Method for recycling residual sintering raw materials after growth of silicon carbide crystals
A technology of crystal growth and silicon carbide, applied in the direction of crystal growth, single crystal growth, single crystal growth, etc., can solve problems such as complex methods
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0027] A method for reusing remaining sintered raw materials after growing silicon carbide crystals, comprising the steps of:
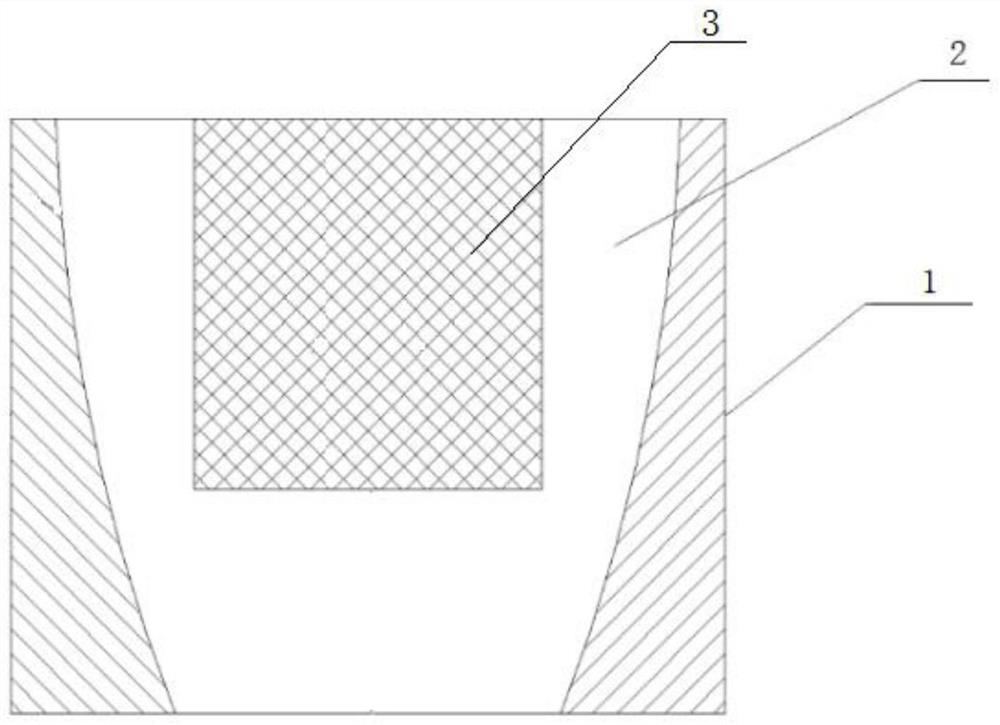
[0028] Step 1. Divide the remaining sintered raw materials after silicon carbide crystal growth in the crucible into graphitization area 1, partial graphitization area 2, and low graphitization area 3, for use;
[0029] Step 2, take the remaining sintered raw materials in the low graphitization area, and make a cylindrical polycrystalline rod for use;
[0030] Step 3, weighing the mass of the cylindrical polycrystalline rod obtained in step 2, then weighing 1-1.5 times the mass of silicon carbide powder for use;
[0031] Step 4. Put the silicon carbide powder weighed in step 3 into the crucible, and then slowly insert the cylindrical polycrystalline rod into the center of the crucible. The insertion depth of the cylindrical polycrystalline rod is such that the upper end of the cylindrical polycrystalline rod is in contact with the silicon carbide The to
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0044] A method for reusing remaining sintered raw materials after growing silicon carbide crystals, comprising the following steps:
[0045] Step 1. Dividing the remaining sintered raw materials after silicon carbide crystal growth in the crucible into graphitized regions, partially graphitized regions, and low graphitized regions for use;
[0046] Step 2, taking the remaining sintered raw materials in the low graphitization area to make a cylindrical polycrystalline rod for use;
[0047] Step 3, weighing the mass of the cylindrical polycrystalline rod obtained in step 2, then weighing 1-1.5 times the mass of silicon carbide powder for use;
[0048] Step 4. Put the silicon carbide powder weighed in step 3 into the crucible, and then slowly insert the cylindrical polycrystalline rod into the center of the crucible. The insertion depth of the cylindrical polycrystalline rod is such that the upper end of the cylindrical polycrystalline rod is in contact with the silicon carbide Th
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0054] According to a method for reusing the remaining sintered raw materials after silicon carbide crystal growth described in the second embodiment, the low graphitization region in step 1 is a cylinder with the center point of the crucible as the center, and the radius length of the cylinder is 0.1 -0.75 times the radius of the crucible, the height of the cylinder is 0.2-0.8 times the height of the crucible.
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap