Trpa1 and trpv4 inhibitors and methods of using the same for organ-specific inflammation and itch
a technology of trpa1 and trpa4, which is applied in the field of trpa1 and trpv4 inhibitors and methods of using the same for organ-specific inflammation and itch, can solve the problems of unable to demonstrate the direct role of trpv4 in itch transmission, and the specificity of trpv4 and trpa1 inhibitors is not known
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Materials and Methods
[0102]Animals.
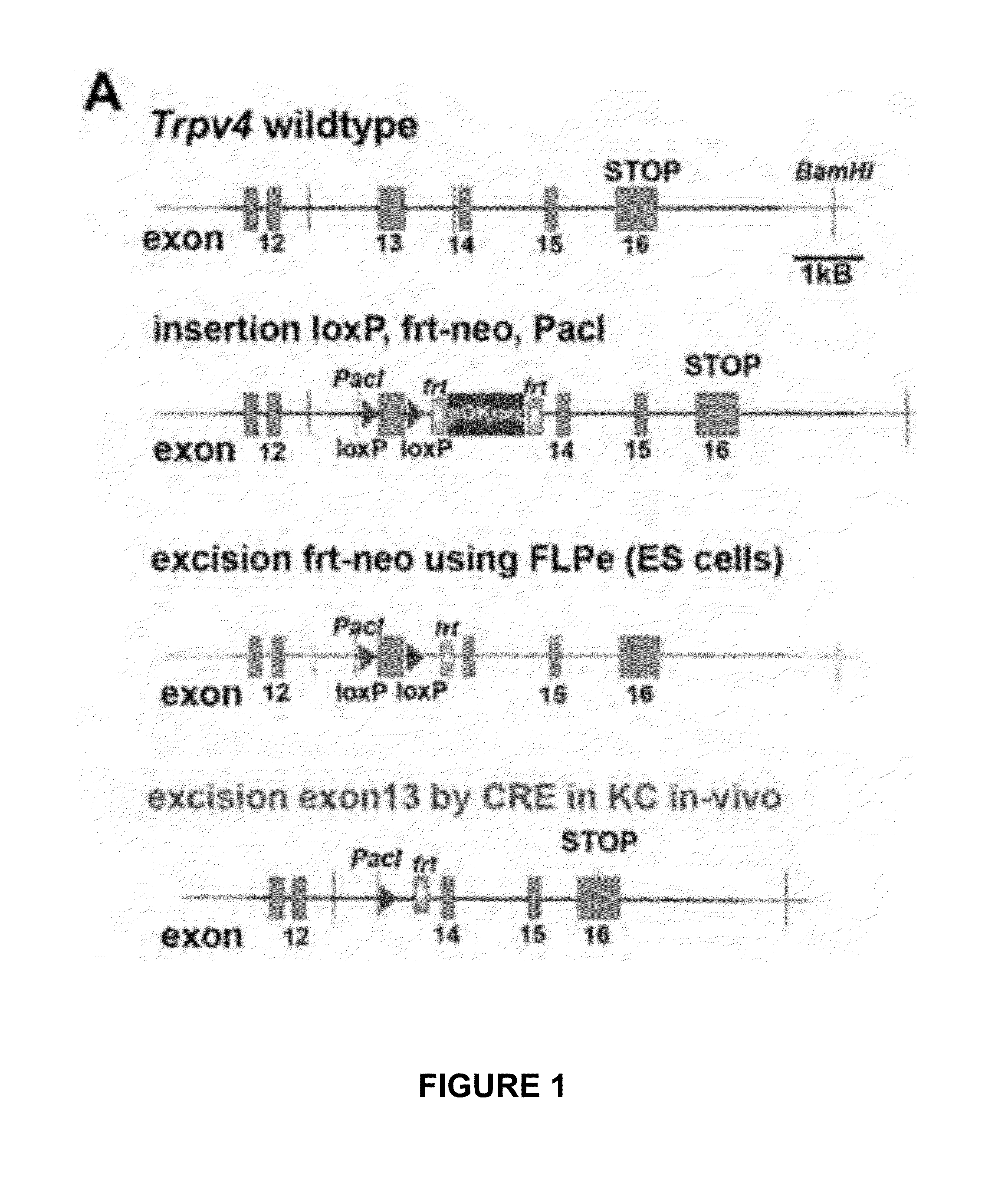
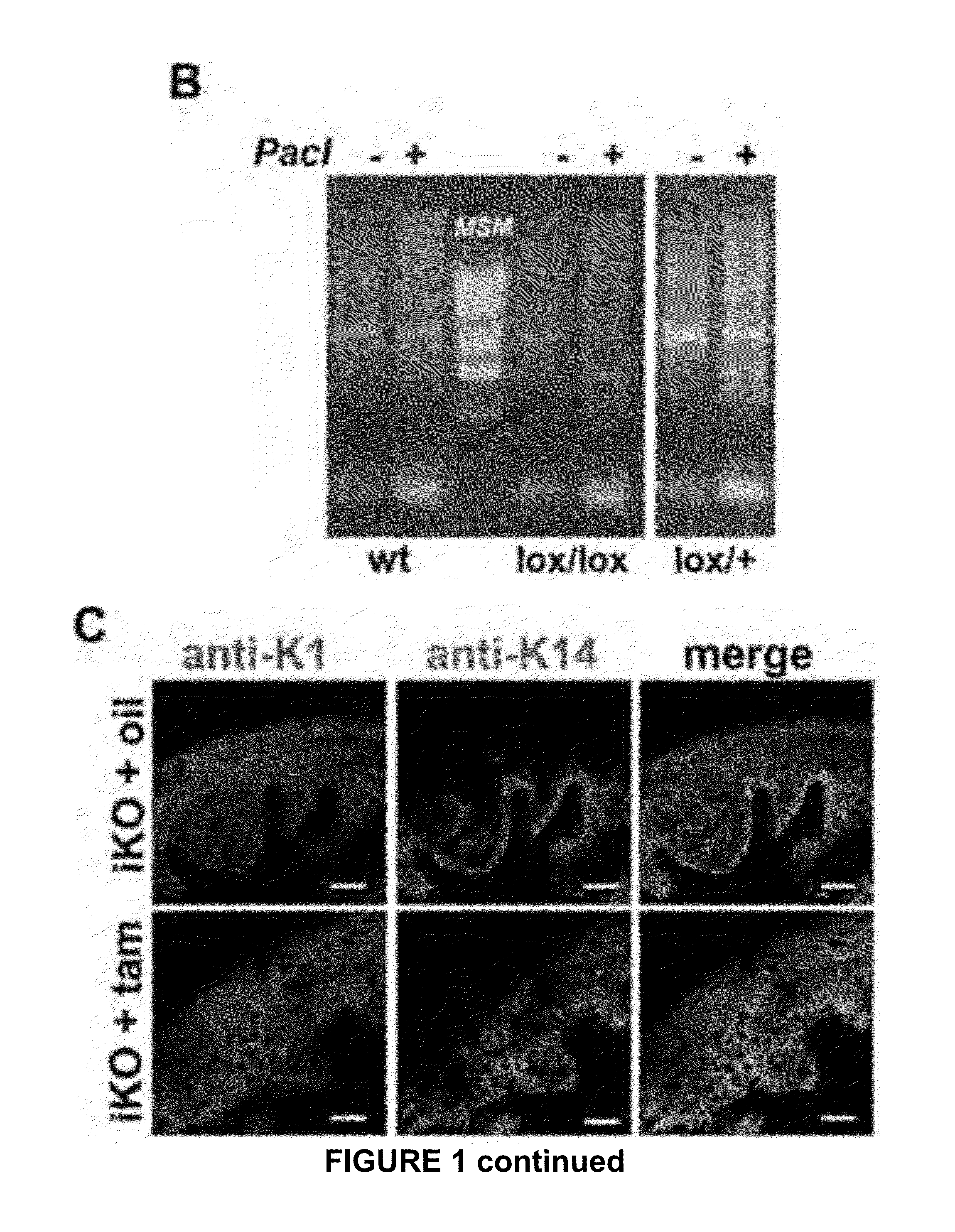
[0103]The Trpv4 genomic locus was engineered so that loxP sites surrounded exon13 which encodes TM5-6. This mutation was propagated in mice which were crossed to K14-CRE-ERtam mice, so that ((Trpv4lox / lox)X(K14-CRE-ERtam))-mice could be induced by tamoxifen administration via oral gavage for 5 consecutive days at 6 mg / day in 0.3 mL cornoil, at age 2-4 months of age, plus a one-time booster two weeks after the last application. Male and female mice were induced equally. Efficiency of knockdown was verified by qRT-PCR for Trpv4 using primers sense 5′-CCTGCTGGTCACCTACATCA (SEQ ID NO: 1) and antisense 5′-CTCAGGAACACAGGGAAGGA (SEQ ID NO: 2), with the former primer located in exon 13. All animal experimentation described here was conducted in full compliance with NIH and Duke University internal guidelines, and under a valid IACUC protocol.
[0104]Using the same genomic clone that was used for generating the Trpv4− / − pan-null mouse, the Trpv4 targeting
example 2
Generation of an Epidermal-Specific, Tamoxifen-Inducible Trpv4 Null Mouse
[0156]To circumvent developmental issues that can arise in gene-targeted mice with ubiquitous deletions, we developed an inducible conditional system to assess the roles of TRPV4 in UVBmediated skin irritation, inflammation, and sensory sensitization. Using mouse ES cells, we first built Trpv4lox / lox mice so that the sizable exon coding for transmembrane domains 5, 6, and the interjacent pore loop was flanked by loxP elements. After crossing to FLPe mice to remove the selection marker, flanked by frt elements, these animals were mated with tamoxifen (tam)-inducible, Keratin-14 (K14)-CREER transgenic mice. The constructs and genotyping are summarized in FIG. 1A-B.
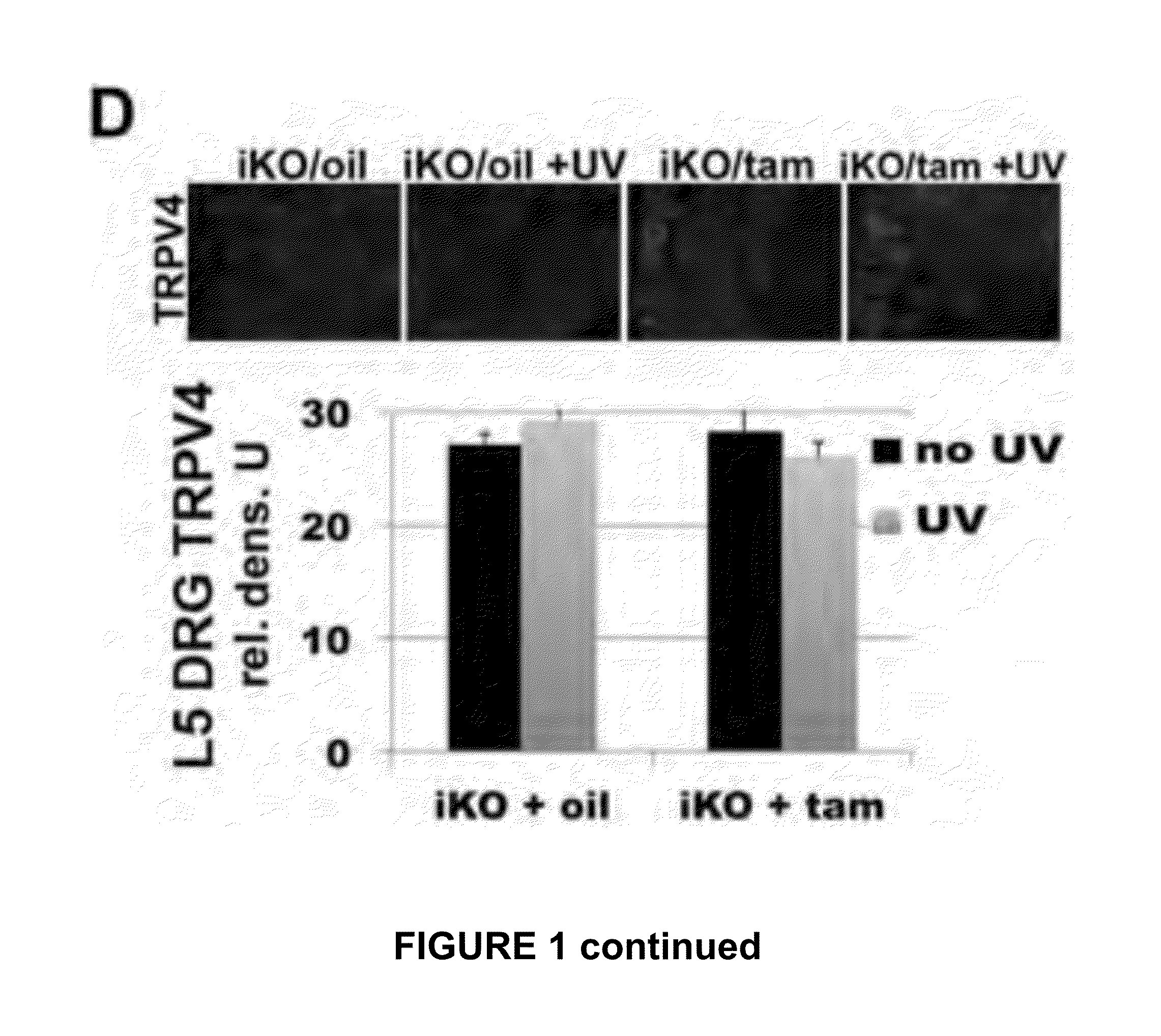
[0157]We focused on adult (2 month) glandular mouse paw-pad skin for our analyses, as it more closely resembles human skin. Tamoxifen-induction resulted in efficient knockdown of Trpv4 expression in skin epidermis, as judged by anti-TRPV4 immunolabeling,
example 3
Nocifensive Behavior Elicited by UVB Exposure is Dependent on Epidermally-Expressed TRPV4
[0159]Underscoring the specificity of Trpv4 gene targeting, peripheral sensory neurons innervating the footpad still showed robust expression of TRPV4 (FIG. 1D). This enabled us to evaluate whether epidermal Trpv4-deficiency critically affects UVB-mediated nocifensive behaviors. For this purpose, we assayed two relevant submodalities—thermal and mechanical stimulation—and compared our iKO mice to pan-null Trpv4− / − and their wild-type (WT) controls (FIG. 3B). 48 hours after UV-exposure, both tamtreated iKO and Trpv4− / − mice displayed much lower sensitivity to noxious radiant heat (Hargreaves' test), also towards noxious mechanical stimulation (using automated von Frey hair testing), than their respective controls. We concluded that epidermal-specific TRPV4 deficiency is equivalent to global Trpv4 ablation in reducing UVB-induced behavioral sensitization to radiant heat and mechanical stimuli, th
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap