Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3 results about "Quantum efficiency" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio, of a photosensitive device or it may refer to the TMR effect of a Magnetic Tunnel Junction. This article deals with the term as a measurement of a device's electrical sensitivity to light. In a charge-coupled device (CCD) it is the percentage of photons hitting the device's photoreactive surface that produce charge carriers. It is measured in electrons per photon or amps per watt. Since the energy of a photon is inversely proportional to its wavelength, QE is often measured over a range of different wavelengths to characterize a device's efficiency at each photon energy level. The QE for photons with energy below the band gap is zero. Photographic film typically has a QE of much less than 10%, while CCDs can have a QE of well over 90% at some wavelengths.
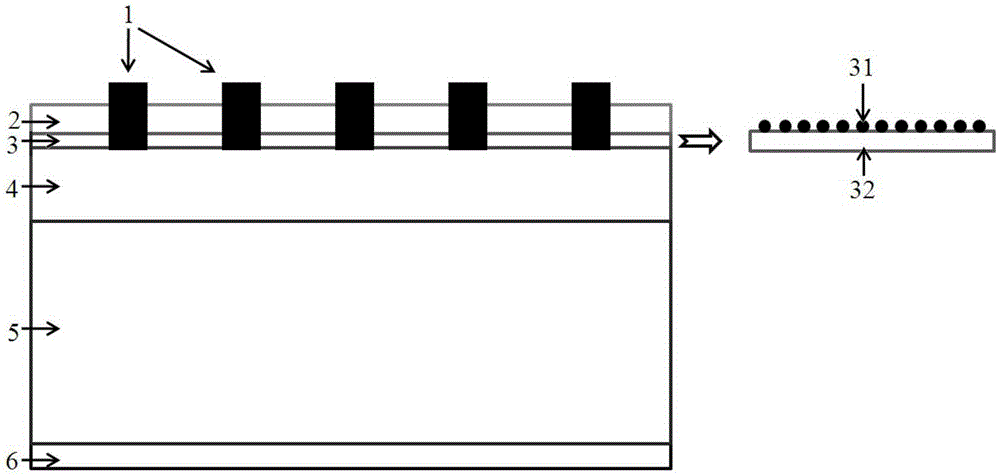
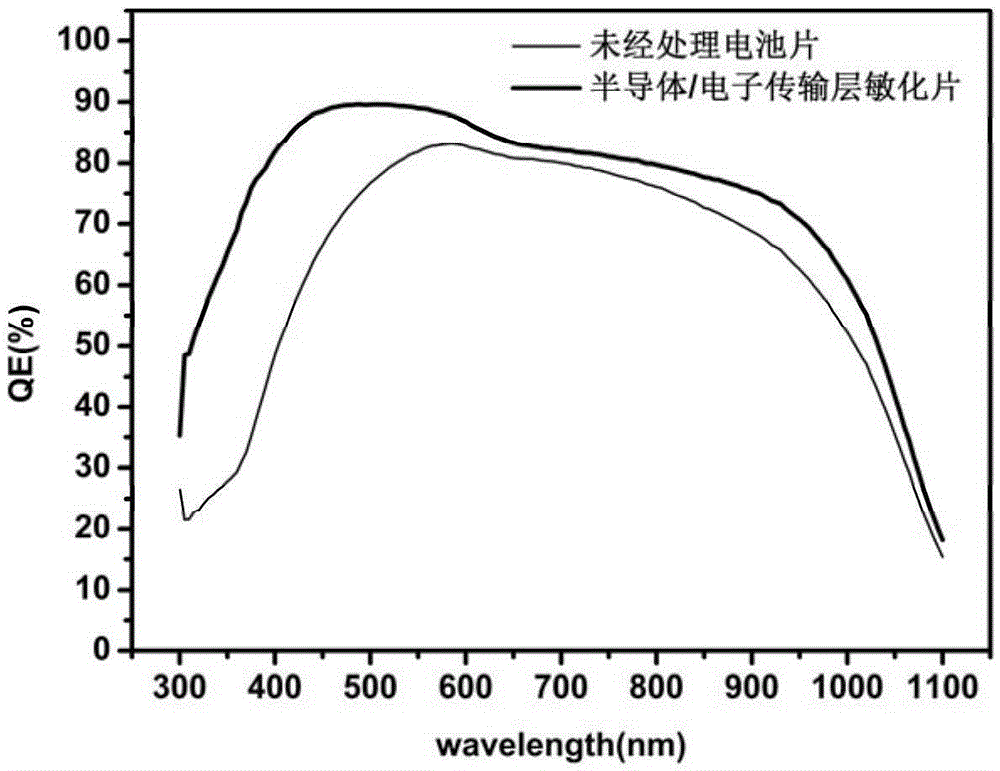
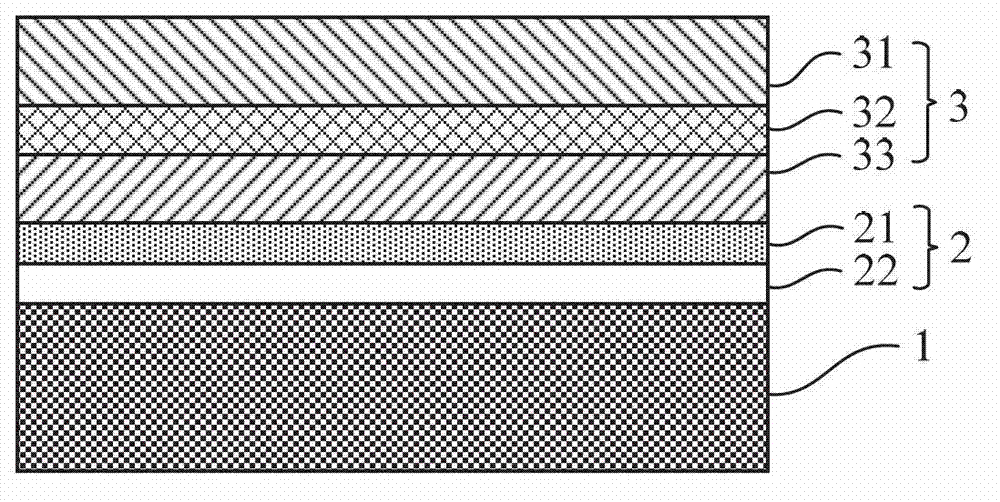
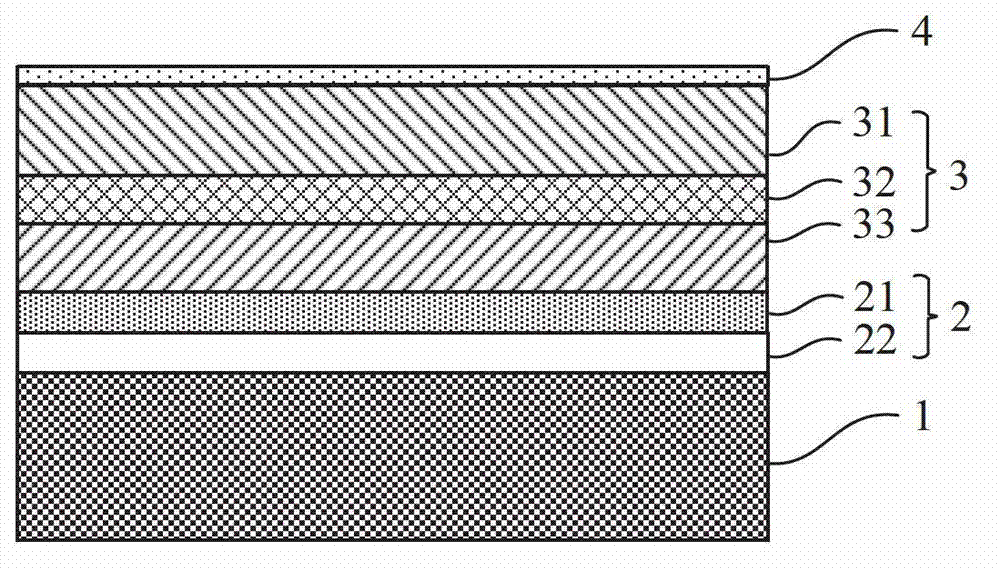
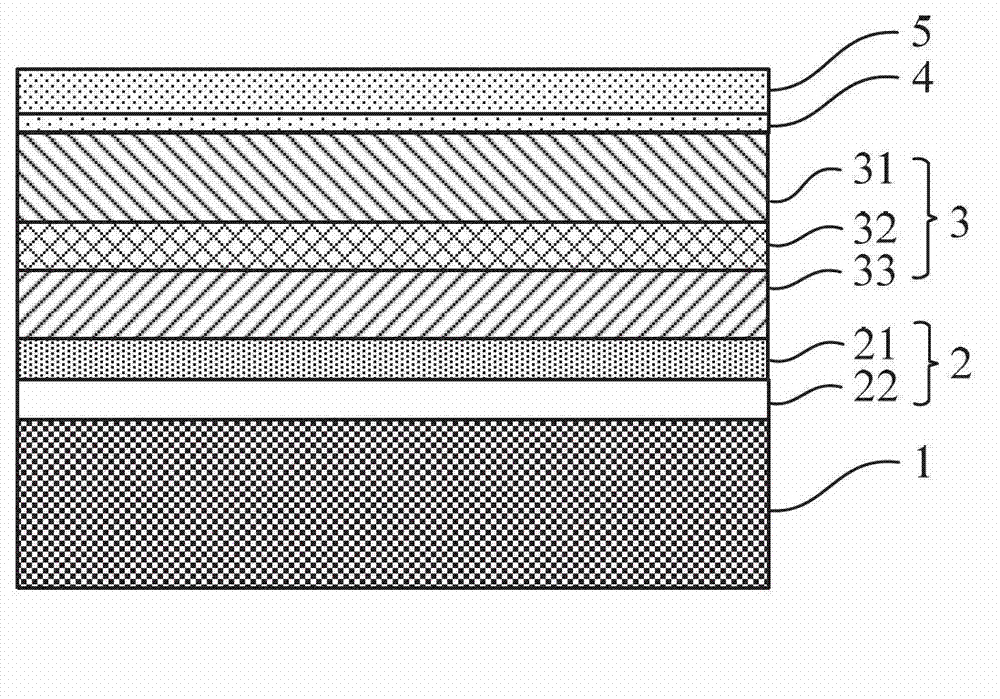
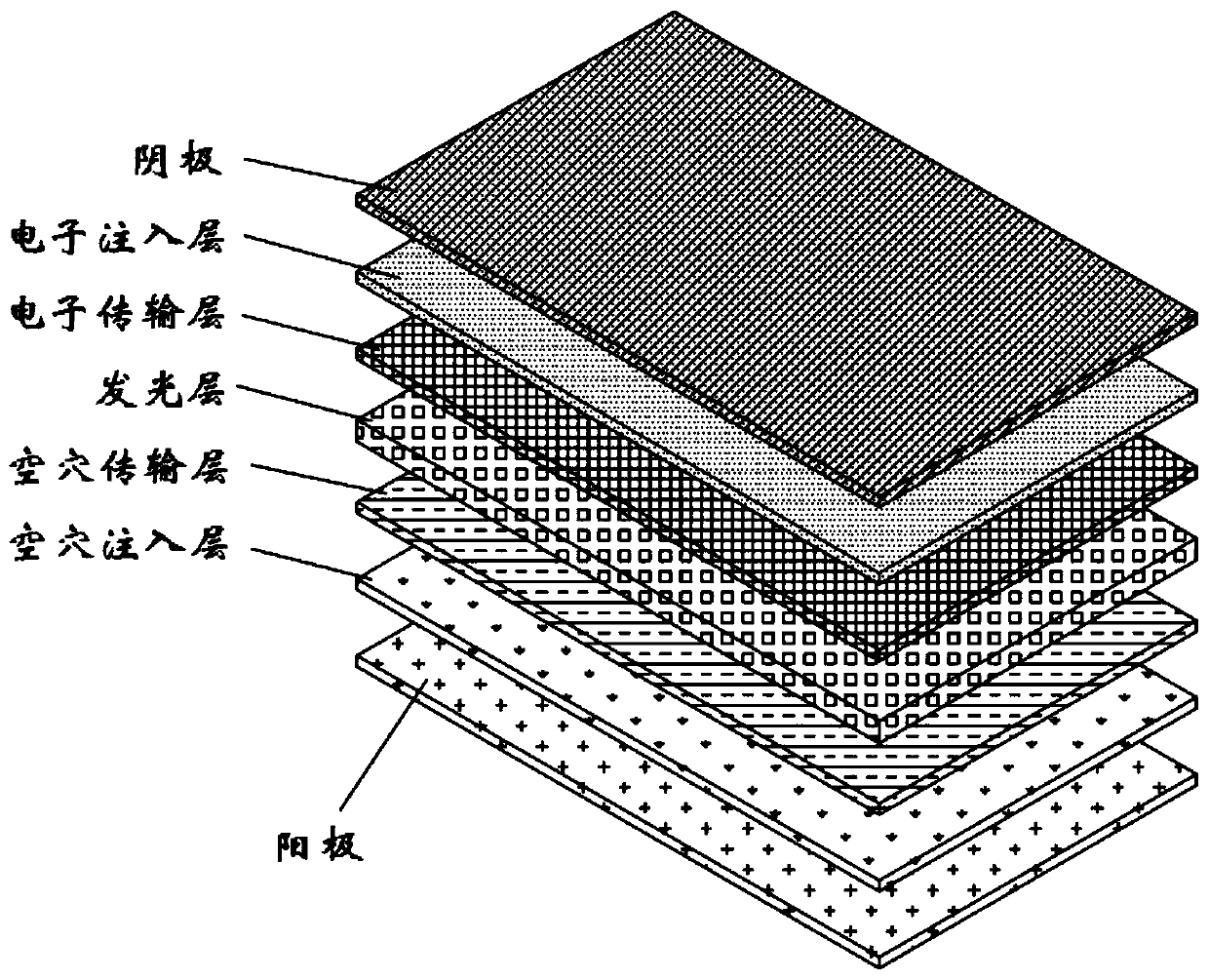
Multi-quantum well photovoltaic battery based on nanometer graphite electron transmission layer, and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105244390AEvenly distributedGood light and heat stabilityLight-sensitive devicesFinal product manufactureElectrical batterySilicon solar cell
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
LED (light-emitting diode) chip and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102931305AImprove external quantum efficiencyAvoid quality defectsSemiconductor devicesQuantum efficiencyLow speed
Owner:宁波安芯美半导体有限公司
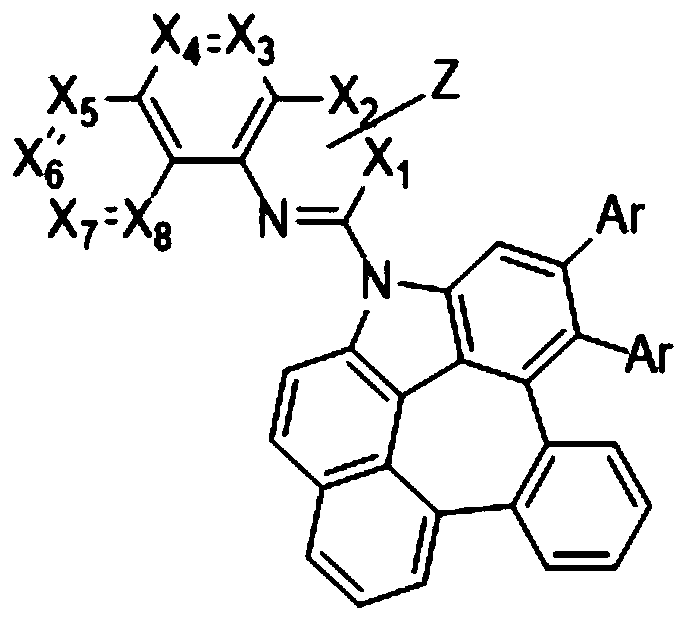
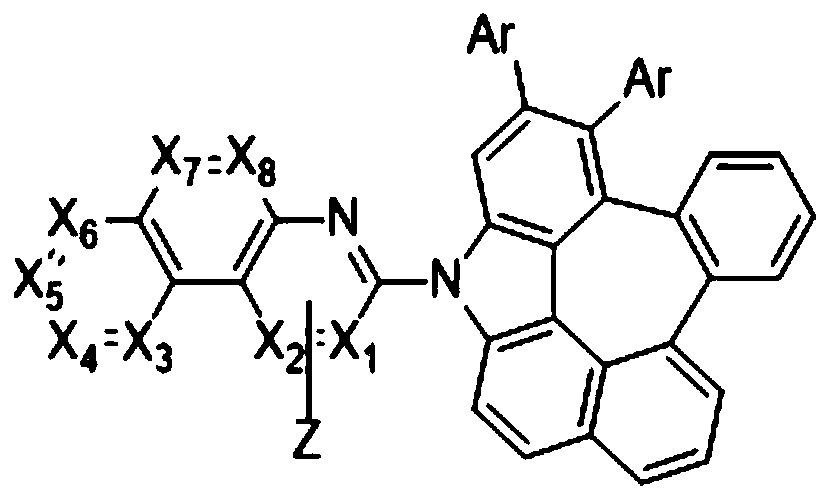
Phosphorescent compound and organic luminescent device employing same
PendingCN110862379AIncrease brightnessImprove current efficiencyOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesQuantum efficiencyAryl
Owner:YURUI SHANGHAI CHEM
Who we serve
- R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
Why Eureka
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Social media
Try Eureka
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap