragging motor by a series of devices; then the dragging motor drives a tested set to operate by a series of devices such as a wind wheel simulator and the like; and the electric energy generated by the tested set is returned to a distribution transformer by a series of devices so that energy feedback is realized. The tested set can simulate the characteristics of a wind turbine under different wind conditions by means of the wind wheel simulator and the output characteristics of the tested set can be detected by the testing system. Meanwhile, the low voltage ride through (LVRT) performance of the tested set can be tested by arranging an LVRT device in the feeding link. The system has the advantages of electric energy saving, flexible configuration and wide applicable power range, capability of testing the control performance and the output power characteristics of the tested set, capability of detecting the low voltage ride through (LVRT) capability of the tested set by adopting the LVRT device, strong compatibility and expansibility and capability of knowing the testing conditions on site in time and meeting multidirectional testing requirements.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA GEOHO ENERGY EQUIP
Turbomachine comprising a system for cooling the downstream face of an impeller of a centrifugal compressor
ActiveUS20080141679A1Lower performance requirementsSimple and effective and economic solutionPump componentsEngine fuctionsCentrifugal compressorTurbine
Owner:SN DETUDE & DE CONSTR DE MOTEURS DAVIATION S N E C M A
System and method for power production using a hybrid helical detonation device
InactiveUS20090102203A1Shorten the lengthFast fillEngine manufactureTurbine/propulsion fuel valvesCombustion chamberDeflagration to detonation transition
The system and method described herein uses a hybrid pulsed detonation engine (PDE) system to drive a turbine that powers an electric generator. The combustion chamber of the PDE is shaped in a helical form, so that the external length of the section is reduced, while maintaining the distance for acceleration to detonation. This allows the achievement of deflagration to detonation transition without the help of turbulence enhancing obstacles, while keeping the overall size of the detonation tube small. The PDE output can be scaled by: increasing the cross sectional area of the detonation chamber; increasing the number of detonation tubes; and increasing the frequency of operation of the PDE. The replacement of conventional deflagrative internal combustion engines, including gas turbines and reciprocating engines, with pulsed detonation engines for electric power generation, may provide fuel savings and have a lower environmental impact.
Owner:LU FR K +4
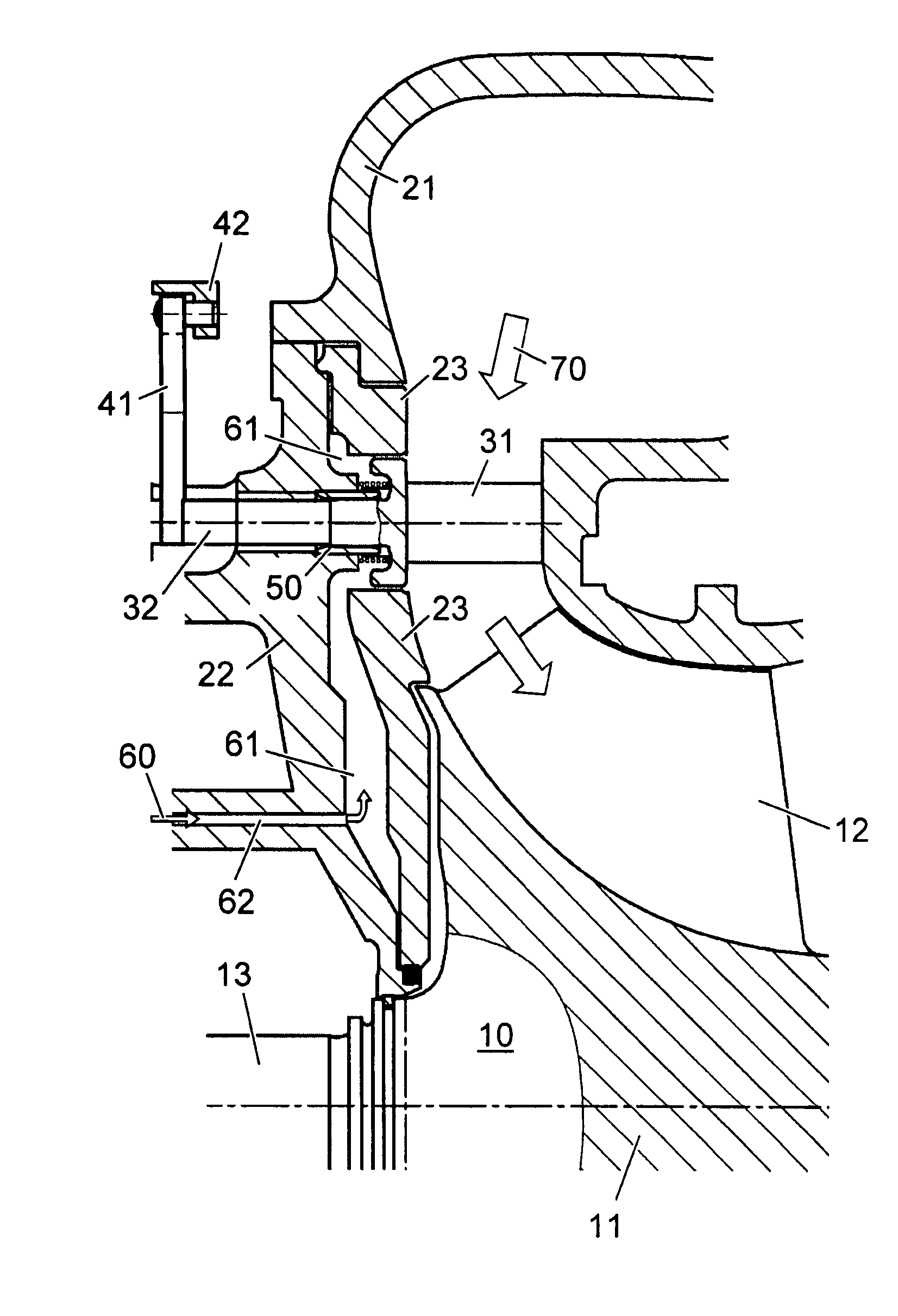
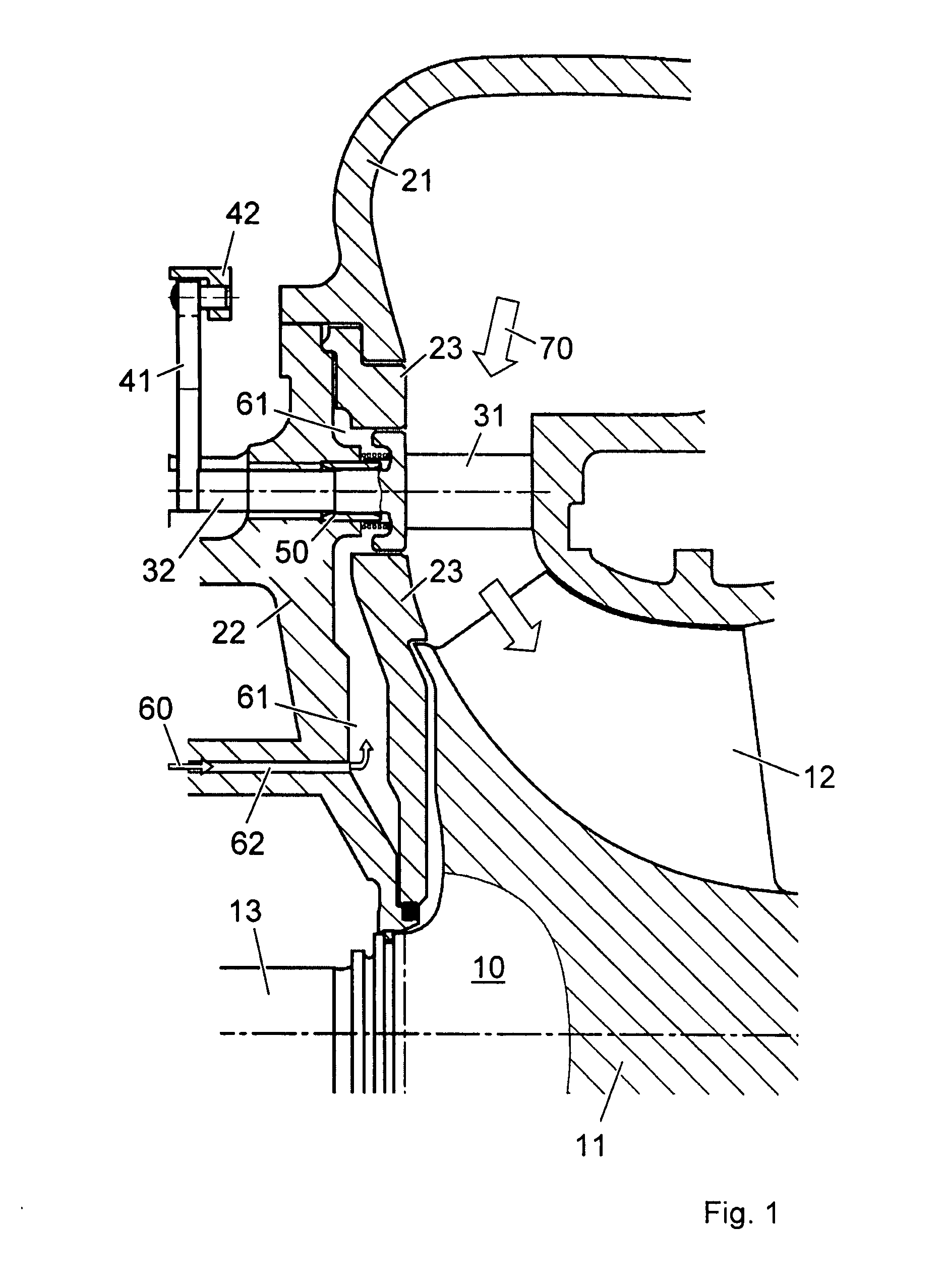
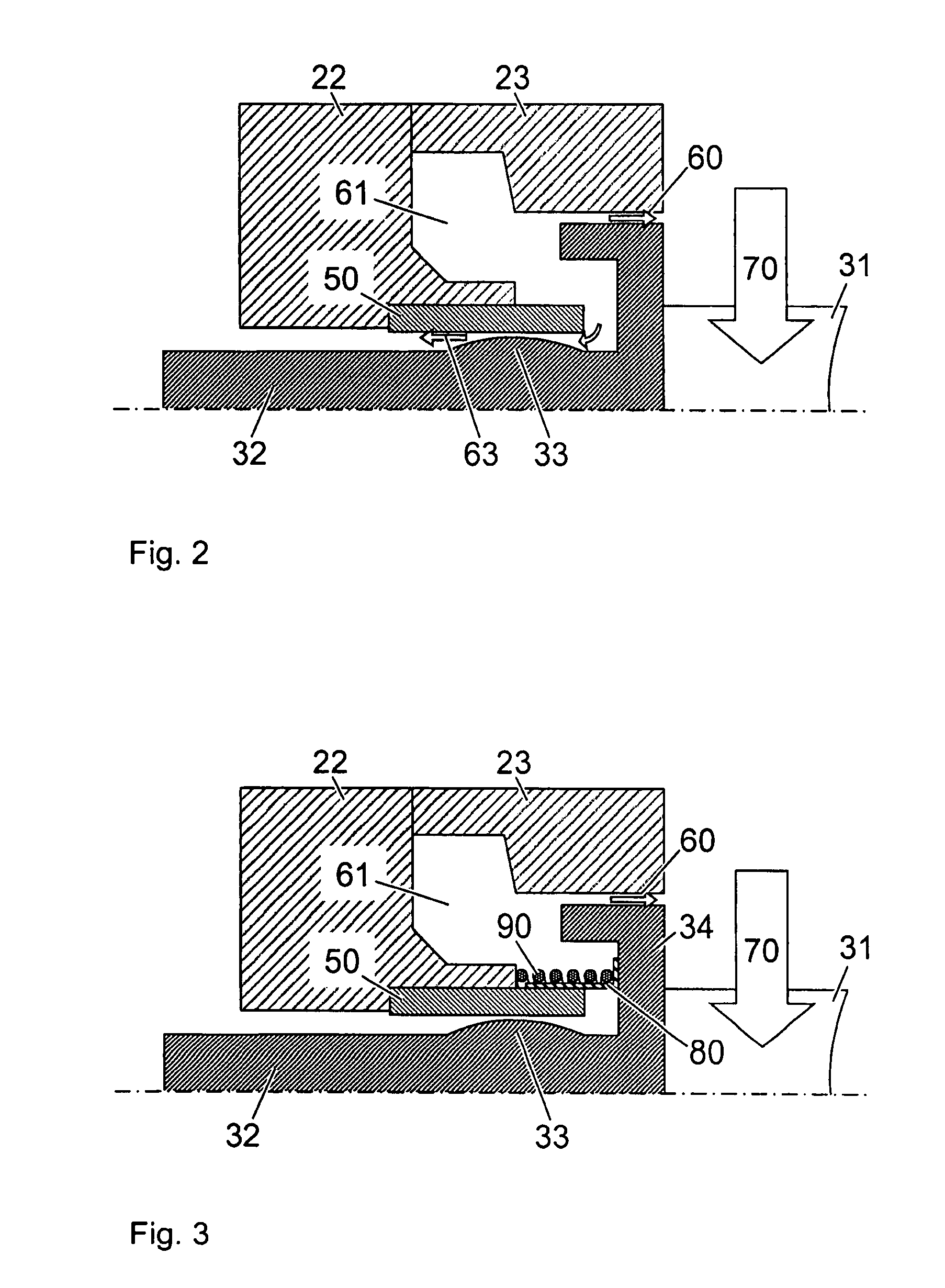
Sealing of variable guide vanes
The guiding device of a turbine has guide vanes which are rotatably mounted in the turbine housing. A sealing sleeve is arranged between the turbine housing and the guide vane stem. The additional axial compression spring ensures that the sealing sleeve is continuously pressed onto the guide vane mating contour, and that the axial gap and also the leakage flow are prevented as a result.
Owner:ABB TURBO SYST
System for damping vibration in a gas turbine engine
InactiveUS20120180500A1Reduce vibrationContinuous combustion chamberEngine fuctionsTurbineGas turbines
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
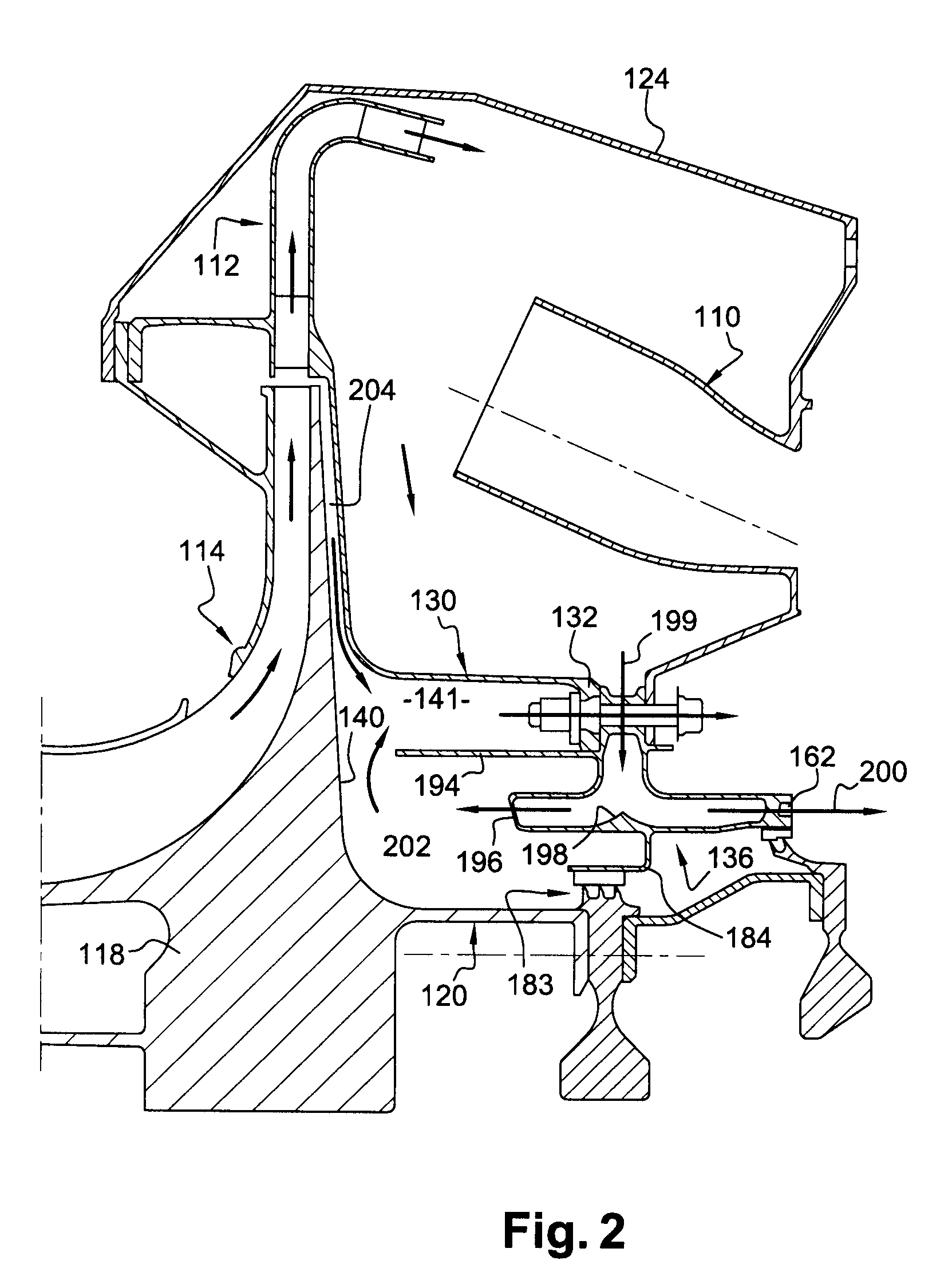
Apparatus and method for cooling a turbine airfoil arrangement in a gas turbine engine
A turbine airfoil arrangement for a gas turbine engine includes an airfoil having an inlet and an exit, the inlet configured to receive a cooling gas flow operable to cool at least part of an other airfoil; and a passage disposed in the airfoil and fluidly coupled to the inlet and the exit, the exit being configured to pass at least some of the cooling gas flow to the other airfoil.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE CORP
Apparatus and process for testing an industrial gas turbine engine and components thereof
ActiveUS20140053641A1Gas-turbine engine testingJet-propulsion engine testingIndustrial gasEngineering
A system and a process for testing a gas turbine engine or component thereof, especially for a large aero gas turbine engine, and for a process for testing a large industrial gas turbine engine that requires large flow capacity and pressure ratios. The system and process may include the use of a large compressed air storage reservoir to provide compressed air to the testing system. Further, the system and process may also include the use of a pre-heating system, which may include a heater and a heat exchange device, to warm the compressed air from the compressed air storage reservoir to a temperature suitable to simulate normal operating conditions of the gas turbine engine or component thereof.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
Diagnostic system and method for monitoring operating conditions of components of a turbine machine
A diagnostic system and method for monitoring operating conditions of turbine machine components (18, 19, 22, 23) that comprise one or more non-contact sensors (24, 31) that detect an operating condition of a turbine component (18, 19, 22, 23) over a defined region of the component. In addition, point sensors (50) are provided that detect and monitor the same operating condition within the defined region. Data generated from the point sensor (50) is used to calibrate the non-contact sensor (24, 31) and the data generated by the non-contact sensor (24, 31).
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
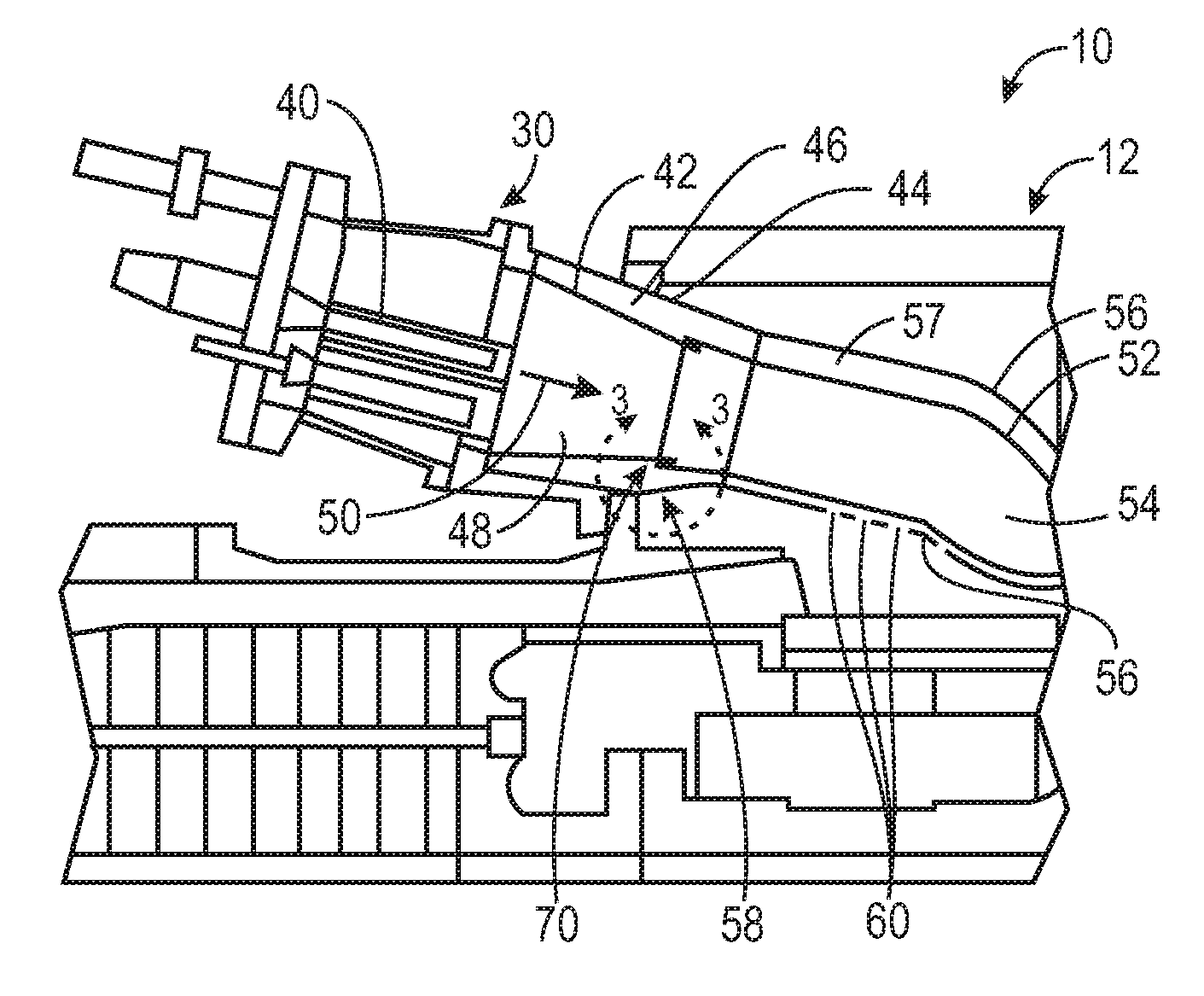
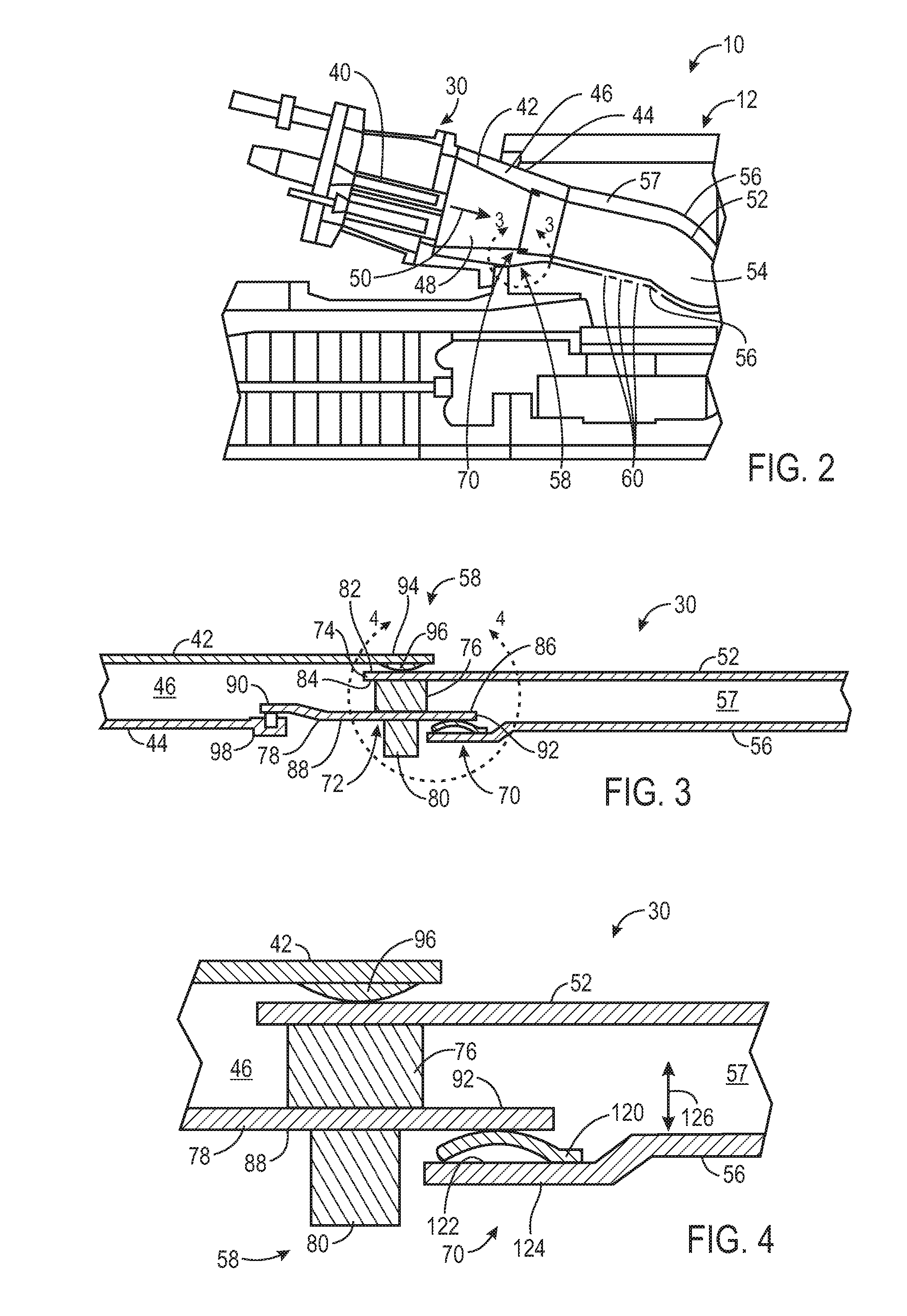
Turbine, particularly useful for small aircraft
InactiveUS20060107647A1Reducing weight and quantityImprove efficiencyRotary bearingsTurbine/propulsion fuel supply systemsCombustion chamberLow speed
A turbine includes a combustion chamber with deflectors generating vortices in a secondary gas flow into the combustion chamber, thereby confining the flame front from penetrating into the cold region of the chamber under variable operating conditions, simplifying cooling of the chamber walls. The turbine further includes devices for decoupling vibrations between the high- and low-speed shafts, including a loosely mounted spline coupling the high-speed shaft to the step-down system and disk dampening means coupling the step-down system to the low-speed output shaft.
Owner:FLORESTAN TECH PTY LTD
Metallic coated cores to facilitate thin wall casting
Owner:RAYTHEON TECH CORP
Onboard supplemental power system at varying high altitudes
ActiveUS20060016197A1Gas turbine plantsTurbine/propulsion fuel controlHybrid systemElectric power system
Systems and methods for supplementing a power system to achieve consistent operation at varying altitudes are disclosed herein. A hybrid power system comprising a single power source driving multiple generators may implement a power recovery turbine to drive a supercharger compressor, which may provide compressed air at increased altitudes. The supplemental power system disclosed herein provides necessary shaft horsepower at high altitudes to drive a generator and produce cooling air.
Owner:STEWARD DAVIS INT
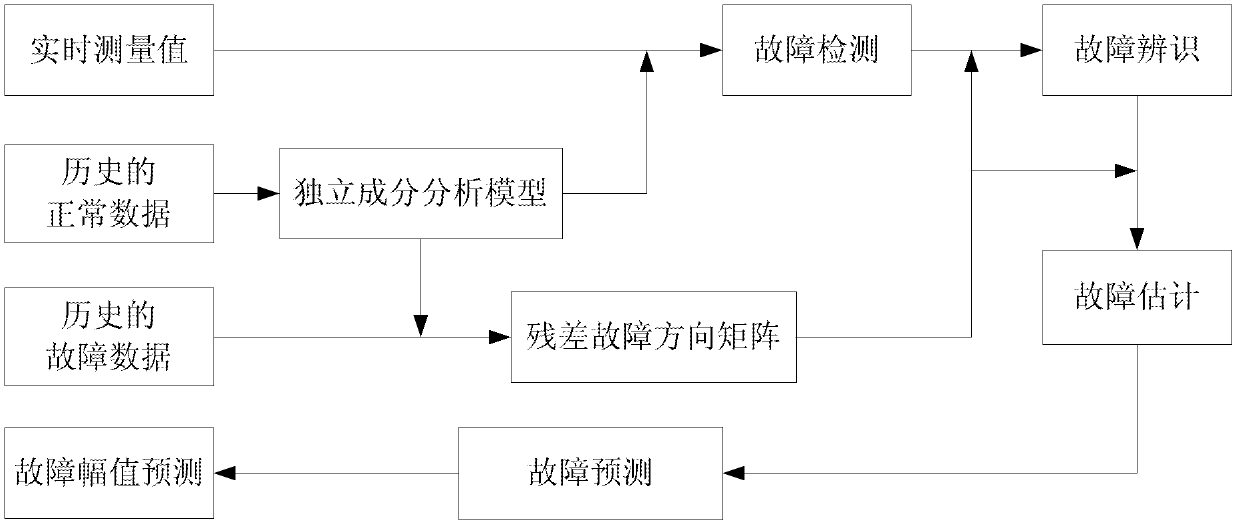
Failure prediction method based on ICA reconstruction
ActiveCN102539192ASolve the problem of not being able to utilize multi-dimensional effective dataImprove forecast accuracySubsonic/sonic/ultrasonic wave measurementStructural/machines measurementReal-time dataAlgorithm
Owner:BEIJING INFORMATION SCI & TECH UNIV
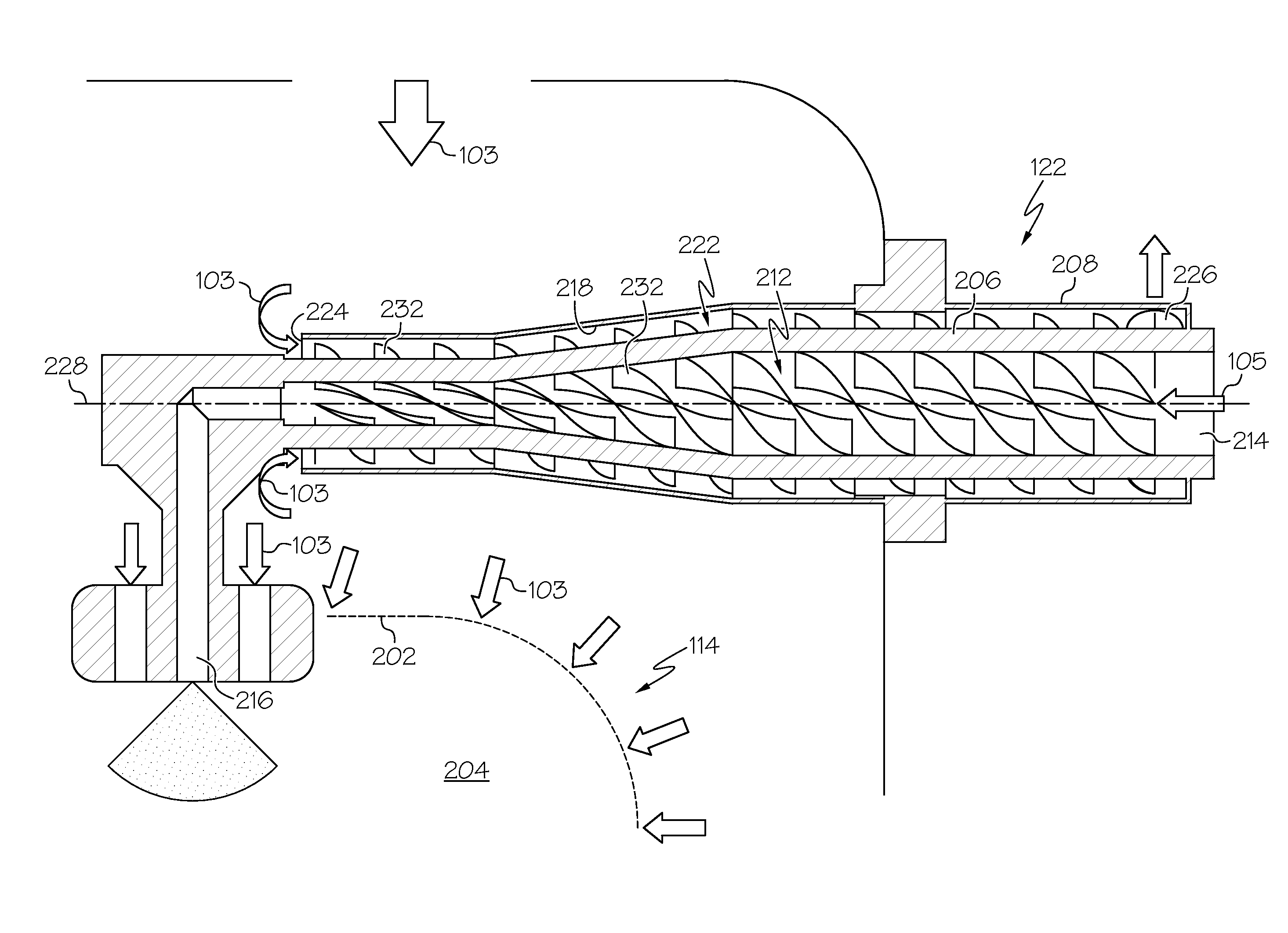
Elevating fountain stage
ActiveCN102031881AEnhance dynamic look and feelPracticalLiquid spraying apparatusTheatresWater flowSpray nozzle
Owner:东莞市环宇文化科技有限公司
Cylinder head with turbine
InactiveUS20120055424A1Large amount of heatA large amountPump componentsEngine fuctionsCylinder headRadial turbine
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Fuel cell automobile air supply system based on organic Rankine cycle and control method thereof
ActiveCN109980251AIncrease net output powerReduce parasitic lossFuel cell heat exchangeReactant parameters controlAxial compressorPlate heat exchanger
The invention discloses a fuel cell automobile air supply system based on an organic Rankine cycle. The system comprises a boosting circuit and a waste heat utilization circuit, wherein the boosting circuit comprises a fuel cell stack, a turbine, a first compressor, a second compressor, a first intercooler, an air compressor, a heat exchanger and a second intercooler, which are sequentially connected; the waste heat utilization circuit comprises an organic working fluid pump, a heat exchanger and an expander connected in sequence; the first compressor is connected to the outside air, the expander is connected to the second compressor for driving the second compressor to operate; when the waste heat utilization circuit is opened, the waste heat of the air compressor flows into the heat exchanger to heat the organic working medium and drive the expander to compress the second compressor; when the waste heat utilization circuit is closed, the second compressor does not operate, and the boosting circuit is a low-pressure boosting circuit. The invention also provides a control method for a fuel cell automobile air supply system based on an organic Rankine cycle.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
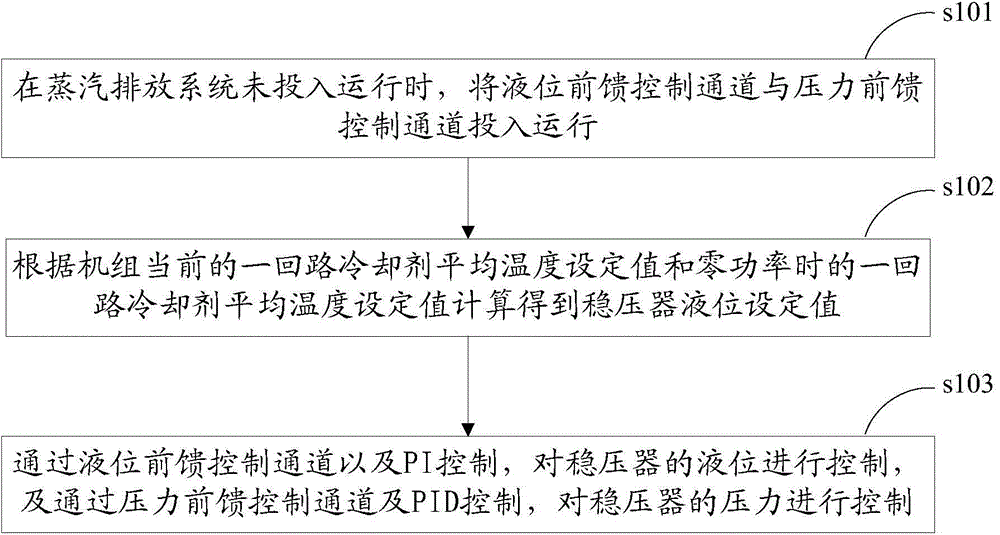
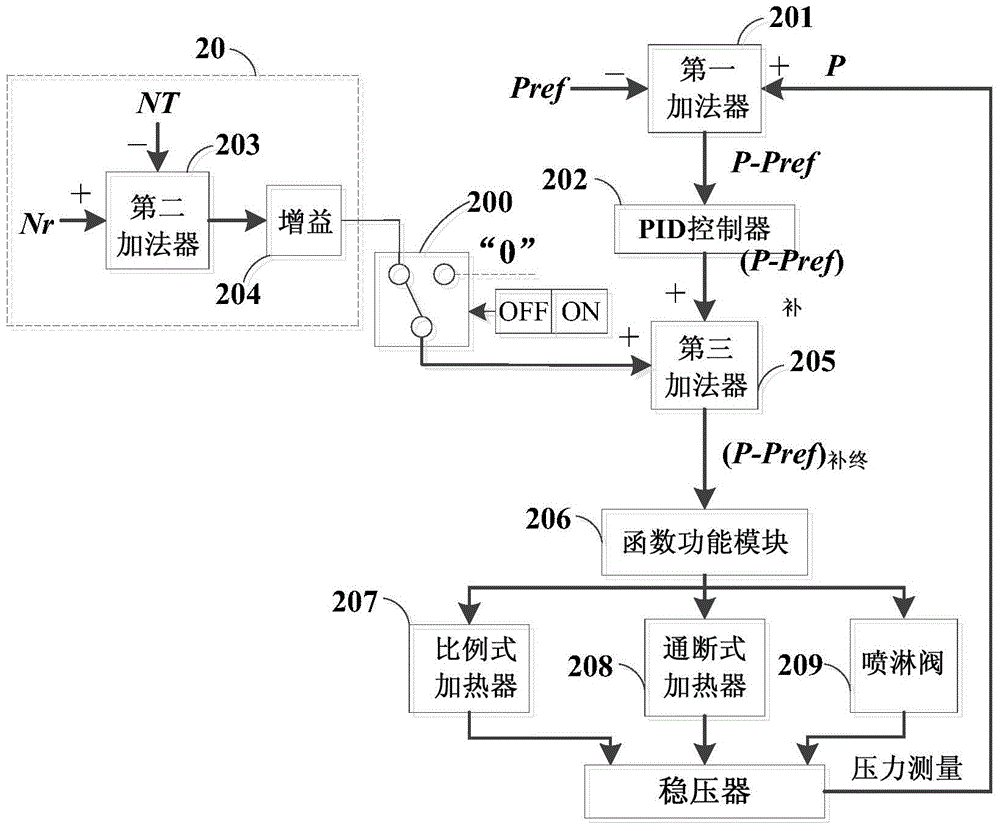
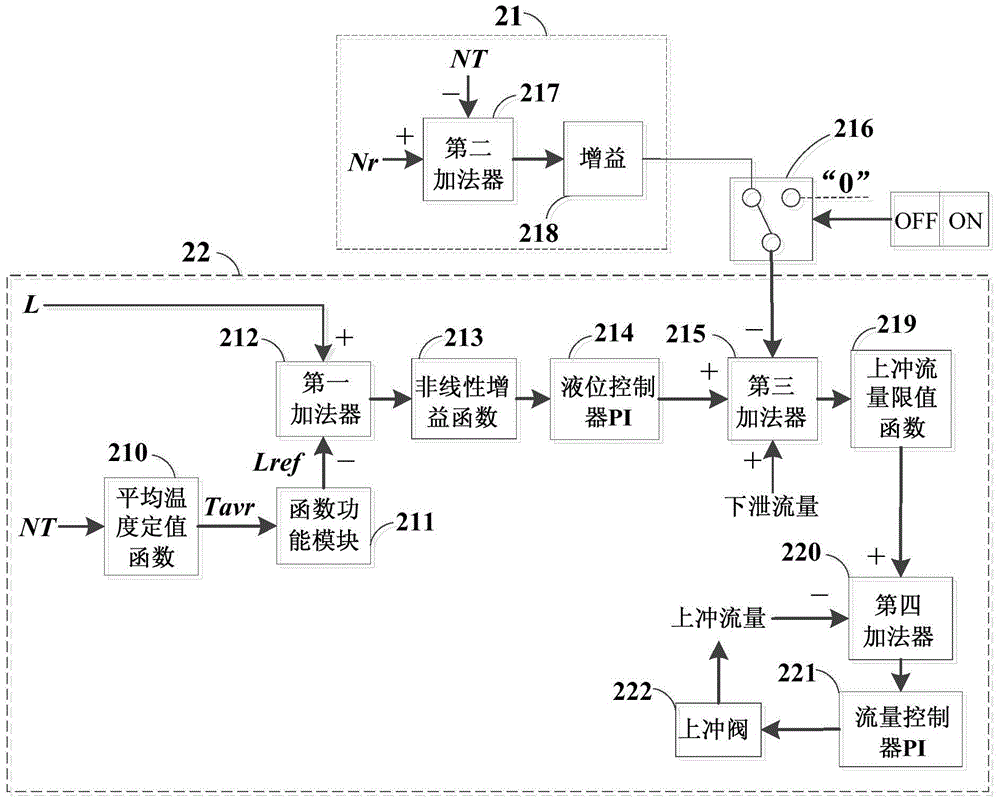
Feedforward-feedback composite control method and system for pressure and liquid level of nuclear power station voltage stabilizer
InactiveCN104637557AImprove controlImprove stabilityNuclear energy generationNuclear power plant controlStable stateNuclear power
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID
Wind jet turbine
InactiveUS20120068670A1Reduce weightIncrease wind speedEmergency protective circuit arrangementsDynamo-electric converter controlEngineeringTurbine
Owner:BERSIEK SHAMEL A
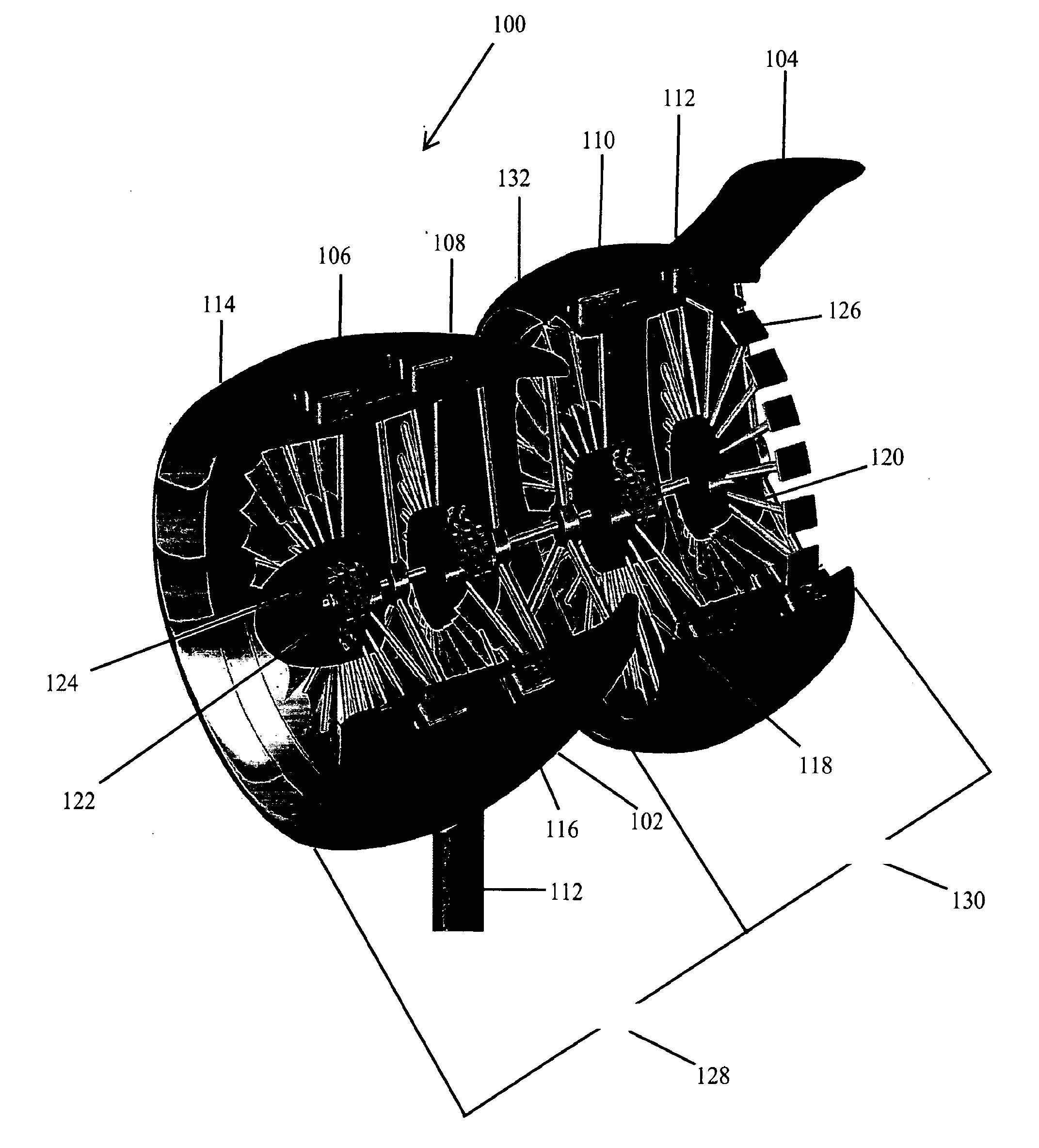
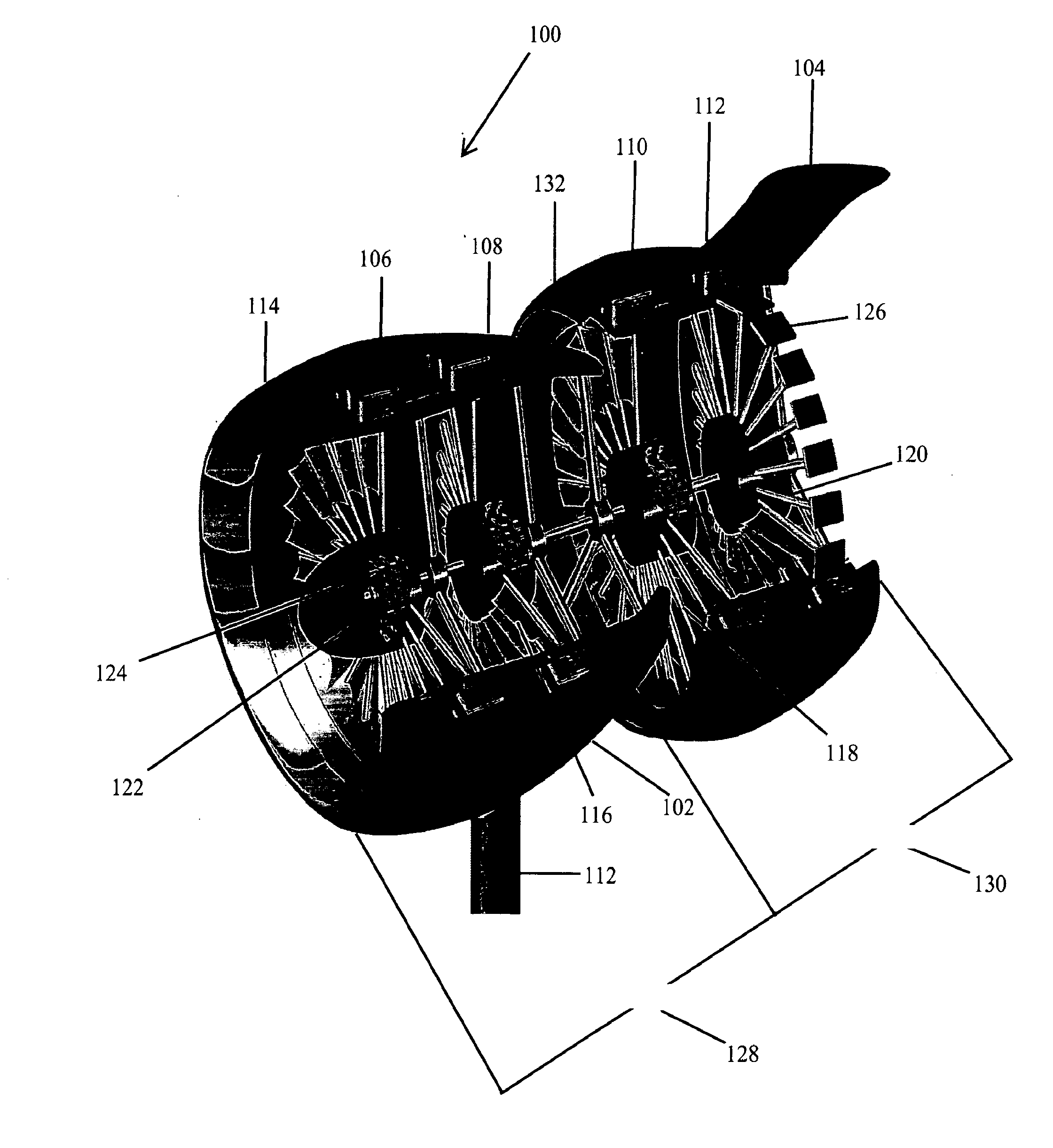
Methods and apparatus for assembling gas turbine engine stator assemblies
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Water treatment system
InactiveUS20120186658A1Increase flow rateHigh performance filtration stageWater treatment parameter controlOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPositive airway pressureWater treatment system
Owner:ACCESS BUSINESS GRP INT LLC
Piezomagnetic turbine loss type reinforced concrete strain sensor and piezomagnetic stain meter thereof
InactiveCN101806577AHigh sensitivityImprove stabilityForce measurement by measuring magnetic property varationFluid pressure measurement by electric/magnetic elementsObservational errorCantilevered beam
The invention discloses a piezomagnetic turbine loss type reinforced concrete strain sensor, and is characterized in that a piezomagnetic turbine loss effect is used as a sensing mechanism to manufacture a piezomagnetic turbine loss type reinforced concrete strain sensor and a piezomagnetic stain meter thereof for measuring surface strain, inner strain and steel bar strain. The sensor is designed with a mechanics model and a deformation structure of a combined cantilever beam or a cantilever curved beam with two elastic free ends. The invention uses a seamless connection technology of whole manufacturing and conical hole connection and a component separation signal processing method. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the characteristics of high sensitivity, good stability, small measuring error, strong reliability, simple structure, low cost and convenient use; and the invention has wide application prospect.
Owner:何思龙
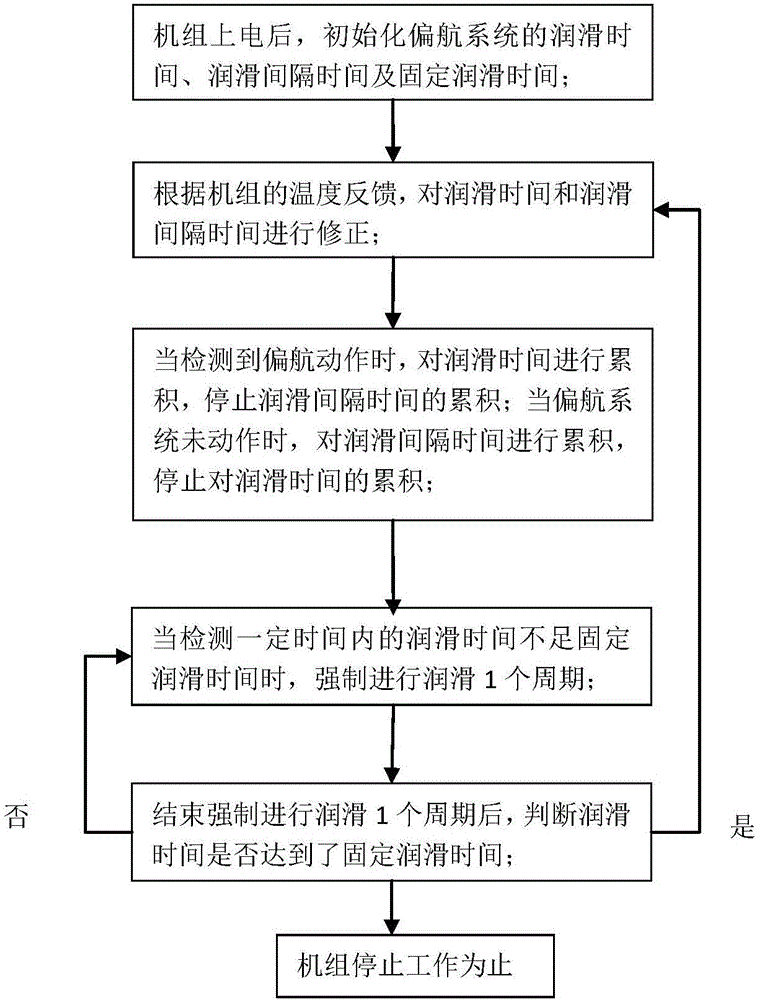
Control method for yaw lubrication system of wind turbine generator set
Owner:CRRC WIND POWER(SHANDONG) CO LTD
Method for repairing a turbine engine vane assembly and repaired assembly
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Cooled aerofoil blade or vane
ActiveUS20110058958A1Promoting a favourable pressure gradientPressure lossEngine manufactureBlade accessoriesTurbineCooling fluid
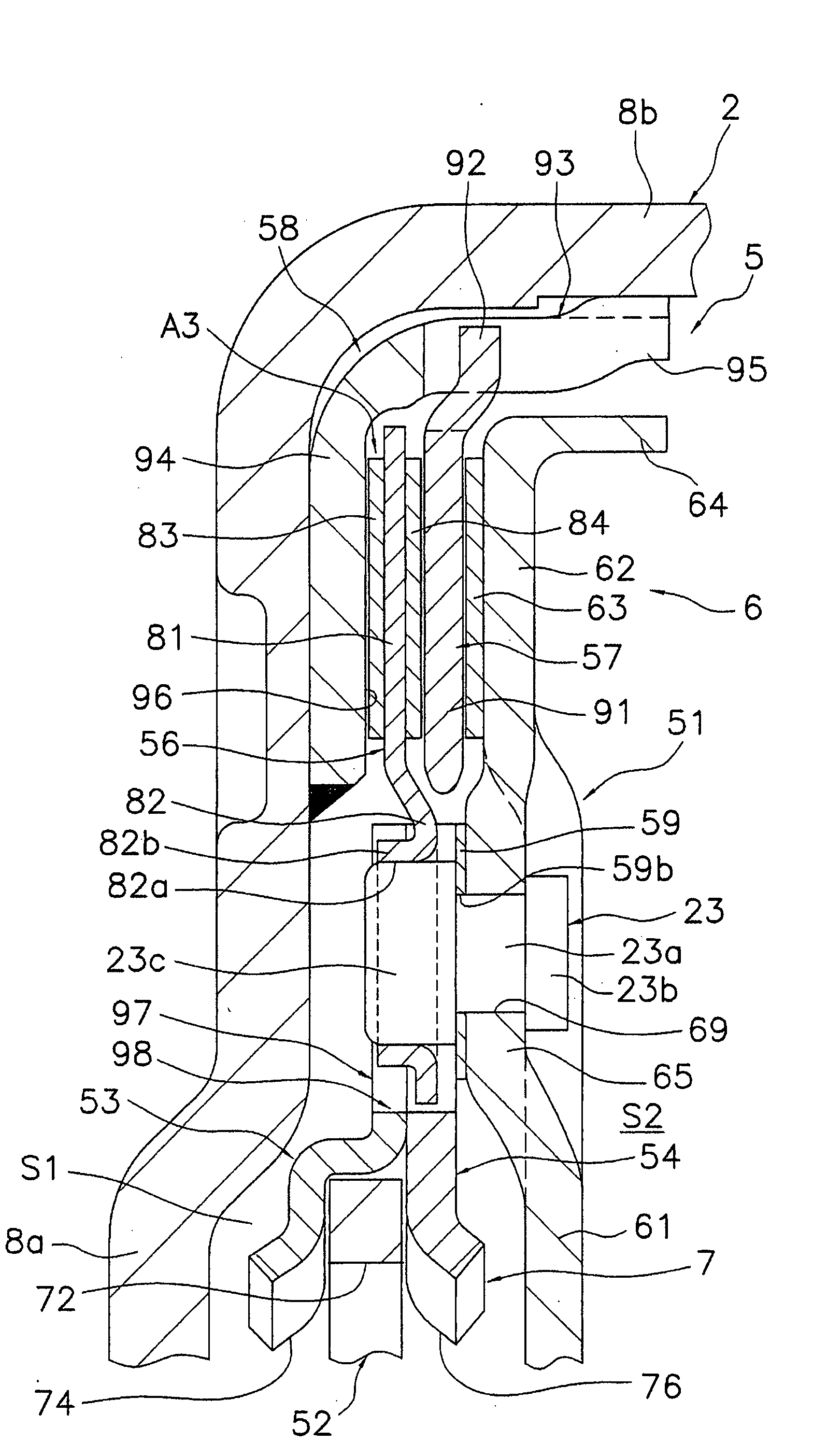
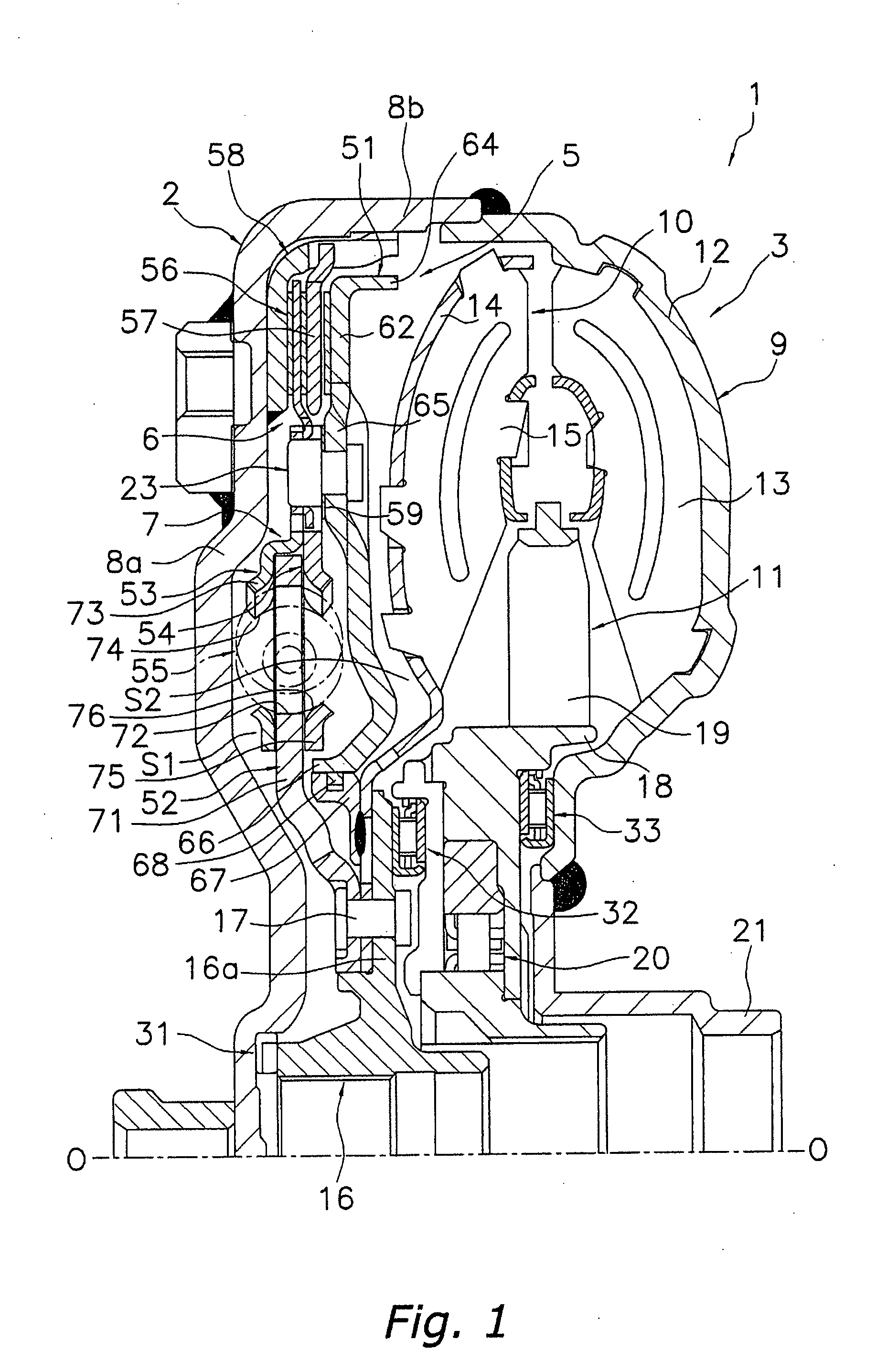
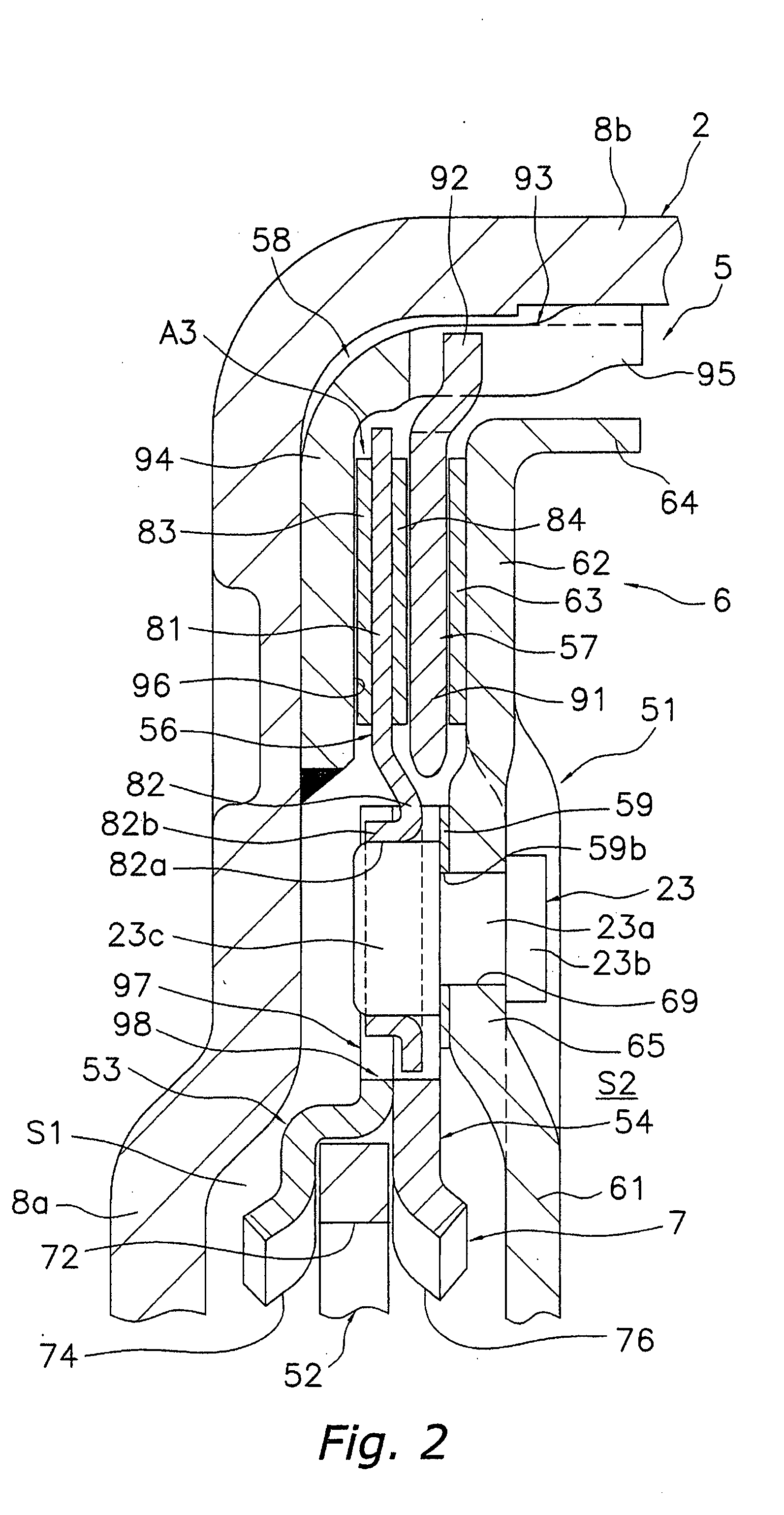
An aerofoil blade or vane (1) suitable for the turbine of a gas turbine engine includes a longitudinally extending aerofoil portion (7) having facing wall parts (20, 22). The wall parts being interconnected by a generally longitudinally extending divider member (17) to partially define first and second cooling fluid passage portions (11, 15) disposed in side-by-side generally longitudinally extending relationship. The first and second passage portions being interconnected in series fluid flow relationship by a bend passage portion (13). The first passage portion is adapted to direct cooling fluid to the bend portion and the second passage portion being adapted to exhaust cooling fluid from the bend portion. The divider member has a first local thickening (33) in the region of the bend portion to provide a localised contraction of the downstream end of the first passage portion to accelerate the cooling fluid flow before it enters the bend passage portion. The divider member has a second local thickening (31) in the region of the bend portion to provide a localised progressive series narrowing and opening of the upstream end of the second passage portion in the general direction of cooling fluid flow.
Owner:ROLLS ROYCE PLC
Low modulus insert for a component of a gas turbine engine
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
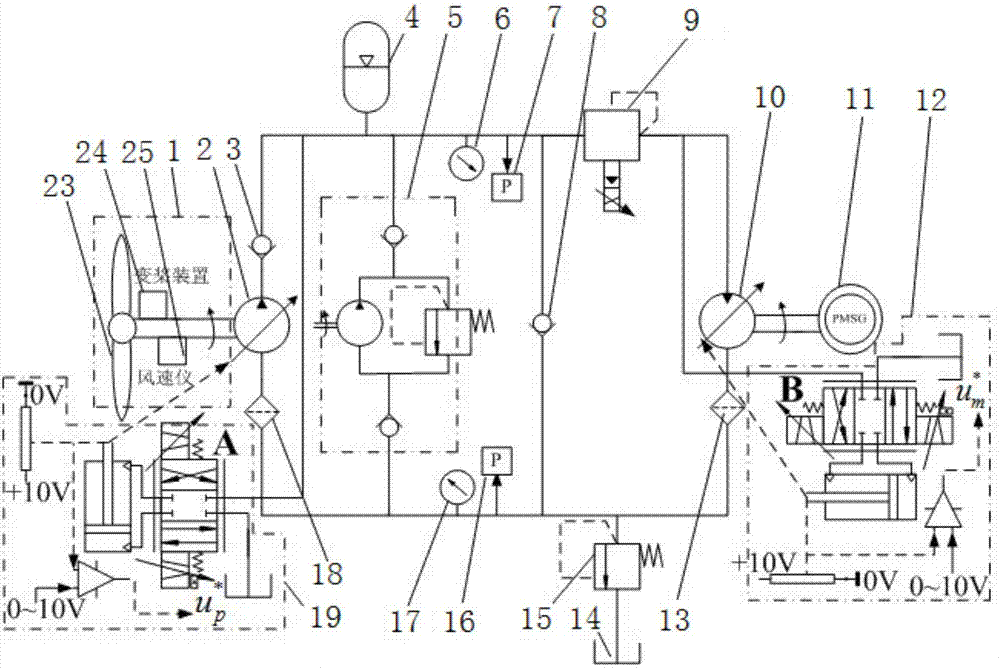
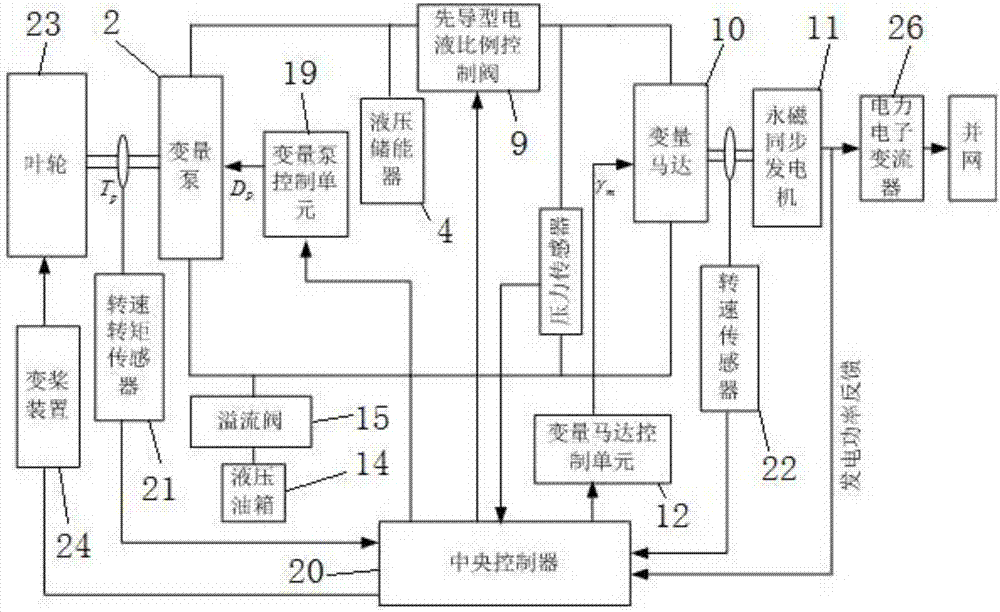
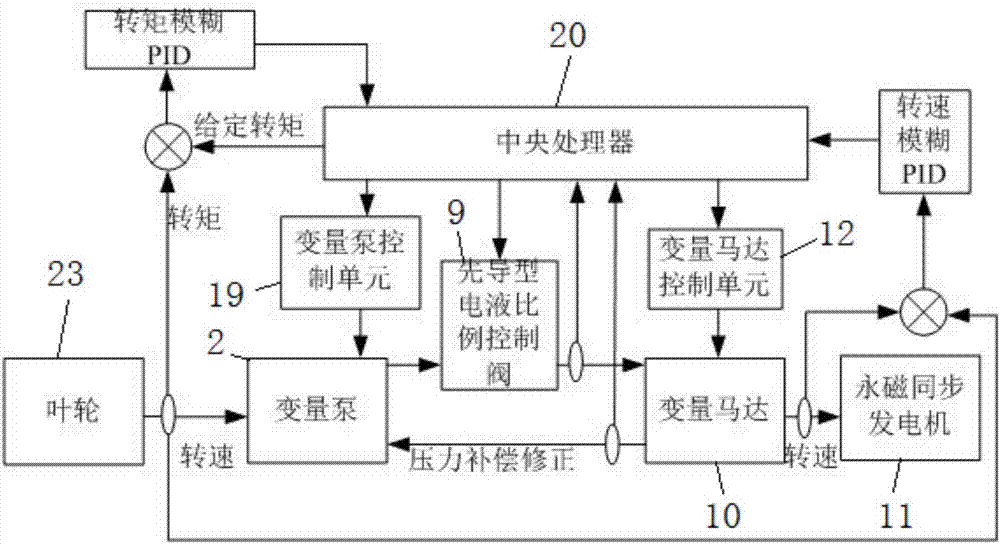
Variable-pitch hydraulic transmission wind turbine and control method thereof
ActiveCN107269466AImprove running qualityRealize variable speed constant frequency controlWind motor controlMachines/enginesProportional controlFuel tank
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
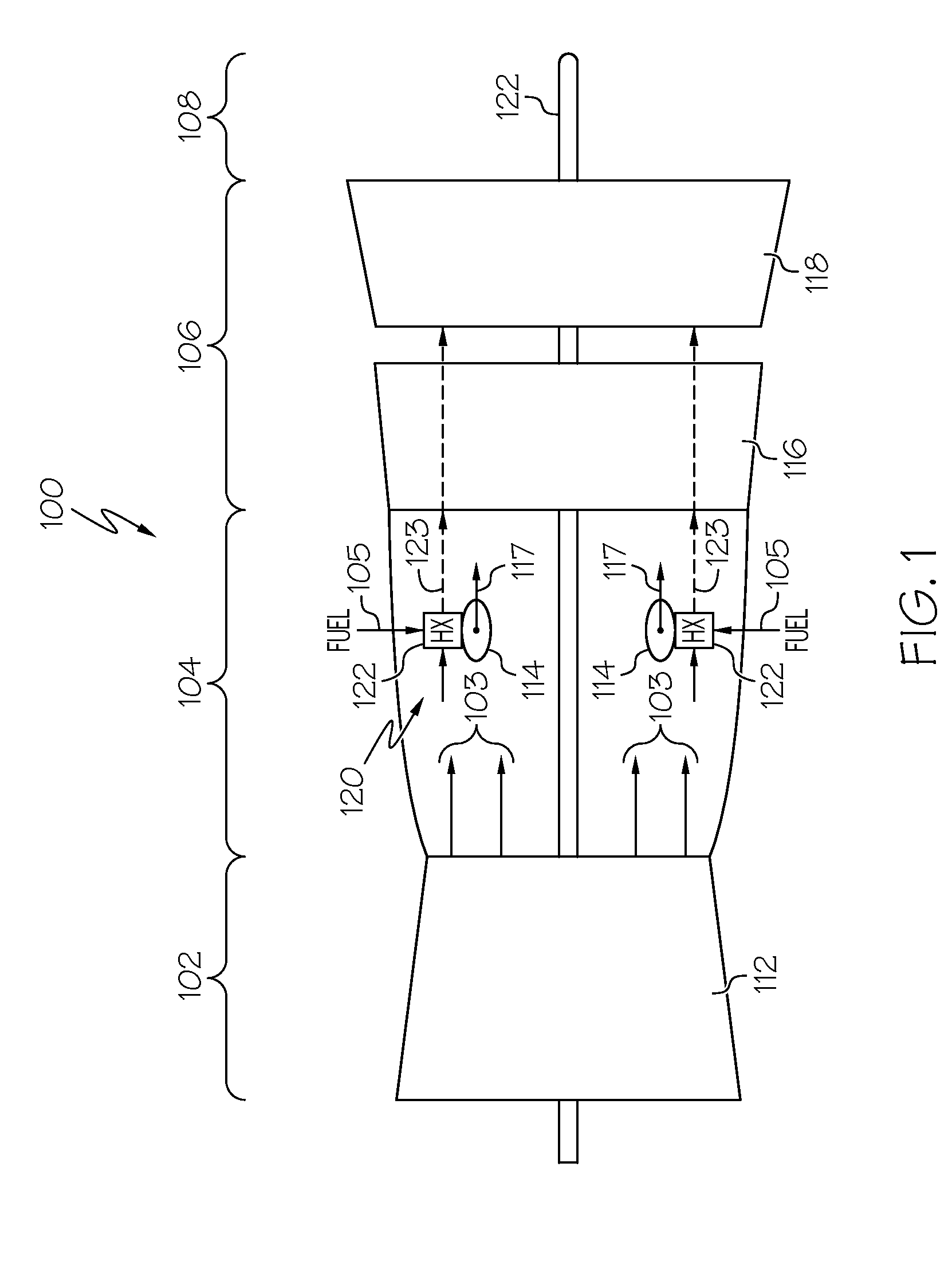
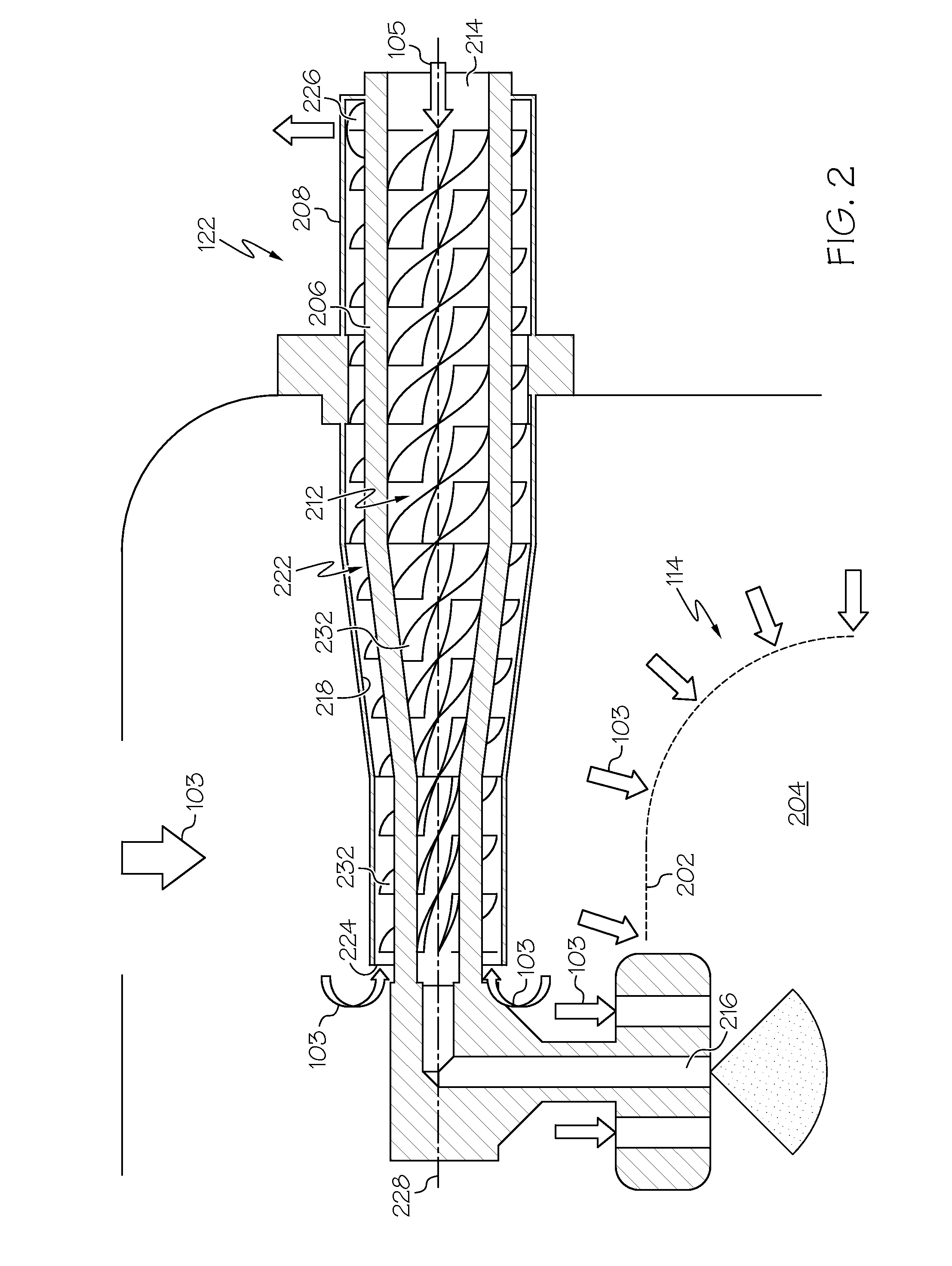
Gas turbine engine fuel cooled cooling air heat exchanger
ActiveUS20160290290A1SFC also risesReduce trafficBurnersContinuous combustion chamberTurbineGas turbines
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap