Production process method for die pressing composite material leaf springs
A composite material board and process method technology, applied in the field of resin-based composite material manufacturing, can solve the problems of low production efficiency, high cost, inability to meet market demand, etc., and achieve the effects of improving production efficiency, realizing mass production, and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0020] Embodiments of the present invention are described in detail below, examples of which are shown in the drawings, wherein the same or similar reference numerals designate the same or similar elements or elements having the same or similar functions throughout. The embodiments described below by referring to the figures are exemplary only for explaining the present invention and should not be construed as limiting the present invention.
[0021] For the production process of the present invention such as figure 1 shown.
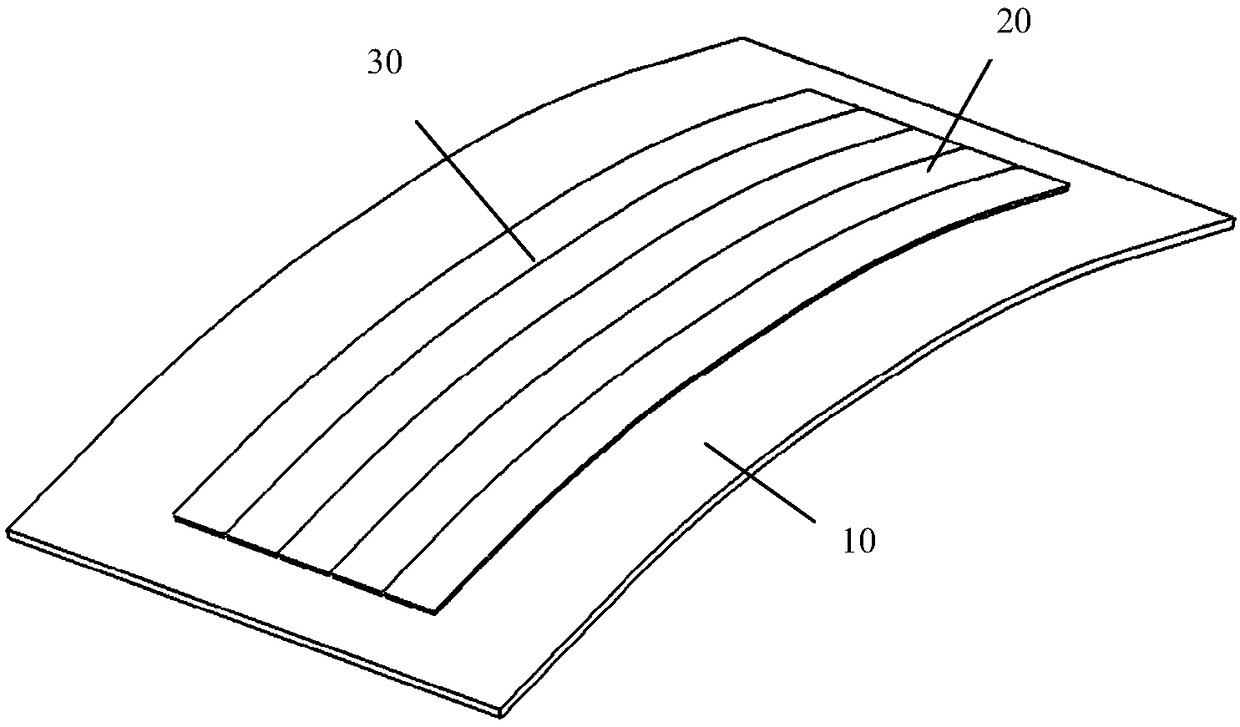
[0022] For a step billet of the present invention and b step billet cutting process such as figure 2 shown. The prepreg is laid up on the laying table 10 to form a monolithic blank 30 , and a laser cutting machine is used to cut the monolithic blank 30 into several strips of blanks 20 according to the required width.
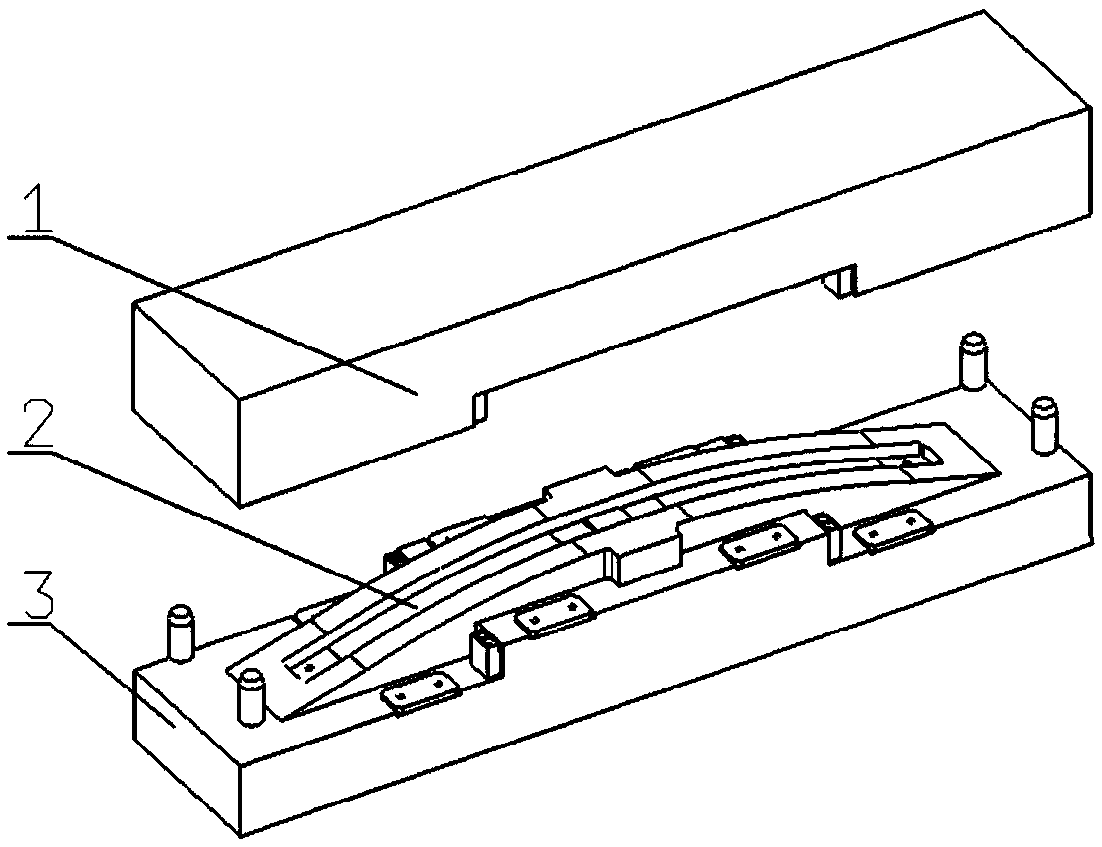
[0023] For the step c of the present invention into the mold process such as image 3 As shown, the blank 20 cut in step b is put into
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap