"nanoparticles for the encapsulation of compounds, preparation thereof and use of same"
a technology of nanoparticles and compounds, applied in the field of nanoparticles for the encapsulation of compounds, preparation thereof and use of same, can solve the problems of not being synthesized by the organism, not being able to use synthetic polymers, and changing the organoleptic characteristics of the target food, so as to avoid toxicity problems, avoid reducing bioavailability, and reduce the effect of bioavailability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparing and Characterizing Empty Casein Nanoparticles. Yield Of the Process for Obtaining them. Influence of the Type of Amino Acid Used on the Stability and Physicochemical Characteristics of the Nanoparticles
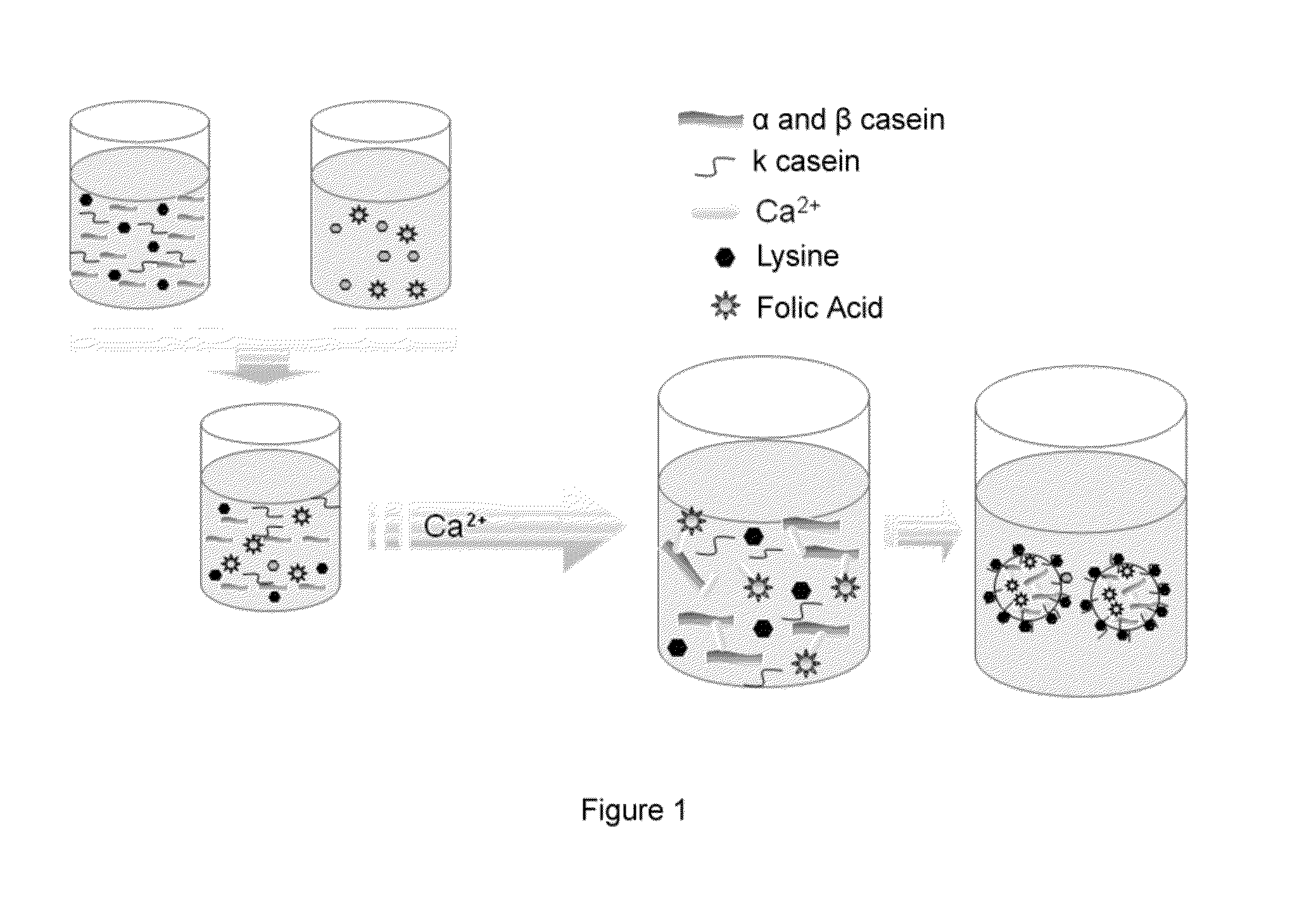
[0171]1 g of sodium caseinate was dissolved together with 90 mg of lysine in 75 mL of water. Subsequently, 40 mL of 0.8% CaCl2 was added to this solution under magnetic stirring and continuous flow. This process was performed in triplicate.
[0172]FIG. 2 (A and B) shows the images obtained by electron transmission microscopy of the casein particles obtained by this method.
[0173]In addition, the same study was performed in the absence of amino acid, or by using 50 mg of arginine instead of lysine, in order to understand the influence of the type of amino acid on the physicochemical characteristics of the particles.
[0174]Table 3 summarizes the main physicochemical parameters of the resulting nanoparticles.
TABLE 3Physicochemical characteristics of the casein nanoparticles (mean ±SD,
example 2
Preparing and Characterizing Casein Nanoparticles Containing Folic Acid. Influence of Lysine and Folic Acid Content on Encapsulation Efficiency
[0189]Different solutions all containing 100 mg of sodium caseinate and variable amounts of lysine (0-8.5 mg) were prepared in a final volume of 7.5 mL of water.
[0190]In addition, 300 mg of folic acid were dissolved together with 400 mg of lysine in 50 mL of water.
[0191]Subsequently, 1 mL of folic acid solution was added to the caseinate solution. After 5 minutes of incubation, 4 mL of 0.8% CaCl2 were added to the mixture under magnetic stirring and continuous flow. This process was performed in triplicate for each type of formulation.
[0192]FIG. 3 shows the images obtained by electron transmission microscopy of the casein particles with encapsulated folic acid obtained by this method.
[0193]The physicochemical characteristics obtained in each case are included in Table 6:
TABLE 6Physicochemical characteristics of the casein nanoparticles withfolic
example 3
Preparing and Characterizing Casein Nanoparticles Containing Folic Acid Dried by Spray Drying. Influence of the Drying Process on the Final Formulation
[0200]Two solutions, both containing 1,000 mg of sodium caseinate and 90 mg of lysine were prepared in a final volume of 75 mL of water.
[0201]In addition, 600 mg of folic acid were dissolved together with 800 mg of lysine in 100 mL of water.
[0202]Subsequently, 7.5 mL of the folic acid solution were added to each caseinate solution. After 5 minutes of incubation 40 mL of 0.8% CaCl2 were added to the mixture under magnetic stirring and continuous flow.
[0203]Finally, one of the formulations was centrifuged for the quantification of folic acid in the supernatant and pellet, while 1,900 mg of lactose was added therein to the other before drying it by means of using a spray dryer. The conditions of the process were:[0204]Air inlet temperature: 90° C.[0205]Air outlet temperature: 45° C.[0206]Air pressure: 6 bar [6×105 Pa][0207]Sample pumping ra
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Pressure | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Percent by mass | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap